Beta Thalassemia Testing Market By Product Type (Prenatal Testing, Perinatal Testing, Preimplantation, DNA Testing, Complete Blood Count (CBC), and Chorionic Villus Sampling), By Application (Next-generation Sequencing, PCR, Microarray, and Others), By End-user (Diagnostic Laboratories, Hospitals, Pharmaceutical Industries, and Others), Region and Companies – Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Oct 2025
- Report ID: 162320
- Number of Pages: 376
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
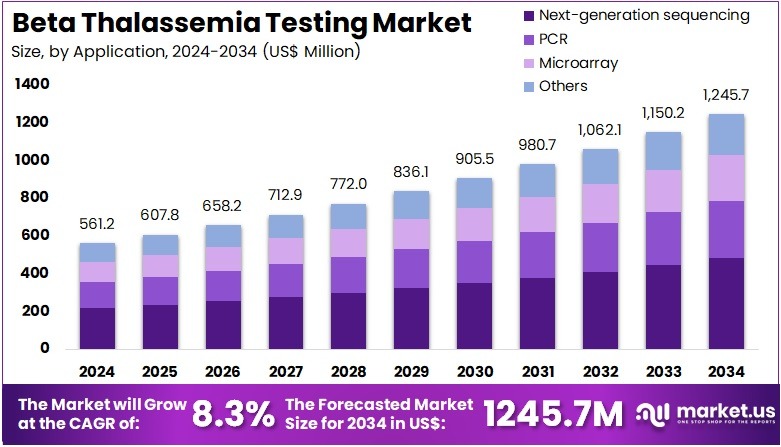
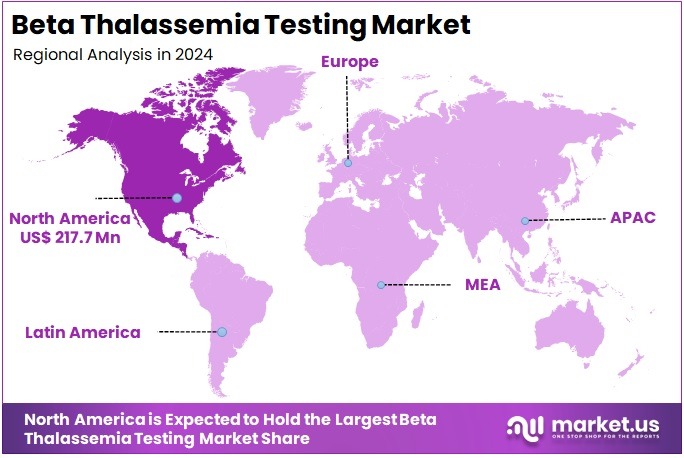
The Beta Thalassemia Testing Market Size is expected to be worth around US$ 1245.7 million by 2034 from US$ 561.2 million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 8.3% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034. North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 38.8% share and holds US$ 271.8 Million market value for the year.
Increasing demand for precision medicine drives the Beta Thalassemia Testing Market, as advancements in genetic therapies require accurate diagnostic tools. In January 2024, the US FDA expanded the indication for Casgevy, a CRISPR-based therapy, to include transfusion-dependent beta-thalassemia. This milestone heightens the need for genetic testing to identify HBB gene mutations, ensuring patients qualify for targeted treatments.
Diagnostic applications span prenatal screening, carrier testing, and pre-treatment assessments, enabling personalized care. Innovations in molecular diagnostics, such as next-generation sequencing, enhance testing accuracy and efficiency. These developments position the market for robust growth as healthcare systems prioritize tailored therapeutic strategies.
Growing awareness of beta-thalassemia prevalence fuels market expansion, as healthcare providers emphasize early detection and screening. In late 2024, the American Society of Hematology published findings revealing that prior estimates of β-thalassemia cases in the US were significantly underestimated. This insight underscores the importance of widespread newborn and carrier screening programs to identify at-risk populations.
Testing applications include population-based screening and diagnostic confirmation for symptomatic patients, supporting proactive disease management. Enhanced screening initiatives drive demand for reliable, high-throughput diagnostic platforms. As public health efforts intensify, the market benefits from increased adoption of systematic testing solutions.
Rising technological innovation propels the Beta Thalassemia Testing Market, with novel diagnostic tools improving accessibility and outcomes. In early 2025, a biotechnology startup secured FDA approval for a groundbreaking detection technology, offering rapid, accurate, and cost-effective testing for beta-thalassemia.
Applications include point-of-care diagnostics and laboratory-based genetic analysis, facilitating timely clinical decisions. These advancements reduce diagnostic turnaround times and enhance affordability, broadening access to testing. Integration of artificial intelligence in result interpretation further streamlines workflows. The market thrives as these innovations empower healthcare providers to deliver precise, early interventions.
Key Takeaways
- In 2024, the market generated a revenue of US$ 561.2 million, with a CAGR of 8.3%, and is expected to reach US$ 1245.7 million by the year 2034.
- The product type segment is divided into prenatal testing, perinatal testing, preimplantation, DNA testing, complete blood count (CBC), and chorionic villus sampling, with prenatal testing taking the lead in 2023 with a market share of 41.2%.
- Considering application, the market is divided into next-generation sequencing, PCR, microarray, and others. Among these, next-generation sequencing held a significant share of 38.7%.
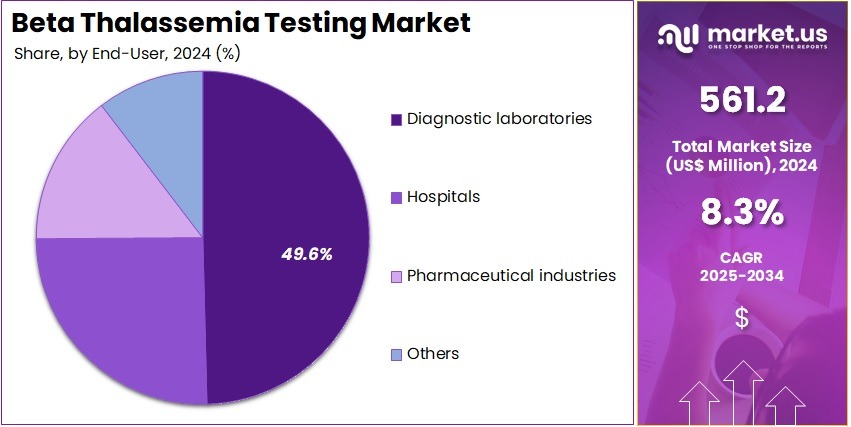
- Furthermore, concerning the end-user segment, the market is segregated into diagnostic laboratories, hospitals, pharmaceutical industries, and others. The diagnostic laboratories sector stands out as the dominant player, holding the largest revenue share of 49.6% in the market.
- North America led the market by securing a market share of 38.8% in 2024.
Product Type Analysis
Prenatal testing holds 41.2% of the Beta Thalassemia Testing market and is projected to continue leading due to increasing awareness about genetic disorders and the importance of early detection. Expectant parents increasingly seek prenatal testing to assess the risk of beta thalassemia in their unborn children, particularly in regions with a high prevalence of hemoglobinopathies. Advancements in non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) and the availability of rapid, accurate assays are likely to drive adoption.
Hospitals and diagnostic centers are implementing these tests to provide timely genetic counseling, which helps families make informed decisions. Government initiatives supporting screening programs and the rising number of high-risk pregnancies are expected to further boost demand. Additionally, increasing access to prenatal healthcare services and improved reimbursement policies are anticipated to encourage wider utilization.
As awareness campaigns grow and technological advancements enhance accuracy and speed, prenatal testing is projected to maintain its dominant position in the market. The combination of safety, non-invasiveness, and reliability makes prenatal testing a preferred choice among healthcare providers and patients.
Application Analysis
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) holds 38.7% of the application segment and is expected to continue its growth trajectory due to its high accuracy, speed, and ability to provide comprehensive genetic information. NGS enables the detection of beta thalassemia mutations at the molecular level, allowing for precise carrier and diagnostic testing. The growing adoption of personalized medicine and genomics-based healthcare is projected to expand the use of NGS in both prenatal and postnatal settings.
Diagnostic laboratories increasingly rely on NGS to perform large-scale screenings and detailed genetic analysis, reducing the time and cost associated with traditional methods. The ability to analyze multiple genes simultaneously and detect rare mutations enhances its clinical utility.
Advancements in sequencing technologies and automated platforms are expected to improve throughput and reliability, driving adoption. As healthcare providers seek comprehensive and rapid testing solutions, NGS is likely to remain the preferred technology for beta thalassemia testing. Increasing collaborations between research institutions and commercial laboratories are also expected to support market growth.
End-User Analysis
Diagnostic laboratories represent 49.6% of the end-user segment and are projected to remain the dominant consumer of beta thalassemia testing due to their capability to provide specialized, high-throughput genetic analysis. These laboratories offer advanced testing services, including prenatal screening, NGS, and DNA-based diagnostics, making them central to early detection and management of beta thalassemia. The rising demand for rapid and accurate genetic testing from hospitals, clinics, and private patients is anticipated to boost laboratory services.
Diagnostic laboratories are increasingly adopting automated platforms and high-precision assays to improve efficiency and reduce turnaround times. Additionally, the growing emphasis on preventive healthcare and carrier screening programs drives consistent demand for laboratory-based beta thalassemia testing. Collaborations with hospitals and pharmaceutical companies further strengthen their market presence.
The availability of specialized personnel and infrastructure enables diagnostic laboratories to handle complex testing protocols effectively, ensuring reliability. As healthcare systems prioritize genetic screening and early intervention strategies, diagnostic laboratories are expected to continue serving as the primary end-users in the beta thalassemia testing market.
Key Market Segments
By Product Type
- Prenatal Testing
- Perinatal Testing
- Preimplantation
- DNA Testing
- Complete Blood Count (CBC)
- Chorionic Villus sampling
By Application
- Next-generation sequencing
- PCR
- Microarray
- Others
By End-user
- Diagnostic Laboratories
- Hospitals
- Pharmaceutical Industries
- Others
Drivers
Increasing Global Prevalence of Beta Thalassemia is Driving the Market
The worldwide rise in beta thalassemia cases has emerged as a critical force propelling the demand for comprehensive testing protocols to enable early detection and intervention strategies. This genetic disorder, characterized by impaired beta-globin chain production, leads to varying degrees of anemia that necessitate routine hematological evaluations and molecular confirmations. As migration patterns redistribute high-risk populations from endemic regions to others, healthcare infrastructures must adapt by expanding screening capacities in primary care and prenatal settings.
The condition’s heritability underscores the importance of carrier identification programs, which rely on accessible diagnostic tools to inform family planning decisions. Public health campaigns increasingly advocate for premarital and preconception testing, amplifying the need for scalable, cost-effective assays. This driver is particularly pronounced in regions with historical malaria exposure, where heterozygous carriers confer survival advantages, perpetuating allele frequencies.
The World Health Organization estimates that approximately 40,000 newborns are affected by beta thalassemia annually, highlighting the persistent epidemiological challenge that fuels diagnostic investments. Such figures compel governments to integrate thalassemia surveillance into national health agendas, boosting procurement of testing reagents and equipment. Technological refinements in high-performance liquid chromatography have streamlined hemoglobin variant profiling, enhancing throughput in high-volume laboratories.
Economically, proactive testing averts the exorbitant costs of lifelong transfusions and chelation therapies for undetected cases. Collaborative initiatives between international agencies and local providers further disseminate validated protocols, ensuring equitable access. In totality, this demographic imperative not only escalates testing volumes but also incentivizes innovation in point-of-care modalities for remote deployments.
Restraints
Diagnostic Complexities and Logistical Barriers in High-Prevalence Regions is Restraining the Market
Intricate diagnostic requirements coupled with infrastructural limitations in endemic areas continue to impede the efficient rollout of beta thalassemia testing, particularly where confirmatory assays demand specialized facilities. Initial screening via complete blood counts often yields ambiguous microcytosis patterns that mimic iron deficiency, necessitating sequential hemoglobin electrophoresis and genetic sequencing for resolution. This multi-tiered approach prolongs turnaround times, exacerbating delays in definitive diagnoses and complicating timely therapeutic escalations.
In rural or under-resourced locales, the scarcity of trained phlebotomists and stable power supplies for equipment hampers sample integrity and result reliability. Moreover, the heterogeneity of mutations—over 200 variants—challenges assay standardization, risking false negatives in diverse ethnic cohorts. Regulatory variances across borders further complicate reagent approvals and quality assurance, deterring seamless global distribution.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention notes that in low-resource settings, up to 50 percent of suspected cases may evade molecular verification due to accessibility constraints, perpetuating undiagnosed carriers. These gaps inflate indirect costs through untreated complications like splenomegaly and cardiac strain. Healthcare disparities amplify this restraint, as marginalized communities face cultural stigmas around genetic inquiries, reducing voluntary participation rates.
Laboratories grapple with reagent shortages amid supply chain disruptions, curtailing operational scalability. Efforts to decentralize testing via dried blood spot kits offer mitigation, yet validation lags in tropical climates. Collectively, these multifaceted hurdles not only constrain market penetration but also underscore the urgency for fortified training and logistics frameworks.
Opportunities
Emergence of Gene Therapy Necessitates Expanded Pre-Treatment Genetic Profiling is Creating Growth Opportunities
The advent of curative gene therapies has illuminated vast prospects for beta thalassemia testing by mandating precise genotypic characterization to stratify patient eligibility and tailor interventions. These novel modalities, targeting autologous hematopoietic stem cells to restore functional globin expression, require detailed mutation mapping to predict phenotypic responses and monitor engraftment success.
As approvals proliferate, testing volumes are poised to surge in referral centers, encompassing pre-infusion sequencing and post-treatment surveillance for chimerism. This paradigm shift incentivizes partnerships between diagnostic developers and biotech innovators, fostering bundled offerings that integrate pharmacogenomics with therapeutic delivery.
Opportunities extend to pharmacovigilance assays that track vector integration and off-target edits, ensuring long-term safety in real-world cohorts. Government reimbursements for companion diagnostics further catalyze adoption, bridging affordability chasms in emerging economies. The Food and Drug Administration’s approval of betibeglogene autotemcel in August 2022 for transfusion-dependent patients exemplifies this catalyst, with over 90 percent achieving transfusion independence in pivotal trials.
Such outcomes validate the economic rationale for upfront genetic investments, potentially offsetting lifetime care expenditures. Innovations in next-generation sequencing panels expedite variant detection, enabling rapid triaging for therapy candidates. As pipeline candidates diversify—encompassing CRISPR-based editors—multiplexed assays will dominate, diversifying revenue streams for test providers. Tele-genetics platforms could democratize access, linking remote clinics to centralized expertise. Ultimately, this therapeutic frontier not only amplifies testing demand but also reorients the market toward precision-driven ecosystems.
Impact of Macroeconomic / Geopolitical Factors
Rising global inflation and tighter venture capital availability are prompting developers in the hemoglobin variant screening market to focus on core assay kits, delaying advanced sequencing integrations to conserve resources. Trade tensions between the U.S. and India, combined with shipping delays through the Malacca Strait, are disrupting supplies of electrophoresis gels, extending development timelines and raising costs for multinational carrier screening programs.
To manage these challenges, some developers are partnering with gel suppliers in Alberta, adopting sustainable practices that simplify regulatory approvals and attract mission-focused funding. Expanding carrier screening mandates in parts of Europe are directing funds toward multiplexed PCR platforms, driving adoption in prenatal care settings.
U.S. tariffs on imported diagnostic consumables are increasing costs for Asian-sourced primers and capillary arrays, making community newborn programs less affordable and slowing technology transfers. These pressures create sourcing uncertainty and occasional disruptions in longitudinal genotype databases. Proactive developers are leveraging federal equity grants to build production hubs in Nevada, launching CRISPR-enhanced variant panels. These strategic moves are strengthening a domestically supported ecosystem, positioning the market for sustainable growth and long-term leadership.
Latest Trends
FDA Approval of CRISPR-Based Casgevy Therapy is a Recent Trend
The regulatory endorsement of CRISPR-engineered Casgevy has signified a landmark progression in beta thalassemia diagnostics during 2024, compelling a reevaluation of testing paradigms to accommodate advanced eligibility assessments. This ex vivo gene editing approach disrupts BCL11A enhancers to elevate fetal hemoglobin, offering transfusion-free prospects for severe genotypes previously deemed intractable. The trend emphasizes comprehensive pre-therapy profiling, integrating whole-exome sequencing to delineate β0/β+ distinctions and co-inherited modifiers.
Clinical validations have illuminated superior efficacy in non-β0 cohorts, prompting guideline revisions for stratified screening protocols. Integration with electronic health records facilitates seamless data flow, optimizing multidisciplinary consultations. This development accelerates the pivot toward curative intents, diminishing reliance on symptomatic palliation.
The Food and Drug Administration authorized Casgevy for patients aged 12 and older with transfusion-dependent beta thalassemia in January 2024, following robust phase 3 evidence of sustained hemoglobin stabilization. Such milestones herald broader accessibility, albeit tempered by manufacturing scalability. Ancillary assays for editing fidelity now permeate workflows, bolstering confidence in durable remissions.
International harmonization of approval pathways anticipates global dissemination, spurring localized adaptations. Forward trajectories include in vivo editing trials, potentially obviating conditioning regimens. This CRISPR inflection not only refines diagnostic acuity but also galvanizes stakeholder synergies in hematologic innovation.
Regional Analysis
North America is leading the Beta Thalassemia Testing Market
In 2024, North America accounted for 38.8% of the global beta thalassemia testing market, driven by expanding newborn screening programs that integrate hemoglobin electrophoresis and DNA analysis to identify carrier status early in high-risk immigrant communities from Mediterranean and Asian origins. Clinical guidelines from the American College of Medical Genetics emphasized routine prenatal carrier screening for at-risk ethnic groups, facilitating informed family planning and reducing disease incidence through preimplantation genetic diagnosis.
The rise in consanguineous marriages among certain populations heightened demand for confirmatory testing in hematology clinics, where automated HPLC methods improved turnaround times for variant detection. Federal funding through the Health Resources and Services Administration supported state-level expansions in genetic counseling services, addressing disparities in access for underserved urban and rural demographics.
Advancements in non-invasive fetal DNA sequencing appealed to obstetricians for safer prenatal assessments, minimizing risks associated with invasive procedures. These developments underscored the region’s proactive approach to hereditary hematology diagnostics. A 2022 study in the International Journal of Neonatal Screening reported that 26 U.S. states included beta thalassemia in their newborn screening panels, enabling early intervention for approximately 1 in 100,000 births affected.
The Asia Pacific region is expected to experience the highest CAGR during the forecast period
Health authorities in Asia Pacific anticipate the beta thalassemia testing sector to expand during the forecast period, as national health campaigns target endemic hotspots with subsidized genetic assays to curb transmission in consanguineous populations. Governments in India and Thailand allocate resources to community-based screening hubs, equipping primary care facilities with PCR kits for rapid carrier identification amid rising urbanization.
Diagnostic developers collaborate with regional labs to refine NGS panels, projecting enhanced detection of rare HBB mutations in diverse ethnic subgroups. Oversight bodies in Indonesia and Vietnam pioneer mobile testing units, positioning remote villages to access hemoglobinopathy profiling without urban referrals. Authorities estimate integrating testing into maternal health registries, alleviating diagnostic delays for hemoglobin E/beta thalassemia variants prevalent in Southeast Asian cohorts.
Local researchers advance multiplex assays, coordinating with public databases to monitor allele frequencies in migrant communities. These efforts establish a scalable framework for preventive genomics. The Global Burden of Disease Study 2021, published in eClinicalMedicine in 2024, estimated 1.2 million prevalent beta thalassemia cases in Southeast Asia in 2021, reflecting sustained regional burden into 2022-2024.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherland
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Leading companies in the hemoglobinopathy diagnostics market are expanding their capabilities by introducing automated HPLC kits that accurately measure HbA2 and HbF levels, enabling faster carrier screening in high-prevalence populations. They collaborate with public health agencies to integrate these tests into national prenatal programs, increasing awareness and participation in endemic regions.
Companies are also investing in multiplex genetic panels that detect HBB gene mutations along with carrier status, supporting precision counseling for at-risk families. Some providers are integrating their assays with point-of-care analyzers, as demonstrated by Bio-Rad’s VARIANT systems, to streamline workflows in clinics with limited resources.
Market leaders are targeting Mediterranean and Southeast Asian regions, aligning testing solutions with local reimbursement structures to take advantage of subsidized demand. Bundled service contracts that include validation support and data analytics strengthen laboratory partnerships and improve operational resilience. These strategic initiatives enhance both accessibility and efficiency, positioning companies to address growing needs in hemoglobinopathy screening.
Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., founded in 1952 and headquartered in Hercules, California, is a key player in life science research and clinical diagnostics, supporting biotechnology and healthcare advancements worldwide. Its VARIANT II platform provides automated ion-exchange chromatography for precise identification of abnormal hemoglobins, aiding beta thalassemia evaluation with minimal manual intervention.
Bio-Rad invests in variant libraries and educational outreach, working with reference laboratories to refine detection protocols across diverse ethnic groups. CEO Norman D. Schwartz oversees operations in more than 30 countries, emphasizing regulatory compliance and innovation in molecular workflows. The company collaborates with screening consortia to deploy scalable solutions, helping reduce disease burdens through accessible diagnostics. By combining analytical precision with strategic partnerships, Bio-Rad maintains its leadership and sets high standards in hemoglobinopathy testing.
Recent Developments
- In March 2024: Thermo Fisher Scientific partnered with a leading healthcare provider to expand Beta-Thalassemia testing access in Southeast Asia, a region with high prevalence. This initiative strengthens the market by improving the availability of advanced diagnostic solutions, driving adoption, and enabling timely identification and management of affected individuals.
- In late 2024: clinical trials of new oral therapies, such as pyruvate kinase activators, demonstrated the need for companion diagnostics to monitor patient response. This requirement accelerates demand in the Beta Thalassemia Testing Market by creating opportunities for specialized diagnostic panels that support personalized medicine approaches and treatment optimization.
Top Key Players in the Beta Thalassemia Testing Market
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- Sysmex Corporation
- QIAGEN N.V.
- PerkinElmer Inc.
- Natera Inc.
- Illumina Inc.
- Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
- Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc.
- BGI Genomics Co. Ltd.
- Abbott Laboratories
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) US$ 561.2 million Forecast Revenue (2034) US$ 1245.7 million CAGR (2025-2034) 8.3% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, COVID-19 Impact, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Product Type (Prenatal Testing, Perinatal Testing, Preimplantation, DNA Testing, Complete Blood Count (CBC), and Chorionic Villus Sampling), By Application (Next-generation Sequencing, PCR, Microarray, and Others), By End-user (Diagnostic Laboratories, Hospitals, Pharmaceutical Industries, and Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia, Netherlands, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Sysmex Corporation, QIAGEN N.V., PerkinElmer Inc., Natera Inc., Illumina Inc., F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc., BGI Genomics Co. Ltd., Abbott Laboratories. Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Beta Thalassemia Testing MarketPublished date: Oct 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Beta Thalassemia Testing MarketPublished date: Oct 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- Sysmex Corporation
- QIAGEN N.V.
- PerkinElmer Inc.
- Natera Inc.
- Illumina Inc.
- Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
- Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc.
- BGI Genomics Co. Ltd.
- Abbott Laboratories










