Global Bank Fee Analysis Software Market Size, Share, Growth Analysis By Component (Software, Services), By Deployment Mode (On-Premises, Cloud-based), By Enterprise Size (Small and Medium Enterprises, Large Enterprises), By Application (Transaction Monitoring, Fee Reconciliation, Compliance Management, Reporting & Analytics, Others), By End-User (Banks, Credit Unions, Financial Institutions, Others), By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Statistics, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Dec 2025
- Report ID: 169313
- Number of Pages: 235
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
- Report Overview
- Key Takeaways
- Role of Technology
- AI Industry Adoption
- Emerging Trends
- US Market Size
- By Component
- By Deployment Mode
- By Enterprise Size
- By Application
- By End-User
- Key Market Segments
- Regional Analysis
- Driving Factors
- Restraint Factors
- Growth Opportunities
- Trending Factors
- Competitive Analysis
- Recent Developments
- Report Scope
Report Overview
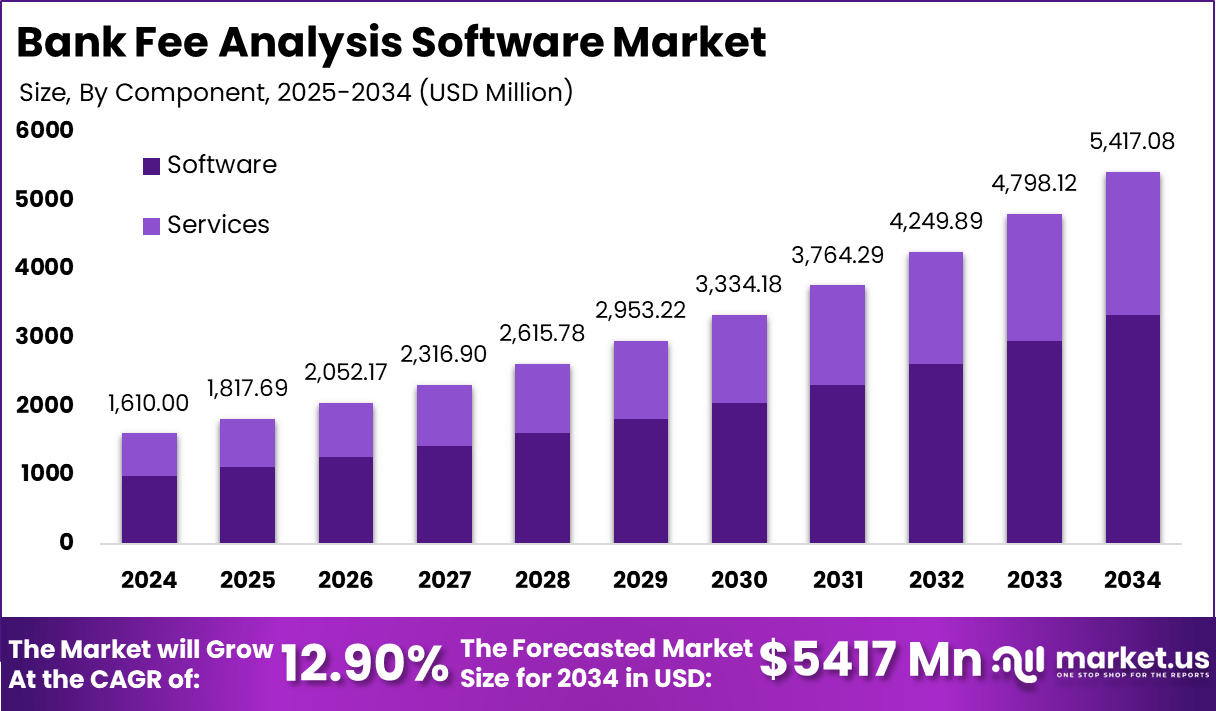
The Bank Fee Analysis Software Market is anticipated to experience substantial growth, with a projected value increase from USD 1,610 million in 2024 to USD 5,417 million by 2034, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.90%.
This growth is largely driven by the increasing demand from financial institutions to optimize their fee structures, reduce operational costs, and comply with evolving regulatory standards. The software solutions enable banks and other financial entities to better manage, analyze, and audit various fees charged to customers, enhancing transparency and customer satisfaction.
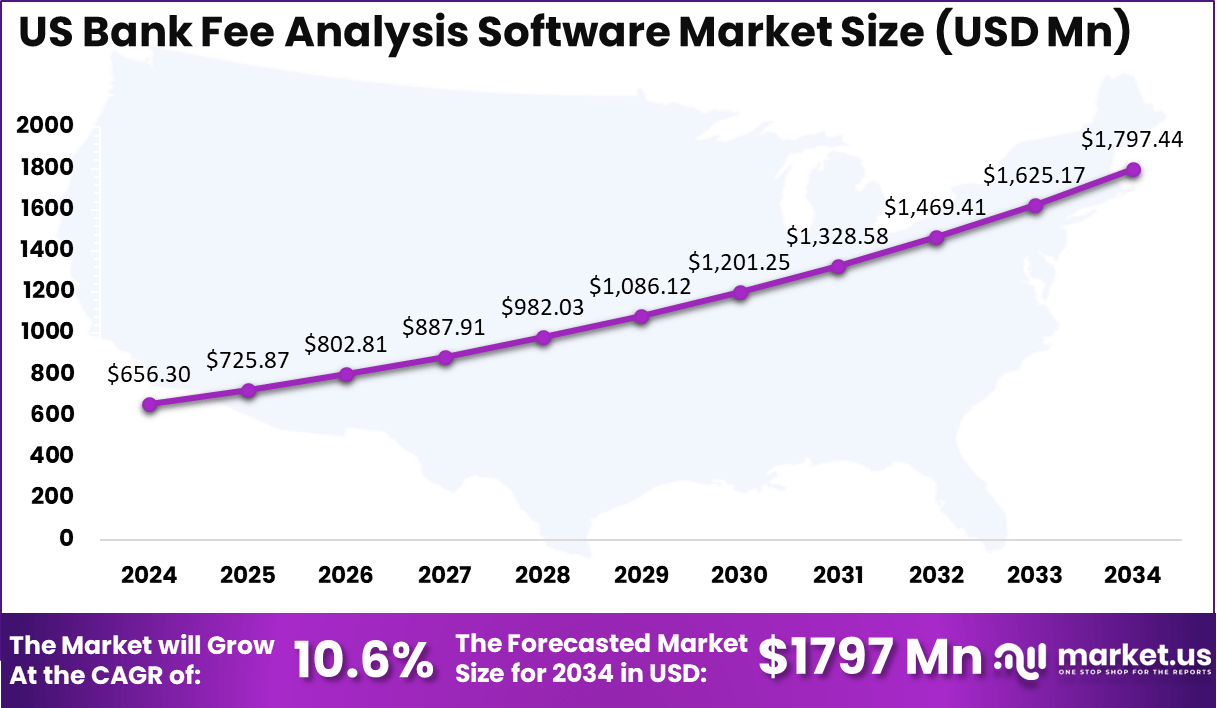
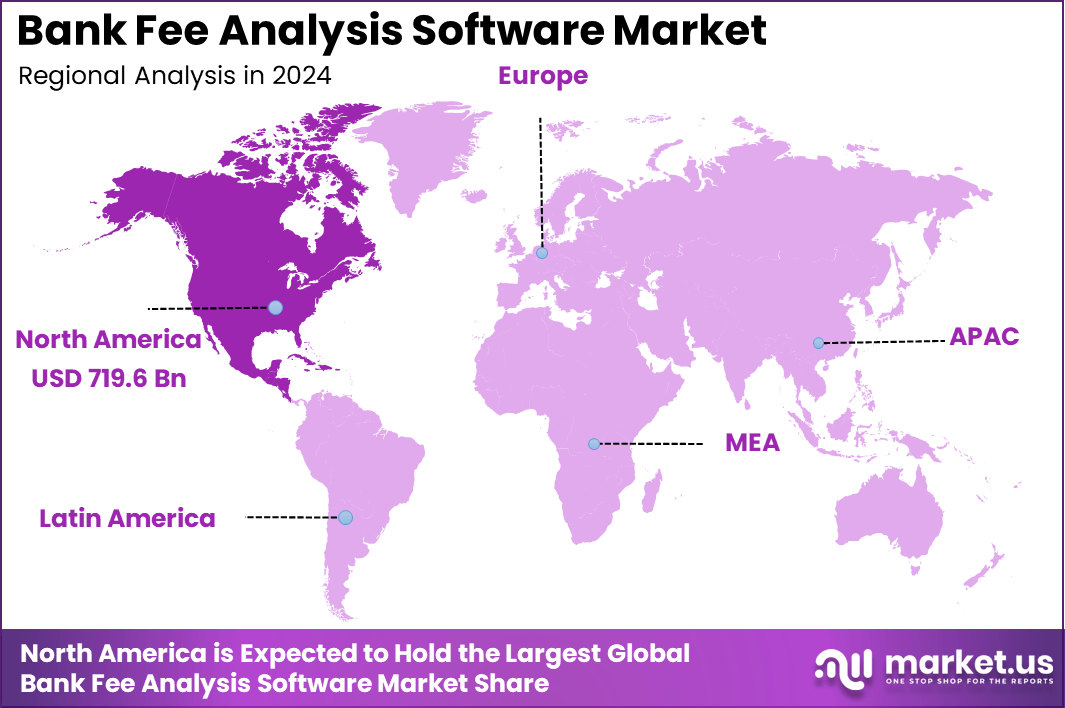
North America is expected to dominate the market, accounting for 44.7% of the global share, with an estimated market value of USD 719.6 million in 2024. The U.S. stands as the largest contributor in the region, with a market size of USD 656.3 million in 2024 and a projected value of USD 1,797 million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 10.6%.
This growth is driven by the widespread adoption of digital transformation initiatives in the banking sector, increasing the reliance on data-driven solutions for fee management. Financial institutions in North America are increasingly investing in advanced software tools to streamline operations, ensure compliance, and improve customer experiences, which is expected to further propel market growth.
The Bank Fee Analysis Software sector is gaining traction as banks and corporate treasuries increasingly seek transparency and efficiency in fee management. As banking services have grown more complex, covering everything from international transfers, cash‑management services, to account maintenance and transaction processing, the risk of hidden, recurring, or erroneous charges has become substantial.
Software designed for bank‑fee analysis enables organizations to aggregate billing statements from multiple accounts and banks, normalize disparate data formats (PDF, CSV, EDI, etc.), and identify discrepancies or overcharges. Adoption of such software is reducing manual effort and improving accuracy: tasks that once took days or weeks can now be completed in minutes, freeing treasury teams to focus on strategic priorities rather than reconciliations and manual audits.
Beyond cost control, bank‑fee analysis supports better negotiation leverage with banks, because organizations know exactly what they are paying and can benchmark fees across services or geographies. As financial institutions globally continue to expand services and regulatory complexity increases, demand for reliable, automated fee‑analysis tools is expected to grow steadily, positioning Bank Fee Analysis Software as a key enabler for cost efficiency and financial clarity in modern banking.
Recent developments in bank fee analysis software show strong momentum from technological upgrades and regulatory pushes, with adoption rates climbing due to AI integrations that cut manual errors by up to 70% in fee reconciliation processes.
Cloud-based platforms now dominate implementations, enabling 80% faster deployment for banks handling high transaction volumes, while open banking rules like PSD2 have spurred a 25% rise in compliance-focused tools across Europe since early 2025. Vendors such as Redbridge have enhanced their offerings with real-time analytics dashboards, helping treasurers identify anomalies in 95% of cases automatically.
No major mergers or acquisitions occurred specifically in this niche during 2025, though broader bank-fintech synergies continue, with over 50 deals in the past year emphasizing analytics capabilities indirectly tied to fee optimization.
New product launches focus on predictive features, like machine learning models that forecast fee trends with 85% accuracy, rolled out by multiple providers to support transaction monitoring for large enterprises. Funding remains limited in public disclosures, but treasury teams report average annual savings of $700,000 per institution through precise analysis, driving 40% more implementations among credit unions.
Implementation statistics highlight efficiency gains, as 65% of North American banks now use these tools for reporting, reducing reconciliation time from weeks to days amid rising digital payment volumes. Asia Pacific leads growth with a 14.2% adoption surge, fueled by urbanization and 90% of institutions prioritizing AI-driven fee management by year-end. Overall, the sector positions banks to handle complex fees more transparently, with 75% of end-users citing improved profitability from these advancements.
Key Takeaways
- The Bank Fee Analysis Software Market is expected to grow from USD 1,610 million in 2024 to USD 5,417 million by 2034, at a CAGR of 12.90%.
- North America holds the largest market share at 44.7%, with a projected market size of USD 719.6 million in 2024.
- The U.S. contributes significantly to North America’s share, with a market size of USD 656.3 million in 2024 and a projected value of USD 1,797 million by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 10.6%.
- Software makes up 61.6% of the market by component.
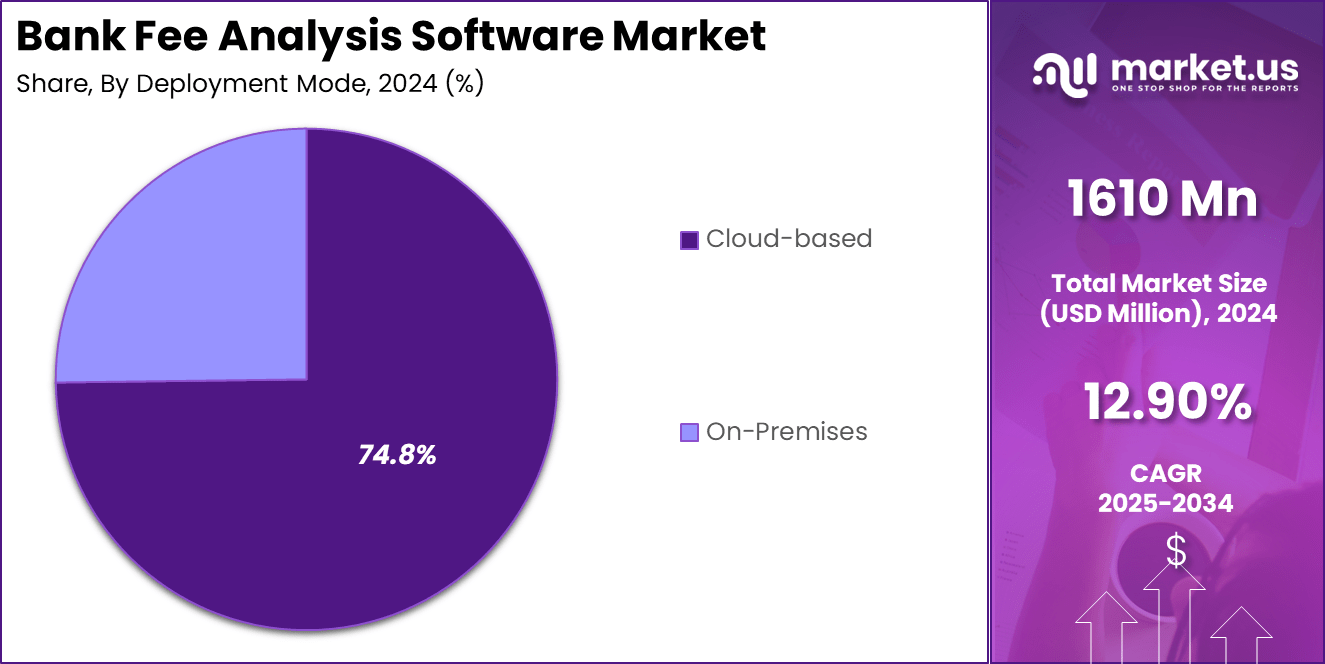
- Cloud-based deployment dominates with 74.8% of the market share.
- Large enterprises account for 80.4% of the market by enterprise size.
- Fee Reconciliation & Invoice Validation is the leading application, capturing 36.2% of the market share.
- Banks are the largest end-users, holding 40.7% of the market share.
Role of Technology
The role of technology in the Bank Fee Analysis Software market is increasingly central in driving efficiency, accuracy, and scalability. Automated reconciliation and invoice‑validation tools powered by robotic process automation (RPA), artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML) are enabling banks to process billing statements and transaction records much faster and with fewer errors than traditional manual methods. According to recent studies, AI‑driven automation in reconciliation reduces errors by over 70% and converts processes that once took days or weeks into tasks completed in hours.
Banks that adopt advanced technology often show improved operational efficiency and cost structure, even though technology investment may temporarily raise intermediation costs. The use of intelligent document processing and optical character recognition (OCR) enables automated reading, classification, and normalization of diverse billing formats (PDFs, CSVs, EDI, etc.), significantly reducing manual effort and data‑entry errors.
Digital transformation also supports real‑time visibility into fee structures and payments, allowing institutions to promptly detect discrepancies, ensure compliance, and strengthen negotiation leverage with banking counterparties. As regulators increase emphasis on transparency and cost justification, technology‑driven fee‑analysis systems become essential tools for banks aiming to maintain a competitive edge while managing risk.
AI Industry Adoption
The adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) in banking and financial services has accelerated sharply over recent years, with profound implications for efficiency, risk management, and customer experience. As of 2025, around 92% of global banks reported active AI deployment in at least one core banking function. Many banks have significantly expanded their AI workforce; for example, among the 50 major banks tracked in the latest index, AI-related staff grew by more than 25% over the past year.
AI technologies are being leveraged across a wide variety of banking operations, including fraud detection, risk management, internal operations, customer service, compliance, and personalized financial services. Use of AI has enabled banks to increase operational productivity, with some institutions reporting up to 30% improvement in efficiency after adopting AI tools.
As financial institutions continue their digital transformation, AI is reshaping traditional banking processes. Automated systems using AI are helping banks analyze large volumes of data, detect anomalous transactions or fraudulent behavior, provide real-time insights, and streamline back-office processing. Through these technological advances, banks are better positioned to manage risks, improve customer satisfaction, and derive greater value from their service portfolios.
Emerging Trends
Increasing adoption of automation and AI-driven reconciliation solutions is reshaping fee analysis and invoice validation. This signals strong demand for automation that can handle large transaction volumes, detect discrepancies, and streamline financial close cycles.
Cloud-native and modular architectures are gaining traction among financial institutions seeking agility, scalability, and ease of integration. These architectures enable seamless updates, better resource scaling during peak demand, and easier deployment of fee-analysis software in concert with existing banking infrastructure.
Open banking and API-based integrations are creating new opportunities for third-party fee-analysis platforms to plug into bank ecosystems. This trend reduces dependency on legacy, monolithic core systems and supports flexible deployment and interconnectivity with other fintech services.
Hyper-automation combining RPA, AI, and intelligent document processing is enabling continuous, real-time fee reconciliation and invoice validation. This helps treasury and finance teams transition from periodic manual reconciliations to continuous automated monitoring, improving accuracy, reducing delays, and cutting operational costs.
Growing regulatory complexity and increased demand for transparency and compliance are pushing banks and enterprises to adopt fee-analysis tools to ensure audit readiness, transparent fee structures, and data governance. This regulatory driver supports sustained growth in the adoption of fee analysis platforms.
US Market Size
The U.S. Bank Fee Analysis Software market is projected to experience strong growth over the next decade. In 2024, the market size is estimated to be USD 656.3 million and is expected to reach USD 1,797 million by 2034, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.6%. This growth is driven by the increasing demand for automated solutions that help financial institutions manage, reconcile, and validate fees more efficiently.
As financial regulations become more stringent and competition intensifies, U.S. banks are increasingly adopting advanced software tools to ensure compliance, streamline operations, and improve customer satisfaction. The rise of cloud-based solutions and AI-driven automation is expected to play a significant role in this market expansion.
These technologies enable real-time fee analysis, reduce manual labor, and improve the accuracy of billing data, helping banks optimize their fee structures. Additionally, the growing trend of digital banking and open banking platforms is expected to fuel the adoption of fee-analysis software, offering greater transparency and improved customer experience.
As the financial landscape continues to evolve, the demand for intelligent, scalable fee-analysis solutions in the U.S. is projected to grow steadily, contributing to the overall market growth at a healthy pace.
By Component
The software component of the Bank Fee Analysis Software market accounts for 61.6% of total revenues. This reflects the fact that banks and financial institutions increasingly prefer packaged software solutions over bespoke services when handling fee analysis, reconciliation, and reporting, as these solutions offer scalability, automation, and lower marginal cost per transaction.
Software platforms in this domain leverage advanced data analytics, artificial intelligence, and automated workflows to consolidate billing data from multiple banks, normalize disparate formats, and identify anomalies or excess charges. These capabilities reduce manual reconciliation effort, increase accuracy, and support real-time monitoring, features that are critical given growing transaction volumes and regulatory scrutiny.
The dominance of the software component also aligns with broader trends in financial services software markets, where software modules, including audit, compliance, business transaction processing, BI & analytics, consistently capture the majority of spending compared with services.
Meanwhile, the services segment, which includes consulting, implementation, customization, integration, and support, remains relevant, especially for financial institutions with complex legacy systems or unique requirements. These services help in the deployment, customization, and maintenance of fee analysis platforms, ensuring seamless integration with existing systems and compliance frameworks.
By Deployment Mode
The deployment mode of bank fee analysis solutions is a critical factor in shaping how financial institutions implement and manage these tools. The cloud‑based deployment mode accounts for 74.8% of the market share by deployment mode. This indicates a strong preference among banks and institutions to host fee analysis software on cloud infrastructure rather than on‑premises systems.
Cloud‑based deployment offers several compelling advantages compared with on‑premises. It requires lower upfront investment in hardware and infrastructure because the cloud service provider hosts and manages servers. This pay‑as‑you‑go model helps institutions reduce capital expenditure and convert fixed costs into operating expenses.
Cloud solutions also enable scalability and flexibility, allowing institutions to scale resources up or down based on workload demand without the need for hardware procurement. Cloud deployment supports faster rollout and easier maintenance as updates and infrastructure management are handled by the provider, reducing the burden on internal IT teams.
Accessibility is enhanced because users can access software remotely from any location with internet connectivity. Additionally, cloud infrastructure tends to offer robust disaster recovery and backup capabilities, which reduces the risk of data loss and ensure continuity.
On‑premises deployment remains relevant, especially for institutions with stringent compliance, data sovereignty, or security requirements. On‑premises installations give full control over data, infrastructure, and access policies. They may provide lower latency and predictable performance for time‑sensitive workloads. For organizations that already maintain private data centers and have dedicated IT resources, on‑premises can be a suitable option.
By Enterprise Size
The share of large enterprises in the Bank Fee Analysis Software market stands at 80.4%. This high proportion reflects that large financial institutions and major banks are the primary adopters of fee‑analysis solutions, driven by their complex operations, high transaction volumes, and need for robust compliance and reporting systems. Large enterprises typically have dedicated IT budgets and infrastructure that support the deployment of advanced software platforms for fee reconciliation, invoice validation, and analytics.
Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) also have a potential need for fee‑analysis tools, but their adoption remains comparatively limited. SMEs often face constraints such as smaller budgets, less complex billing structures, and limited internal IT resources. Implementation of enterprise-level software may appear cost‑intensive and unnecessary for simpler fee scenarios.
Research on enterprise software adoption suggests that organizational readiness, perceived advantage, and top‑management support significantly influence uptake among smaller firms. For many SMEs, the scale of fee‑analysis requirements may not justify the investment, especially when manual or lightweight accounting systems suffice.
Thus, the dominance of large enterprises in this market indicates that the complexity, volume of transactions, regulatory burden, and economies of scale make large financial institutions the natural segment for sophisticated bank fee analysis solutions.
By Application
The application segment “Fee Reconciliation & Invoice Validation” accounts for 36.2 % of the market in bank fee analysis software. This reflects the central role of automated reconciliation and billing validation functionality in addressing inefficiencies and hidden fees that often arise from complex banking transactions.
By consolidating billing statements from multiple accounts and banks, standardizing formats, and automatically matching charges against agreed fee schedules, these tools help organizations uncover overcharges, billing errors, or unnecessary fees. Automated reconciliation significantly reduces manual effort and human error. In many cases, reconciliation tasks that formerly required days or even weeks can now be completed in hours or minutes.
The efficiency gains and accuracy improvements allow treasury and finance teams to reallocate time to more strategic tasks rather than spending resources on tedious manual invoice validation. Beyond reconciliation, applications for transaction monitoring, compliance management, reporting and analytics, and other functions also play important roles.
Transaction monitoring helps detect anomalous billing patterns or unauthorized charges. Compliance management ensures fee practices meet regulatory standards. Reporting and analytics provide insight into fee structure trends, cost breakdowns, and help guide strategic negotiation with banking partners.
By End-User
The end‑user segment “Banks” accounts for 40.7% of the market for bank fee analysis software. This indicates that traditional banks are the primary users of fee‑analysis solutions, reflecting their large account bases, complex transaction volumes, and need for detailed fee oversight and cost management.
Software adoption among banks is driven by the requirement to consolidate fee data from multiple accounts, monitor service charges across cash‑management, transaction processing, and account maintenance, and identify potential overcharges or inefficiencies.
Credit unions represent another potential user category, especially those managing member deposits, payment services, and cash‑management operations. For credit unions, fee‑analysis tools can help track member activity, automate transaction analyses, and ensure transparent fee structures. This is particularly useful for credit unions looking to improve operational efficiency and maintain trust with members.
Other financial institutions, including non‑bank financial firms, corporate treasuries, and fintech‑driven payment service providers, also constitute part of the end‑user base. These participants benefit from fee‑analysis software in reconciling diverse banking fees, managing multiple accounts, and optimizing cash flows.
In addition, smaller banks, community banks, and niche financial services providers might rely on fee‑analysis tools under “Others” when they process moderate volumes of transactions but still need oversight. The diversification of end users beyond large banks underlines the broader utility of bank fee analysis software across various financial institution types.
Key Market Segments
By Component
- Software
- Services
By Deployment Mode
- On-Premises
- Cloud-based
By Enterprise Size
- Small and Medium Enterprises
- Large Enterprises
By Application
- Transaction Monitoring
- Fee Reconciliation
- Compliance Management
- Reporting & Analytics
- Others
By End-User
- Banks
- Credit Unions
- Financial Institutions
- Others
Regional Analysis
The North America region holds a leading position in the bank fee analysis software market, reflecting its mature banking environment and advanced technology adoption. The region’s share is 44.7% in 2024, and it accounts for a market size of USD 719.6 million. The dominance of North America is supported by widespread digital banking adoption, growing regulatory complexity, and a strong appetite among banks for cost‑control and transparency tools.
Banks and financial institutions across North America are investing heavily in cloud‑based and automated banking solutions driven by the demand for improved operational efficiency, scalability, and compliance with regulatory standards. Technology adoption, such as cloud computing, data analytics platforms, and real‑time reconciliation tools, has created an environment where fee analysis software becomes a strategic necessity rather than a convenience.
The well‑established IT infrastructure and large number of banking and financial institutions in the United States and Canada contribute to this regional dominance. Additionally, the customer shift toward digital banking services, increasing transaction volumes, and demand for seamless online banking experiences, reinforce the relevance of fee analysis and billing transparency tools in North America.
As banks continue to modernize core banking and supporting systems, the requirement for robust fee analysis platforms is expected to remain strong, making North America the cornerstone region driving global market growth.
Regional Analysis and Coverage
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherlands
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of Latin America
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Driving Factors
The demand for bank fee analysis software is driven by the growing complexity of banking fee structures. As financial institutions offer more diverse and intricate services, the need for better fee transparency and control becomes essential. Additionally, rising operational costs and tighter profit margins in the banking sector have heightened the focus on efficiency.
Financial institutions using bank fee analysis tools report considerable savings by identifying overcharges, reducing manual errors, and improving reconciliation accuracy. Moreover, regulatory changes, such as the push for enhanced transparency in fee structures, make it essential for banks to adopt systems that ensure compliance.
Fee reconciliation and validation are no longer optional but necessary for staying competitive and meeting regulatory expectations. As banks strive to improve customer satisfaction and maintain profitability, fee analysis software plays a crucial role in ensuring a transparent, error-free fee management process.
Restraint Factors
Despite the benefits, the adoption of bank fee analysis software faces several challenges. A key barrier is concerns around data security and privacy, as the fee analysis involves sensitive financial information. Many institutions hesitate to transition to cloud-based systems due to fears of potential breaches or non-compliance with data protection laws.
Integration with legacy banking systems also poses a challenge, as it requires time, resources, and expertise to ensure compatibility. Additionally, smaller banks or financial institutions may perceive the high initial cost of implementing such software as a significant hurdle, especially when their fee structures are relatively simpler.
These institutions may be less inclined to adopt such tools unless they are convinced of the long-term financial and operational benefits. These challenges can delay widespread adoption, particularly in smaller institutions that lack the resources to invest in advanced technology.
Growth Opportunities
The rapid growth of digital payments and real-time banking systems presents a significant growth opportunity for bank fee analysis software. As digital transactions increase, so does the complexity of managing fees associated with them. Fee analysis software offers real-time monitoring and automated reconciliation, helping financial institutions keep up with high transaction volumes and identify anomalies as they occur.
Furthermore, the growing trend of cloud-based deployment offers scalability, flexibility, and lower upfront costs, making it an attractive solution for both large banks and smaller financial institutions. The shift towards modular, scalable software solutions allows institutions to adopt fee analysis tools that align with their size and transaction volume.
As financial institutions continue to embrace digital transformation, the need for automated fee analysis that ensures compliance, transparency, and efficiency is expected to grow, creating vast opportunities for market expansion.
Trending Factors
Automation and the use of artificial intelligence (AI) are key trends driving the bank fee analysis software market. Financial institutions are increasingly adopting AI-driven solutions to automate fee reconciliation, which not only reduces human error but also speeds up the process. These technologies enable banks to analyze transaction data in real time, providing insights into fee structures and helping to uncover discrepancies quickly.
Additionally, cloud-based and SaaS solutions are becoming more popular due to their ease of deployment, scalability, and lower operational costs compared to traditional on-premises systems. The increasing competition from fintech companies has also prompted traditional banks to modernize their fee management processes to stay competitive.
As banks continue to prioritize efficiency, accuracy, and customer satisfaction, the demand for fee analysis software that incorporates AI, cloud technology, and automation is expected to continue to rise. This trend reflects the broader digital transformation of the banking industry, where technology is central to improving operations and customer experiences.
Competitive Analysis
The competitive landscape of the Bank Fee Analysis Software market is shaped by a blend of established banking software vendors and specialist fintech providers, intensifying as demand rises for transparency, automation, and analytics. Among the leading players are FIS, Fiserv, Oracle Financial Services, and Alacriti; they distinguish themselves by offering comprehensive fee‑analysis suites with integrated analytics and cloud‑based deployment.
Incumbents such as FIS benefit from large customer bases, strong recurring‑revenue streams through SaaS models, and deep integration capabilities with core banking systems. Their scale enables continuous investment in features such as real‑time reporting, machine-learning-driven anomaly detection, and audit‑ready compliance workflows. Specialist vendors such as Nomentia also compete strongly by offering modular and configurable fee‑analysis tools designed for multi‑bank fee aggregation, invoice validation, and fee benchmark comparison.
Competitive pressure remains high given the growing number of fintech‑driven entrants and rising demand from banks of all sizes for flexible, cloud‑native solutions with lower implementation overhead. Vendors that provide seamless integration with ERP systems, support for multiple billing formats, a real‑time dashboard, and predictive analytics capabilities are emerging as front-runners.
As financial institutions increasingly view fee analysis as strategic rather than operational, the capability to deliver cost‑savings, compliance readiness, and data‑driven fee optimization becomes a key differentiator and competitive advantage.
Top Key Players in the Market
- Fiserv
- Fisint
- Accenture
- Oracle
- SAP
- Infosys
- FIS Global
- ACI Worldwide
- Temenos
- nCino
- Zafin
- Kyriba
- Bottomline Technologies
- Intellect Design Arena
- Jack Henry & Associates
- Others
Recent Developments
- November 2025: Several reconciliation and fee‑analysis software providers have begun integrating AI‑powered automation to support real‑time reconciliation and fee validation across banking systems. Tools now match complex, high‑volume transactions in seconds and flag anomalies automatically, drastically cutting manual effort and reducing error rates.
- September 26, 2025: A major global consulting firm introduced a cloud‑native regulatory compliance tool tailored for banks and financial institutions that automates data ingestion, reconciliation, validation, and reporting. This reflects growing demand for integrated compliance and fee‑analysis solutions under tightening regulatory regimes.
- Mid‑2025: Financial institutions have increasingly shifted to digital reconciliation workflows, enabling continuous payment and transaction monitoring rather than traditional periodic cycles. This supports real‑time fee and transaction validation, better fraud detection, and faster financial closing processes.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 1610 Million Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 5417 Million CAGR(2025-2034) 12.90% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue forecast, AI impact on Market trends, Share Insights, Company ranking, competitive landscape, Recent Developments, Market Dynamics, and Emerging Trends Segments Covered By Component (Software, Services), By Deployment Mode (On-Premises, Cloud-based), By Enterprise Size (Small and Medium Enterprises, Large Enterprises), By Application (Transaction Monitoring, Fee Reconciliation, Compliance Management, Reporting & Analytics, Others), By End-User (Banks, Credit Unions, Financial Institutions, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia, Netherlands, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, Rest of Latin America; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Fiserv, Fisint, Accenture, Oracle, SAP, Infosys, FIS Global, ACI Worldwide, Temenos, nCino, Zafin, Kyriba, Bottomline Technologies, Intellect Design Arena, Jack Henry & Associates, Others Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited Users and Printable PDF)  Bank Fee Analysis Software MarketPublished date: Dec 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Bank Fee Analysis Software MarketPublished date: Dec 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Fiserv
- Fisint
- Accenture
- Oracle
- SAP
- Infosys
- FIS Global
- ACI Worldwide
- Temenos
- nCino
- Zafin
- Kyriba
- Bottomline Technologies
- Intellect Design Arena
- Jack Henry & Associates
- Others










