Quick Navigation
Overview
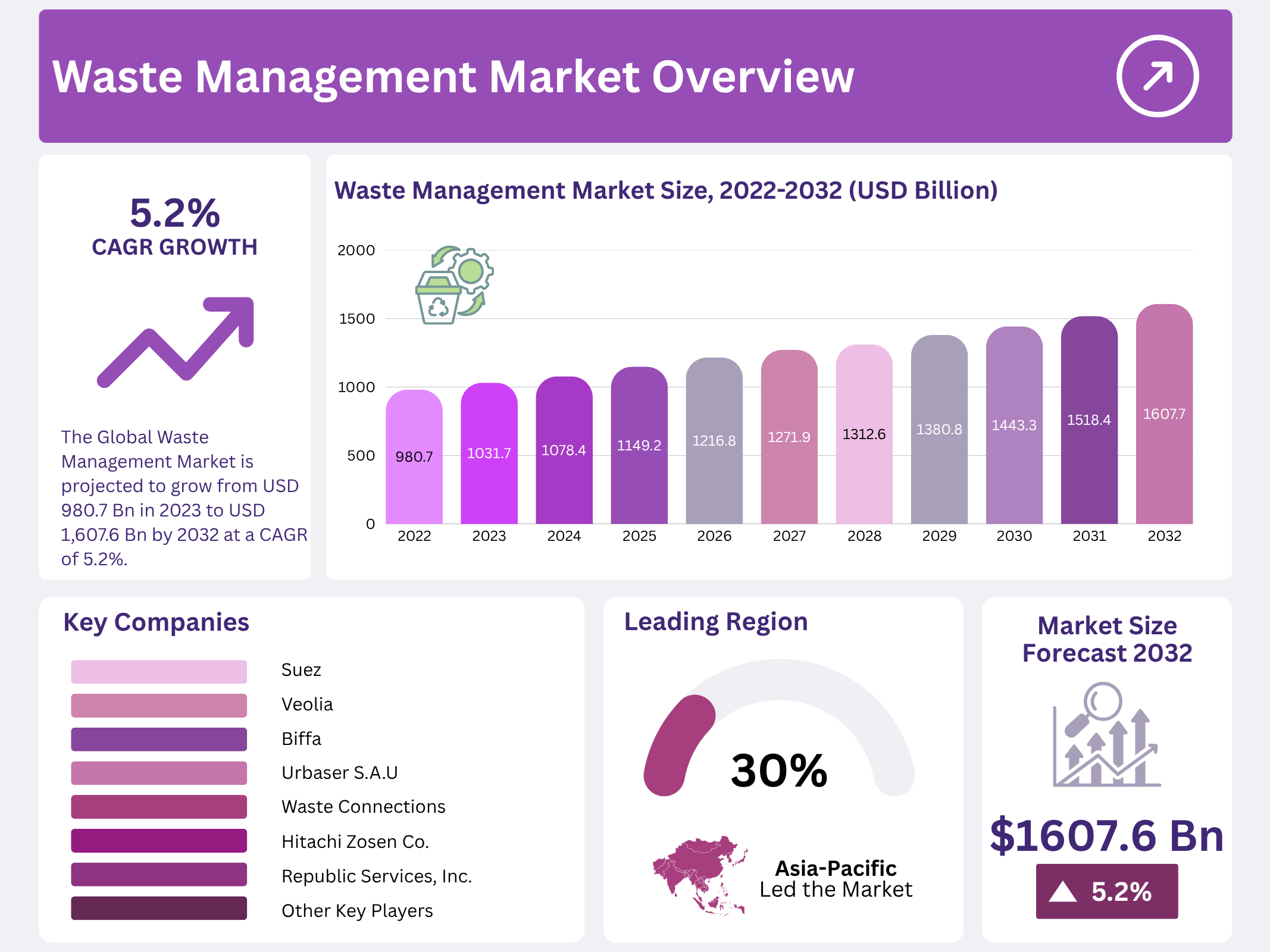
New York, NY – October 28, 2025 – The Global Waste Management Market was valued at USD 980.7 billion and is projected to reach USD 1,607.6 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 5.2% from 2023 to 2032. Stringent government regulations, including the Recovery Act and Resource Conservation and Waste Shipment Regulation, are key drivers of this market. During the COVID-19 pandemic, waste generation from commercial and industrial sectors declined as operations were halted or reduced, while household waste surged due to lockdowns.
With the reopening of manufacturing facilities in 2021 and widespread vaccination programs, the waste recycling sector regained momentum. Rising global awareness about safe waste disposal for protecting both human and animal health has encouraged the adoption of new waste treatment and recycling methods. Waste management companies are under increasing pressure to handle and recycle hazardous waste containing substances like heavy metals and sodium compounds safely and efficiently.
The industry remains highly consolidated, dominated by major players such as Veolia, Covanta, Valrico, and Waste Management Inc. These firms benefit from strong customer bases, established reputations, and advanced processing technologies. Consequently, high capital investment requirements and technological barriers limit new entrants, reducing competitive intensity and maintaining the dominance of established players in the market.
Key Takeaways
- The Global Waste Management Market is projected to grow from USD 980.7 billion in 2023 to USD 1,607.6 billion by 2032 at a CAGR of 5.2%.
- Industrial waste holds a 79% market share, fueled by rapid industrialization and urbanization.
- Waste collection dominates with a 59% share, focusing on segregation and storage maintenance.
- The residential sector leads with a 47% share, driven by consumer goods and online shopping.
- Asia-Pacific holds a 30% revenue share, led by dense populations in China and India.
Report Scope
| Report Features | Description |
|---|---|
| Market Value (2022) | USD 980.7 Billion |
| Forecast Revenue (2032) | USD 1,607.6 Billion |
| CAGR (2023-2032) | 5.2% |
| Segments Covered | Waste Type (Municipal Waste, Medical Waste, Industrial Waste, and E-Waste), By Service Type (Collection, Transportation, and Disposal), By End-User (Residential, Commercial, and Industrial) |
| Competitive Landscape | Waste Management, Suez, Veolia, Valicor, Waste Connections, Republic Services, Biffa, Clean Harbors, Covanta Holding, Daiseki, Hitachi Zosen, Remondis Se & Co. Kg, Urbaser, Fcc Environment, Biomedical Waste Solutions, and Stericycle |
Key Market Segments
By Waste Type
The Industrial waste segment holds the largest market share at 79%. The waste management market is categorized into municipal waste, medical waste, industrial waste, and e-waste. Industrial waste dominates due to rapid industrialization and urbanization, which significantly increases waste generation. Improper management of industrial waste can lead to pollution of lakes and groundwater, harming wildlife and vegetation.
Approximately 7 billion people are projected to reside in urban areas, driving a surge in urban waste. The COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 led to lockdowns in countries like the U.S., India, and China, increasing residential waste due to remote work. Over the forecast period, fueled by rapid technological advancements that shorten the lifespan of electronic products, thus increasing e-waste.
Medical waste also saw a spike between 2020 and 2021 due to heightened diagnostic and treatment activities for COVID-19. Proper medical waste management is critical in hospitals, clinics, and diagnostic centers to prevent the spread of diseases like whooping cough and diarrhea.
By Service Type
The Collection segment leads with a 59% market share. The market is segmented into collection, transportation, and disposal. Waste collection involves segregation, loading, unloading, selecting suitable storage areas, and maintaining these areas at a safe distance from waste sources. Regular cleaning and maintenance of storage sites are essential.
Transportation requires careful handling to prevent spillage or leakage, especially for liquid and hazardous waste, which must be transported in secure, leak-proof vehicles. Non-hazardous waste can be sent directly to recycling facilities. Disposal methods include recycling, incineration, composting, landfills, and open dumping. Proper disposal is vital to avoid environmental degradation and health risks, such as HIV or hepatitis infections.
By End-User
The Residential segment dominates with a 47% market share. The market is divided into residential, commercial, and industrial end-users. Residential waste, primarily from single- and multi-family homes, includes consumer durables, fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG), e-waste, and packaging materials. Rising disposable incomes and the growing popularity of online shopping have increased plastic waste in this sector.
The industrial segment is another key contributor, with waste generated from construction, oil and gas, chemical, nuclear, and agricultural industries. This waste includes solids, liquids, and gases, both hazardous and non-hazardous. The chemical, oil and gas, and nuclear industries are the primary sources of hazardous waste. Growing global demand for chemicals, energy, and materials is expected to increase industrial waste, creating opportunities for service providers specializing in hazardous waste collection, treatment, and disposal.
Regional Analysis
The Asia-Pacific region led the waste management market, capturing a 30% revenue share. This dominance stems from its dense population, with China and India being the most populous countries. The region includes key markets like Japan, South Korea, and other Pacific Rim nations, all contributing to significant waste generation due to rapid urbanization and industrial growth.
The Asia-Pacific market is poised for the fastest growth over the forecast period, driven by increasing urban populations and expanding construction activities. Rising drilling operations and infrastructure development are generating substantial waste, necessitating efficient management solutions. Growing urban centers in emerging markets like India and China are fueling demand for advanced waste handling to address environmental and health concerns.
Key industry players are focusing on cost-effective, sustainable, and technologically advanced waste management solutions to meet this demand. For instance, in December 2017, Keppel Corporation (China) secured a contract to design and operate Hong Kong’s first integrated waste management facility. With ongoing garbage management reforms and infrastructure improvements, the region is set to see sustained demand for innovative waste management services.
Top Use Cases
- Municipal Solid Waste Handling: Cities collect everyday trash from homes and streets to keep areas clean and healthy. Teams sort items like food scraps and papers, then transport them to processing sites. This prevents diseases from spreading and reduces bad smells in neighborhoods. Recycling parts helps save resources, making urban living more sustainable for growing populations.
- Industrial Waste Processing: Factories produce leftovers like chemicals and metals during manufacturing. Proper handling involves safe storage and treatment to avoid harming workers or nearby water sources. Companies reuse materials where possible, turning waste into new products. This cuts pollution and supports eco-friendly operations, helping industries meet green standards.
- Healthcare Waste Disposal: Hospitals generate items like used needles and bandages that carry germs. Strict rules guide separation, sterilization, and incineration to stop infections from spreading. Safe transport ensures no risks during movement. This protects patients, staff, and communities, while promoting trust in medical services through clean practices.
- Construction Debris Recycling: Building sites create rubble, wood, and concrete scraps from projects. On-site sorting allows the reuse of materials like bricks for new structures. Hauling recyclables to facilities reduces landfill use and lowers transport costs. This speeds up projects and builds a greener construction sector focused on resource efficiency.
- E-Waste Recovery Programs: Old gadgets like phones and computers pile up quickly with tech upgrades. Collection drives and drop-off points gather them for safe dismantling. Valuable metals get extracted for reuse, while harmful parts are neutralized. This curbs toxic leaks into soil and encourages longer device lifespans among users.
Recent Developments
1. Suez
Suez is advancing its ecological transformation goals, focusing on plastic recycling and carbon capture. Recent developments include expanding its plastic recycling capacity in Europe and launching new projects to enhance water and waste circularity. The company is also investing in advanced sorting technologies to improve recovery rates for industrial and municipal clients, reinforcing its commitment to a sustainable, low-carbon economy.
2. Valicor Environmental Services
Valicor, a leading provider of non-hazardous wastewater and solid waste disposal services, continues its strategic growth through acquisitions. Recently, it expanded its geographic footprint and service capabilities by acquiring assets in the Midwest and South. This growth enhances its ability to serve the energy, manufacturing, and environmental sectors, providing critical recycling and disposal solutions while strengthening its position as a key independent operator in the market.
3. Veolia
Veolia completed its acquisition of Suez in 2023, creating a global environmental services leader. The merged entity is now focused on integrating operations and delivering synergies. Recent priorities include deploying advanced solutions for water, waste, and energy management to help industrial clients and cities decarbonize. The new Veolia is leveraging its expanded scale to accelerate investment in circular economy and climate change mitigation technologies.
4. Waste Connections
Waste Connections continues to execute a disciplined growth strategy, highlighted by strategic acquisitions to expand its service footprint in secondary and exclusive markets. Financially, the company has reported consistent revenue growth and strong cash flow, allowing for increased shareholder returns. It is also making significant investments in landfill gas-to-energy projects, turning methane emissions into renewable natural gas (RNG) to create value and support sustainability goals.
5. Republic Services, Inc.
Republic Services is aggressively expanding its recycling and renewable energy capabilities. Key developments include the opening of new Polymer Recovery Facilities for advanced plastic recycling and significant investments in landfill gas-to-energy projects. The company is also on track with its massive “Blueprint 100” initiative to modernize its recycling infrastructure across the U.S., aiming to increase processing capacity and purity of recycled commodities.
Conclusion
Waste Management is evolving into a vital pillar of sustainable living, where innovative approaches turn everyday discards into opportunities for renewal. With cities expanding and industries thriving, the focus shifts toward smarter collection, advanced recycling, and energy recovery methods that ease environmental pressures without straining resources. Governments and businesses are teaming up to foster circular systems, ensuring waste no longer burdens our planet but fuels progress. This path promises healthier communities and resilient economies, inviting everyone to rethink trash as tomorrow’s treasure.










