Quick Navigation
Overview
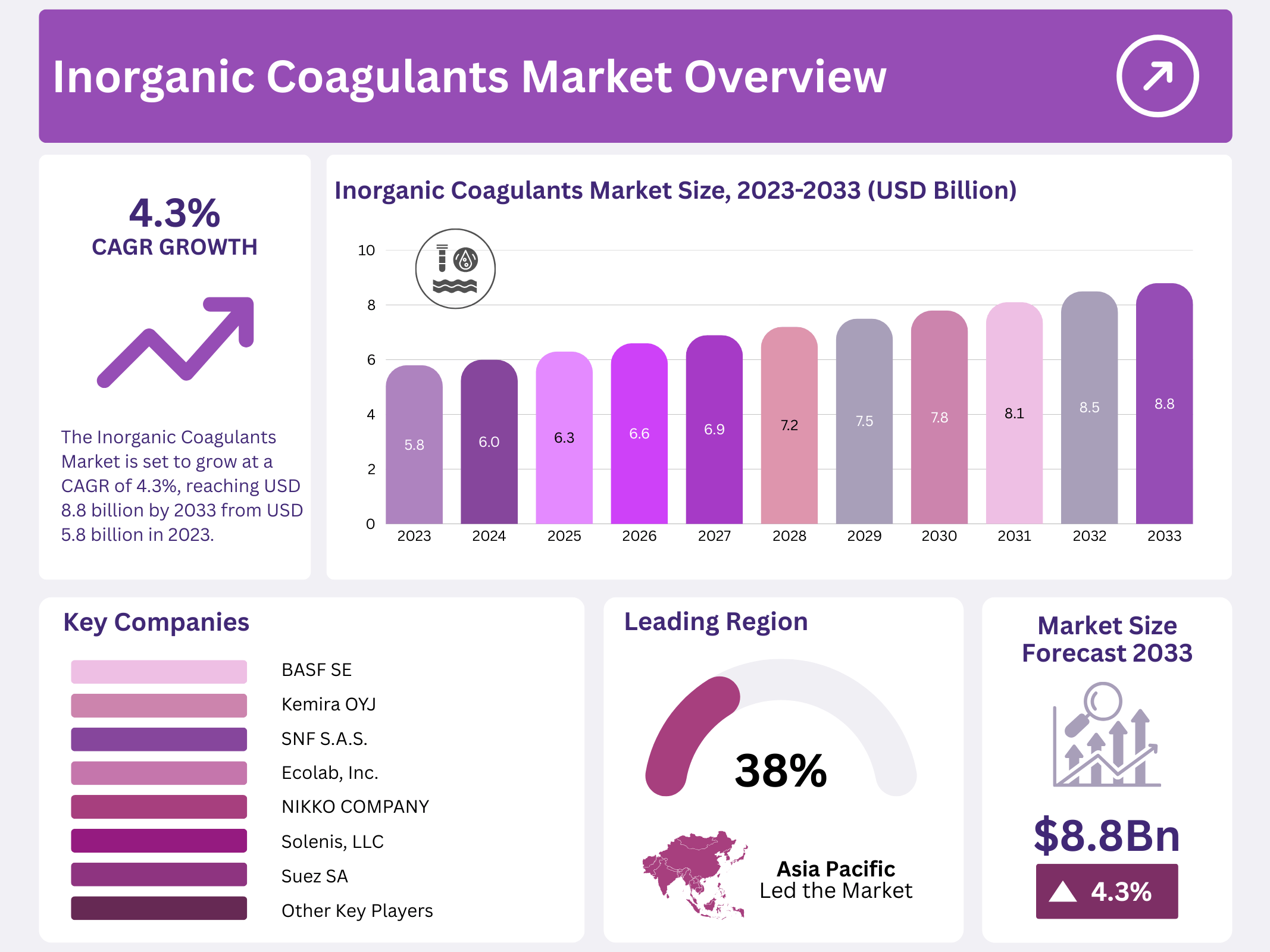
New York, NY – December 30, 2025 – The Global Inorganic Coagulants Market is projected to reach approximately USD 8.8 billion by 2033, up from USD 5.8 billion in 2023, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.3% during the forecast period from 2023 to 2033. This growth is mainly driven by increasing demand for clean drinking water, rising investments in wastewater treatment infrastructure, and stricter environmental regulations worldwide.
Inorganic coagulants are chemical compounds, primarily metal salts, widely used in water and wastewater treatment processes. Their primary function is to destabilize fine suspended particles present in water, allowing them to clump together and form larger particles. This process facilitates the removal of impurities through sedimentation, filtration, or precipitation, thereby enhancing overall water clarity and safety.
Commonly used inorganic coagulants include aluminum sulfate (alum), ferric chloride, and polyaluminum chloride (PAC). These materials are highly effective in reducing turbidity, color, and organic contaminants in water. By promoting the formation of dense, settleable flocs, inorganic coagulants play a vital role in improving water quality across municipal, industrial, and environmental applications.
Key Takeaways
- The Inorganic Coagulants Market is set to grow at a CAGR of 4.3%, reaching USD 8.8 billion by 2033 from USD 5.8 billion in 2023.
- Aluminum Coagulants’ dominance, including sulfate and chloride, held over 62.4% market share in 2023, favored for water and wastewater treatment.
- Liquid Inorganic Coagulants secured 56.2% market share in 2023, known for ease of use and efficient water treatment application.
- Municipal Water Treatment claimed a dominant 62.7% market share in 2023, showcasing inorganic coagulants’ crucial role in ensuring clean drinking water.
- Asia-Pacific (APAC) leads the global Inorganic Coagulants Market, holding over 38.5% share and valued at USD 2.03 billion.
Report Scope
| Report Features | Description |
|---|---|
| Market Value (2023) | USD 5.8 Billion |
| Forecast Revenue (2033) | USD 8.8 Billion |
| CAGR (2024-2033) | 4.3% |
| Segments Covered | By Derivative(Acrylic Esters, Butyl Acrylate, Ethyl Acrylate, Methyl Acrylate, 2-Ethylhexyl Acrylate, Others), Acrylic Polymer(Superabsorbent Polymers, Water Treatment Polymers, Others, Others), By Application(Paint and Coatings, Adhesives & Sealants, Detergents, Textiles, Diapers and Feminine Hygien Product, Water Treatment, Personal Care Products, Others) |
| Competitive Landscape | BASF SE, Kemira OYJ, Solenis, LLC, Ecolab, Inc., SNF S.A.S., Danaher Corporation, Evonik Industries AG, Suez SA, Nouryon, Lonza Group Ltd, Kurita Water Industries, Ltd., Huntsman Corporation, GEO Specialty Chemicals, Inc., Ixom Operations Pty., Ltd., Feralco AB |
Key Market Segments
By Type
In 2023, Aluminum-based Coagulants dominated the inorganic coagulants market, accounting for more than 62.4% of the total share. This segment includes key products such as aluminum sulfate, polyaluminum sulfate, aluminum chloride, polyaluminum chloride, aluminum chlorohydrate, and sodium aluminate.
These coagulants are widely used in water and wastewater treatment due to their strong ability to destabilize suspended particles and promote the formation of larger flocs, which improves impurity removal. Among them, aluminum sulfate and polyaluminum chloride are especially prominent, driven by their high efficiency, adaptability, and proven performance across a wide range of water treatment applications.
By Form
In 2023, the Liquid Form led the inorganic coagulants market, capturing over 56.2% of the total market share. Liquid coagulants are highly favored for their ease of handling, accurate dosing, and rapid dispersion in water treatment systems. These advantages enhance operational efficiency and ensure consistent coagulation performance in both water and wastewater treatment processes. The flexibility of liquid formulations allows their use across various treatment conditions, making them a preferred option for municipalities and industrial operators seeking effective and dependable water purification solutions.
By End Use
In 2023, the Municipal Water Treatment sector held a dominant position in the inorganic coagulants market, representing more than 62.7% of total demand. This highlights the crucial role of inorganic coagulants in meeting the increasing demand for safe and clean drinking water.
Their reliable coagulation performance supports effective clarification and purification processes in public water supply systems. In addition to municipal use, inorganic coagulants are extensively applied in industrial water treatment, textiles, food and beverage processing, pulp and paper, chemicals and fertilizers, oil and gas, mining and mineral processing, and other industries, supporting a broad range of water treatment requirements.
Regional Analysis
Asia-Pacific (APAC) led the Inorganic Coagulants Market, capturing more than 38.5% of the global market share, with the market valued at approximately USD 2.03 billion. This strong position reflects steady growth supported by high demand across the region.
The dominance of APAC highlights the widespread adoption of inorganic coagulants across multiple industries. Rapid expansion in sectors such as water and wastewater treatment, textiles, and chemicals has been a key driver of demand, reinforcing the region’s importance in the global market.
Sustained economic growth, large-scale infrastructure projects, and increasing manufacturing activities across emerging economies further boosted the consumption of inorganic coagulants. Additionally, population growth and the rising middle-class base have increased the need for clean water, industrial processing, and chemical production, all of which rely heavily on inorganic coagulants, thereby supporting continued market expansion in the region.
Top Use Cases
- Water Treatment in Municipal Plants: Municipal drinking water facilities are the primary consumers of inorganic coagulants. They are essential for treating raw surface water from rivers and lakes. The coagulants, like aluminum sulfate, clump together fine particles and organic matter. This allows for their easy removal, ensuring the water is clear, safe, and meets regulatory standards before reaching households and businesses.
- Industrial Wastewater Management: Industries such as textiles, chemicals, and mining generate wastewater laden with pollutants. Inorganic coagulants are crucial here for pretreatment. They effectively remove heavy metals, dyes, and suspended solids. This process reduces the contaminant load, protecting public sewer systems and lowering the cost of further treatment required to meet stringent environmental discharge permits.
- Stormwater Runoff Treatment: Urban runoff carries oils, sediments, and pollutants from roads into water bodies. Inorganic coagulants are deployed in retention ponds and treatment systems to address this non-point source pollution. They rapidly settle out suspended solids and associated contaminants. This application is vital for protecting aquatic ecosystems and maintaining water quality in urban environments.
- Sludge Thickening and Dewatering: A major byproduct of water treatment is sludge, which is expensive to dispose of. Inorganic coagulants, particularly ferric chloride, are used as conditioning agents. They bind water within the sludge, creating larger clumps. This significantly improves the efficiency of dewatering equipment, reducing sludge volume and weight, thereby drastically cutting transportation and disposal costs.
- Phosphorus Removal in Eutrophication Control: Excess phosphorus in wastewater causes harmful algal blooms in lakes. Inorganic coagulants, especially those based on iron and aluminum, are highly effective at phosphorus removal. They react with dissolved phosphate to form an insoluble solid that settles out. This application is critical for wastewater plants in sensitive watersheds to prevent ecosystem damage.
Recent Developments
1. BASF SE
BASF continues to advance its portfolio with a focus on efficiency and sustainability. Their Zetag and Alkan brands of polyaluminium chloride (PACl) coagulants are engineered for optimized sludge dewatering and lower total cost of operation in water treatment. Recent R&D emphasizes products that work across a wide pH range and reduce residual aluminium in treated water.
2. Kemira OYJ
Kemira is investing in the circular economy for inorganic coagulants. A key development is the PIX and PAX range of iron and aluminium salts, now increasingly produced using recycled raw materials, reducing the carbon footprint. Their “Eco-Care” labeling highlights products with a verified lower environmental impact, supporting customers in achieving sustainability goals in municipal and industrial wastewater treatment.
3. Solenis, LLC
Solenis focuses on high-performance, tailored inorganic coagulant blends. Their Bioscrub 300 series combines inorganic coagulants with proprietary additives to enhance contaminant removal, particularly in challenging industrial process water. Recent developments target improved phosphorus removal and reduced sludge volume in applications like pulp/paper and mining, aiming for lower lifecycle costs and operational simplicity.
4. Ecolab, Inc.
Through its Nalco Water business, Ecolab integrates inorganic coagulants into smart, data-driven solutions. Their 3D TRASAR technology for water management can optimize the feed of coagulants like PACl in real-time, preventing over- or under-dosing. This digital approach maximizes performance, ensures consistency, and minimizes chemical waste and environmental discharge, moving beyond selling commodities to providing managed outcomes.
5. SNF S.A.S.
While a leader in organic flocculants, SNF complements its range with inorganic coagulants like ferric chloride and PACl. The recent strategy emphasizes supplying integrated coagulant-flocculant systems for a synergistic effect. Their developments focus on reliable, on-time supply and technical support for these inorganic products, ensuring they work seamlessly with their polymers to provide complete clarification and sludge dewatering packages.
Conclusion
The market for inorganic coagulants remains robust, underpinned by their irreplaceable role in global water security and environmental protection. Their cost-effectiveness, reliability, and proven efficacy in treating diverse water streams ensure sustained demand. While facing competition from alternative organic polymers, inorganic coagulants are expected to maintain a dominant market share, particularly in large-scale and demanding applications, due to their powerful performance and economic advantages in solid-liquid separation processes.










