Quick Navigation
Overview
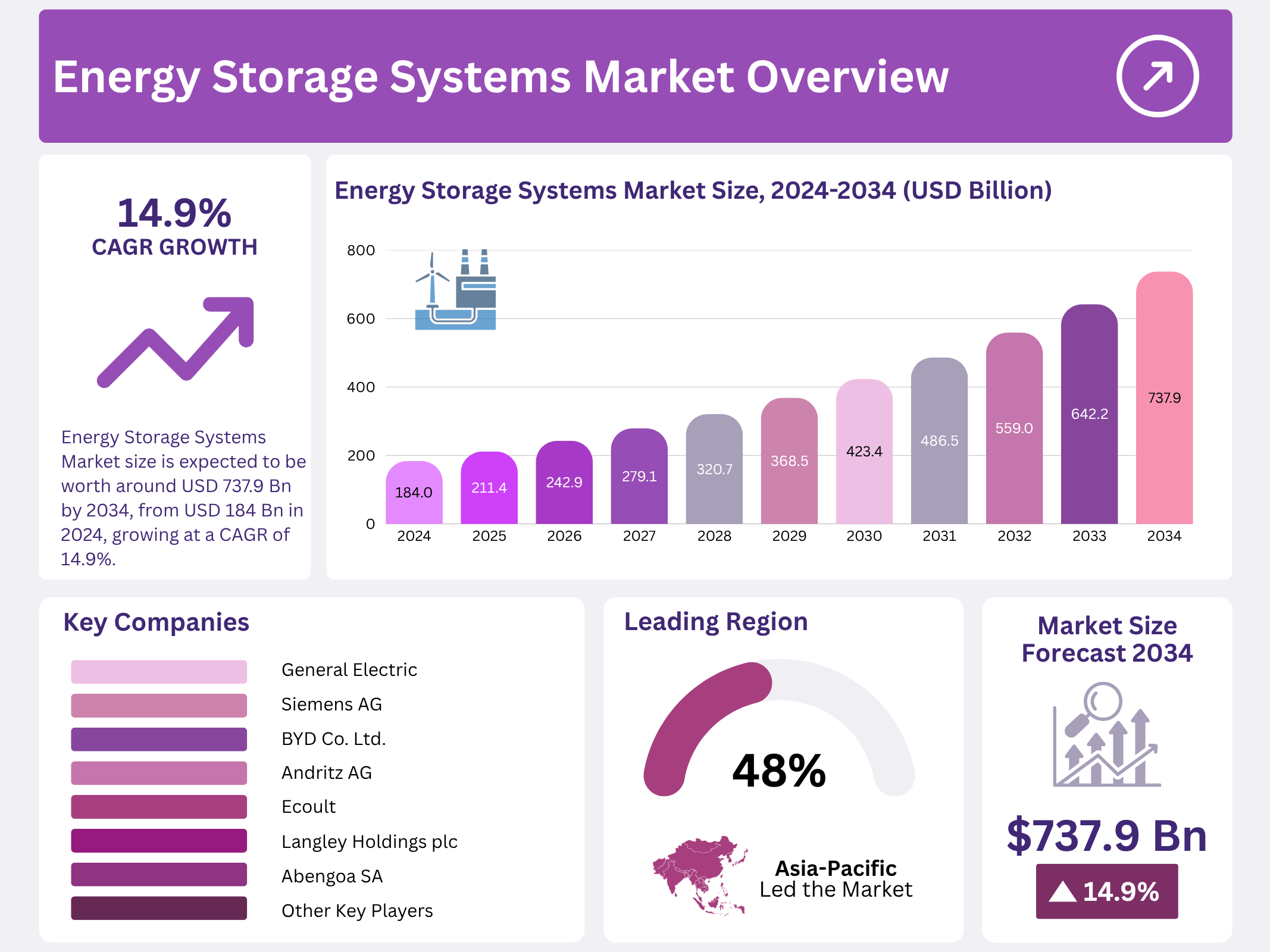
New York, NY – October 22, 2025 – The Global Energy Storage Systems (ESS) Market is projected to reach USD 737.9 billion by 2034, rising from USD 184.0 billion in 2024, and expanding at a CAGR of 14.9% between 2025 and 2034. Energy storage systems are purpose-built technologies designed to store electricity for later use, ensuring balance between energy supply and demand, improving grid reliability, and supporting the integration of intermittent renewable sources like solar and wind.
These technologies include battery storage, thermal storage, pumped hydro, and mechanical systems, each offering unique capabilities across generation, transmission, and distribution networks. ESS are increasingly deployed across utility, industrial, commercial, and residential sectors, as well as in electric vehicles and remote power systems, to enhance energy efficiency, provide backup power, and manage energy costs effectively. They play a pivotal role in optimizing grid operations and facilitating the shift toward decentralized renewable energy systems.
According to Germany’s Federal Network Agency, the nation’s installed battery storage capacity exceeded 6 GW in 2024, underscoring rapid adoption in both residential and grid-scale applications. Globally, the market’s momentum is supported by rising renewable energy investments, supportive government policies, and ongoing grid modernization initiatives. Together, these forces are positioning energy storage systems as indispensable components of a sustainable, resilient, and low-carbon energy future.
Key Takeaways
- The Global Energy Storage Systems Market is projected to be valued at USD 184.0 billion in 2024, at a CAGR of 14.9% and is estimated to reach USD 737.9 billion by 2034.
- Among technologies, electrochemical energy storage accounted for the largest market share of 79.3%.
- Among applications, utility accounted for the majority of the market share at 48.1%.
- Asia Pacific is estimated as the largest market for energy storage systems with a share of 48.3% of the market share.
Report Scope
| Report Features | Description |
|---|---|
| Market Value (2024) | USD 184.0 Billion |
| Forecast Revenue (2034) | USD 737.9 Billion |
| CAGR (2025-2034) | 14.9% |
| Segments Covered | By Technology (Electrochemical Energy Storage (Lithium-ion, Lead-acid, Nickel-based, Flow Batteries, Others), Mechanical Energy Storage (Pumped Hydro Storage, Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES), Flywheels), Thermal Energy Storage, Others), By Application (Utility, Commercial & Industrial (Transportation, Critical Infrastructure, Infrastructure & Commercial Buildings, Others), residential) |
| Competitive Landscape | General Electric, Siemens AG, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd., BYD Co., Ltd., Panasonic Corporation, LG Energy Solution Ltd, Andritz AG, Samsung SDI Co., Ltd., Ecoult, Langley Holdings plc, Saft, BrightSource Energy Inc, Abengoa SA, Baltimore Aircoil Company, Voith GmbH & Co. KGaA, Other Key Players |
Key Market Segments
Technology Segment Analysis
The electrochemical energy storage segment led the market in 2024, capturing a dominant 79.3% revenue share. This growth is driven by the widespread adoption of lithium-ion batteries, valued for their high energy density, efficiency, and decreasing costs. These systems are critical for grid stabilization, renewable energy integration, and electric vehicle applications. Ongoing innovations in battery technology, coupled with rising energy demands in the utility and commercial sectors, continue to propel this segment’s expansion.
Application Segment Analysis
In 2024, the utility segment held a commanding 48.1% market share. This dominance stems from the growing integration of renewable energy sources, increased need for grid stability, and significant investments in large-scale energy storage projects by government and private utilities. Utility-scale storage systems play a vital role in managing the intermittent nature of solar and wind power, ensuring energy reliability, and facilitating effective peak load management.
Geopolitical Impact Analysis
The ongoing trade disputes among the United States, China, and the European Union have profoundly disrupted the global energy storage market, impacting supply chains and production capacities. Tariffs imposed during the Trump administration have significantly raised the cost of importing batteries and critical materials, particularly from China, which supplies over 90% of lithium-ion battery cells for U.S. energy storage projects. This dependency makes the sector highly susceptible to trade policy shifts.
As the leading global manufacturer of lithium-ion batteries, China dominates the clean energy supply chain. In response to U.S. tariffs, China implemented export controls and licensing requirements for critical raw materials essential for battery and energy storage technologies. In April 2025, China intensified these restrictions by limiting exports of seven rare earth elements and specialized magnets, crucial for electric vehicle batteries, renewable energy systems, and advanced defense technologies.
After the U.S. imposed tariffs as high as 145% on Chinese battery imports, China retaliated with tariffs of up to 125% on select U.S. goods, including clean energy products. This tit-for-tat tariff escalation has caused widespread disruptions in global supply chains, increased demand for non-Chinese battery suppliers, and triggered significant price volatility. U.S. developers, seeking alternative suppliers, now face heightened competition, resulting in elevated costs and longer lead times in global markets.
These geopolitical tensions are reshaping the energy storage landscape, delaying project development and increasing investment risks worldwide. However, they are also catalyzing strategic shifts, as nations strive to bolster domestic battery manufacturing and diversify supply chains to mitigate reliance on imports vulnerable to trade policy fluctuations.
Regional Analysis
In 2024, the Asia-Pacific region solidified its position as the dominant force in the global energy storage systems market, capturing 48.3% of the market share. This leadership is fueled by rapid advancements in renewable energy, growing electricity demand, and substantial investments in grid modernization.
Key countries, including China, Japan, South Korea, India, and Australia, are prioritizing energy storage to enhance grid stability, manage peak loads, and integrate renewable energy sources like solar and wind. China remains the regional frontrunner, leveraging large-scale government-backed projects and a robust battery manufacturing ecosystem. Japan and South Korea are making significant strides in advanced battery technologies and smart grid infrastructure.
Meanwhile, emerging markets such as India and Southeast Asia are accelerating adoption through supportive policies, rural electrification initiatives, and declining battery costs. With ongoing regulatory frameworks, financial incentives, and technological advancements, the Asia-Pacific region is poised to lead global energy storage development in both scale and innovation.
Top Use Cases
- Grid Stabilization: Energy storage systems help keep the power grid steady by quickly adjusting to sudden changes in supply and demand. They act like a buffer, releasing stored power during peaks to prevent blackouts and support reliable electricity flow for homes and businesses, making the entire network more resilient and efficient in everyday operations.
- Renewable Energy Integration: These systems store extra power from sources like solar panels and wind turbines when production is high, then release it when the sun isn’t shining or wind isn’t blowing. This smooths out the ups and downs of green energy, helping communities rely more on clean power without wasting resources or facing shortages.
- Peak Shaving for Businesses: Companies use energy storage to cut down on high electricity bills by saving power during cheap off-peak hours and using it during expensive peak times. This smart approach lowers costs, reduces strain on the grid, and lets firms focus on growth rather than energy expenses.
- Microgrids for Remote Areas: In places far from main power lines, like rural villages or islands, storage systems create self-contained mini-grids that combine local renewables with backup power. They ensure lights stay on during outages, support essential services, and promote energy independence without relying on distant infrastructure.
- Electric Vehicle Support: Energy storage powers charging stations for electric cars, storing grid energy for fast refills during low-demand periods. This eases the load on highways and cities, speeds up the shift to greener transport, and makes driving electric more convenient for daily commuters and fleets alike.
Recent Developments
1. General Electric
GE Vernova has commissioned its first GridStar Lithium battery energy storage system for East Kentucky Power Cooperative. This 5-MW/10-MWh project marks a significant step in providing reliable, dispatchable power to the grid. The system will enhance grid stability and support the integration of more renewable energy sources, showcasing GE’s commitment to the energy transition through its scalable storage solutions.
2. Siemens AG
Siemens Smart Infrastructure has launched its Siestorage battery energy storage system, complemented by a comprehensive digital ecosystem. This integrated solution, scalable up to 100 MW, is designed for commercial and industrial applications. It focuses on optimizing energy costs, ensuring backup power, and providing grid services. The platform uses AI for performance analytics and predictive maintenance, representing Siemens’ holistic approach to decentralized energy management.
3. Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Mitsubishi Power is a leader in large-scale storage, having deployed the 1,200 MWh Gemini project in Nevada. Their solution combines battery storage with AI-powered software for grid stabilization and renewable energy time-shifting. Recently, they announced a strategic partnership with TEPCO to create a new battery storage platform, focusing on enhancing grid resilience and accelerating the adoption of clean energy in Japan and other global markets.
4. BYD Co. Ltd.
BYD continues to advance its Blade Battery technology, known for its safety and longevity, into the utility-scale storage market. Their recent projects include massive installations in China, Europe, and the US. BYD’s systems are designed for high energy density and long cycle life, supporting grid peak shaving and renewable firming. The company is aggressively expanding its global manufacturing footprint to meet the soaring demand for its energy storage products.
5. Panasonic Corporation
Panasonic is focusing on integrating its high-quality, cylindrical lithium-ion batteries into residential and commercial storage systems. A key development is their partnership with Evergen to optimize solar self-consumption and virtual power plant (VPP) participation in Australia using Panasonic’s batteries. They are also advancing R&D for next-generation solid-state batteries, aiming for higher capacity and improved safety for future energy storage applications.
Conclusion
Energy Storage Systems as a cornerstone of the clean energy shift, quietly transforming how we handle power in a world hungry for renewables. They’re bridging the gap between unpredictable sources like sun and wind with our steady needs, fostering smarter grids that adapt without fuss. Falling tech costs and supportive policies are speeding up adoption across homes, factories, and far-off spots, while new designs promise even longer life and greener builds. These systems aren’t just backups; they’re enablers of a flexible, sustainable future where energy flows smarter and cleaner for everyone.










