Quick Navigation
Overview
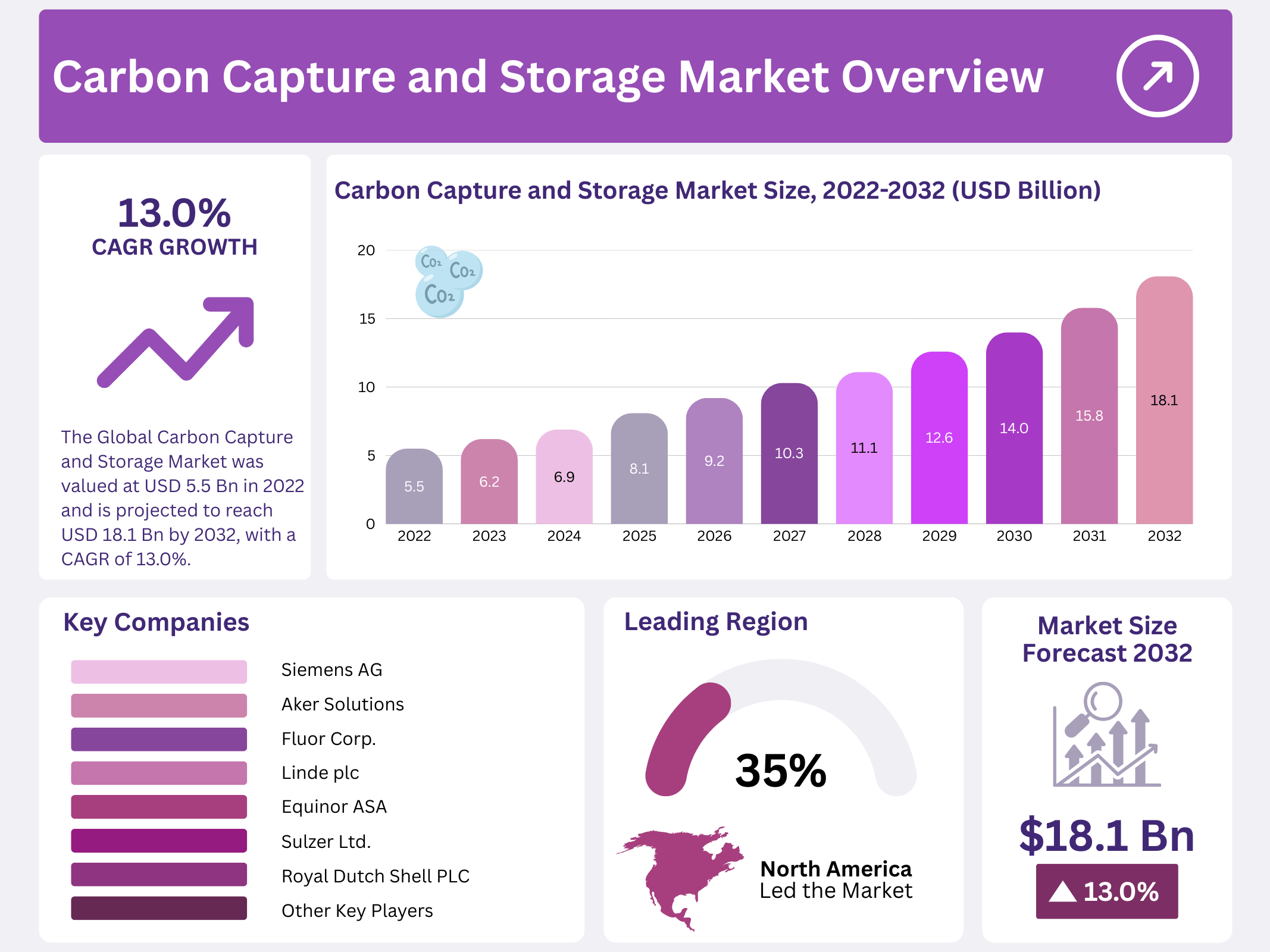
New York, NY – December 11, 2025 – In 2022, the global Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) Market was valued at USD 5.5 Billion and is projected to grow steadily to reach USD 18.1 Billion by 2032, registering a strong CAGR of 13% between 2023 and 2032. This growth reflects the rising focus on reducing industrial carbon emissions as governments and industries adopt cleaner energy and emission-control solutions.
Carbon capture and storage is a process that captures carbon dioxide released from fossil-fuel-based activities such as power generation, steel production, and cement manufacturing. Once captured, the carbon dioxide is transported through pipelines or alternative methods, such as ships, and then safely stored in deep underground geological formations. This prevents carbon dioxide from entering the atmosphere, helping to lower environmental damage and reduce long-term climate risks.
Global industrial expansion and population growth continue to increase demand for energy, materials, and manufactured goods, leading to higher carbon dioxide emissions. As industrialization accelerates, carbon emissions have reached critical levels, driving the need for effective mitigation technologies. Carbon capture and storage helps reduce the overall carbon footprint and supports climate protection efforts, which is encouraging more companies and industries to invest in and adopt CCS solutions worldwide.
Key Takeaways
- The Global Carbon Capture and Storage Market was valued at USD 5.5 Bn in 2022 and is projected to reach USD 18.1 Bn by 2032, with a CAGR of 13% (2023–2032).
- Pre-combustion capture technology dominates with 65.8% revenue share due to its high efficiency and performance.
- Power generation is the leading end-use segment, holding 64.6% market share, driven by high CO₂ emissions from coal-fired plants.
- North America leads the global CCS market with 35.8% revenue share, supported by strong oil & gas activity and strict emission regulations in the US and Canada.
Report Scope
| Report Features | Description |
|---|---|
| Market Value (2022) | USD 5.5 Bn |
| Forecast Revenue (2032) | USD 18.1 Bn |
| CAGR (2023-2032) | 13.0% |
| Segments Covered | By Technology – Pre-combustion, Post-combustion, Oxy-combustion, and Industrial Process; By End-Use Industry – Power Generation, Oil & Gas, Metal Production, Cement, and Other End-Use Industries |
| Competitive Landscape | Siemens AG, Aker Solutions, Dakota Gasification Company, Fluor Corp., Linde plc, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd., Equinor ASA, Royal Dutch Shell PLC, Sulzer Ltd., Exxon Mobil Corporation, and Other Key players |
Key Market Segments
By Technology Analysis
Pre-combustion technology leads the global carbon capture and storage market, accounting for a dominant 65.8% revenue share among available technologies. The market is segmented into pre-combustion, post-combustion, oxy-combustion, and industrial processes, with pre-combustion standing out due to its efficiency and performance advantages. This technology captures CO₂ before fuel combustion by converting fossil fuels into a mixture of hydrogen and carbon dioxide through the water–gas shift reaction, followed by CO₂ removal using acid gas separation methods.
The growth of pre-combustion technology is supported by its lower energy penalty and higher carbon capture efficiency compared to other methods. These benefits make it especially suitable for large-scale industrial and power applications, where reducing operating costs and maximizing capture rates are critical. As industries seek reliable and energy-efficient carbon reduction solutions, pre-combustion technology continues to gain strong adoption across global CCS projects.
By End-Use Industry Analysis
Power generation dominates the end-use industry segment of the global carbon capture and storage market, holding a significant 64.6% revenue share. The market is categorized into power generation, oil & gas, metal production, cement, and other industrial sectors, with power generation leading due to its high emission intensity. Coal-fired power plants, in particular, are among the largest contributors to global carbon dioxide emissions.
To address rising emission levels, governments across regions are enforcing strict environmental regulations aimed at reducing greenhouse gas output from power producers. As a result, many power generation companies are investing in carbon capture and storage systems to comply with regulations and lower their environmental impact. This regulatory pressure, combined with the urgent need to decarbonize electricity production, continues to drive strong growth in the power generation segment of the global CCS market.
Regional Analysis
North America dominates the global carbon capture and storage market, accounting for a leading 35.8% share of total revenue. This strong regional position is supported by rising oil and gas activities along with strict government policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions. The United States and Canada play a central role in this growth, supported by favorable regulatory frameworks, funding support, and early adoption of large-scale CCS projects.
A growing number of companies across North America have integrated carbon capture and storage into their operations to comply with environmental regulations and meet emission reduction targets. Heightened awareness of climate change, combined with firm government action, has accelerated investments in CCS infrastructure. These factors continue to strengthen North America’s leadership in the global market.
Europe ranks as the second-largest regional market for carbon capture and storage, driven by expanding deployment of CCS projects and the adoption of advanced capture technologies. Strong climate commitments, innovation-focused policies, and cross-border collaboration in carbon reduction initiatives are supporting the steady growth of the CCS market across European countries.
Top Use Cases
- Enhancing Oil Recovery: In the oil industry, captured carbon dioxide is injected into aging reservoirs to push out more oil, making extraction easier and more efficient. This approach not only boosts production from existing wells but also safely stores the gas underground, helping energy companies extend the life of their assets while cutting emissions from drilling operations.
- Cleaning Up Power Plants: Power stations burning fossil fuels or biomass can install capture tech to trap carbon dioxide right at the source before it escapes into the air. This keeps electricity flowing reliably while slashing pollution, allowing utilities to meet stricter environmental rules and transition toward greener energy without shutting down plants prematurely.
- Greening Heavy Industries: Factories making cement, steel, or chemicals often release huge amounts of carbon during production. By adding capture systems, these plants can grab the gas and store it away, enabling them to keep manufacturing essential goods with far less environmental impact and stay competitive in a world demanding sustainable materials.
- Producing Cleaner Hydrogen: Natural gas reforming creates hydrogen for clean fuels, but it also produces carbon dioxide as a byproduct. Pairing this process with capture and storage turns it into low-emission “blue hydrogen,” opening doors for industries like transportation and manufacturing to adopt hydrogen without adding to climate woes.
- Turning Waste into Fuels and Materials: Captured carbon can be reused to make new products like biofuels, building blocks for concrete, or even jet fuel components. This shifts it from a pollutant to a valuable resource, sparking innovation in recycling emissions and creating fresh revenue streams for companies focused on circular economies.
Recent Developments
Siemens AG
- Siemens Energy is advancing carbon capture with its post-combustion technology, notably at the Wilhelmshaven gas-fired power plant pilot in Germany. They focus on solvent-based capture and integrating systems with renewable energy to improve efficiency. Their SPPA-P3000 control system optimizes CCS operations for industrial and power applications.
Aker Solutions
- Aker Solutions, through its subsidiary Aker Carbon Capture, is scaling its Just Catch modular capture technology. Recent milestones include securing a large contract for a facility at Twence’s waste-to-energy plant in the Netherlands. They are also advancing the CO₂ capture and liquefaction project at Norcem’s Brevik cement plant, one of the world’s first industrial-scale cement CCS projects.
Dakota Gasification Company
- Dakota Gasification operates the Great Plains Synfuels Plant, which has captured and sequestered over 40 million tons of CO₂ since 2000 via the Weyburn-Midale project. Recent developments focus on enhancing storage monitoring and exploring new utilization pathways. They continue to be a leading example of commercial-scale CO₂ capture from coal gasification for enhanced oil recovery.
Fluor Corp.
- Fluor, with its EcoCircle technology, provides engineering and project management for major CCS initiatives. Recently, Fluor completed front-end engineering and design for the Alberta Carbon Grid and is involved in the large-scale Carbonvert and Talos project along the U.S. Gulf Coast, aiming to create a major hub for industrial carbon storage.
Linde plc
- Linde engineers and constructs large-scale CCS plants using its proprietary solvent technology. A key recent project is the joint development with BASF of the OASE blue process for carbon capture. Linde is also a partner in the Norwegian Full-Scale CCS project, aiming to transport and securely store CO₂ from industrial sources under the North Sea.
Conclusion
Carbon Capture and Storage is emerging as a cornerstone technology in the shift to a low-carbon world, bridging the gap for sectors tough to decarbonize, like energy and manufacturing. With growing policy support and investment enthusiasm, it promises to unlock sustainable growth by turning emissions into stored assets or useful inputs, fostering resilient supply chains and innovation.










