Quick Navigation
Overview
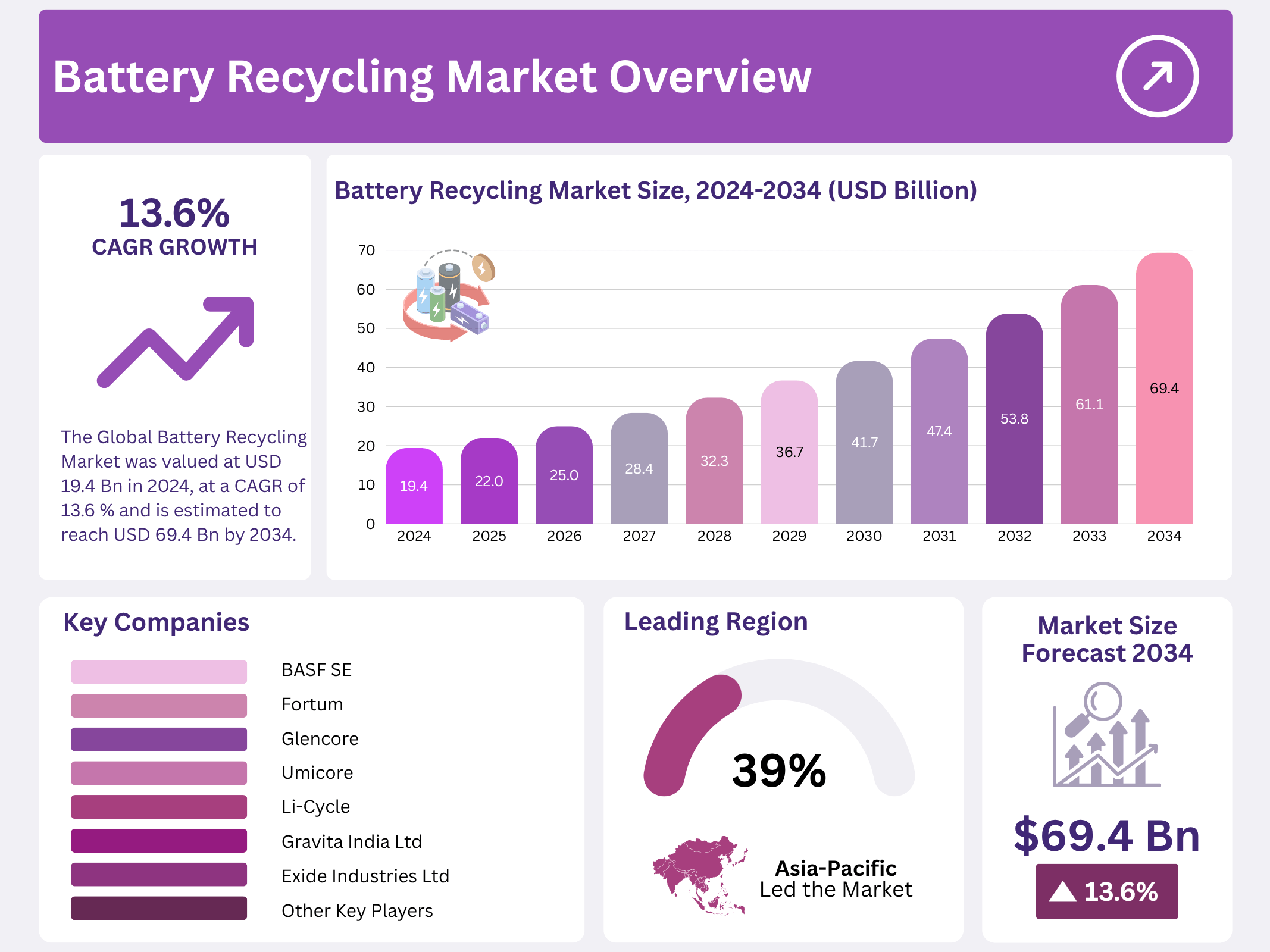
New York, NY – October 27, 2025 – The Global Battery Recycling Market is projected to reach USD 69.4 billion by 2034, growing from USD 19.4 billion in 2024 at a CAGR of 13.6% from 2025 to 2034. Battery recycling focuses on recovering valuable materials such as nickel, lithium, cobalt, and graphite from used batteries for reuse in new battery production or other applications. With the surge in demand for batteries—driven by electric vehicles (EVs), portable electronics, and renewable energy storage recycling has become essential to reduce dependence on raw material mining and mitigate environmental harm from improper disposal.
The rising global population and widespread adoption of battery-powered devices have intensified waste management challenges, as batteries contain toxic elements and heavy metals that can contaminate ecosystems. Recycling offers a sustainable solution by lowering carbon emissions and supporting a circular economy that reuses critical materials.
As global demand for energy storage continues to escalate, the battery recycling industry is emerging as both an environmental necessity and an economic opportunity, fostering sustainable industrial growth. Notably, consumer electronics (CE) represent 50% of the global lithium-ion battery market and consume 39% of the cobalt used in LIBs, underscoring the urgent need for efficient recycling systems to recover valuable resources and minimize environmental impact.
Key Takeaways
- The Global Battery Recycling Market was valued at USD 19.4 billion in 2024, at a CAGR of 13.6 % and is estimated to reach USD 69.4 billion by 2034.
- Among sources, automotive batteries accounted for the largest market share of 61.2%.
- Among battery chemistries, lead-acid accounted for the majority of the market share at 72.1%.
- By technology, pyrometallurgy accounted for the largest market share of 56.2%.
- By end-use, material extraction accounted for the majority of the market share at 48.2%.
- Asia-Pacific is estimated as the largest market for battery recycling with a share of 39.4% of the market share.
Report Scope
| Report Features | Description |
|---|---|
| Market Value (2024) | USD 19.4 Billion |
| Forecast Revenue (2034) | USD 69.4 Billion |
| CAGR (2025-2034) | 13.6% |
| Segments Covered | By Source (Automotive Batteries, (Passenger Cars, Light & Heavy Commercial, Others (2 & 3 Wheelers), Industrial Batteries, Consumer & Electrical Appliance Batteries), By Battery Chemistry (Lithium-ion, (Lithium Cobalt Oxide (LCO), Lithium Manganese Oxide (LMO), Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide (NMC), Lithium Nickel Cobalt Aluminum Oxide (NCA), Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP), Others), Lead-acid, Nickel-based, Flow Batteries, Others), By Technology (Pyrometallurgy, Hydrometallurgy, Mechanical Separation), By End-use (Material Extraction, Disposal, Reuse, Repackaging & Second Life) |
| Competitive Landscape | BASF SE, Accurec Recycling GmbH, Fortum, Glencore, Umicore, Exide Industries Ltd, Gravita India Ltd., Li-Cycle, RecycLiCo Battery Materials, Tata Chemicals Ltd., American Battery Technology Company, Cirba Solutions, Gopher Resource LLC, East Penn Manufacturing, Aqua Metals, Eco-Bat Technologies, Ganfeng Lithium Group Co., Ltd., Lithion Recycling Inc., EnerSys, Redwood Materials, Inc., Element Resources LLC, Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Limited, Stena Recycling, REDUX Recycling GmbH, Other Key Players. |
Key Market Segments
Source Analysis
The battery recycling market is categorized by source into automotive batteries, industrial batteries, and consumer & electrical appliance batteries. In 2024, the automotive batteries segment accounted for a dominant 61.2% revenue share, driven by the surge in electric vehicle (EV) adoption and the growing volume of end-of-life EV batteries requiring recycling. Stringent government regulations promoting sustainable practices and the need to recover critical materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel have further boosted recycling efforts in the automotive sector. This trend is expected to persist as the global EV fleet expands and recycling technologies advance.
Battery Chemistry Analysis
The market, segmented by battery chemistry, includes lithium-ion, lead-acid, nickel-based, flow batteries, and others. In 2024, lead-acid batteries held a commanding 72.1% market share, primarily due to their extensive use in conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. Their cost-effectiveness, established recycling infrastructure, and long-standing role in automotive and backup power systems solidify their market leadership. Despite the emergence of newer battery technologies, lead-acid batteries remain a cornerstone of the recycling sector.
Technology Analysis
The market, based on technology, is divided into pyrometallurgy, hydrometallurgy, and mechanical separation. In 2024, pyrometallurgy captured a significant 56.2% market share, owing to its effectiveness in recovering valuable metals like nickel, cobalt, and copper across various battery chemistries. Its established industrial processes, high throughput, and scalability make it the preferred method for large-scale battery recycling. Its ability to process diverse battery types further reinforces its market dominance.
End-Use Analysis
The market, segmented by end-use, includes material extraction, disposal, and reuse, repackaging & second life. In 2024, material extraction led with a 48.2% market share, driven by the increasing demand for critical raw materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which are essential for new battery production. Efficient recycling processes enable the recovery of these materials, fueling the growth of material extraction. The focus on reducing reliance on mined resources and advancing a circular economy further strengthens this segment’s market position.
Geopolitical Impact Analysis
Geopolitical Impact of U.S. Tariffs on the Global Battery Recycling Market
Escalating geopolitical tensions and trade restrictions between the United States and China, coupled with broadening U.S. tariffs on imports from multiple countries, are profoundly disrupting the global battery recycling market. Specifically, U.S. tariffs on Chinese-made batteries are elevating the costs of new batteries, which in turn reduces demand for replacements and diminishes the supply of end-of-life batteries available for recycling.
Moreover, these tariffs inflate raw material prices, eroding the economic viability of recycling operations, while supply chain interruptions delay processing timelines and impede overall industry expansion and operational efficiency. The most recent U.S. tariffs on Chinese-made batteries are slated to culminate at 82% by January 2026, more than doubling the price of these imports.
This includes an additional 34% tariff layered atop existing measures—such as a prior 20% tariff plus two 10% increments—alongside baseline duties like the 3.4% global tariff on lithium-ion batteries and the Section 301 tariff, currently at 7.5% but scheduled to climb to 25% in 2026. These cumulative levies are poised to fracture international supply chains, hampering both battery manufacturing and downstream recycling activities.
Regional Analysis
In 2024, the Asia Pacific region commanded a leading 39.4% of the global battery recycling market, propelled by rigorous environmental regulations and surging electric vehicle (EV) adoption in powerhouses like China, Japan, and South Korea. As EV penetration deepens, the imperative for robust battery recycling intensifies, addressing the mounting challenge of end-of-life battery disposal. This EV boom underscores the urgency for sophisticated recycling methodologies to reclaim high-value materials, including lithium, cobalt, and nickel, thereby fueling accelerated market expansion.
Governments across the region are championing battery recycling through comprehensive environmental mandates, which are pivotal in molding market dynamics. These policies not only incentivize manufacturers to innovate and integrate cutting-edge recycling technologies but also establish stringent guidelines for battery collection, treatment, and disposal. Such regulatory frameworks are indispensable for safeguarding the environmentally sound and streamlined recycling of spent batteries, especially lithium-ion variants prevalent in EVs and energy storage applications.
Top Use Cases
- Electric Vehicle Battery Recovery: As more electric cars hit the roads, old batteries from these vehicles become a prime source for recycling. Companies collect them at dealerships or service centers, break them down to pull out key metals like lithium and cobalt, and reuse those in making new batteries. This keeps costs down for car makers and cuts down on digging up fresh raw stuff from the earth.
- Consumer Electronics Reuse: Gadgets like phones, laptops, and cameras pack small rechargeable batteries that wear out fast. Recycling spots at stores or drop-off bins let folks hand them in easily. The process sorts out valuable bits like nickel and copper, turning waste into fresh parts for new devices. It helps families stay green without hassle.
- Industrial Backup Power Revival: Big factories and data centers rely on heavy-duty batteries for emergency power. When these give out, recycling turns them into a goldmine for lead and acids. Firms ship them to plants that melt and refine safely, feeding back materials for stronger, greener power setups. This boosts business reliability on a budget.
- Second-Life Energy Storage: Worn-out batteries from cars or tools still hold juice for less demanding jobs. Recyclers test and repack them into home solar setups or grid backups, storing extra energy from sunny days. It stretches battery life, saves money on new units, and smooths out power needs for neighborhoods.
- Lead-Acid Auto Battery Refresh: Classic car starters use lead-acid batteries that last for years but eventually fail. Auto shops take them back with deposit refunds, grinding them up to reclaim lead for new ones. This loop keeps roads running affordably while dodging toxic dumps, making it a win for drivers everywhere.
Recent Developments
1. BASF SE
BASF is expanding its battery recycling footprint in Europe. A key development is the inauguration of its new commercial-scale battery recycling prototype plant in Schwarzheide, Germany, in 2023. This facility uses innovative hydrometallurgical processes to recover metals like lithium, nickel, and cobalt from end-of-life batteries and production scrap, aiming to create a closed-loop for the European battery value chain.
2. Accurec Recycling GmbH
German specialist Accurec is advancing its proprietary battery recycling technology. The company is focusing on scaling its unique vacuum pyrolysis and mechanical treatment process, which allows for high recovery rates of valuable materials with low energy consumption. Recent efforts are geared towards building industrial-scale plants to process larger volumes of lithium-ion batteries, emphasizing the recovery of high-purity cobalt, nickel, and lithium compounds from the black mass.
3. Fortum
Finnish energy company Fortum has achieved a significant milestone in its battery recycling journey. In 2023, Fortum’s Finnish plant successfully produced and delivered its first batch of recycled, battery-grade lithium hydroxide to a European customer. This breakthrough demonstrates a viable, low-CO2 European supply chain for critical raw materials, moving beyond just nickel and cobalt recovery to close the loop on lithium.
4. Glencore
Glencore is leveraging its position as a leading miner and marketer of metals to form strategic partnerships in battery recycling. A key recent move is the framework agreement with Li-Cycle. Glencore will supply manufacturing scrap and end-of-life batteries and has invested in Li-Cycle, supporting the development of a new European hub in Italy. This integrates recycled materials directly into Glencore’s global metal supply network.
5. Umicore
Umicore is executing a global expansion strategy for its battery recycling solutions. In 2024, it announced the construction of a new battery recycling plant in Poland, complementing its existing facility in Hoboken, Belgium. This new plant will focus on processing black mass into critical battery metals. Umicore is also pioneering the use of renewable energy at its sites to ensure its recycled materials have an ultra-low carbon footprint.
Conclusion
Battery recycling stands as a smart pivot toward a greener world, where tossed-out power packs turn into tomorrow’s fuel for clean tech. As electric rides and gadgets boom, this loop grabs back rare goodies like lithium and cobalt, easing the hunt for new mines and slashing trash piles. Governments nudge it along with smart rules on safe handling, while fresh tricks like gentle water washes make it cheaper and kinder to our planet. In the end, it’s building a circle where waste fades, costs drop, and everyone powers up sustainably, a quiet game-changer for steady energy flows ahead.










