Quick Navigation
Overview
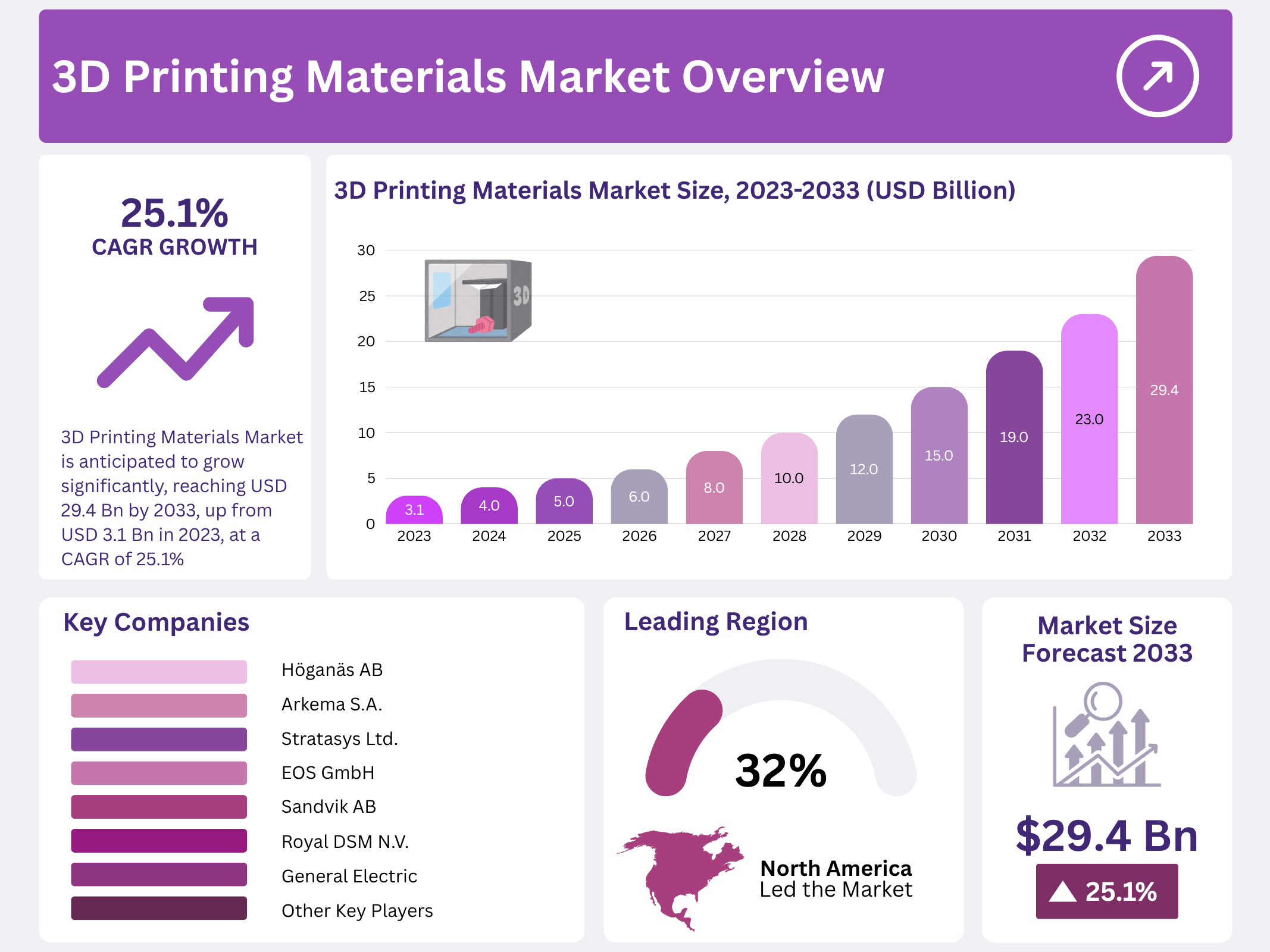
New York, NY – November 07, 2025 – The Global 3D Printing Materials Market is anticipated to grow significantly, reaching USD 29.4 billion by 2033, up from USD 3.1 billion in 2023, at a robust CAGR of 25.1% between 2023 and 2033. This growth is primarily driven by advancements in additive manufacturing technologies and the increasing demand for customized, lightweight, and high-performance products across diverse industrial sectors.
Industries such as aerospace & defense, automotive, and healthcare are increasingly adopting 3D printing materials for prototyping, tooling, and end-use production. The use of metals, polymers, and composites in 3D printing enables faster design iterations, reduced waste, and enhanced manufacturing flexibility, which are reshaping production workflows and reducing overall costs.
Furthermore, continuous technological innovation, improved material performance, and supportive government initiatives are expanding 3D printing applications across new domains. As industries move toward sustainable and efficient manufacturing, the adoption of advanced 3D printing materials is expected to accelerate, transforming conventional manufacturing into a more agile and environmentally responsible process.
Key Takeaways
- The 3D Printing Materials Market is predicted to expand significantly, with an anticipated value of USD 29.4 billion by 2033 from USD 3.12 billion in 2023, showing a remarkable 25.1% Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR).
- Plastic materials dominate the market, accounting for over 33.2% in 2023 due to their versatility and cost-effectiveness, widely used in the automotive and healthcare industries.
- Aerospace & defense claimed a significant market share of over 33.4% in 2023, relying on 3D printing materials for lightweight yet robust components. Medical applications, including prosthetics and implants, also contribute to market growth.
- North America held a substantial market share in 2023 (32.1%), likely to expand due to increased investments and demand within the region, particularly in metals from industries like consumer electronics, defense, aerospace, and automotive
Report Scope
| Report Features | Description |
|---|---|
| Market Value (2023) | USD 3.1 Billion |
| Forecast Revenue (2033) | USD 29.4 Billion |
| CAGR (2024-2033) | 25.1% |
| Segments Covered | By Type (Metals, Ceramics, Plastics, Others), By form:(Powder, Filament, Liquid), By technology: (FDM, SLS, SLA, DMLS, Others), By application:(Prototyping, Manufacturing, Others), By end-use(Aerospace, Healthcare, Automotive, Consumer Go, Construction, Others) |
| Competitive Landscape | Höganäs AB, 3D Systems Corporation, General Electric, Arkema S.A., Royal DSM N.V., Stratasys Ltd., Evonik Industries AG., EOS GmbH, Sandvik AB, Other Key Major players |
Key Market Segments
By Type
In 2023, plastic materials dominated the 3D printing materials market, capturing over 33.2% share. Their versatility, cost-effectiveness, and widespread use in the automotive and healthcare industries drive this leadership. Key types include photopolymers and thermoplastics, alongside ceramics and plywood filaments.
Material choice hinges on mechanical properties, manufacturing traits, aesthetics, and cost. Enhanced durability and flexibility are poised to boost demand across all application sectors. High-performance materials will benefit from thermoplastics’ low costs, with growth fueled by rising needs for lightweight, resilient parts in aerospace & defense, automotive, medical, and other industries.
By Form
Powder-based 3D printing technologies, such as Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) and Electron Beam Melting (EBM), rely on powdered materials. These include metals (iron, copper, bronze), plastics, ceramics, and composites. Lasers or electron beams fuse layers to build complex geometries, ideal for aerospace components and functional parts in automotive and healthcare.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), a leading method, uses filament-form materials, primarily thermoplastics like PLA, ABS, PETG, and nylon. The filament is heated, extruded through a nozzle, and layered to form objects. FDM’s popularity stems from its ease of use, affordability, and excellence in rapid prototyping.
By Technology
Fused Deposition Modeling/Fused Filament Fabrication (FDM/FFF): This extrusion-based technology melts thermoplastic filaments through heated nozzles, building objects layer by layer. Its accessibility, simplicity, and low cost have driven adoption in prototyping, product development, education, and beyond. Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): SLS uses high-powered lasers to sinter powdered materials—plastics, metals, or ceramics—layer by layer into fused 3D objects. It excels in aerospace, automotive, and medical applications for producing strong, intricate, and economically viable parts.
By Application
Rapid prototyping remains a core 3D printing application, enabling fast, affordable prototype creation. This allows designers and engineers in automotive, aerospace, consumer goods, and electronics to test ideas, refine designs, and visualize products pre-mass production. The technology has advanced to manufacturing end-use parts. Aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and electronics sectors leverage additive manufacturing for complex geometries, custom designs, and lightweight structures, integrating it into core production processes.
By End-Use
In 2023, aerospace and defense led with over 33.4% market share, using 3D printing for lightweight, durable components to enhance innovation and efficiency. The healthcare segment is set for strong growth, driven by 3D-printed prosthetics, implants (e.g., hip and knee replacements), surgical tools, and models for complex operations. Consumer products and industrial segments will expand, propelled by manufacturing booms in China, Japan, and other economies, plus rising ceramic use in home decor, art, and sculpture.
Regional Analysis
North America commanded a 32.1% share of the global 3D printing materials market, with continued expansion anticipated due to heightened producer investments and robust demand from key regional players prioritizing technological innovation and material advancements. Supportive government policies, a vast manufacturing ecosystem, substantial R&D funding for high-performance materials, and widespread availability of 3D printing products are poised to propel industry growth.
Rising disposable incomes and elevated living standards will further fuel high product demand. Throughout the forecast period, North America’s market is expected to experience surging demand for metals across consumer electronics, defense, aerospace, and automotive sectors.
Growth will also be bolstered by the expanding adoption of metals, ceramics, and photopolymers for intricate design and manufacturing applications. In the Asia Pacific, rapid industrialization and infrastructure development will drive 3D printing materials market expansion, while North America will additionally benefit from increased R&D investments in nations such as China, India, Japan, and Indonesia aimed at modernizing aerospace and defense equipment.
Top Use Cases
- Aerospace Components: Engineers craft lightweight yet strong parts like turbine blades and brackets using durable metal powders and composites. These materials endure extreme heat and stress, cutting fuel use and speeding up custom designs for aircraft. This boosts efficiency in building safer, faster planes without heavy waste from old methods.
- Custom Medical Devices: Doctors create tailored prosthetics, implants, and surgical guides from biocompatible resins and flexible polymers. These fit patients perfectly, improving comfort and recovery times. Soft, skin-safe options allow quick in-house printing, making healthcare more personal and accessible for everyone needing unique support.
- Automotive Prototypes: Teams build test parts like engine mounts and dashboards with tough thermoplastics like nylon or ABS. These handle vibrations and impacts well, helping designers spot issues early. It saves time and money by allowing fast tweaks before full production rolls out.
- Architectural Models: Builders print detailed scale replicas of buildings and bridges using layered resins for smooth finishes. This lets them check light flow and structures easily, spotting design flaws upfront. Eco-friendly filaments reduce material use, making planning greener and more precise for urban projects.
- Consumer Product Tools: Makers produce jigs, fixtures, and ergonomic handles from lightweight nylon filaments. These speed up assembly lines by holding pieces steady and easing worker strain. Simple to customize on-site, they cut downtime and improve factory flow for everyday gadgets and appliances.
Recent Developments
1. Höganäs AB
Höganäs is advancing metal 3D printing with its proprietary Digital Metal technology, focusing on high-precision binder jetting. Recent developments include launching new stainless-steel and titanium powders tailored for this process, enabling the mass production of small, complex components with excellent surface finish. Their efforts are geared towards high-volume industrial applications in sectors like medtech and consumer goods, pushing the boundaries of design and manufacturing efficiency.
2. 3D Systems Corporation
3D Systems has expanded its Figure 4 platform with new rigid, durable, and elastomeric materials to meet demanding production needs. A key innovation is the introduction of biocompatible, sterilizable resins for healthcare, such as dental surgical guides and medical devices. They are also developing high-performance materials for SLA and SLS technologies, focusing on isotropy, temperature resistance, and recyclability to serve aerospace, automotive, and healthcare industries with production-grade parts.
3. General Electric
Operating through its GE Additive division, the company is heavily invested in advancing metal additive manufacturing. A key focus is on developing and qualifying novel nickel and titanium superalloys, like the AMPERPRINT series, for its H2 Binder Jet systems and direct energy deposition. These materials are designed for high-volume production of large, complex parts in the aerospace and energy sectors, aiming to improve performance, reduce cost, and accelerate certification processes.
4. Arkema S.A.
Arkema, through its Sartomer resin line, is a leader in advanced photopolymer solutions. Recent highlights include the launch of its N3xtDimension range of sustainable, high-performance resins derived from bio-sourced materials. They are also pioneering new engineering and elastomeric grades for DLP and LCD 3D printing that offer enhanced toughness, heat resistance, and recyclability. These developments target the automotive, consumer goods, and electronics markets, supporting the shift towards more environmentally conscious manufacturing.
5. Royal DSM N.V.
Following its acquisition by Covestro, the former DSM additive manufacturing portfolio continues to innovate under the Additive Manufacturing business entity. Recent developments include expanding its Arnitel thermoplastic copolyester (TPC) portfolio for powder-based processes like SLS and HSS, creating flexible, durable parts. They have also launched new bio-based, glass-filled, and flame-retardant filaments for FDM, focusing on circularity and high-performance applications in mobility, healthcare, and consumer goods.
Conclusion
3D printing materials are transforming how industries create things, blending creativity with smart production. From flexible polymers for quick prototypes to tough metals for real-world parts, these options open doors to custom designs that fit exact needs without excess waste. Sectors like healthcare and automotive lean on them for faster, greener workflows, while new eco-friendly blends push boundaries toward sustainable growth.










