Global Vegetable Carbon Market By Source (Coconut Shells, Wood, Peat, Cellulose Residues, Others), By End User (Food and Beverages, Cosmetics, Pharmaceuticals, Others), By Distribution Channel (Hypermarkets and Supermarkets, Food Specialty Stores, Pharmacy, Cosmetic Discounters, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Dec 2025
- Report ID: 172168
- Number of Pages: 198
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
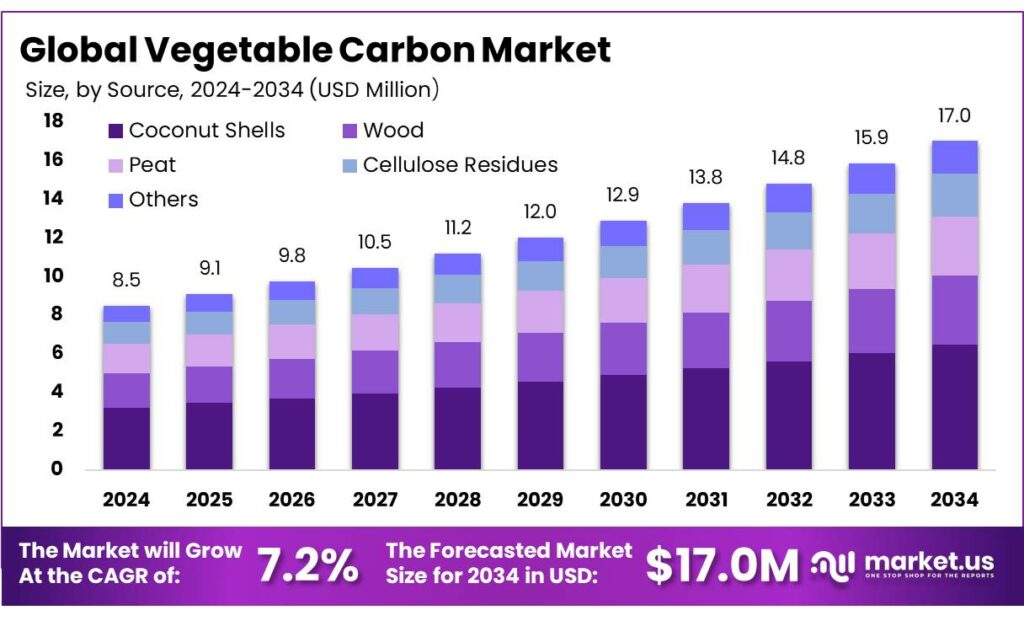
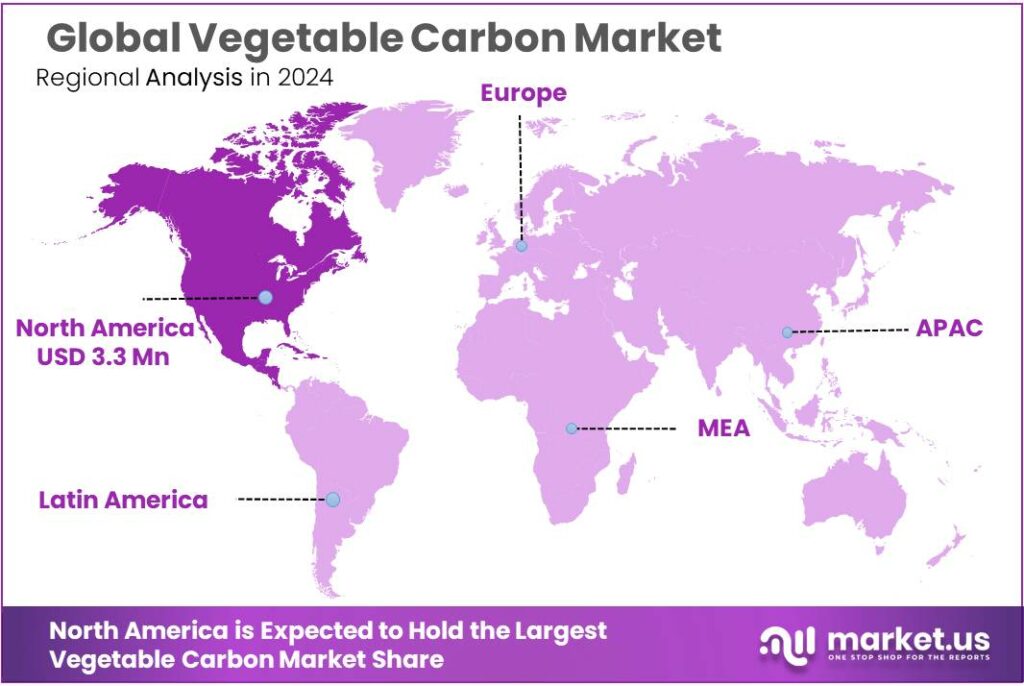
The Global Vegetable Carbon Market size is expected to be worth around USD 17.0 Million by 2034, from USD 8.5 Million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 7.2% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024 North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 38.9% share, holding USD 3.3 Million in revenue.
Vegetable carbon, also known by its food additive code E153, is a natural black pigment derived from carbonisation of plant-related materials such as wood, coconut shells, peat, or other biomass. As a food additive, it functions primarily as a colourant, providing an intense black hue in products like confectionery, baked goods, cheese rinds, and specialty beverages without affecting flavour or nutritional profiles.
Several government and regulatory trends influence the industry’s trajectory. Conversely, in the United States, the FDA has not approved vegetable carbon for food use, highlighting regulatory divergence that shapes global supply chains and market entry strategies. The growing global organic and natural foods sector itself — valued at over USD 150 billion worldwide in 2022, with strong growth in Europe and North America — also creates favorable downstream demand for natural additives like vegetable carbon.
In the European Union, E153 is approved under Regulation (EC) No. 1333/2008 and evaluated by EFSA, although it has no ADI formally allocated by JECFA, and its use is subject to specified food categories. In contrast, in the United States, vegetable carbon is not authorised as a food colour additive under current FDA regulations, reflecting divergent global regulatory landscapes for colouring agents.
Government and regulatory frameworks play a pivotal role in shaping industry adoption. In the EU, vegetable carbon (E153) is officially recognized and permitted as a food additive, with safety evaluations by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) that indicate no safety concerns at authorized use levels. In contrast, U.S. regulatory policy currently excludes vegetable carbon from food color authorization, though broader initiatives to phase out synthetic dyes and expand natural alternatives suggest evolving opportunities.
Key Takeaways
- Vegetable Carbon Market size is expected to be worth around USD 17.0 Million by 2034, from USD 8.5 Million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 7.2%.
- Coconut Shells held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 38.6% share in the vegetable carbon market.
- Food and Beverages held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 39.7% share in the vegetable carbon market.
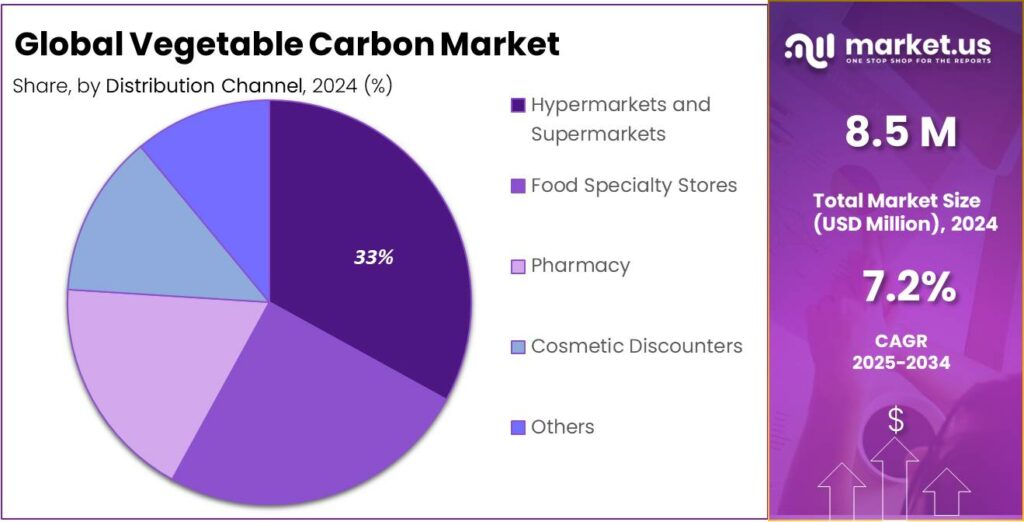
- Hypermarkets and Supermarkets held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 33.5% share in the vegetable carbon market.
- North America held a dominant position in the vegetable carbon market, capturing more than a 38.9% share and accounting for a market value of approximately USD 3.3 million.
By Source Analysis
Coconut Shell–Based Vegetable Carbon leads with a 38.6% share, supported by sustainability and strong food-grade demand
In 2024, Coconut Shells held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 38.6% share in the vegetable carbon market. This leadership can be attributed to the wide availability of coconut shells as an agricultural by-product and their high carbon content, which makes them suitable for producing food-grade and pharmaceutical-grade vegetable carbon. In major coconut-producing regions, coconut shells are generated in large volumes every year, ensuring stable raw material supply and cost efficiency for manufacturers.
By End User Analysis
Food and Beverages lead the vegetable carbon market with 39.7% share driven by natural colorant demand
In 2024, Food and Beverages held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 39.7% share in the vegetable carbon market. This strong position is largely due to the increasing demand for natural and clean-label ingredients in bakery, confectionery, beverages, and specialty food products. Manufacturers are increasingly replacing synthetic black colorants with vegetable carbon derived from plant sources, such as coconut shells and wood, to meet consumer preferences for safer and more sustainable products.
By Distribution Channel Analysis
Hypermarkets and Supermarkets dominate with 33.5% share due to wide reach and consumer convenience
In 2024, Hypermarkets and Supermarkets held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 33.5% share in the vegetable carbon market. This leadership is driven by the extensive reach of these retail channels, which allow manufacturers to connect directly with end consumers seeking natural and clean-label food products. The growing popularity of packaged foods, bakery items, confectioneries, and beverages that use vegetable carbon as a natural black colorant has contributed significantly to sales through these outlets.
Key Market Segments
By Source
- Coconut Shells
- Wood
- Peat
- Cellulose Residues
- Others
By End User
- Food and Beverages
- Cosmetics
- Pharmaceuticals
- Others
By Distribution Channel
- Hypermarkets and Supermarkets
- Food Specialty Stores
- Pharmacy
- Cosmetic Discounters
- Others
Emerging Trends
Shift from Synthetic to Natural Food Colorants Boosting Demand for Vegetable Carbon
One of the most notable trends shaping the food industry today — and with direct relevance to vegetable carbon — is the ongoing shift away from synthetic food dyes and toward natural, plant‑based colorants. This trend isn’t just a buzzword on packaging or a social media hashtag; it reflects real, measurable changes in consumer expectations, government actions, and food formulation practices that influence how millions of people eat every day.
People today read labels more often than they used to, and many are making choices based not only on taste but on what ingredients mean to their health and values. A survey by the International Food Information Council reported that about 70% of consumers actively seek products with natural ingredients, showing that the desire for clean, understandable foods is influencing everyday purchasing decisions. This isn’t driven by companies trying to sell products — this comes from individuals and families who want food that fits their belief in health, safety, and transparency.
Governments and regulators are also responding to these evolving preferences. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has recently expanded the range of natural color additives allowed in foods, approving three new plant‑derived or mineral‑based colorants, such as butterfly pea flower extract and algae‑derived pigments. This regulatory move makes it easier for manufacturers to reformulate products with natural color alternatives instead of relying on petroleum‑based dyes.
This trend is also economic and practical. Manufacturers know that products labeled with recognizable natural ingredients often command premium prices and can strengthen brand loyalty among health‑conscious buyers. According to broader data on natural colorants, products promoted with clear natural ingredient claims tend to have higher purchase frequency among health‑minded consumer groups — particularly younger generations such as Millennials and Gen Z — which now make up a large portion of grocery shoppers.
Drivers
Rising Consumer Demand for Natural & Clean-Label Food Colorants
One of the most powerful forces shaping the vegetable carbon (E153) industry today is the global shift in consumer preferences towards natural ingredients and clean-label foods. People are no longer satisfied with ingredients they can’t pronounce or that come with a reputation for health risks. Instead, they want food that feels honest, transparent, and rooted in nature — and this emotional preference is now backed by hard numbers from trusted food authorities and government sources.
The demand for natural food colors has a strong regulatory and safety dimension as well. In the European Union, food additives like vegetable carbon must meet stringent safety assessments before being permitted for use — and their presence on labels means consumers can see exactly what’s in their food. When customers know what they’re eating, they feel more confident, which further fuels demand for natural food colorants over synthetic alternatives. In contrast to artificial dyes, which have faced public scrutiny and regulatory warnings, natural plant-based colorants are perceived as gentler and healthier.
Meanwhile, in the United States, significant policy shifts are reinforcing this consumer-led movement toward cleaner-label products. In 2025 the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved three new food color additives from natural sources, including butterfly pea flower extract and algae-derived blue pigments, specifically to give food manufacturers safe, natural options for coloring foods. This kind of government action tells manufacturers that adopting natural color solutions isn’t just trendy — it’s officially supported.
This rise in consumer awareness isn’t only about health. Many people today are thinking about food in a holistic sense — how ingredients affect not only their bodies, but also sustainability and environmental impact. Natural food colorants like vegetable carbon are seen as plant-based, renewable, and more eco-friendly than petrochemically derived synthetic dyes, which reinforces their appeal among environmentally conscious shoppers.
Restraints
Regulatory Restrictions and Safety Concerns Limiting Use of Vegetable Carbon (E153)
One of the strongest forces holding back the wider adoption of vegetable carbon (E153) in the food industry isn’t lack of interest from makers or consumers — it’s the patchwork of regulatory restrictions and safety concerns that make many companies hesitant to use it broadly. This isn’t just technical legal language on paper. It affects real decisions about what goes into food products, how they’re labeled, and whether they can be sold at all in big markets like the United States or India.
At the heart of this restraint is the fact that vegetable carbon is not universally approved as a food colorant around the world. In the United States, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has banned Vegetable Carbon from use in foods due to concerns about impurities such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), which are substances that, at high levels, can pose health risks including carcinogenic potential. This ban means that products sold in the U.S. — one of the world’s largest food markets — cannot legally contain E153 as a color additive, regardless of consumer demand for natural alternatives.
India’s regulatory framework also reflects caution. According to food safety research, Vegetable Carbon is considered “restricted” in India and is not listed among FSSAI’s generally permitted food colour additives. Instead, its use may only be approved on a case-by-case basis under a category of “Non-Specified Food & Food Ingredients,” which requires individual permissions before a manufacturer can include it in a product. This kind of regulatory uncertainty creates friction: companies must invest time and resources into regulatory submissions just to be allowed to use E153, slowing down product development compared to more straightforwardly approved colorants.
Even in regions where E153 is allowed, like the European Union, strict safety evaluation processes continue to influence how confidently producers use it. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) reviewed vegetable carbon and noted that toxicological data were too limited to set an Acceptable Daily Intake (ADI) — a numerical safety benchmark many regulators rely on. EFSA’s opinion emphasized the need for tight control of contaminants such as benzo[a]pyrene, a known carcinogenic PAH, keeping its level in food-grade E153 below 1.0 µg/kg to avoid safety concerns.
Opportunity
Rising Regulatory Support for Natural Food Colorants as Synthetic Dyes Are Phased Out
One very real and meaningful growth opportunity for vegetable carbon and other natural food colorants stems from global regulatory changes that favor safer, plant‑derived ingredients over synthetic dyes. This isn’t just bureaucratic jargon — it’s about how governments and food safety agencies are slowly listening to public health concerns and consumer voices, and adjusting the food system so families feel more confident about what’s on their tables.
In recent years, regulators in major markets such as the United States have taken visible steps to open the door wider for natural color alternatives. On May 9, 2025, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved three new food color additives derived from natural sources, including pigments from algae and flower petals, for use in a range of food products from beverages to candy. These approvals are part of a broader initiative by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) to encourage food manufacturers to move away from petroleum‑based synthetic dyes and embrace safe, natural options.
In the European Union, regulatory frameworks already permit vegetable carbon under the E‑number E153, meaning it has passed safety assessments and can be used in foods subject to labeling requirements. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) rigorously evaluates food colours before approving them for use, which builds trust among manufacturers and consumers alike that these ingredients meet modern safety standards. This system creates an environment where natural colorants like vegetable carbon have a clear, regulated pathway to be used in everything from gourmet desserts to everyday snacks.
These regulatory openings happen alongside broader health‑driven changes. For example, regulators are actively reconsidering some synthetic dyes. In the U.S., dyes like Red Dye No. 3 have been banned due to potential health concerns, and food authorities are signaling a phased reduction of other synthetic colorants. This trend reinforces why food makers are increasingly interested in natural alternatives — they want to avoid future regulatory hurdles and the costly reformulations that come with them.
Regional Insights
North America leads the vegetable carbon market with 38.9% share, valued at USD 3.3 million in 2024
In 2024, North America held a dominant position in the vegetable carbon market, capturing more than a 38.9% share and accounting for a market value of approximately USD 3.3 million. The region’s leadership is driven by a combination of strong consumer demand for natural and clean-label food ingredients, regulatory support for plant-based colorants, and a well-established processed food and beverage industry. Manufacturers in the region are increasingly substituting synthetic black colorants with vegetable carbon in bakery, confectionery, and beverage applications to align with consumer preferences for safe and sustainable ingredients.
The growth in North America is further supported by rising health awareness, where consumers are actively seeking products made from natural sources. The region also benefits from advanced food processing infrastructure, robust supply chains, and high purchasing power, which facilitate the adoption of vegetable carbon in both commercial and retail products. For example, specialty baked goods, black-colored confectionery, and functional beverages increasingly incorporate vegetable carbon due to its natural pigmentation and non-toxic properties.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Dynasty Colourants Co., Ltd. is a China‑based manufacturer of dyestuffs, organic pigments and specialty chemicals, with origins dating to 1994 and an annual output exceeding 5,000 metric tons delivered to customers across 50+ countries. The company’s product range spans multiple colourant categories and supports diverse industrial applications, including textiles, plastics, coatings and cosmetics, reflecting broad technical expertise and global reach.
Univar Food Ingredients is a major global distributor supplying food‑grade additives, flavourings and functional ingredients, including natural colourants such as vegetable carbon. The company supports extensive food processing sectors worldwide through broad product availability, logistics infrastructure and technical compliance services tailored to regulatory requirements in multiple markets.
Jiangmen Goody’s Food Co., Ltd. has more than 50 years of experience in food ingredient research and development and markets a well‑known brand. The company’s portfolio includes food colourants, flavourings and additives used in baked goods, confectionery and beverage sectors, supported by decades of industry presence and regional market penetration.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Dynasty Colourants Co., Ltd.
- Hawkins Watts Australia
- Jiangmen Goody’s Food Co., Ltd.
- Univar Food Ingredients
- Bolise Co., Ltd.
- Holland Ingredients
- Others
Recent Industry Developments
Holland Ingredients B.V. operates an FSSC 22000-approved production site where liquid colour formulations are produced in various concentrations and packaged from 500 g bottles up to 500 kg IBC units, serving both smaller artisan producers and larger industrial clients across Europe and beyond.
In 2024, Jiangmen Goody’s Food Co., Ltd reported an annual revenue range of roughly USD 10 million–USD 50 million with approximately 40% of sales coming from exports to markets in Asia, Middle East, Africa and beyond, demonstrating its global reach as a supplier of bakery ingredients, food additives and collected functional powders.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 8.5 Mn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 17.0 Mn CAGR (2025-2034) 7.2% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Source (Coconut Shells, Wood, Peat, Cellulose Residues, Others), By End User (Food and Beverages, Cosmetics, Pharmaceuticals, Others), By Distribution Channel (Hypermarkets and Supermarkets, Food Specialty Stores, Pharmacy, Cosmetic Discounters, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Dynasty Colourants Co., Ltd., Hawkins Watts Australia, Jiangmen Goody’s Food Co., Ltd., Univar Food Ingredients, Bolise Co., Ltd., Holland Ingredients, Others Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- Dynasty Colourants Co., Ltd.
- Hawkins Watts Australia
- Jiangmen Goody's Food Co., Ltd.
- Univar Food Ingredients
- Bolise Co., Ltd.
- Holland Ingredients
- Others










