Global Solar Power Mobile Devices Market Size, Share, And Analysis Report By Device Type (Smartphones, Tablets, Laptops, Wearable Devices, Portable Chargers), By Solar Technology (Monocrystalline Solar Cells, Polycrystalline Solar Cells, Thin-Film Solar Cells), By Application (Consumer Electronics, Outdoor And Camping Gear, Emergency Power Supply, Industrial Applications, Commercial Use) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends, and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Feb 2026
- Report ID: 177342
- Number of Pages: 393
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
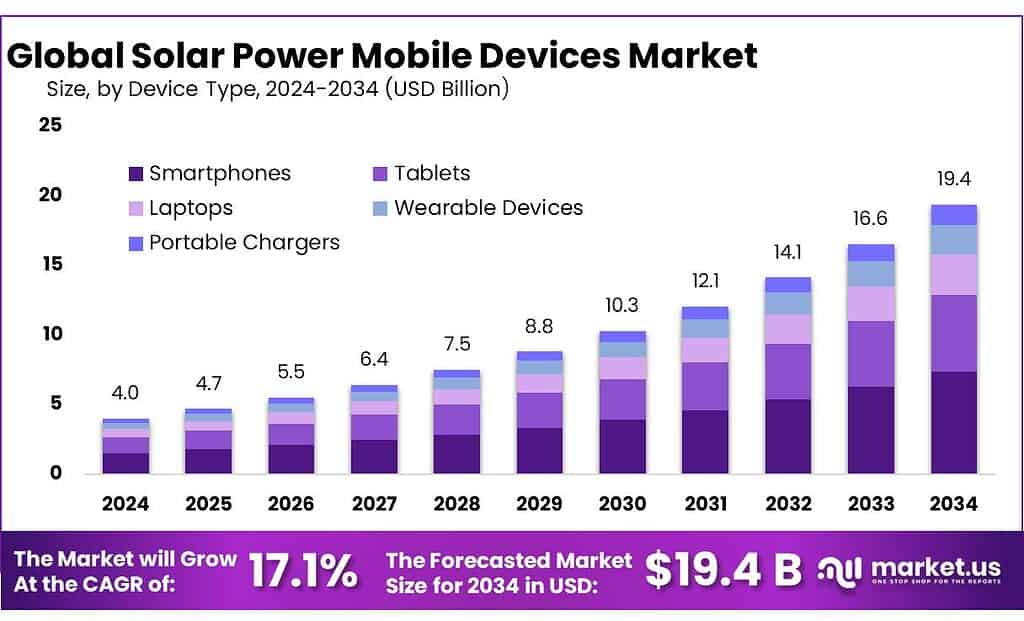
The Global Solar Power Mobile Devices Market is expected to be worth around USD 19.4 Billion by 2034, up from USD 4.0 Billion in 2024, and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 17.1% from 2025 to 2034. The North America segment maintained 43.8%, supporting a Solar Power Mobile Devices value of USD 192.0 Mn.
Solar power mobile devices—such as solar phone chargers, solar power banks, solar-powered feature phones, rugged field tablets with PV add-ons, and pico-solar kits with USB charging—sit at the intersection of the consumer electronics, off-grid energy, and outdoor recreation value chains. The segment’s core promise is simple: convert ambient sunlight into reliable, low-voltage power for personal connectivity, even where grid access is weak or expensive. This positioning has become more relevant as mobile connectivity scales; by end-2023, 4.6 billion people were using mobile internet globally, widening the addressable base for portable charging solutions.
The broader industrial scenario is favorable because both upstream solar economics and downstream device dependence are improving at the same time. Global PV capacity surpassed 2.2 TW by end-2024, reflecting rapid additions and a deeper supply chain for modules and small-form-factor panels. At the same time, the economics of solar electricity have structurally improved: the global weighted-average LCOE for newly commissioned utility-scale solar PV fell to about USD 0.044/kWh in 2023, down roughly 90% versus 2010—an anchor signal that keeps component pricing and investor appetite supportive across the solar value chain. In parallel, solar PV investment in capacity additions surpassed USD 480 billion in 2023, signaling durable capital formation behind the ecosystem these mobile products rely on.
Demand-side pull is equally clear. In 2025 there were about 9.2 billion mobile-cellular subscriptions globally, reinforcing how essential phone uptime has become for consumers and workers. Connectivity upgrades amplify the need for reliable power, especially as 5G subscriptions reached around 3 billion and 5G population coverage was estimated at 55% in 2025—raising battery drain expectations and increasing the value of dependable charging in motion. For market sizing logic, the off-grid energy channel is a practical proxy: the off-grid solar sector was estimated to benefit over 560 million people as of 2023, and more than 50 million off-grid solar products were sold across 2022–2023—an installed-base reality that supports repeat purchases of portable charging and accessory ecosystems.
Market drivers cluster around reliability, policy tailwinds, and cost economics. Reliability is reinforced by the sheer scale of smartphone demand—worldwide smartphone shipments were forecast by IDC to reach 1.25 billion units in 2025, keeping charging needs high even as device efficiency improves. Policy support also amplifies the ecosystem: in India, official updates reported solar installed capacity reaching 132.85 GW in November 2025, reflecting an enabling environment for distributed solar awareness and downstream devices. In the United States, the IRS states the Residential Clean Energy Credit equals 30% of qualifying costs for eligible clean-energy property installed from 2022 through December 31, 2025, supporting broader consumer familiarity with solar and storage economics.
Key Takeaways
- Solar Power Mobile Devices Market is expected to be worth around USD 19.4 Billion by 2034, up from USD 4.0 Billion in 2024, and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 17.1%.
- Smartphones held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 38.5% share in the Solar Power Mobile Devices Market.
- Monocrystalline Solar Cells held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 59.2% share in the Solar Power Mobile Devices Market.
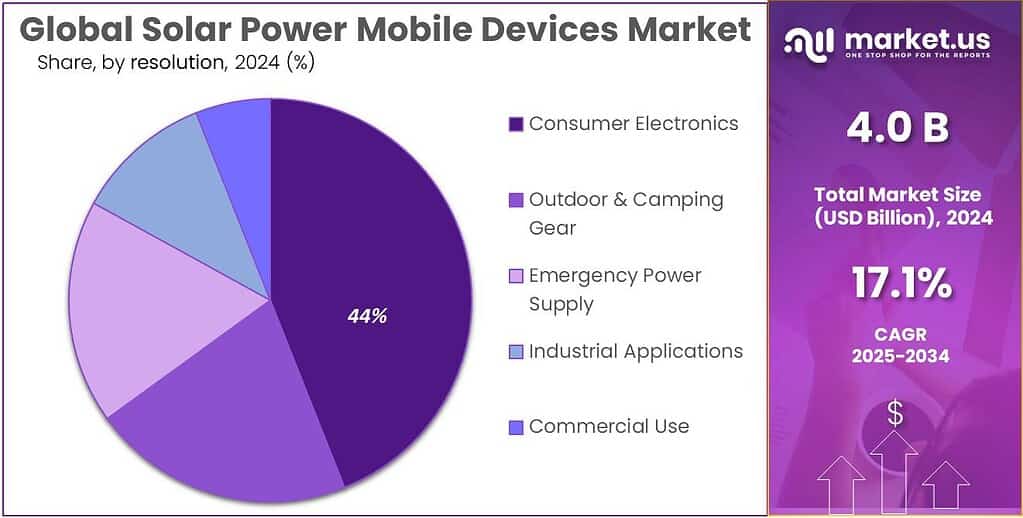
- Consumer Electronics held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 44.7% share in the Solar Power Mobile Devices Market.
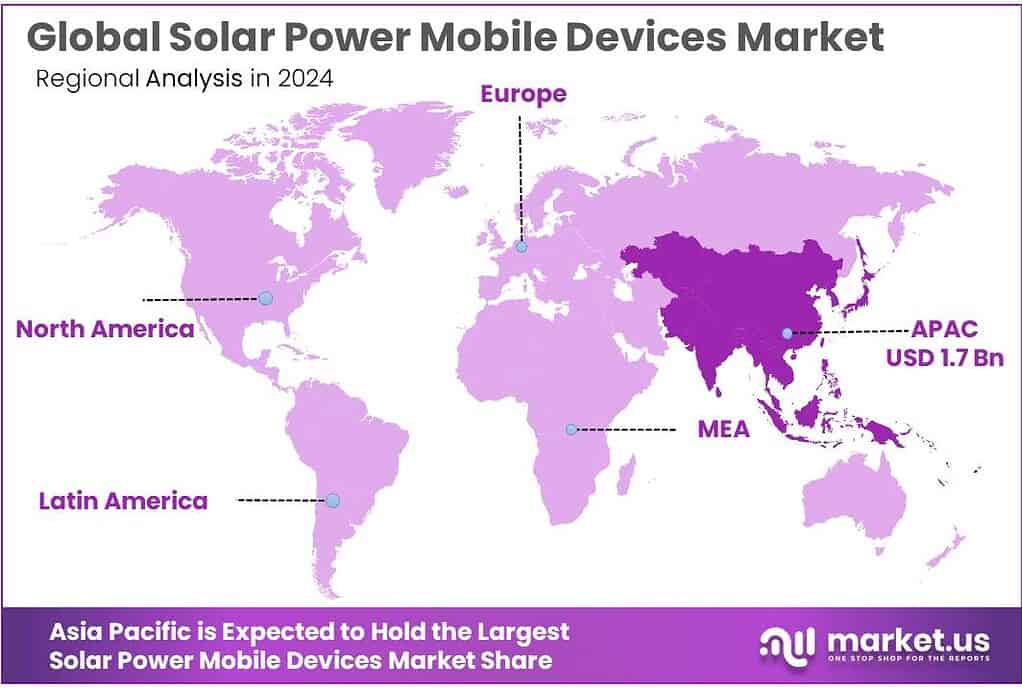
- North America led the Solar Power Mobile Devices Market, with the region holding a dominant 43.8% share and reaching USD 1.7 Bn in value.
By Device Type Analysis
Smartphones lead the Solar Power Mobile Devices Market with a strong 38.5% share in 2024.
In 2024, smartphones held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 38.5% share in the Solar Power Mobile Devices Market. Their strong lead comes from rising global smartphone usage, increasing dependence on high-capacity batteries, and growing consumer demand for portable off-grid charging.
As more users rely on continuous connectivity for payments, social communication, and work, the need for reliable solar-powered charging accessories has accelerated—especially in regions facing inconsistent grid power. The rapid spread of outdoor activities, travel, and remote-working cultures has further pushed consumers toward solar-charging solutions designed specifically for phones, as these remain the most widely used personal devices globally.
By Solar Technology Analysis
Monocrystalline Solar Cells dominate with a strong 59.2% share due to their high efficiency and reliability.
In 2024, Monocrystalline Solar Cells held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 59.2% share in the Solar Power Mobile Devices Market. Their leadership comes from their superior efficiency, longer lifespan, and ability to generate higher power output even in low-light conditions—a key advantage for portable chargers, solar power banks, and off-grid mobile solutions.
Consumers increasingly prefer monocrystalline-based products because they deliver faster charging and stable performance outdoors, making them ideal for travelers, field workers, remote users, and regions with inconsistent electricity access. As solar-powered mobility becomes more mainstream, this technology has become the preferred choice for manufacturers designing compact yet powerful charging devices.
By Application Analysis
Consumer Electronics lead the market with a solid 44.7% share driven by rising portable energy demand.
In 2024, Consumer Electronics held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 44.7% share in the Solar Power Mobile Devices Market. This segment leads because smartphones, tablets, wearables, and personal gadgets increasingly depend on continuous power availability, especially as digital lifestyles expand globally. Consumers are now using solar-powered chargers and portable panels as reliable backup options for travel, outdoor use, and daily mobility.
The growing popularity of remote work, outdoor recreation, and off-grid digital access has pushed users toward solar-powered solutions that keep their devices running without relying on traditional grid electricity. These trends have made consumer electronics the primary driver of demand across the solar mobile ecosystem.
Key Market Segments
By Device Type
- Smartphones
- Tablets
- Laptops
- Wearable Devices
- Portable Chargers
By Solar Technology
- Monocrystalline Solar Cells
- Polycrystalline Solar Cells
- Thin-Film Solar Cells
By Application
- Consumer Electronics
- Outdoor & Camping Gear
- Emergency Power Supply
- Industrial Applications
- Commercial Use
Emerging Trends
“Food-and-farm digitization” is pushing solar charging from a gadget into a daily utility
One major latest trend in Solar Power Mobile Devices is the shift toward purpose-built solar charging kits designed for food supply chains and food-assistance workflows, not just for travel or camping. As food systems digitize, a charged phone is becoming as essential as transport and storage. Farmers use mobile tools for advisory messages, ordering inputs, and coordinating sales, while field teams and beneficiaries increasingly depend on phones for registration and support updates. This trend is changing what buyers expect from solar products: durability over looks, predictable output over peak claims, and “workday readiness” over occasional backup use.
This trend is tightly linked to the growth of cash and digital delivery in food support programs. World Food Programme reported that in 2024 its operation in Chad became its seventh-largest cash-based transfer program globally, reaching 1.9 million people and delivering USD 73 million in transfers between March and December. When assistance and market purchasing depend on digital channels, device uptime becomes a practical requirement. That is why solar-powered phone charging—through small panels, rugged power banks, or charging hubs—fits naturally into last-mile operations, especially where grid power is unstable.
On the agriculture side, the same “mobile-first” behavior is expanding through advisory and input platforms. International Fund for Agricultural Development highlights an example where a digital advisory and input supply app is used by more than 50,000 farmers and 40 input suppliers, with community extension workers trained to support adoption. When tens of thousands of users rely on phones in daily farm routines, solar charging becomes an easy add-on for distributors and cooperatives—often bundled with extension services, input delivery, or training days. In practical terms, this drives demand for faster top-ups, USB-C compatibility, weather-resistant panels, and “charge-and-carry” designs that survive dust, heat, and transport.
Drivers
Reliable off-grid power for always-on mobile connectivity is the biggest growth driver
One major driving factor for Solar Power Mobile Devices is the rising need to keep phones and small electronics powered when electricity is unavailable, unreliable, or too costly. This need is no longer niche—it is tied to how people communicate, learn, trade, and access services. In many regions, mobile is the primary way people connect to the internet, so “battery anxiety” becomes a daily friction point. By the end of 2023, 4.6 billion people were using mobile internet worldwide, meaning a very large base of users depends on a charged device for essential tasks, not just entertainment.
The same reality is visible through the energy-access gap. When households cannot count on grid power, solar charging shifts from “nice to have” to practical infrastructure. In 2023, over 666 million people still lived without electricity access, according to the World Bank’s SDG7 tracking update, which underlines why portable solar charging remains relevant across rural communities and low-income urban pockets. For manufacturers and distributors, this demand pattern is attractive because it is recurring: consumers replace cables, upgrade power banks, and adopt higher-capacity chargers as device usage grows. This also supports multi-product baskets—foldable solar panels, solar power banks, and integrated phone-charging kits—rather than a one-time purchase.
A particularly strong pull comes from the food and humanitarian ecosystem, where a charged phone is often the gateway to support. Food assistance is increasingly linked to digital identification, cash-based transfers, and mobile communications that help families secure essentials locally. For example, a World Food Programme annual country report (Chad) notes that in 2024, over 202,000 beneficiaries received USD 3.8 million in cash-based transfers—systems that commonly rely on mobile access and basic digital readiness at the household level.
Restraints
Quality and performance uncertainty restrains adoption, because many buyers cannot risk unreliable charging
A major restraining factor for Solar Power Mobile Devices is inconsistent real-world performance, which creates low trust and slows repeat purchases. Small solar chargers and power banks often look similar on the shelf, yet output can vary sharply with panel quality, wiring, and charge-controller design. In practice, cloudy weather, heat, shading, and poor panel encapsulation can reduce charging speed enough that users feel the product “doesn’t work,” even when it is technically functioning. This trust gap becomes a real commercial barrier because buyers of low-cost devices usually make decisions based on a single experience—if the first unit disappoints, they revert to conventional power banks or wall charging and do not upgrade.
The industry also faces a credibility problem when products are sold with optimistic wattage claims that are hard to achieve outside test conditions. This pushes retailers and institutional buyers to demand recognized safety and durability standards, but not all low-cost imports meet those benchmarks consistently. The International Electrotechnical Commission standard IEC 61730-1:2023 outlines fundamental construction requirements to reduce risks such as electrical shock and fire hazards for PV modules, setting expectations that serious suppliers must satisfy to win long-term contracts. However, certification and quality assurance add cost and time, which can squeeze margins for entry-level products and reduce the number of offerings that remain competitive in price-sensitive markets.
Affordability pressure is especially sharp when solar charging competes with everyday essentials. This is where the food sector becomes a useful lens for understanding demand constraints. When household budgets tighten, spending shifts toward staples first, and “backup energy” purchases get delayed. The FAO Food Price Index averaged 127.2 in 2025, which was 4.3% higher than the 2024 average—an indicator that food costs remained elevated year over year for many consumers.
Funding constraints in food assistance operations can amplify the same restraint on the institutional side. When humanitarian budgets are under pressure, agencies prioritize food delivery over non-core equipment, even if that equipment would improve resilience. The World Food Programme reported that projected 2025 resources were expected to drop by 34% compared with 2024, forcing cuts that could affect up to 16.7 million people. In South Sudan, WFP described severe constraints where 2.7 million people receiving assistance were down to 50–70% rations.
Opportunity
Food-system digitization creates a big opportunity for solar-powered mobile charging in farms and last-mile assistance
A major growth opportunity for Solar Power Mobile Devices is the fast expansion of digital tools across agriculture and food assistance, where a working phone is now treated like basic infrastructure. Farmers, traders, extension workers, and aid recipients increasingly rely on mobile apps for advisories, input ordering, cash transfers, and local purchasing. In many rural areas, the weakest link is not the phone itself—it is dependable charging. This opens a clear path for solar chargers, solar power banks, and rugged solar kits designed for daily field use, especially where grid power is unreliable or expensive.
The opportunity becomes more concrete when food organizations scale digital platforms that depend on consistent mobile access. In 2024, World Food Programme reported that Chad became its seventh-largest cash-based transfer operation globally, assisting 1.9 million people with USD 73 million in transfers between March and December 2024. As cash and voucher delivery expands, the operational need for charging grows in parallel—field staff must keep devices running for registration and monitoring, while recipients often need phones for notifications and transaction steps. This is where solar power mobile devices move from being “consumer accessories” to being practical enablers of food access.
In 2025, the same pattern shows up in rural development programs that push app-led agriculture. International Fund for Agricultural Development highlighted a digital agriculture initiative where an advisory and input supply app was being used by more than 50,000 farmers and 40 input suppliers. When adoption reaches tens of thousands of farmers, the market opens for bundled solar charging solutions sold through input networks, cooperatives, and extension channels—often alongside agritech onboarding.
Government initiatives add a second layer of momentum, because they expand solar familiarity across rural livelihoods and indirectly improve acceptance of solar-powered charging products. In India, the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy states that the PM-KUSUM scheme aims to add 34,800 MW of solar capacity by March 2026. While PM-KUSUM is focused on agriculture energy assets, its broader impact is to normalize solar as a dependable everyday power source in farming communities. As solar becomes visible on farms—pumps, feeders, or decentralized installations—solar phone charging and small mobile power devices become easier to justify as “useful tools,” not experimental gadgets.
Regional Insights
North America dominates with 43.8% share, supported by USD 1.7 Bn in regional demand momentum.
In 2024, North America led the Solar Power Mobile Devices Market, with the region holding a dominant 43.8% share and reaching USD 1.7 Bn in value. This leadership is closely tied to high mobile-device dependence and a mature outdoor and emergency-preparedness culture that favors portable backup power. A practical driver is grid disruption: U.S. Energy Information Administration reported U.S. customers experienced an average of 11 hours of electricity interruptions in 2024, with major hurricanes accounting for 80% of outage hours, reinforcing consumer interest in alternative charging options during events and travel.
The industrial backdrop is also favorable because solar adoption is expanding rapidly across the region, which helps normalize solar use and supports wider availability of compatible components and accessories. The EIA noted that nearly 70 GW of new U.S. solar generating capacity projects are scheduled to come online in 2026–2027, representing a 49% increase in U.S. solar operating capacity compared with end-2025—a trend that strengthens retail presence, installer ecosystems, and consumer familiarity with solar-powered products beyond rooftops.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Anker strengthens its solar power mobile device portfolio through high-efficiency panels and PowerIQ-enabled solar power banks. The company maintains strong global traction, selling products in over 100+ countries and serving more than 80 million users annually. Its portable solar line benefits from durable 21W–100W panels and rapid-charging USB-C outputs, positioning Anker as a leading premium segment supplier.
RavPower accelerates its presence in solar-enabled mobile charging by integrating high-density batteries and fast-charging circuitry. The company’s products reach consumers in 50+ global markets, and its power banks often exceed 20,000 mAh capacity. By pairing compact foldable panels with PD-supported power solutions, RavPower appeals to value-focused users seeking reliable hybrid solar charging options.
Samsung benefits from global smartphone leadership, shipping more than 260 million devices annually, which directly fuels demand for solar charging accessories. Operating in over 70+ countries, Samsung complements its ecosystem with solar-compatible power banks and rugged outdoor charging solutions. Its strong R&D spending—exceeding USD 20 billion yearly—supports advanced battery integration and next-generation solar accessory innovation.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Anker Innovations
- Goal Zero
- RavPower
- Xiaomi Corporation
- Samsung Electronics
- Panasonic Corporation
- SunPower Corporation
- Duracell Inc.
- Renogy
- Aukey
Recent Industry Developments
In 2024, Samsung’s Device eXperience (DX) Division achieved a 93.4% renewable energy transition rate for its operations, reflecting a strong company-wide push to reduce environmental impact and source more clean power, including through solar power purchase agreements (PPAs) at key sites like Gumi and Gwangju.
In 2025, Goal Zero’s operations and product support were further strengthened by a USD 13.4 M funding round that helps it develop solar integration, storage technology, and durable designs aimed at outdoor and off-grid users.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 4.0 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 19.4 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 17.1% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Device Type (Smartphones, Tablets, Laptops, Wearable Devices, Portable Chargers), By Solar Technology (Monocrystalline Solar Cells, Polycrystalline Solar Cells, Thin-Film Solar Cells), By Application (Consumer Electronics, Outdoor And Camping Gear, Emergency Power Supply, Industrial Applications, Commercial Use) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Anker Innovations, Goal Zero, RavPower, Xiaomi Corporation, Samsung Electronics, Panasonic Corporation, SunPower Corporation, Duracell Inc., Renogy, Aukey Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Solar Power Mobile Devices MarketPublished date: Feb 2026add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Solar Power Mobile Devices MarketPublished date: Feb 2026add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Anker Innovations
- Goal Zero
- RavPower
- Xiaomi Corporation
- Samsung Electronics
- Panasonic Corporation
- SunPower Corporation
- Duracell Inc.
- Renogy
- Aukey










