Global Sodium Salt Battery Market Size, Share and Report Analysis By Type (Sodium-Nickel-Chloride Battery, Sodium-Sulfur Battery, Sodium-Ion Battery), By Battery Capacity (Low-Capacity Sodium Salt Batteries (Less than 5 kWh), Medium-Capacity Sodium Salt Batteries (5 kWh to 100 kWh), High-Capacity Sodium Salt Batteries (Over 100 kWh)), By Application (Energy Storage System, Electric Vehicles, Consumer Electronics, Others), By End Use (Residential, Industrial and Commercial, Utilities, Transportation, Electronics, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Feb 2026
- Report ID: 178299
- Number of Pages: 394
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
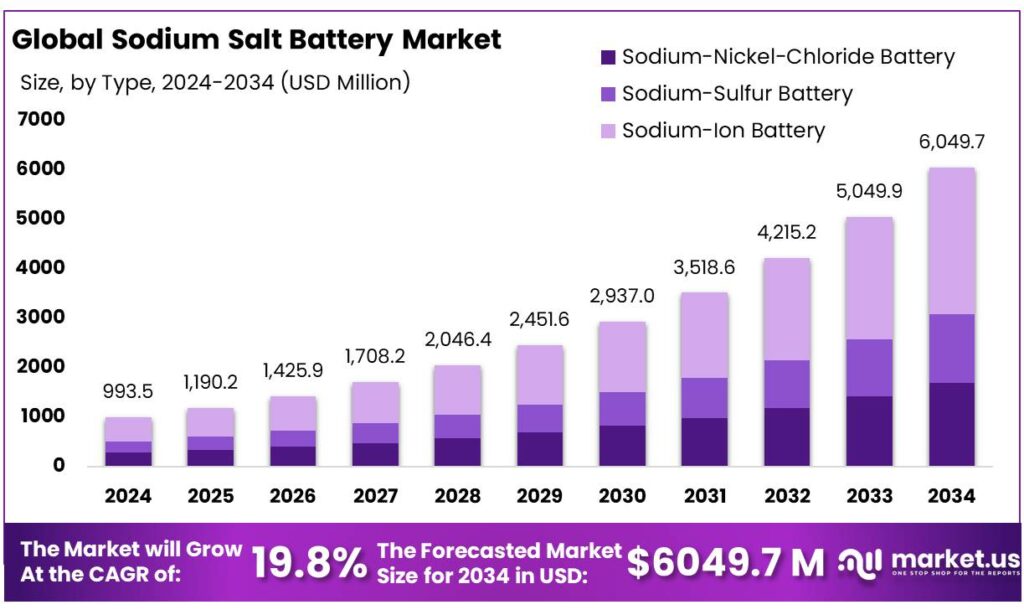
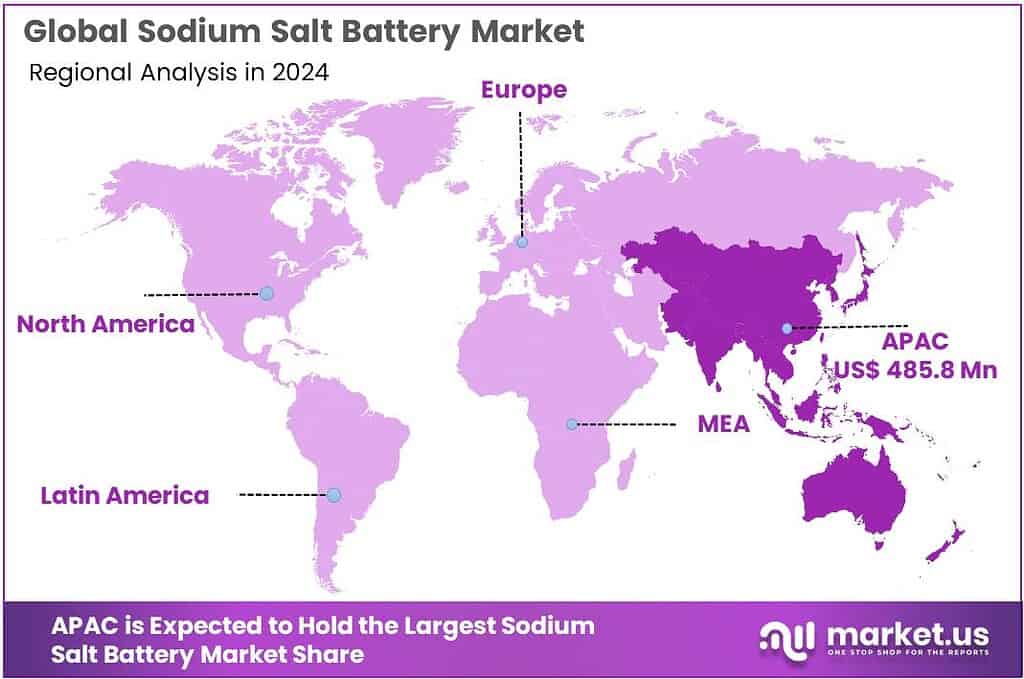
The Global Sodium Salt Battery Market is expected to be worth around USD 6049.7 Million by 2034, up from USD 993.5 Million in 2024, and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 19.8%, from 2025 to 2034. Asia Pacific accounted for 48.9%, reaching USD 485.8 Mn.
The sodium salt battery industry – typically referring to sodium-ion and sodium-sulfur systems that use sodium salts as charge carriers – is emerging as one of the most credible alternatives to lithium-ion in stationary storage and selected mobility segments.
- The technology benefits from the abundance of sodium and the ability to reuse much of the existing lithium-ion manufacturing footprint, positioning it well as global battery storage scales. Global battery storage capacity grew by about 120% in 2023 to reach 55.7 GW, with China alone rising to 27.1 GW and the United States to 16.2 GW, underscoring the scale of the addressable market for lower-cost chemistries such as sodium salt batteries.
In its 2025 World Energy Investment assessment, the International Energy Agency expects total global energy investment to reach USD 3.3 trillion, of which clean energy accounts for USD 2.2 trillion; within that, battery storage alone is forecast to attract roughly USD 66 billion, creating a large pool of capital that sodium salt solutions can tap.
At the project level, Natron Energy’s plan to invest USD 1.4 billion in a sodium-ion battery plant in North Carolina, scaling capacity from 600 MW to 24 GW per year, illustrates how new entrants are betting on sodium chemistry for data centers, industrial backup and fast-charging infrastructure.
- Government initiatives are a major structural driver. China’s “14th Five-Year Plan for New Energy Storage Development” targets more than 30 GW of new energy storage capacity by 2025, up from 3.3 GW in 2020, and explicitly calls for R&D into sodium-ion and other next-generation batteries.
Shanxi’s implementation plan sets a goal of 6 GW of new energy storage by 2025, further anchoring demand for cost-competitive chemistries. Policy analyses also highlight that the same national plan lists sodium-ion batteries as a “key direction” for new energy storage core technologies, placing sodium salt systems alongside lithium-ion in China’s long-term industrial strategy.
Similar signals are visible in other major economies. In Japan, the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) has supported sodium-based storage as part of broader next-generation battery programs; for FY2025, an energy storage subsidy scheme allocated 36.3 billion yen to 37 grid-scale battery and electrolysis projects, building domestic capability that can benefit sodium technologies.
Key Takeaways
- Sodium Salt Battery Market is expected to be worth around USD 6049.7 Million by 2034, up from USD 993.5 Million in 2024, and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 19.8%.
- Sodium-Ion Battery held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 49.7% share.
- Medium-Capacity Sodium Salt Batteries (5 kWh to 100 kWh) held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 47.6% share.
- Energy Storage System held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 48.1% share.
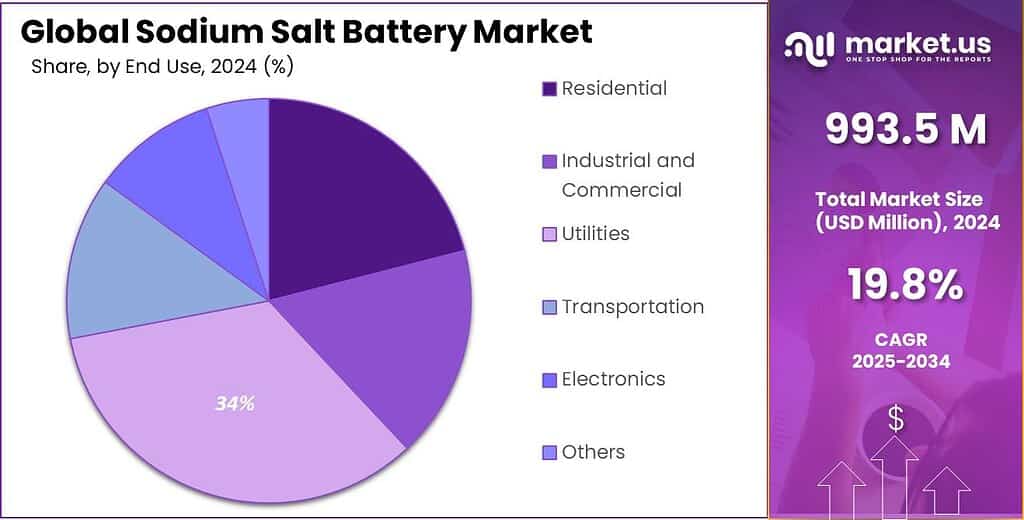
- Utilities held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 34.5% share.
- Asia Pacific is the dominating region in the Sodium Salt Battery market, holding 48.9% share and reaching USD 485.8 Mn.
By Type Analysis
Sodium-Ion Battery leads with 49.7% share driven by cost advantage and raw material availability
In 2024, Sodium-Ion Battery held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 49.7% share. The segment gained strong traction as manufacturers and utilities looked for alternatives to lithium-based chemistries amid raw material supply concerns and price volatility. Sodium-ion technology is being increasingly adopted for stationary energy storage systems, particularly in grid balancing and renewable energy integration projects, where cost stability and safety performance are more critical than ultra-high energy density. During 2024, pilot-scale production lines transitioned into early commercial deployments, especially in Asia and parts of Europe.
By Battery Capacity Analysis
Medium-Capacity Sodium Salt Batteries lead with 47.6% share driven by rising commercial and community storage demand
In 2024, Medium-Capacity Sodium Salt Batteries (5 kWh to 100 kWh) held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 47.6% share. This capacity range has become the preferred choice for commercial buildings, small industrial facilities, telecom towers, community solar projects, and distributed renewable installations. The segment offers a balanced combination of storage depth, cost efficiency, and installation flexibility, making it suitable for both backup power and daily energy management applications. During 2024, deployment increased as businesses looked to manage peak demand charges and improve energy reliability without investing in large-scale utility systems.
By Application Analysis
Energy Storage System leads with 48.1% share as utilities expand grid reliability solutions
In 2024, Energy Storage System held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 48.1% share. This segment emerged as the primary application area for sodium salt batteries as utilities and commercial operators accelerated investments in grid stability and renewable energy integration. Sodium-based systems are increasingly deployed in stationary storage projects where safety, longer cycle life, and cost predictability matter more than compact size.
By End Use Analysis
Utilities lead with 34.5% share as grid operators prioritize stable storage deployment
In 2024, Utilities held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 34.5% share. This leadership reflects the growing role of sodium salt batteries in supporting grid reliability, renewable integration, and peak demand management. Utility providers increasingly adopted sodium-based storage systems for substation-level deployment and distributed energy balancing, particularly where long cycle life and safety performance are critical. During 2024, utilities focused on strengthening grid resilience against load fluctuations and renewable intermittency, which created steady demand for stationary battery installations.
Key Market Segments
By Type
- Sodium-Nickel-Chloride Battery
- Sodium-Sulfur Battery
- Sodium-Ion Battery
By Battery Capacity
- Low-Capacity Sodium Salt Batteries (Less than 5 kWh)
- Medium-Capacity Sodium Salt Batteries (5 kWh to 100 kWh)
- High-Capacity Sodium Salt Batteries (Over 100 kWh)
By Application
- Energy Storage System
- Electric Vehicles
- Consumer Electronics
- Others
By End Use
- Residential
- Industrial and Commercial
- Utilities
- Transportation
- Electronics
- Others
Emerging Trends
Sodium-salt batteries are moving from pilots to mass production scale
A clear latest trend in the sodium salt battery market is the shift from “promising chemistry” to real industrial scale—meaning bigger factories, standardized cell formats, and product roadmaps that look closer to mainstream lithium systems. In 2025, leading manufacturers began speaking less about lab performance and more about repeatable production, safety-by-design, and long cycle life, because buyers in grid storage and industrial backup want proven operating behavior and predictable supply.
- A strong example is CATL’s public release on its sodium-ion product line, where it states an energy density of 175 Wh/kg for its Naxtra sodium-ion passenger EV battery, along with claims of over 10,000 cycles as part of its positioning around durability and lower maintenance needs.
This “industrialization trend” is not limited to one brand. In the U.S., large-scale manufacturing announcements also point to momentum. Reuters reported that Natron Energy planned a $1.4 billion sodium-ion battery plant in North Carolina and described a capacity expansion from 600 MW at its existing Michigan site to 24 GW annually for the new facility—illustrating how quickly the market conversation has moved toward gigawatt-scale output rather than pilot deployments.
Public programs are reinforcing this trend because governments want alternative chemistries that reduce dependence on constrained materials while supporting domestic manufacturing capability. Argonne National Laboratory highlighted a $50 million consortium effort (LENS) intended to accelerate sodium-ion battery development as a lower-cost and more sustainable alternative, with an emphasis on technology that can be manufactured at scale.
Drivers
Abundant, low-risk sodium supply chain is the key growth driver
In 2024, one major driving factor for the Sodium Salt Battery market was the push to build battery supply chains around materials that are widely available, easier to source, and less exposed to price shocks. Sodium fits that requirement because it is anchored in a mature, high-volume industrial ecosystem that already supplies multiple essential sectors, including food and chemicals. For example, the U.S. Geological Survey estimates domestic salt production at ~42 million tons in 2023, while ~41 million tons were sold/used, with an estimated total value of ~$2.6 billion—evidence that salt and sodium inputs already move through established logistics, refining, and quality controls at scale.
The same “industrial familiarity” shows up clearly in food and public-health guidance, which is one reason sodium supply chains are heavily measured and standardized. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends adults consume less than 2,000 mg/day of sodium, which is equivalent to less than 5 g/day of salt—a benchmark that is widely used by food manufacturers, regulators, and health agencies when they monitor sodium use and labeling practices.
Government-backed innovation programs have also strengthened this driver by lowering early commercialization barriers. In the United States, Argonne National Laboratory highlighted a $50 million consortium focused on advancing sodium-ion batteries as a lower-cost and more sustainable alternative, aimed at accelerating materials development and manufacturing readiness. Alongside that, the U.S. Department of Energy’s Advanced Materials and Manufacturing Technologies Office (AMMTO) released a funding opportunity totaling $15.7 million to improve manufacturability and scalability for emerging technologies including sodium-ion batteries.
Restraints
Lower Energy Density Compared to Established Lithium Technologies
One major restraining factor for the Sodium Salt Battery market is its relatively lower energy density compared to widely adopted lithium-based batteries. While sodium is abundant and cost-stable, the performance gap in terms of energy storage per kilogram remains a technical limitation, especially for high-performance mobility and compact storage applications. For example, according to reporting from Reuters, CATL announced its sodium-ion battery with an energy density of 175 Wh/kg, positioning it for specific use cases but still below the higher densities commonly associated with advanced lithium-ion chemistries.
The contrast becomes clearer when examining broader battery industry expansion. The International Energy Agency (IEA) reported that the global battery market exceeded USD 150 billion in 2025, driven primarily by lithium-ion deployment across electric vehicles and energy storage. The scale and maturity of lithium-ion manufacturing create strong competition. Existing gigafactories, established supply agreements, and optimized production lines mean lithium-based batteries continue to benefit from manufacturing efficiency and performance refinement.
Interestingly, the sodium supply chain itself is not the constraint. According to the U.S. Geological Survey, U.S. salt production reached approximately 42 million tons in 2023, with a value of about $2.6 billion, demonstrating abundant availability and stable industrial handling. Additionally, the World Health Organization recommends adults consume less than 2,000 mg/day of sodium, equivalent to less than 5 g/day of salt, showing that sodium is closely monitored and regulated within food and public health systems.
Opportunity
Grid-scale and distributed storage buildout is the biggest growth opportunity
A major growth opportunity for Sodium Salt Batteries is the fast expansion of stationary energy storage, especially at the grid edge and in distributed systems where safety, cost stability, and supply security matter more than squeezing every last bit of energy density. Battery storage is no longer a “nice-to-have” add-on; it is becoming core infrastructure for power systems that are adding more variable solar and wind. The International Energy Agency notes that the global market for battery storage doubled in 2023 to over 90 GWh, lifting total battery storage in use to more than 190 GWh.
- In 2024, utilities and commercial developers kept pushing storage into more locations—substations, feeder lines, microgrids, and behind-the-meter sites—because these systems can reduce congestion, provide ancillary services, and stabilize local reliability. The IEA highlights that over 40 GW of battery storage was added in 2023 (double the prior year’s increase), with growth split between utility-scale (65%) and behind-the-meter (35%) systems.
The IEA reports the global lithium-ion battery market exceeded USD 150 billion in 2025, up over 20% from 2024—an indicator of how large, strategic, and supply-sensitive the storage ecosystem has become. At the same time, power demand from digital infrastructure is rising, and resilience expectations are rising with it. The IEA’s World Energy Outlook 2025 executive summary points to expected data-centre investment of USD 580 billion in 2025, reinforcing why backup power and grid flexibility are becoming board-level priorities.
Public-sector support strengthens this growth path by accelerating scale-up from pilots to repeatable manufacturing. In the United States, Argonne National Laboratory described a $50 million consortium effort to develop sodium-ion batteries as a lower-cost, more sustainable alternative and improve technology readiness. The U.S. Department of Energy also released a funding opportunity of $15.7 million to improve manufacturability and scalability of next-generation storage options, explicitly including sodium-ion batteries.
Regional Insights
Asia Pacific dominates with 48.9% share and USD 485.8 Mn, backed by unmatched battery manufacturing scale
Asia Pacific is the dominating region in the Sodium Salt Battery market, holding 48.9% share and reaching USD 485.8 Mn. The region’s lead is strongly linked to its deep battery industrial base, where cell manufacturing, materials processing, and system integration sit close together, reducing cost and speeding up commercialization for newer chemistries such as sodium-salt. The International Energy Agency notes that China has almost 85% of global battery cell production capacity, which gives Asia Pacific a practical advantage in scaling alternative battery platforms once they pass performance validation.
On the demand side, Asia Pacific benefits from both mobility and grid drivers that create steady pull for storage technologies. The IEA reports over 11 million electric cars were sold in China in 2024, and electric cars accounted for almost half of all car sales in the country—an indicator of how large and investment-ready the regional battery ecosystem has become. While sodium batteries are not yet the main EV chemistry, this manufacturing momentum supports faster learning curves, supplier readiness, and cost-down pathways for sodium-based products.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
NGK is a long-standing stationary storage supplier with sodium-based technology experience, which supports its positioning as sodium-salt batteries scale beyond pilots. In FY2024 (ended March 31, 2025), NGK reported ¥619.513B net sales, ¥81.241B operating income, and ¥54.933B profit attributable to owners of the parent, indicating financial headroom for manufacturing and product investment. Its sustainability reporting also lists 19,540 employees (as of March 31, 2024), supporting global production and service coverage.
Altech Batteries is advancing sodium-chloride solid-state concepts for stationary use, positioning itself around safety and supply-chain simplicity. For the year ended 30 June 2025, the company reported 24 permanent employees, signaling a lean development model. Its segment reporting shows Total Revenue of $176,490 (FY2025) and discloses 112,650,000 performance rights on issue at 30 June 2025, reflecting an incentive structure aligned with project milestones rather than large-scale commercialization today.
Faradion is an IP-driven sodium-ion technology player founded in 2011, with founders named publicly and a defined patent base. The company states its portfolio comprises 21 current patent families (including 8 granted), providing defensibility in cathode/anode/electrolyte and safety domains. A major strategic milestone was Reliance’s agreement to acquire 100% of Faradion for an enterprise value of £100M, alongside a planned £25M growth investment to accelerate rollout—an indicator of industrial backing for commercialization.
Top Key Players Outlook
- GE Energy
- NGK INSULATORS, LTD.
- Altech Batteries Ltd
- Faradion
- CATL
- HiNa Battery Technology Co., Ltd
- Altris
- Aquion Energy
- TIAMAT Energy
Recent Industry Developments
In 2025, GE Vernova reported $38.068B total revenues, $3.710B free cash flow, and $150.238B backlog, which signals a large pipeline of utility and grid projects where sodium-based storage can be bundled as an “affordable, safe” option when customers don’t need maximum energy density.
In 2025, Altech published further prototype progress, reporting 650+ charge–discharge cycles with no detectable capacity loss, up to 92% energy efficiency and near-100% coulombic efficiency for prototype cells; for the 60 kWh pack, it highlighted around 88% round-trip efficiency and 110+ cycles with no observable capacity fade under varied load profiles, including pulses up to 50 A.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 993.5 Mn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 6049.7 Mn CAGR (2025-2034) 19.8% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Type (Sodium-Nickel-Chloride Battery, Sodium-Sulfur Battery, Sodium-Ion Battery), By Battery Capacity (Low-Capacity Sodium Salt Batteries (Less than 5 kWh), Medium-Capacity Sodium Salt Batteries (5 kWh to 100 kWh), High-Capacity Sodium Salt Batteries (Over 100 kWh)), By Application (Energy Storage System, Electric Vehicles, Consumer Electronics, Others), By End Use (Residential, Industrial and Commercial, Utilities, Transportation, Electronics, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape GE Energy, NGK INSULATORS, LTD., Altech Batteries Ltd, Faradion, CATL, HiNa Battery Technology Co., Ltd, Altris, Aquion Energy, TIAMAT Energy Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- GE Energy
- NGK INSULATORS, LTD.
- Altech Batteries Ltd
- Faradion
- CATL
- HiNa Battery Technology Co., Ltd
- Altris
- Aquion Energy
- TIAMAT Energy










