Global Shape Memory Polymer Market Size, Share Analysis Report By Form (Films, Sheets, Tubes, Fibers, Foams), By Material (Polyurethane (PU), Epoxy, Polylactide (PLA), Others), By End-Use (Medical, Automotive, Textile, Aerospace, Construction, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Feb 2026
- Report ID: 177837
- Number of Pages: 316
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
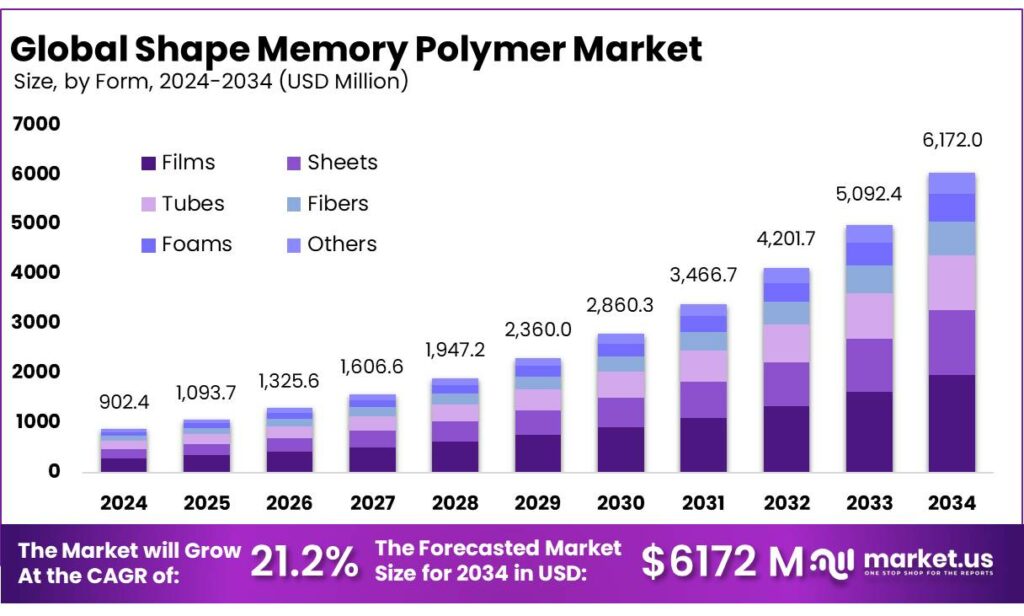
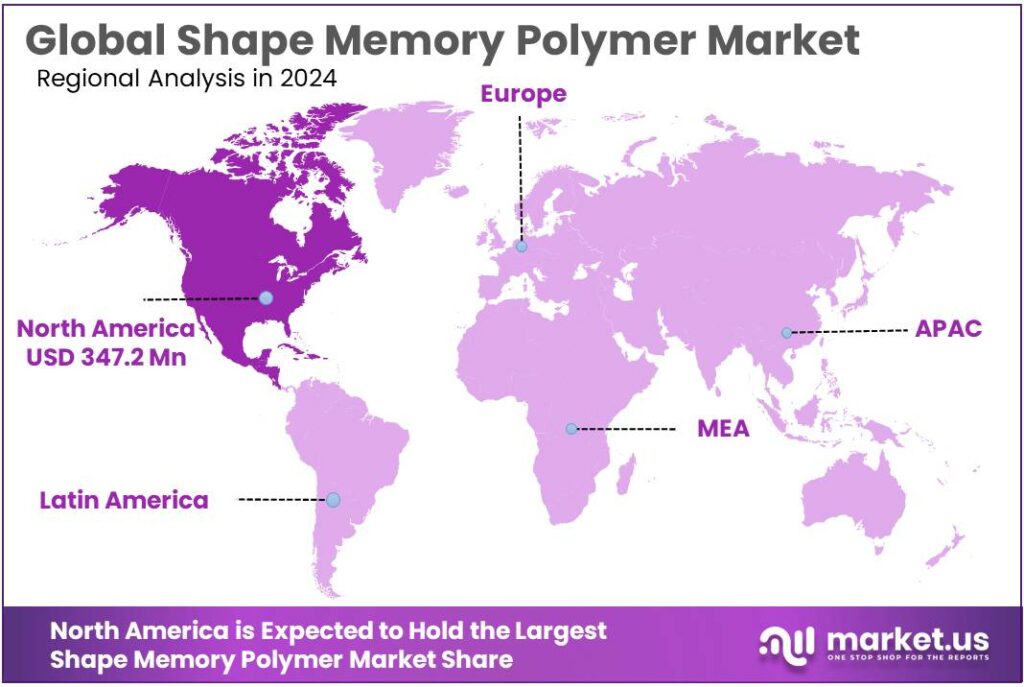
The Global Shape Memory Polymer Market is expected to be worth around USD 6172.0 Million by 2034, up from USD 902.4 Million in 2024, and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 21.2% from 2025 to 2034. The North America segment maintained 38.5%, supporting a Psychedelic Mushrooms value of USD 347.2 Mn.
Shape memory polymers (SMPs) are “smart” plastics that can be deformed into a temporary shape and later recover their original geometry when triggered. In industrial terms, SMPs sit between commodity polymers and high-value functional materials: they are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and easier to process than shape memory alloys, while still enabling controlled actuation, self-deployment, sealing, and morphing structures.
A common engineering benchmark is the transition temperature window, because it dictates when recovery starts and how fast it completes; for example, one high-temperature epoxy SMP reported a glass transition around ~130 °C, which makes it relevant for elevated-temperature aerospace or industrial hardware rather than body-temperature devices.
From an industry scenario standpoint, SMP adoption is closely tied to where lightweight, deployable, and self-actuating behavior creates measurable system-level value. In aerospace, NASA has continued to mature shape memory polymer composites for deployable structures; a NASA Langley program describes scale-up work targeting controlled deployment and < 3 mm RMS shape accuracy in relevant environments—an indicator that SMP composites are moving beyond lab coupons toward qualification-style demonstrations.
In Europe, public R&D funding is also supporting “smart” polymer systems, including a CORDIS-listed project reporting an EU contribution of €3,218,277 for a shape-memory sensor concept in a biological context—evidence of policy-backed pull for functional polymers in health-adjacent applications.
Public funding also signals momentum: an EU CORDIS project tied to 3D-printed polymer design/validation lists an EU contribution of €216,240 (April 2025), reflecting ongoing government-backed work to industrialize advanced polymer architectures.
In aerospace and high-performance engineering, SMP composites are being engineered for reliable, repeatable deployment with tight dimensional control in relevant environments. A NASA technical report (2024) describes a 3-meter-scale shape-memory polymer composite test article intended to demonstrate efficient stowage and controlled deployment while maintaining shape accuracy of < 3 mm RMS error, highlighting the practical performance targets industry must meet for flight-like structures and mechanisms.
Key Takeaways
- Shape Memory Polymer Market is expected to be worth around USD 6172.0 Million by 2034, up from USD 902.4 Million in 2024, and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 21.2%.
- Films held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 32.6% share in the Shape Memory Polymer market.
- Polyurethane (PU) held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 47.1% share in the Shape Memory Polymer market.
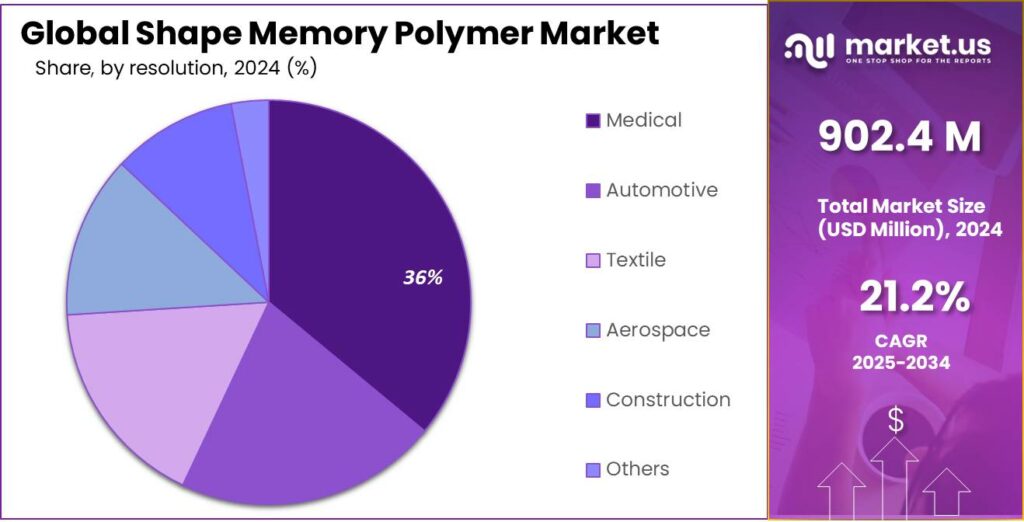
- Medical held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 36.7% share in the Shape Memory Polymer market.
- North America dominates at 38.5% (347.2 Mn), powered by healthcare demand and aerospace-grade materials adoption.
By Form Analysis
Films lead Shape Memory Polymer market with 32.6% share driven by flexible and adaptive applications
In 2024, Films held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 32.6% share in the Shape Memory Polymer market. This strong position reflects how widely film-based SMP materials are being used across industries that require lightweight, thin, and highly adaptable components. Film formats are easier to process, laminate, and integrate into multilayer systems compared to bulk forms. Their flexibility allows manufacturers to design smart surfaces, responsive layers, and compact structures that can change shape when exposed to heat or other triggers.
By Material Analysis
Polyurethane (PU) leads with 47.1% share driven by flexibility and wide industrial use
In 2024, Polyurethane (PU) held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 47.1% share in the Shape Memory Polymer market. This strong leadership comes from PU’s excellent balance of elasticity, durability, and ease of processing. Compared to other SMP materials, polyurethane offers better flexibility and higher strain recovery, making it highly suitable for applications that require repeated shape changes without losing structural performance. Its soft and adaptable nature allows it to respond efficiently to thermal triggers, which is one of the most common activation methods used in industrial applications.
By End-Use Analysis
Medical sector leads with 36.7% share driven by rising minimally invasive procedures
In 2024, Medical held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 36.7% share in the Shape Memory Polymer market. This leadership is strongly linked to the growing use of smart materials in minimally invasive treatments and advanced medical devices. Shape memory polymers are increasingly used in stents, embolization devices, sutures, orthopedic supports, and other implantable tools where controlled expansion and soft recovery are essential. Their ability to change shape inside the human body with temperature activation makes them highly valuable for precision-based procedures.
Key Market Segments
By Form
- Films
- Sheets
- Tubes
- Fibers
- Foams
By Material
- Polyurethane (PU)
- Epoxy
- Polylactide (PLA)
- Others
By End-Use
- Medical
- Automotive
- Textile
- Aerospace
- Construction
- Others
Emerging Trends
4D printing is turning SMPs into programmable parts for smart packaging and devices
A major latest trend in Shape Memory Polymers (SMPs) is the fast move from “material in a lab” to programmable components made by additive manufacturing (often called 4D printing). In simple terms, companies and research teams are no longer treating SMPs as just another polymer grade. They are designing parts so the shape change is the feature: a printed film, latch, valve, or deployable structure that stays flat during shipping and then changes form when it hits a specific temperature or environment.
This trend is showing up most clearly where the real-world pain is obvious—especially in food and cold-chain logistics. Food organizations are putting hard numbers on waste, and those numbers are pushing packaging teams to try smarter, more functional materials. UNEP’s Food Waste Index reporting notes that in 2022 the world generated 1.05 billion tonnes of food waste, equal to 132 kg per person, and nearly one-fifth of food available to consumers. It also breaks down where that waste happens: 60% household, 28% food service, and 12% retail.
Food safety adds another reason this trend is gaining attention. WHO states that unsafe food causes 600 million cases of foodborne disease and 420,000 deaths each year, with a heavy burden on young children. As a result, packaging is being asked to do more to protect product integrity and discourage mishandling. SMP components that change shape in a visible way (for example, a seal that “pops” or a lock that cannot be reset after overheating) fit the industry’s preference for clear, low-maintenance signals.
Government-backed innovation funding is also helping 4D printing and SMP development move faster. The European Union’s Horizon Europe programme lists an indicative budget of €93.5 billion for 2021–2027, which keeps advanced materials and manufacturing research well supplied with public support. In addition, the European Commission has communicated that the Horizon Europe Work Programme for 2026–2027 dedicates €4.9 billion to climate action, reinforcing the broader push for technologies that cut waste and emissions across value chains (including food systems).
Drivers
Food-waste pressure is accelerating demand for “active” packaging where SMPs can add real functionality
One major driving factor for Shape Memory Polymers (SMPs) is the rising pressure on the food system to cut waste, extend shelf life, and prove compliance—pushing brands toward smarter materials rather than “passive” packaging. The scale of the problem is hard to ignore: the UN Environment Programme (UNEP) reported that 1.05 billion tonnes of food waste were generated in 2022, equal to 132 kg per person, and about 19% of food available to consumers. FAO has also highlighted that roughly one-third of food produced for human consumption is lost or wasted—around 1.3 billion tonnes.
This is where SMPs fit in a practical way. In food and cold-chain settings, the commercial need is often very specific: detect temperature abuse, create tamper-evident behaviors, improve sealing performance, or enable pack designs that respond to heat exposure. SMPs can be engineered to change shape at a defined trigger temperature, which makes them useful as a mechanical “signal” layer. The key point is not futuristic tech—it is operational control. As retailers and food service operators tighten quality checks, any material that can provide a visible, physical change linked to handling conditions becomes valuable because it reduces disputes, returns, and safety risk.
Policy and regulatory direction is adding fuel to this shift. In the European Union, the European Commission lists the Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation (2025) as a main law in this area, reflecting the move from broad recycling targets toward stricter, harmonized packaging rules across the region. Separate compliance briefings around PPWR also note it was published in the EU Official Journal on January 22, 2025, and entered into force on February 12, 2025, which keeps packaging redesign and material innovation on executive agendas.
Restraints
Strict food-contact regulations and compliance costs are slowing broader SMP adoption in packaging
One major restraining factor for Shape Memory Polymers (SMPs), especially in food-related applications, is the complexity and cost of regulatory approval for food-contact materials. While SMPs offer smart functionality such as temperature-triggered sealing or tamper evidence, they cannot be used in food packaging without meeting strict safety standards. This compliance pathway often delays commercialization and increases development costs, limiting rapid adoption in high-volume sectors like food packaging.
In the United States, any new food-contact substance must go through the Food Contact Notification (FCN) process managed by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The FDA maintains a public inventory of effective FCNs, and each approval is specific to intended use conditions, temperature exposure, and food types. According to the FDA’s official Food Contact Substances program, manufacturers must submit detailed toxicology, migration, and exposure data before commercialization is permitted. This process is mandatory and can take several months for review, depending on the complexity of the material formulation.
In Europe, the regulatory framework is equally demanding. Food-contact materials must comply with Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004, which requires that materials do not transfer constituents to food in quantities that could endanger human health. Additionally, packaging manufacturers must align with the newer Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR), which was published in the Official Journal of the European Union on January 22, 2025 and entered into force on February 12, 2025.
Opportunity
smart food packaging that cuts waste and improves safety
A major growth opportunity for shape memory polymers (SMPs) is next-generation food packaging and cold-chain protection, where packaging is expected to do more than just contain food. Food companies and regulators are putting real pressure on waste reduction and food safety, and that pressure is creating space for “active” materials that can physically respond to temperature or handling events. SMPs are well suited to this because they can be engineered to change shape at a defined trigger point—meaning a package feature can move, lock, open, or deform in a controlled way when exposed to heat or other stimuli.
The scale of food waste alone makes the business case hard to ignore. UNEP reports that in 2022 the world generated 1.05 billion tonnes of food waste, equal to 132 kg per person, and 60% of that waste happened at the household level. FAO has also long highlighted that roughly one-third of food produced for human consumption is lost or wasted—about 1.3 billion tonnes. When companies see losses at this scale, the packaging conversation changes: features that reduce spoilage, limit temperature abuse, and prevent leakage/tampering stop looking like “nice to have” upgrades and start looking like risk control.
Food safety adds a second strong tailwind. WHO estimates that unsafe food causes 600 million cases of foodborne disease and 420,000 deaths each year, and notes that the burden falls heavily on young children. That is exactly why packaging is increasingly expected to protect product integrity and reduce contamination risks. SMP features that improve seal reliability, discourage tampering, or indicate mishandling can support safer distribution—especially for high-risk categories like ready-to-eat foods.
Regulation is also pushing packaging innovation forward in 2024–2025. In the EU, the Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation is now a central framework; the European Commission notes the PPWR entered into force in February 2025, with broad application following later. In the U.S., the FDA’s food contact system shapes what can be used at scale: FDA explains that companies submit Food Contact Substance Notifications and the agency has a mandated 120-day review window, while FDA maintains a public inventory of effective notifications.
Regional Insights
North America dominates at 38.5% (347.2 Mn), powered by healthcare demand and aerospace-grade materials adoption
In the Shape Memory Polymer market, North America was the dominating region in 2024, accounting for 38.5% share and about 347.2 Mn, supported by a strong mix of medical-device innovation, aerospace engineering programs, and mature polymer processing infrastructure. A key demand engine is healthcare, where advanced polymers are adopted faster when the clinical and funding environment is deep.
Medical manufacturing strength also matters because SMPs are often embedded into higher-value device systems rather than sold as standalone commodities. The U.S. government’s SelectUSA medical technology overview notes that the U.S. remains the largest medical device market and that U.S. medical device exports exceeded $103 billion in 2023, underlining the region’s large, globally connected device supply base that can pull specialty polymers into scaled production.
Regulatory infrastructure in North America further supports commercialization pace. FDA confirms that any 510(k) submitted after October 1, 2023 must be submitted electronically using eSTAR, which helps standardize submissions and can reduce friction for device developers working with advanced materials.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Ashland focuses on specialty chemicals used in coatings, adhesives, and performance materials—areas where SMP formulations often rely on tailored additives and binder systems. In fiscal 2024, Ashland reported sales of $2,113 million and an employee count of about 3,200. The company identifies Guillermo Novo as CEO, and its corporate office address is listed in Wilmington, Delaware (500 Hercules Road)—useful for verifying corporate filings and governance details. These capabilities support downstream SMP development through formulation know-how and specialty ingredient supply.
BASF is a major upstream enabler for SMPs because many commercial SMP systems are polyurethane-based and require specialty monomers, additives, and processing know-how. BASF reported €65.3 billion in sales for 2024 and disclosed total employees of 111,822 as of Dec 31, 2024. In governance updates, BASF states Dr. Markus Kamieth became Chairman of the Board of Executive Directors on April 25, 2024 (leadership continuity is important for long-cycle materials investments). BASF’s scale supports SMP adoption in automotive, industrial, and electronics applications.
Covestro is tightly aligned with SMP demand because polyurethane chemistry underpins many shape-memory formulations used in medical devices, wearables, and smart textiles. Covestro reported 2024 sales of €14,179 million. In corporate disclosures, Covestro lists Dr. Markus Steilemann as CEO and states it employed approximately 17,500 people (full-time equivalents) at the end of 2024; it also identifies its headquarters base in Leverkusen. This combination of PU know-how plus global production footprint makes it a direct materials enabler for SMP development.
Top Key Players Outlook
- 3M Company
- Ashland Global Holdings Inc.
- Aveka Inc.
- BASF SE
- Covestro AG
- DOW Coming
- Dupont De Nemours, Inc.
- Evonik Industries AG
- Huntsman International LLC
- Lubrizol Corporation
- Natureworks LLC
- SMP Technologies Inc.
- Spintech, LLC
Recent Industry Developments
In 2024, 3M reported total sales of $24.6 billion and returned $3.8 billion to shareholders, while cash from operations was $1.8 billion—a solid base that supports ongoing materials development and customer programs that can include SMP-style applications in medical and industrial components.
In 2025, Ashland expects sales in the range of $1.90 billion–$2.05 billion with an adjusted EBITDA target of $430 million–$470 million, highlighting a business focus on profitable growth and technical leadership even as markets shift.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 902.4 Mn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 6172.0 Mn CAGR (2025-2034) 21.2% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Form (Films, Sheets, Tubes, Fibers, Foams), By Material (Polyurethane (PU), Epoxy, Polylactide (PLA), Others), By End-Use (Medical, Automotive, Textile, Aerospace, Construction, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape 3M Company, Ashland Global Holdings Inc., Aveka Inc., BASF SE, Covestro AG, DOW Coming, Dupont De Nemours, Inc., Evonik Industries AG, Huntsman International LLC, Lubrizol Corporation, Natureworks LLC, SMP Technologies Inc., Spintech, LLC Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Shape Memory Polymer MarketPublished date: Feb 2026add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Shape Memory Polymer MarketPublished date: Feb 2026add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- 3M Company
- Ashland Global Holdings Inc.
- Aveka Inc.
- BASF SE
- Covestro AG
- DOW Coming
- Dupont De Nemours, Inc.
- Evonik Industries AG
- Huntsman International LLC
- Lubrizol Corporation
- Natureworks LLC
- SMP Technologies Inc.
- Spintech, LLC










