Global Sequestrants Market Size, Share and Report Analysis By Product Type (Natural, Synthetic), By Form (Dry, Liquids), By End Use (Food and Beverages, Pharmaceuticals, Packaging and Coating, Cosmetics, Others), By Distribution Channel (Wholesale, Speciality Stores, Online Retail, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Feb 2026
- Report ID: 176257
- Number of Pages: 369
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
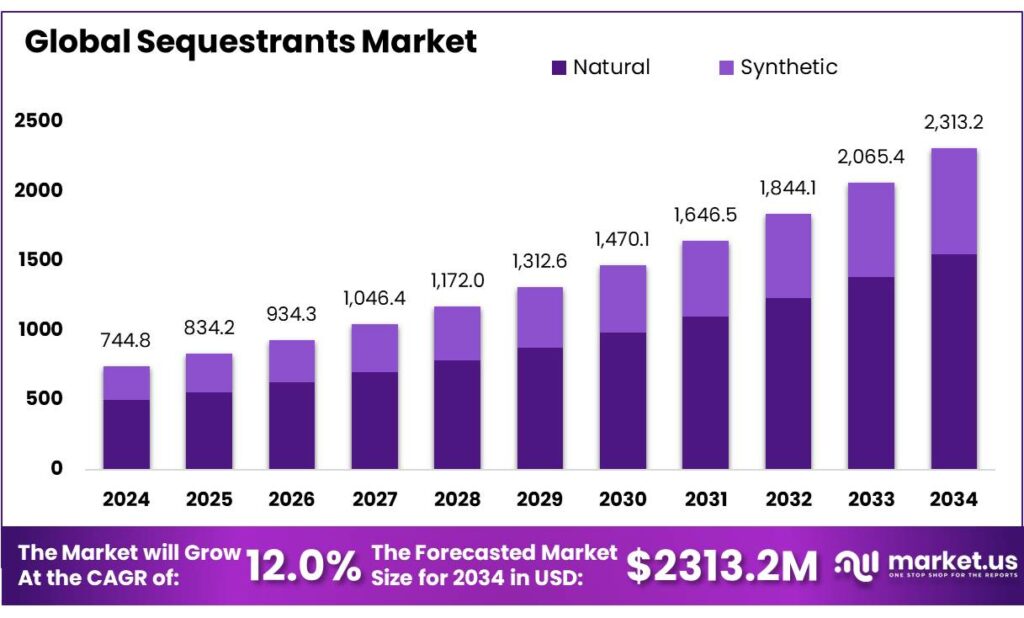
Global Sequestrants Market size is expected to be worth around USD 2313.2 Million by 2034, from USD 744.8 Million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 12.0% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024 Asia Pacific held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 42.3% share, holding USD 16.9 Billion in revenue.
Sequestrants are functional additives used to bind trace metal ions such as iron and copper that can speed up oxidation, discoloration, off-flavors, and texture breakdown in processed foods. In commercial formulations, they are typically added in very small doses—just enough to stabilize sensitive systems like emulsions, brines, and heat-treated products—so manufacturers can protect taste consistency, appearance, and shelf life across long distribution cycles.
From an industrial scenario standpoint, sequestrants sit quietly behind the scale of modern food processing. For example, global milk production reached 965.7 million tonnes in 2023, underlining how large the dairy pipeline is for applications where mineral binding helps protect flavor in fortified drinks and processed cheese systems.
Seafood is another major arena: total fisheries and aquaculture production hit 223.2 million tonnes in 2022, expanding the volume of canned and processed aquatic products where metal-catalyzed reactions can affect color and storage stability. Meat processing also remains vast at the global level, with world meat production reaching 374 million tonnes in 2024, supporting steady demand for phosphate systems and chelation strategies that help manage moisture retention and oxidative stability in prepared products.
Key driving factors are closely tied to quality retention and compliance-safe formulation. Regulators explicitly frame how these additives may be used and at what limits, shaping procurement and R&D decisions. In the United States, calcium disodium EDTA is permitted in specific foods at defined maximum levels—for instance, 33 ppm in canned carbonated soft drinks and 220 ppm in pickled cabbage/cucumbers—illustrating how sequestrants are positioned as precise, controlled tools rather than broad preservatives.
In Europe, risk assessment is also guiding tighter optimization: EFSA set a group acceptable daily intake (ADI) for phosphate additives at 40 mg/kg body weight per day and has highlighted that intakes may exceed this level for some consumers, reinforcing the push toward more efficient dosing and product-category discipline.
Future growth opportunities are increasingly linked to waste reduction, reformulation, and nutrition-forward processing. With 1.05 billion tonnes of food waste generated in 2022—about 19% of food available to consumers—food companies have strong commercial motivation to extend usable life without compromising label integrity or safety.
Key Takeaways
By Product Type Analysis
Natural Sequestrants dominate with 67.2% share due to rising clean-label adoption
In 2024, Natural held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 67.2% share as food and beverage manufacturers continued shifting toward ingredient lists that are simple, recognizable, and plant-derived. This momentum reflects the strong preference among consumers for natural preservation methods, particularly in categories like beverages, dairy, snacks, and processed foods where natural chelators such as citric acid, ascorbic acid, and rosemary extract help maintain color, flavor, and product stability.
The surge in clean-label launches has strengthened the presence of natural sequestrants, with companies choosing them to replace synthetic additives while still ensuring oxidation control and mineral binding performance.
By Form Analysis
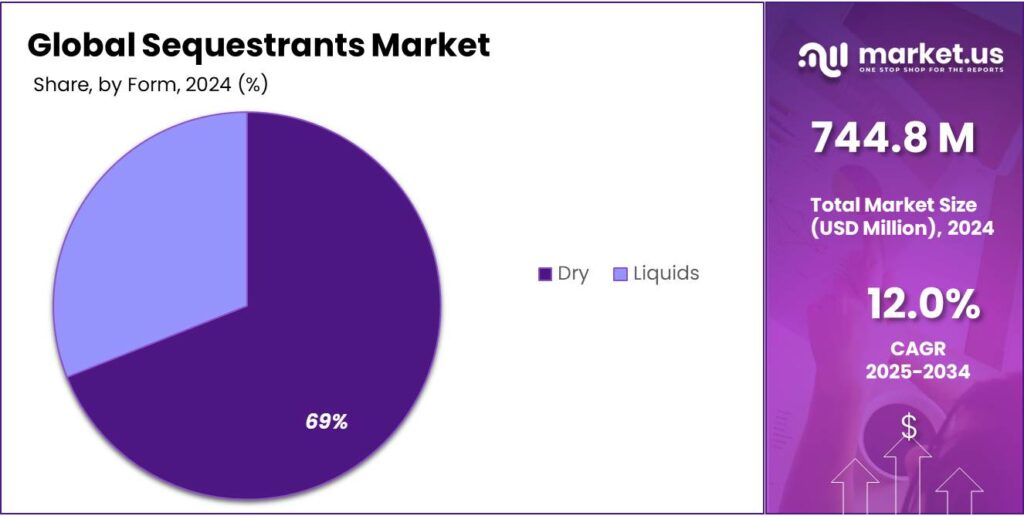
Dry Sequestrants dominate with 69.1% share due to their wide usability and long shelf stability
In 2024, Dry held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 69.1% share as manufacturers preferred powdered and granulated sequestrants for their ease of handling, accurate dosing, and compatibility with large-scale food processing systems.
Dry forms are widely used across bakery, dairy, beverages, snacks, and processed meats because they blend smoothly with dry mixes, reduce moisture-related degradation, and provide consistent performance during production. This convenience has made them the preferred choice in industries where precise formulation is critical for maintaining product color, flavor, and oxidative stability.
By End Use Analysis
Food and Beverages dominate with 49.6% share as manufacturers rely heavily on sequestrants for quality stability
In 2024, Food and Beverages held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 49.6% share, driven by the sector’s consistent need to control oxidation, maintain color, and preserve flavor integrity during processing and storage. Food producers widely use sequestrants in canned foods, dairy products, beverages, dressings, and bakery mixes, where metal ions such as iron and copper can accelerate spoilage and impact product taste.
The ability of sequestrants to bind these ions effectively makes them essential for ensuring shelf stability in high-volume production environments. This strong functional role has kept the food and beverage segment at the forefront of demand.
By Distribution Channel Analysis
Wholesale dominates with 43.8% share due to its strong supply reach and bulk procurement advantages
In 2024, Wholesale held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 43.8% share as manufacturers and large food processors continued to rely on bulk procurement channels for consistent and cost-effective sourcing of sequestrants.
Wholesale distributors play a key role in supplying large quantities of citrates, phosphates, and other chelating agents to food, beverage, and industrial users who require stable supply chains and competitive pricing. Their ability to manage inventory, provide timely deliveries, and offer standardized product batches has made wholesale the preferred channel for companies operating at high production volumes.
Key Market Segments
By Product Type
- Natural
- Phytic Acid
- Citric Acid
- Tannins
- Alginates
- Pectin
- Synthetic
- Calcium Disodium
- Calcium Chloride
- Calcium Acetate
- Glucono Delta-Lactone
- Sodium Gluconate
- Potassium Gluconate
- Sodium Tripolyphosphate
- Sodium Hexametaphosphate
By Form
- Dry
- Powder
- Granules
- Crystal
- Liquids
By End Use
- Food and Beverages
- Bakery & Confectionary
- Ready to Eat/ Instant Food
- Frozen Food
- Brewing Industry
- Others
- Pharmaceuticals
- Packaging and Coating
- Cosmetics
- Others
By Distribution Channel
- Wholesale
- Speciality Stores
- Online Retail
- Others
Emerging Trends
Clean-label sequestration is the latest trend, as brands replace synthetic chelators with familiar acids and plant-based stabilizers
One major latest trend in sequestrants is the shift toward clean-label and naturally recognizable chelation systems, especially in packaged foods and beverages that face long shelf-life demands. Instead of relying heavily on synthetic options, many manufacturers are reformulating with ingredients that consumers already know—such as citric acid, ascorbic acid, and certain plant extracts—while still aiming to control oxidation, color change, and flavor drift. This trend is not only about marketing; it reflects the daily pressure of keeping quality consistent in products that travel long distances, sit in retail storage, and still need to taste “fresh” when opened.
A big reason this trend is accelerating is the global push to reduce food waste. The UNEP Food Waste Index findings show the scale clearly: in 2022, the world generated 1.05 billion tonnes of food waste, and that equals nearly 19% of all food available to consumers. When companies see that level of waste, they look for stability tools that protect quality longer—yet they also want ingredient lists that feel simple. This is exactly where natural-style sequestrants gain space: they help reduce metal-driven oxidation in products like ready-to-drink beverages, fruit preparations, sauces, and fortified foods, while appearing more acceptable on labels.
Regulatory signals are also shaping this “natural-first” direction. In Europe, EFSA’s re-evaluation of phosphate additives set a group Acceptable Daily Intake (ADI) at 40 mg/kg body weight per day and flagged that some consumers may exceed this level. This type of guidance pushes processors to be more selective with phosphate-based sequestrant systems and to explore alternatives where performance allows. Companies are increasingly trying to get the same stability effect through combinations—using mild chelation, pH adjustment, and antioxidant pairing—rather than leaning on a single additive at higher use levels.
In the United States, the same “tight control” mindset exists through detailed use limits. For example, U.S. rules allow calcium disodium EDTA in specific foods with maximum levels such as 33 ppm in canned carbonated soft drinks and 220 ppm in pickled cabbage/cucumbers. When limits vary by product type, it encourages manufacturers to simplify their formulation approach across multiple SKUs. That often means using more “universally accepted” natural acids where feasible, so product teams can scale recipes faster without heavy regulatory mapping.
Drivers
Reducing quality loss and food waste is a major driver pushing sequestrants into everyday food processing
A major driving factor for sequestrants is the food industry’s constant fight against quality loss during processing, storage, and long-distance distribution. When tiny amounts of metal ions like iron and copper are present, they can speed up oxidation and trigger visible changes—color darkening, flavor staling, and texture weakening. Sequestrants help by binding those metals before they cause damage. This is especially valuable for packaged foods that must stay stable for weeks or months, where even small quality shifts can lead to returns, complaints, and write-offs.
The scale of global food production makes this need practical, not theoretical. In dairy alone, global milk production reached 965.7 million tonnes in 2023, meaning a massive volume of products—fortified milk drinks, flavored dairy beverages, processed cheese, and dessert mixes—move through supply chains where taste and color must stay consistent.
The meat industry adds its own pressure: world meat production reached 374 million tonnes in 2024, which supports high output of processed and ready-to-cook formats that are sensitive to oxidation and storage conditions. In large factories, ingredient tools that improve stability at low dosages become valuable because they can be applied across multiple product lines without changing the core recipe structure.
Food waste reduction also strengthens this driver. In 2022, the world generated 1.05 billion tonnes of food waste, equal to about 19% of food available to consumers, with waste spread across households, food service, and retail. This pushes producers and regulators to prioritize solutions that keep products acceptable for longer, without changing how consumers use them. In that environment, sequestrants are attractive because they support shelf stability and visual appeal—two key triggers behind early disposal—while being used in tightly controlled quantities.
Regulatory clarity is another reason this driver translates into real purchasing decisions. In the United States, rules explicitly allow calcium disodium EDTA in specific foods with stated maximum limits, such as 33 ppm in canned carbonated soft drinks and 220 ppm in pickled cabbage and pickled cucumbers. This kind of defined framework gives manufacturers confidence to use sequestrants for flavor, color, and texture retention without crossing compliance boundaries. It also supports investment in standardized premixes and bulk ingredient supply, because plants can replicate the same performance across sites and batches.
Restraints
Regulatory scrutiny and intake limits are a major restraint slowing wider use of sequestrants in food processing
One of the strongest restraining factors for the sequestrants market is the growing regulatory scrutiny around how often and how much these additives can be used in food products. Governments and scientific bodies are increasingly cautious about long-term exposure to certain chelating agents, especially synthetic ones like EDTA and phosphates. This caution does not eliminate their use, but it tightens the margins under which food companies operate, making formulation changes slower and more complex.
A clear example comes from the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), which reassessed phosphate additives and introduced a group Acceptable Daily Intake (ADI) of 40 mg/kg body weight per day, expressed as phosphorus. EFSA further reported that some population groups—especially children—may exceed this ADI when consuming multiple processed foods containing phosphate salts. This puts pressure on manufacturers to reformulate, reduce usage levels, or seek natural alternatives. The requirement to stay below the ADI is not simply a guideline; it directly influences how producers evaluate sequestrant content during R&D and final product release.
In the United States, rules under Title 21 of the Code of Federal Regulations tightly define where sequestrants such as calcium disodium EDTA may be used and in what quantities. For instance, EDTA is capped at 33 parts per million (ppm) in canned carbonated soft drinks and 220 ppm in pickled cabbage and pickled cucumbers. These detailed limits—varying from product to product—restrict manufacturers from applying sequestrants broadly, even when they offer real shelf-life benefits. As food companies explore global exports, they must also reconcile these U.S. rules with separate European, Canadian, and Asian frameworks, adding further complexity.
Another limiting factor is the rapid growth of processed foods, which amplifies the challenge of keeping intake levels within approved margins. For example, global packaged food sales continue to rise, and worldwide food waste remains extremely high at 1.05 billion tonnes in 2022, representing about 19% of all food available to consumers. While sequestrants could help stabilize many foods contributing to waste, producers must balance the benefit of reducing spoilage against regulatory restrictions and consumer acceptability. This tension slows down broader adoption.
Opportunity
Food fortification and “nutrition-by-design” products create a strong growth runway for sequestrants in 2025
A major growth opportunity for sequestrants is the fast expansion of food fortification and mineral-enriched products, where trace metals must remain stable, bioavailable, and visually appealing over the full shelf life. When manufacturers add iron, zinc, calcium, or micronutrient blends into flour, beverages, dairy drinks, and nutrition powders, they often face side effects like oxidation, taste drift, or color changes. Sequestrants help by binding reactive metal ions and keeping the formula steady, which reduces product complaints and protects brand consistency. This makes sequestrants a practical “support ingredient” for companies scaling fortified product portfolios in mass markets.
The policy backdrop is already large and still widening. World Health Organization notes that, as of 2016, about 34.1% of the world’s industrially milled wheat flour was fortified with at least iron or folic acid. The same WHO resource also states that over 80 countries have legislation to fortify wheat flour, with additional legislation covering maize products and rice in multiple countries. This matters for sequestrants because every new fortification mandate increases the volume of foods where mineral stability becomes a daily production issue—especially for high-throughput mills and beverage plants that cannot afford batch variation.
In 2025, the opportunity becomes even clearer because fortification growth is happening alongside rising pressure to reduce food waste. United Nations Environment Programme reports that the world generated about 1.05 billion tonnes of food waste in 2022, equal to roughly 19% of food available to consumers, spanning households, food service, and retail. That scale encourages practical investments in stability tools that reduce early quality failure—off-flavors, discoloration, or texture issues—before products ever reach the consumer. Sequestrants fit this need because they can slow metal-catalyzed deterioration in sensitive categories like fortified beverages, canned vegetables, processed fruit, and ready-to-eat meals.
Regional Insights
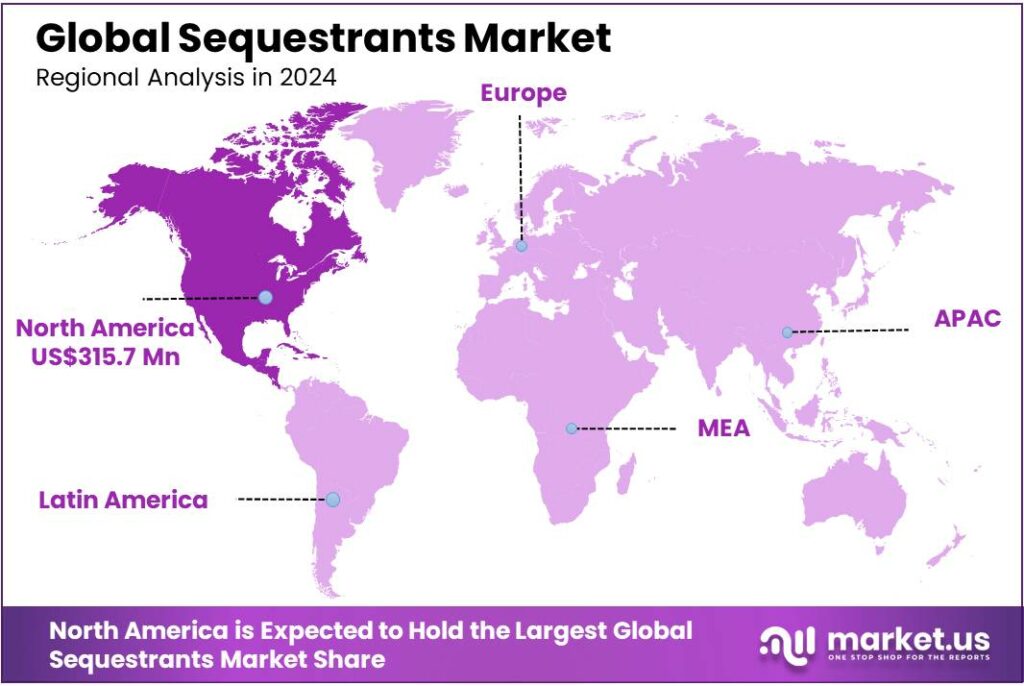
North America dominates the Sequestrants market with a 42.4% share, valued at USD 315.4 Mn, supported by high-volume processed food output.
In 2024, North America held a dominant position in the sequestrants market, capturing more than 42.4% share and reaching about USD 315.4 Mn. This leadership is closely linked to the region’s large-scale packaged and processed food ecosystem, where sequestrants are used to bind trace metals and protect color, flavor, and shelf stability in beverages, dairy, sauces, canned foods, and frozen meals. The manufacturing base is deep on both sides of the border. In Canada, meat product manufacturing recorded sales of $43.8 billion in 2024, while dairy product manufacturing reached $19.6 billion and grain & oilseed milling totaled $18.9 billion, showing the scale of categories that routinely use stabilizing ingredient systems.
By 2025, the region’s demand outlook remains supportive because producers are under strong pressure to reduce quality losses and avoid waste across long distribution chains. In the United States, food waste is estimated at between 30–40% of the food supply, reinforcing the need for formulation tools that improve stability and reduce early spoilage. Canada shows similar industrial pull through breadth and export exposure: its food and beverage manufacturing industry includes nearly 15,000 establishments (2024), employs over 315,000 people (2024), and reported food and beverage exports of about $59.7B.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Cargill Inc. – Cargill, Incorporated is a U.S.-based multinational food and industrial products company with reported revenue of USD 165 billion in 2022 and over 160,000 employees globally. While best known for food ingredients and agricultural supply, Cargill also supplies specialty industrial chemical solutions and bio-based additives that support stabilization and quality in food processing and allied sectors.
Wang Pharmaceuticals & Chemicals – Established in 1986, Wang Pharmaceuticals & Chemicals is an Indian manufacturer and exporter of bulk drugs, pharmaceutical excipients, and food additive chemicals such as sodium citrate, potassium citrate, and citric acid used as sequestrants in food and beverage formulations. The company reports an approximate annual turnover of USD 4 million, serving both domestic and international markets.
Anmol Chemicals – Founded in 1976, Anmol Chemicals Private Limited is an Indian specialty chemical manufacturer with over 47 years of industry history. It generated around ₹76.9 crore in revenue for the latest reported year, and produces a range of food additives, mineral fortifiers, excipients, and speciality chemical ingredients used across food, pharmaceutical, and nutraceutical segments.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Connect Chemicals
- Cargill Inc.
- Wang Pharmaceuticals & Chemicals
- CHT
- Anmol Chemicals
- Northstar Chemical
- Jungbunzlauer
- Bell Chem
- Enartiss
Recent Industry Developments
In 2025, Cargill continues operating as one of the largest global agrifood suppliers, with reporting noting an employee base of about 155,000 worldwide—an indicator of execution capacity across sourcing, processing, and ingredient distribution that underpins its role in supplying citrate-based sequestration solutions to industrial food customers.
In 2024–2025, Anmol Chemicals continued to strengthen its presence in the sequestrants and food additives sector by supplying quality mineral salts, chelating agents, and food-grade chemicals that help stabilize beverages, dairy, and fortified products. Based in Mumbai, India, the company has been operating since 1976 with over 47 years of experience in specialty chemicals, pharmaceutical excipients, and FCC-certified food additives that meet international standards such as WHO-GMP, ISO 22000, and FSSAI certification, which supports safer sequestrant use in processed foods.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD {{val1}} Forecast Revenue (2034) USD {{val2}} CAGR (2025-2034) {{cagr}}% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Product Type (Natural, Synthetic), By Form (Dry, Liquids), By End Use (Food and Beverages, Pharmaceuticals, Packaging and Coating, Cosmetics, Others), By Distribution Channel (Wholesale, Speciality Stores, Online Retail, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Connect Chemicals, Cargill Inc., Wang Pharmaceuticals & Chemicals, CHT, Anmol Chemicals, Northstar Chemical, Jungbunzlauer, Bell Chem, Enartiss, Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
- Natural
-
-
- Connect Chemicals
- Cargill Inc.
- Wang Pharmaceuticals & Chemicals
- CHT
- Anmol Chemicals
- Northstar Chemical
- Jungbunzlauer
- Bell Chem
- Enartiss










