Global Robotic De-Nesting Systems Market By Product Type (Automatic Robotic De-Nesting Systems, Semi-Automatic Robotic De-Nesting Systems), By System (Standalone, Integrated, Flexible/Mobile), By Application (Food and Beverage, Pharmaceuticals, Packaging, Automotive, Electronics, Others), By Regional Analysis, Global Trends and Opportunity, Future Outlook By 2025-2034
- Published date: Dec. 2025
- Report ID: 170800
- Number of Pages: 243
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
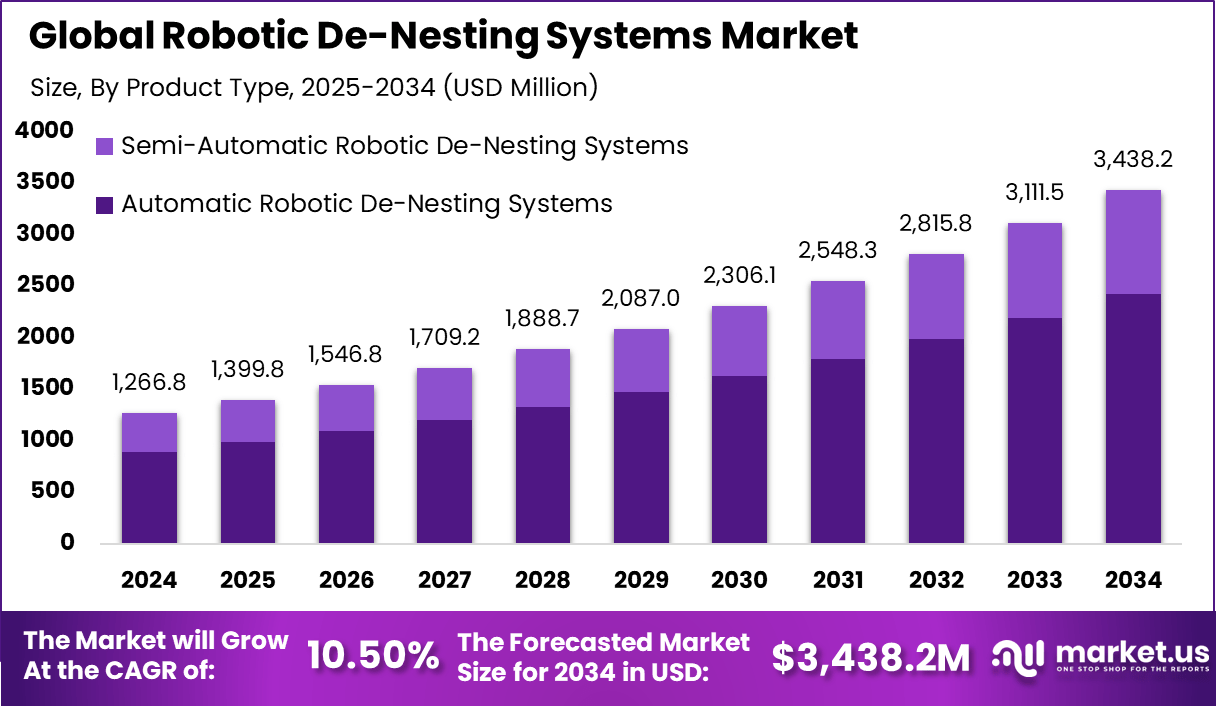
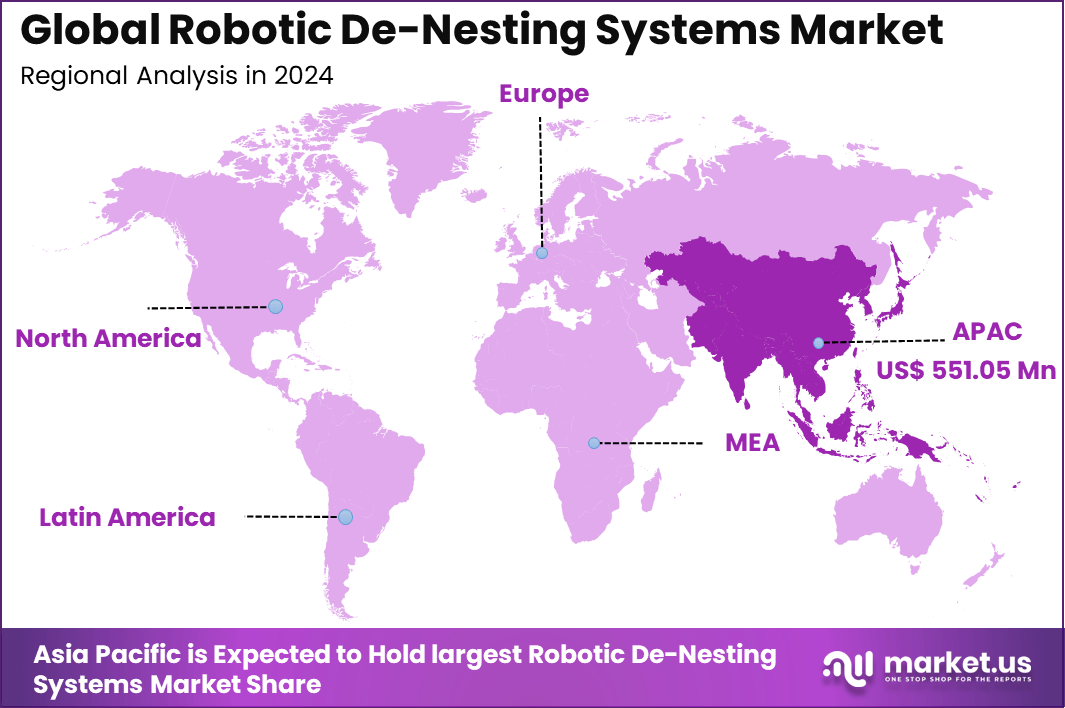
The Global Robotic De-Nesting Systems Market generated USD 1,266.8 million in 2024 and is predicted to register growth from USD 1,399.8 million in 2025 to about USD 3,438.2 million by 2034, recording a CAGR of 10.50% throughout the forecast span. In 2024, Asia Pacific held a dominan market position, capturing more than a 43.5% share, holding USD 1.3 Billion revenue.
The robotic de-nesting systems market refers to automated solutions that separate, orient, and feed stacked or nested parts for downstream processing in manufacturing and logistics environments. These systems are designed to handle a variety of components such as trays, boxes, sheets, molded parts, and packaged items, where manual de-nesting is traditionally labour intensive.
By using robotics, machine vision, and adaptive grippers, de-nesting robots improve throughput, consistency, and safety in operations. Adoption has increased across industries such as consumer goods, automotive, electronics assembly, pharmaceuticals, and food packaging where precise handling of nested parts is critical.
This market plays a crucial role in improving efficiency and accuracy at early stages of automated production workflows. Robotic de-nesting systems serve as the gateway between bulk stacked supplies and downstream processes such as assembly, inspection, or packaging. Accurate de-nesting reduces jams, misfeeds, and production interruptions that can cascade into costly delays. These systems improve quality control by ensuring correct orientation and singulation before parts enter high speed lines.
Growth in this market is driven by rising labour costs, persistent workforce shortages, and the need for higher throughput in competitive manufacturing environments. Manual de-nesting is often slow and ergonomically demanding, leading manufacturers to seek robotic alternatives that can operate continuously with repeatable precision. Advances in machine vision, force sensing, and adaptive gripping technologies have expanded the capability of robots to handle diverse and complex part geometries safely and reliably.
Top Market Takeaways
- By product type, automatic robotic de-nesting systems held 70.6% of the market, as they quickly separate stacked parts without damage.
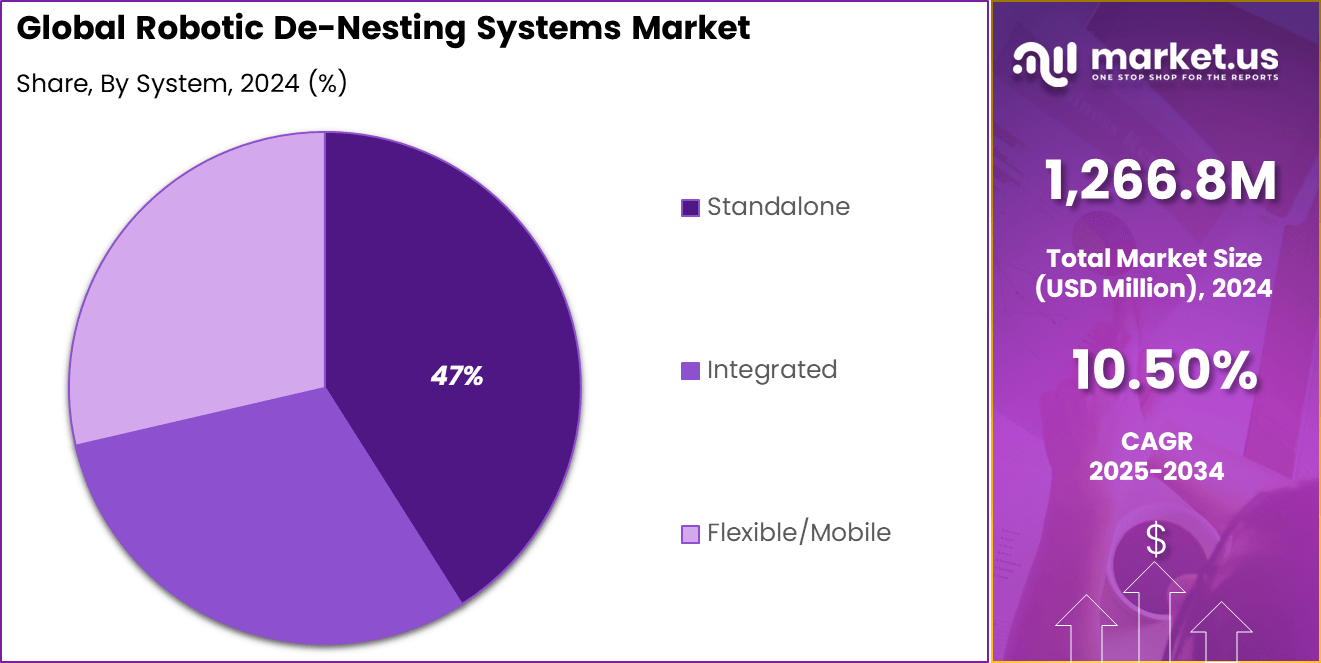
- By system, standalone de-nesting cells captured 47.3% share, offering easy setup for single production lines.
- By application, automotive led with 40.2%, used for handling sheet metal and plastic parts in car making.
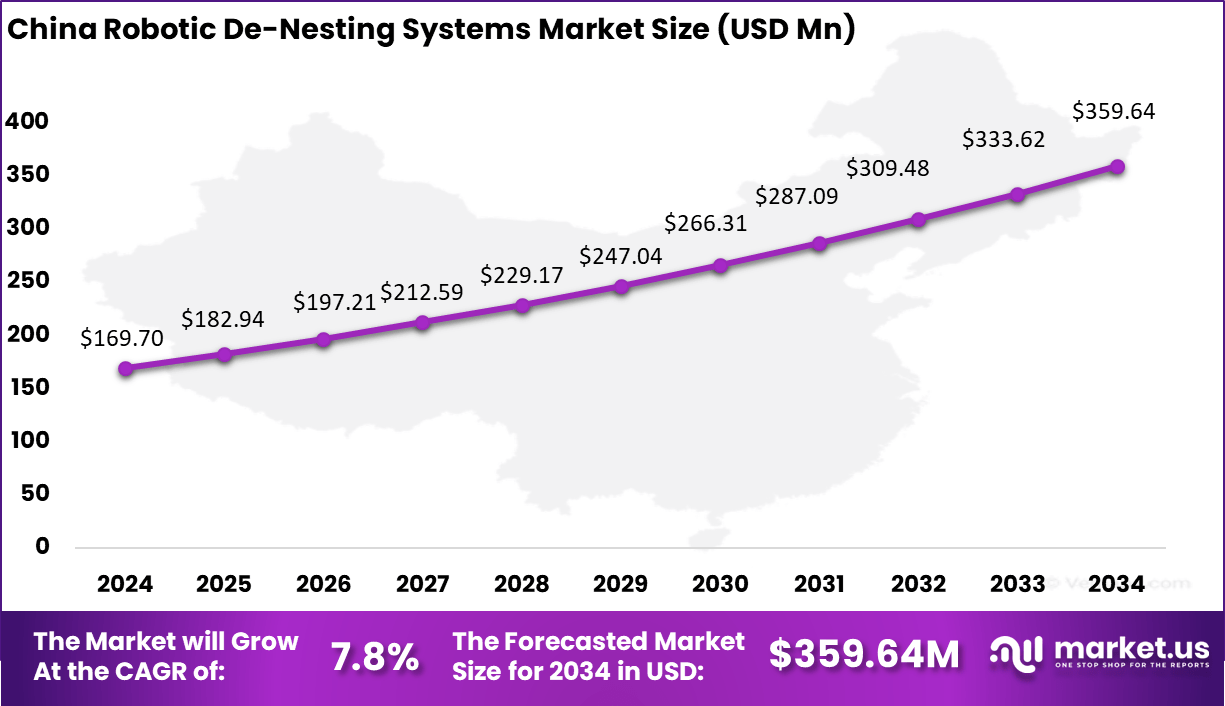
- Asia Pacific took 43.5% of the global market, with China at USD 169.7 million in 2025 and growing at a CAGR of 7.8%.
Product Type Analysis
Automatic robotic de-nesting systems account for 70.6% of the market, showing strong preference for fully automated solutions that separate and feed stacked or nested parts without manual intervention. These systems are widely used in production environments where speed, accuracy, and consistency are critical. Automatic de-nesting reduces dependence on manual labor and ensures steady part flow to downstream processes such as welding, machining, or assembly.
From an operational view, automatic systems help manufacturers maintain high throughput while minimizing handling errors and workplace fatigue. They are designed to handle complex part geometries and varying stack patterns with reliable precision. The strong share of this segment reflects the growing focus on automation to improve productivity, safety, and process stability in high-volume manufacturing operations.
System Analysis
Standalone de-nesting cells hold 47% of the system segment, highlighting their flexibility and ease of deployment. These cells operate as independent units that can be integrated into existing production lines with minimal changes. Their modular nature allows manufacturers to add de-nesting capabilities without fully redesigning plant layouts.
Standalone systems are also valued for their ability to support different production requirements. They can be repositioned or reconfigured as manufacturing needs evolve. This adaptability makes them suitable for facilities that handle multiple part types or variable production volumes. The solid adoption of standalone de-nesting cells reflects industry demand for scalable and easy-to-integrate automation solutions.
Application Analysis
The automotive sector accounts for 40.2% of application demand, making it the largest end-use area for robotic de-nesting systems. Automotive production involves handling large volumes of metal and plastic components that are often stacked or nested for storage and transport. Robotic de-nesting ensures consistent and damage-free separation of these parts, supporting smooth assembly line operations.
In automotive plants, precision and timing are essential to avoid production delays. De-nesting robots help maintain continuous material flow and reduce bottlenecks at critical stages. Their adoption is driven by the industry’s emphasis on automation, worker safety, and quality control. The strong presence of automotive applications reflects ongoing investments in advanced manufacturing technologies within the sector.
Increasing Adoption Technologies
Key technologies supporting adoption include advanced vision systems, AI-assisted object recognition, flexible end-of-arm tooling, and collaborative robots equipped with force feedback. Machine vision enables accurate detection of nested parts and guides robotic arms for precise pick points. Adaptive grippers and soft robotics tools help manage parts with delicate surfaces or variable nesting conditions.
Integration with factory control systems and real-time analytics allows remote monitoring and predictive maintenance, which increases system uptime and reliability. Organizations adopt robotic de-nesting systems to increase throughput, reduce dependency on manual labour, and improve workplace safety.
Robots reduce repetitive strain and physical effort on workers while lowering error rates associated with human handling. Improved singulation and orientation contribute directly to smoother downstream automation and lower defect rates. Manufacturing operators also value how de-nesting automation supports consistent production performance and enables better use of human labour for higher value tasks.
Key Benefits
- Improved operational efficiency through continuous feeding
- Consistent part orientation supports downstream automation
- Reduced manual handling improves workplace safety
- Higher throughput improves overall line productivity
- Lower rejection rates due to precise and gentle handling
Key Usage Areas
- Automotive plants for separating metal and plastic components
- Food and beverage facilities for handling trays and containers
- Pharmaceutical production for packaging and filling lines
- Electronics manufacturing for delicate component handling
- Consumer goods factories for high speed assembly operations
Emerging Trends
Key Trend Description Vision AI Pick Trays Cameras combined with AI identify stacked trays accurately and pick the correct ones at high speed. Soft Grippers Gentle Flexible rubber grippers hold thin trays securely without causing cracks or bending. High Speed Lines Robots de stack large volumes of trays per minute to support busy packaging operations. Clean Food Safe Wash friendly components help prevent contamination in food and pharmaceutical facilities. Quick Change Tools Grippers can be replaced within seconds to handle different tray shapes and pack types. Growth Factors
Key Factors Description Food Pack Demand Up Rising demand for ready to eat and packaged food increases the need for fast tray handling. No Workers Shortage Robots replace manual tasks in areas where labor shortages and fatigue are common. Clean Rules Strict Hygiene regulations require automated handling to reduce direct human contact. Factory Speed Push Manufacturers focus on higher line speeds with fewer stoppages using automation. Robots Get Cheap Lower equipment costs allow small and mid size plants to adopt tray de nesting robots. Key Market Segments
By Product Type
- Automatic Robotic De-Nesting Systems
- Semi-Automatic Robotic De-Nesting Systems
By System
- Standalone
- Integrated
- Flexible/Mobile
By Application
- Food and Beverage
- Pharmaceuticals
- Packaging
- Automotive
- Electronics
- Others
Regional Analysis
Asia Pacific accounted for 43.5% share, supported by strong manufacturing output across automotive, electronics, food processing, and packaging industries. The region has seen steady adoption of robotic de nesting systems to improve material handling efficiency and reduce manual intervention in high volume production lines.
Demand has been driven by the need to handle delicate and irregular components with consistent accuracy, while maintaining high throughput. As factories continue to focus on automation to control labor costs and improve process stability, de nesting systems have become an important part of end of line and feeding operations.
China reached a market value of USD 169.7 Mn and is projected to grow at a 7.8% CAGR, reflecting steady but sustained automation adoption in manufacturing. Robotic de nesting systems are increasingly used to support high speed production and reduce dependency on manual sorting and separation tasks.
Adoption has been particularly strong in automotive components, appliance manufacturing, and food packaging, where consistent part presentation directly affects downstream process efficiency. Growth in China has also been supported by the country’s expanding base of domestic automation suppliers and system integrators. Localized production and cost competitive solutions have made de nesting systems more accessible to mid sized manufacturers.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherlands
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Competitive Analysis
ABB, FANUC, KUKA, and Yaskawa lead the robotic de-nesting systems market with high precision robots used to separate stacked parts, containers, and food items in automated production lines. Their systems improve throughput, reduce manual handling, and ensure consistent product flow. These companies focus on accuracy, speed, and reliable operation in high volume manufacturing.
Schneider Electric, Rockwell Automation, Universal Robots, Stäubli, Kawasaki Heavy Industries, and Omron strengthen the market with flexible robotic arms, vision guided de-nesting, and collaborative robot solutions. Their technologies support handling of varied shapes and delicate products. These providers emphasize safety, easy integration, and adaptability across production environments.
Marel, BluePrint Automation, JLS Automation, Brillopak, FlexLink, Scott Automation and Robotics, Schubert Group, and other players expand the landscape with application specific de-nesting systems for food, beverage, and packaging lines. Their offerings focus on hygienic design, modular layouts, and end to end line integration.
Top Key Players in the Market
- ABB Ltd.
- Fanuc Corporation
- KUKA AG
- Yaskawa Electric Corporation
- Schneider Electric SE
- Rockwell Automation, Inc.
- Universal Robots A/S
- Stäubli International AG
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- Omron Corporation
- Marel hf.
- BluePrint Automation (BPA)
- JLS Automation
- Brillopak Ltd.
- FlexLink (Coesia Group)
- Scott Automation & Robotics
- Schubert Group
- Others
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the Robotic De-Nesting Systems market is expected to remain stable and positive as manufacturers focus on improving production speed and consistency. These systems are being adopted to separate and feed stacked or nested parts accurately into downstream processes such as machining, forming, and packaging.
Rising use of mixed product lines and frequent changeovers is increasing the need for flexible de-nesting solutions that can handle different shapes and materials. Over time, better vision guidance, adaptive gripping, and easier integration with existing production lines are likely to improve reliability and reduce setup effort.
Opportunities lie in
- High mix manufacturing environments: Flexible de-nesting systems can support frequent product changes without long downtime.
- Integration with vision and AI tools: Advanced sensing can improve part recognition and reduce picking errors.
- Labor replacement in repetitive tasks: Robots can reduce dependence on manual part separation in demanding factory operations.
Recent Developments
- January 2025 – ABB Ltd. expanded its OmniCore robotics control platform into food, beverage and consumer packaged goods applications, positioning the controller as the core for high‑speed pick‑and‑place and tray handling cells that include robotic de‑nesting functions on primary and secondary packaging lines.
- April 2025 – BluePrint Automation (BPA) highlighted new applications of its Spider 100v robotic stacking platform where the same system is engineered to handle product accumulation, nesting and de‑nesting of trays within secondary packaging cells
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 1,266.8 Mn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 3,438.2 Mn CAGR(2025-2034) 10.50% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue forecast, AI impact on Market trends, Share Insights, Company ranking, competitive landscape, Recent Developments, Market Dynamics and Emerging Trends Segments Covered By Product Type (Automatic Robotic De-Nesting Systems, Semi-Automatic Robotic De-Nesting Systems), By System (Standalone, Integrated, Flexible/Mobile), By Application (Food and Beverage, Pharmaceuticals, Packaging, Automotive, Electronics, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia, Netherlands, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, Rest of Latin America; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape ABB Ltd., Fanuc Corporation, KUKA AG, Yaskawa Electric Corporation, Schneider Electric SE, Rockwell Automation, Inc., Universal Robots A/S, Stäubli International AG, Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd., Omron Corporation, Marel hf., BluePrint Automation (BPA), JLS Automation, Brillopak Ltd., FlexLink (Coesia Group), Scott Automation & Robotics, Schubert Group, Others Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three license to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Robotic De-Nesting Systems MarketPublished date: Dec. 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Robotic De-Nesting Systems MarketPublished date: Dec. 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- ABB Ltd.
- Fanuc Corporation
- KUKA AG
- Yaskawa Electric Corporation
- Schneider Electric SE
- Rockwell Automation, Inc.
- Universal Robots A/S
- Stäubli International AG
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- Omron Corporation
- Marel hf.
- BluePrint Automation (BPA)
- JLS Automation
- Brillopak Ltd.
- FlexLink (Coesia Group)
- Scott Automation & Robotics
- Schubert Group
- Others










