Global Pharmaceutical Lipids Market Analysis By Product (Triglycerides, Phospholipids, Sphingolipids, Sterols, Fatty Acids, Others), By Source (Plant-derived, Animal-derived, Synthetic), By Delivery System (Liposomes, Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs), Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN), Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC), Lipid Emulsions, Self-Emulsifying Systems (SEDDS/SMEDDS)), By Route of Administration (Parenteral, Oral, Topical, Inhalation), By Application (Small-Molecule Drugs & Vaccine Delivery, Biologics & Peptides, Nucleic-Acid Therapies, Parenteral Nutrition), By End-User (Pharmaceutical & Biopharmaceutical Companies, CDMOs, Academic & Research Institutes, Hospitals & Clinical Centers) By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Nov 2025
- Report ID: 165831
- Number of Pages: 322
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
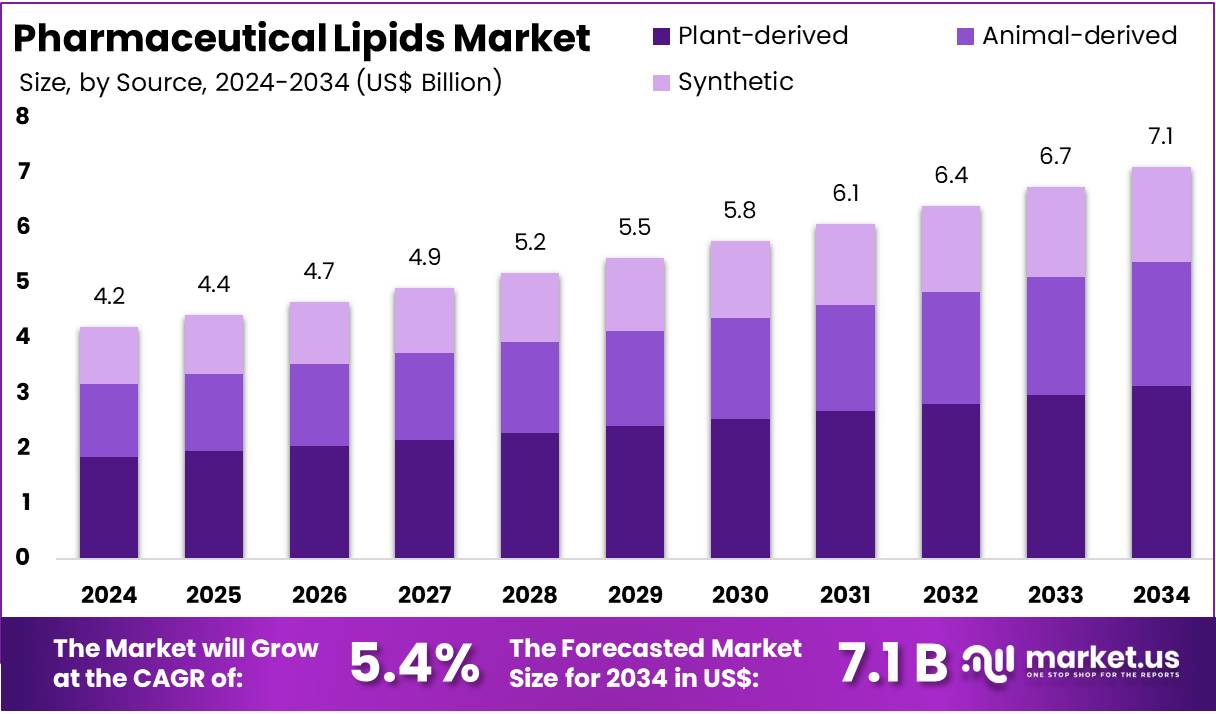
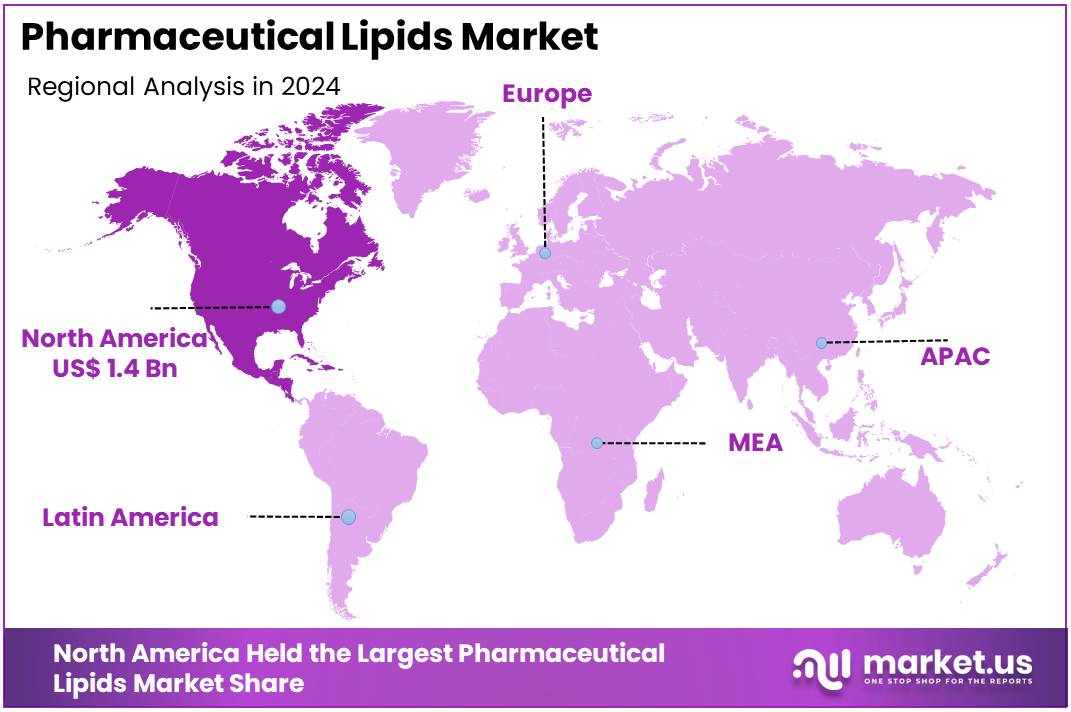
The Global Pharmaceutical Lipids Market size is expected to be worth around US$ 7.1 Billion by 2034, from US$ 4.2 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 5.4% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 33.5% share and holds US$ 1.4 Billion market value for the year.
Pharmaceutical lipids are specialized fat-based molecules that play a critical role in drug formulations. These lipids act as functional excipients in many drugs, helping to improve solubility, bioavailability, and enable controlled or targeted release. Their use in tablets, injectables, vaccines, and lipid-based nanoparticles has become essential in modern medicine. The demand for lipid-based drug delivery systems is growing, driven by the expansion of biologics, mRNA vaccine pipelines, and the increasing investments in advanced formulation technologies.
One of the primary drivers for growth in the pharmaceutical lipids market is the rise in chronic non-communicable diseases (NCDs) worldwide. The World Health Organization (WHO) reports that NCDs like cardiovascular disease, cancer, and diabetes were responsible for 75% of global deaths in 2021. With an aging global population, the number of people over 60 is expected to increase from 1.0 billion in 2020 to 2.1 billion by 2050. As people live longer, they often need long-term medications, creating a sustained demand for safe and well-tolerated formulations, which lipid-based systems can provide.
In addition to chronic diseases, the rapid rise in diabetes and related metabolic disorders is contributing to the increased need for pharmaceutical lipids. The prevalence of diabetes has doubled from 7% to 14% globally between 1990 and 2022. As of 2022, WHO estimates that over 830 million people worldwide live with diabetes. This trend is expected to continue, with projections indicating 853 million cases by 2050. Many of the drugs for treating diabetes and its complications are poorly soluble, making lipid-based excipients essential for effective delivery, particularly in oral and injectable therapies.
The pharmaceutical lipids sector is further supported by the increasing proportion of poorly water-soluble molecules in the global drug pipeline. Studies indicate that approximately 40% of approved drugs and 90% of drug candidates are poorly water-soluble. Lipid-based formulations improve the solubility of these drugs, enabling better absorption in the body. For example, lipid nanoparticles, self-emulsifying systems, and nanoemulsions are being used more frequently to overcome solubility barriers, which has resulted in higher demand for pharmaceutical lipids in drug formulations.
Innovations and Drivers Shaping the Future of Pharmaceutical Lipids
Another key factor contributing to the growth of the pharmaceutical lipids market is the proven clinical success of lipid-based drug delivery systems. These systems have been used in many marketed products to improve solubility, bioavailability, and cellular uptake. For instance, the success of lipid nanoparticle (LNP) technology in the delivery of mRNA vaccines during the COVID-19 pandemic has significantly boosted confidence in lipid-based systems. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) notes that lipid nanoparticles were crucial in the delivery of mRNA vaccines, offering protection to the mRNA and facilitating cellular uptake.
According to the European Medicines Agency, mRNA vaccines like Comirnaty, which use lipid nanoparticles to encapsulate nucleoside-modified mRNA, have revolutionized vaccinology. This broad, real-world use has not only demonstrated the effectiveness of lipid-based delivery systems but also built trust among regulators, clinicians, and manufacturers. This has spurred further investments in pharmaceutical lipids, particularly in the fields of gene therapies, vaccines, and other nucleic-acid-based products. The increasing confidence in LNP technology has paved the way for more widespread adoption of lipid-based systems.
Regulatory clarity also supports the growth of the pharmaceutical lipids market. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has issued guidelines that help reduce scientific and regulatory uncertainty regarding lipid-based products. Detailed guidance on liposome drug products, for example, addresses key areas such as chemistry, manufacturing, controls, and bioavailability. These guidelines help pharmaceutical companies better understand regulatory expectations and encourage the use of high-quality, well-characterized lipid excipients in their formulations.
The advancements in lipid chemistry and formulation science have played a significant role in the growth of pharmaceutical lipids. Lipid nanoparticles, for instance, are capable of encapsulating a wide range of compounds, including small molecules, nucleic acids, and peptides. These technical capabilities are increasingly utilized in oncology, immunology, and rare disease therapies. New lipid-based systems, such as solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers, offer improved protection for sensitive molecules and enable sustained or targeted release, making them ideal for modern drug delivery systems.
Key Takeaways
- The global pharmaceutical lipids market was projected to reach nearly US$ 7.1 billion by 2034, expanding from US$ 4.2 billion in 2024 at a 5.4% CAGR.
- Triglycerides were identified as the leading product category in 2024, accounting for over 43% of total pharmaceutical lipid demand across global applications.
- Plant-derived lipids were reported as the primary source segment in 2024, securing more than 44.1% of the overall market share.
- Liposomes emerged as the dominant delivery system in 2024, representing more than 31.3% of the global pharmaceutical lipids utilization.
- Parenteral administration was highlighted as the major route in 2024, capturing over 36.8% of the market due to widespread clinical adoption.
- Small-molecule drugs and vaccine delivery applications contributed the largest share in 2024, accounting for more than 38.2% of total usage.
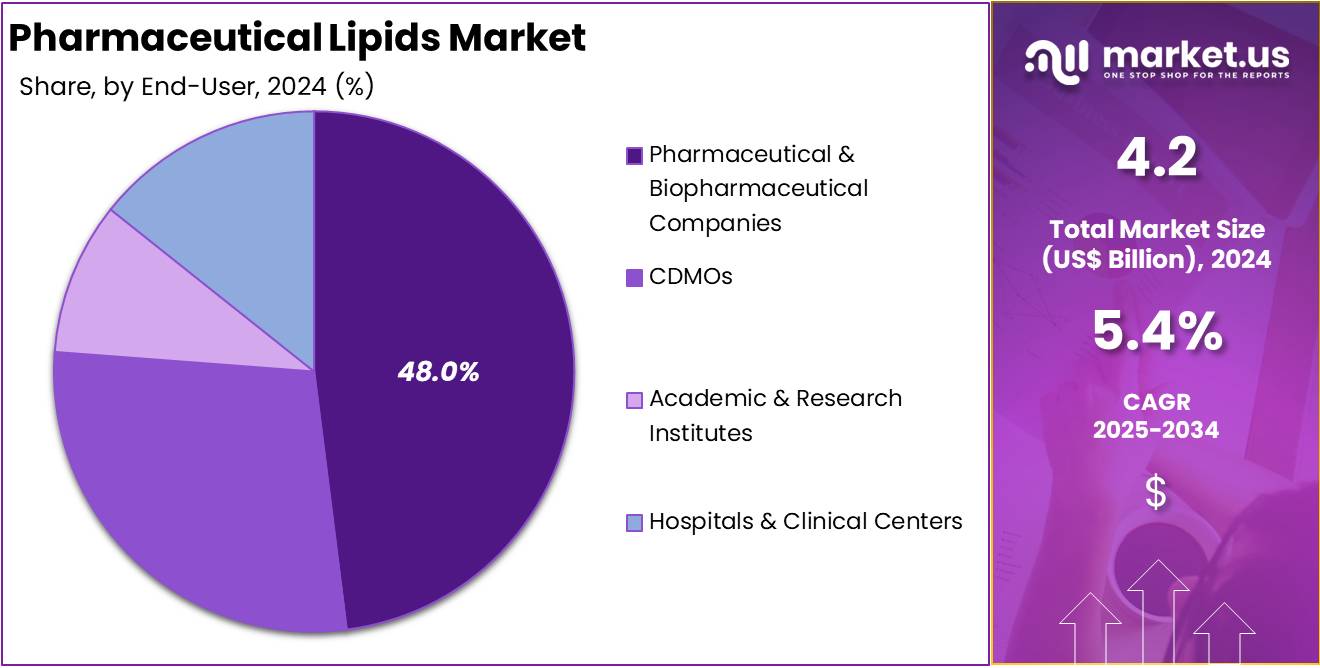
- Pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical companies were recognized as the principal end users in 2024, holding over 48% of the global market share.
- North America maintained the leading regional position in 2024, representing more than 33.5% of the market and generating approximately US$ 1.4 billion.
Product Analysis
In 2024, the Triglycerides held a dominant market position in the Product Segment of the Pharmaceutical Lipids Market, and captured more than a 43.0% share. This segment gained strength due to wide functional use in formulations. It supported better solubility and stability. Strong adoption in parenteral nutrition also increased demand. Its compatibility with key APIs encouraged steady uptake. The segment is expected to maintain leadership as lipid-based delivery systems continue to advance.
Phospholipids held a significant portion of the market as their role in liposomal delivery supported strong uptake. These ingredients improved targeted release and enhanced stability. Their use in vaccines and advanced therapies remained high. Sphingolipids recorded moderate demand due to their function in cell signaling. Interest grew in metabolic and neurological applications. Higher production costs limited wider use but research activity continued to expand. Their niche benefits supported cautious but steady market penetration.
Sterols maintained a modest share as they supported emulsion stability in many formulations. Their use as precursors in hormone and vitamin synthesis added further value. Fatty acids showed stable growth because they aided permeability and enhanced oral and topical performance. Omega-based formulations increased adoption. The Others category, including glycolipids and specialty compounds, met niche therapeutic needs. Research in personalized medicine encouraged gradual uptake and improved long-term prospects. These factors supported predictable and balanced segment expansion.
Source Analysis
In 2024, the Plant-derived held a dominant market position in the Source Segment of the Pharmaceutical Lipids Market, and captured more than a 44.1% share. Demand for natural excipients increased due to strong safety perceptions. Raw material availability also supported steady production. Consistent quality enhanced adoption in key formulations. Their use expanded in vaccines, biologics, and targeted delivery systems. Ongoing research on plant-based carriers strengthened market penetration. Growth was supported by rising interest in sustainable pharmaceutical ingredients.
Animal-derived lipids maintained a stable presence in the market. Their long-standing functional benefits supported continued use in complex formulations. These lipids showed strong biocompatibility, which improved their acceptance in injectable products. Growth was limited by regulatory concerns and strict sourcing requirements. Supply variability also created challenges for manufacturers. Despite such constraints, demand persisted in applications requiring specific lipid characteristics. Specialized formulations continued to rely on animal-based sources, keeping the segment relevant within controlled pharmaceutical environments.
Synthetic lipids recorded steady expansion driven by demand for high-purity materials. Their controlled structures supported predictable performance in advanced delivery systems. Adoption increased in nucleic acid therapies and mRNA-based platforms. Innovation in custom-engineered lipids improved efficiency across development pipelines. These lipids reduced variability and enhanced reproducibility in complex formulations. Wider use in gene therapies also strengthened segment outlook. Continuous advancements in synthetic design positioned this category for sustained growth in technologically intensive pharmaceutical segments.
Delivery System Analysis
In 2024, the Liposomes held a dominant market position in the Delivery System Segment of the Pharmaceutical Lipids Market. The segment captured more than a 31.3% share. Strong adoption was driven by rising use in oncology and vaccine delivery. Liposomes improved drug stability and reduced toxicity. Demand increased as scalable processes became more common. Advancements in lipid composition also supported wider uptake. The segment remained the preferred choice for complex therapeutic formulations across global markets.
Lipid Nanoparticles showed steady growth in 2024. Their adoption increased due to expanding nucleic acid therapies. Strong interest in RNA platforms supported this rise. LNPs enabled efficient intracellular delivery and improved stability. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles also advanced during the year. Their controlled-release benefits enhanced usage. SLNs offered high stability and suitable production methods. These features supported consistent demand. Their compatibility with diverse drug molecules enabled broader application in multiple therapeutic categories.
Nanostructured Lipid Carriers expanded rapidly in 2024. Their improved loading capacity strengthened adoption. NLCs delivered better release control than earlier lipid systems. Lipid Emulsions continued to record stable demand. Their use in clinical nutrition supported growth. Improved safety processes aided wider acceptance. Self-Emulsifying Systems also gained traction. These systems improved absorption for poorly soluble drugs. Their flexible design and simple production encouraged further development. Adoption increased as oral lipid-based delivery gained strategic importance.
Route of Administration Analysis
In 2024, the Parenteral segment held a dominant market position in the Route of Administration segment of the Pharmaceutical Lipids Market, and captured more than a 36.8% share. This leadership was supported by high use in injectable formulations. Lipid emulsions and liposomal carriers improved solubility and stability. Demand increased with the growth of biologics and mRNA technologies. Faster therapeutic action and precise delivery also strengthened adoption. The segment continued to benefit from strong clinical acceptance.
The oral segment registered a significant share and showed steady expansion. Growth was supported by lipid-based systems that improved absorption. Self-emulsifying technologies enhanced bioavailability for poorly soluble drugs. Demand increased across chronic therapy areas. The topical segment also expanded at a stable pace. Lipids enhanced skin penetration and moisture retention. Their use in creams, ointments, and transdermal systems rose steadily. Non-invasive delivery options further supported adoption across dermatology and cosmetic applications.
The inhalation segment recorded gradual growth in 2024. Lipid-based carriers improved pulmonary deposition and supported targeted delivery to the respiratory tract. Their use increased in asthma, COPD, and infectious disease treatments. Controlled absorption and improved stability supported wider clinical interest. The segment gained momentum with innovations in respiratory drug design. Overall, the market showed balanced progress across administration routes. However, parenteral formulations continued to lead due to advanced technologies and strong therapeutic demand.
Application Analysis
In 2024, the Small-Molecule Drugs & Vaccine Delivery held a dominant market position in the Application Segment of the Pharmaceutical Lipids Market and captured more than a 38.2% share. The segment grew due to strong adoption of lipid excipients in established formulations. Demand increased for stable delivery systems. Rising vaccine programs supported sustained use. Consistent improvements in lipid purity also enhanced performance. Broader clinical acceptance reinforced the segments leadership position.
The Biologics & Peptides segment showed strong participation in the market. Its growth was supported by wider use of lipids to improve stability and solubility. Demand rose for formulations that protect sensitive peptide structures. The segment gained momentum due to increasing development of targeted therapies. Nucleic-acid therapies also expanded. Rapid progress in RNA and DNA platforms strengthened adoption. Lipid nanoparticles improved delivery efficiency and supported broader clinical pipelines across emerging therapeutic areas.
The Parenteral Nutrition segment recorded stable advancement in the market. Its growth was linked to rising demand for safe lipid emulsions in critical care settings. Higher incidence of malnutrition and metabolic disorders increased product use. Continuous improvements in formulation quality supported clinical outcomes. Broader adoption across hospitals strengthened uptake. Pharmaceutical lipids maintained essential roles in energy delivery. Their diverse applications reinforced overall market expansion and ensured sustained interest from therapy developers worldwide.
End-User Analysis
In 2024, the Pharmaceutical & Biopharmaceutical Companies held a dominant market position in the End-User Segment of the Pharmaceutical Lipids Market, and captured more than a 48.0% share. This segment showed strong demand for lipid excipients. Growth was driven by expanding biologics pipelines. Companies used high-purity lipids in vaccines and targeted therapies. Rising adoption of lipid nanoparticles supported new drug platforms. Continuous R&D spending reinforced the leadership of the segment.
CDMOs recorded stable growth as outsourcing increased. Their capabilities in complex formulation and scale-up supported wider use of pharmaceutical lipids. Many organizations upgraded facilities to handle sterile lipid processing. Academic and research institutes also advanced lipid innovation. Their work focused on nanoparticles, liposomes, and emerging delivery systems. Public funding supported collaborative studies. These developments strengthened early-stage research and accelerated the adoption of novel lipid technologies. This momentum enhanced translational outcomes in drug development.
Hospitals and clinical centers held a smaller share but showed steady usage. Demand was driven by parenteral nutrition and lipid-based injectables. Clinical trials increased the consumption of lipid formulations. Adoption remained stable due to established treatment protocols. The broader end-user landscape reflected diverse applications. Pharmaceutical companies led growth, while CDMOs and research institutes supported development. Their combined activity sustained market expansion and strengthened long-term opportunities within lipid-based therapeutic platforms today.
Key Market Segments
By Product
- Triglycerides
- Phospholipids
- Sphingolipids
- Sterols
- Fatty Acids
- Others
By Source
- Plant-derived
- Animal-derived
- Synthetic
By Delivery System
- Liposomes
- Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs)
- Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN)
- Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC)
- Lipid Emulsions
- Self-Emulsifying Systems (SEDDS/SMEDDS)
By Route of Administration
- Parenteral
- Oral
- Topical
- Inhalation
By Application
- Small-Molecule Drugs & Vaccine Delivery
- Biologics & Peptides
- Nucleic-Acid Therapies
- Parenteral Nutrition
By End-User
- Pharmaceutical & Biopharmaceutical Companies
- CDMOs
- Academic & Research Institutes
- Hospitals & Clinical Centers
Drivers
High Share of Poorly Water-Soluble Drug Candidates Requiring Lipid-Based Delivery
The expansion of poorly water-soluble drug candidates has been identified as a major catalyst for the pharmaceutical lipids market. A rising share of new molecules demonstrates limited solubility in gastrointestinal fluids. This trend has increased the need for advanced formulation systems. As a result, demand for lipids as functional excipients has grown steadily. Their use has become essential for improving dissolution and absorption. The growth of the market can be attributed to the strategic shift toward lipid-based delivery to support successful product development.
Formulation challenges linked to poor solubility have reinforced the importance of triglycerides, phospholipids, fatty acid esters, and ionizable lipids. These excipients support enhanced bioavailability and consistent therapeutic exposure. Consequently, the market is being propelled by the continuous introduction of complex APIs. The rising formulation complexity has encouraged wider adoption of lipid-based systems. This driver is expected to remain strong as more innovative molecules enter development pipelines. Thus, pharmaceutical lipids are positioned as critical enablers of oral delivery performance.
According to Liebert Publications, nearly 70% of new drug candidates show poor solubility in gastrointestinal fluids. This issue directly limits oral bioavailability and overall clinical success. Study by MDPI further reports that only about 8% of novel drug candidates possess both adequate solubility and permeability. For instance, developers are increasingly turning to lipid systems to overcome these limitations. These statistics highlight the scale of solubility-related barriers and their role in driving demand for lipid-based formulation technologies.
For example, evidence presented in PubMed Central shows that lipid-based excipients and lipid-based drug delivery systems offer reliable tools for improving solubility and bioavailability. These systems are frequently applied in oral and capsule formulations to support efficient absorption. Research indicates that such approaches are particularly effective for modern, hydrophobic molecules. The increasing reliance on these excipients illustrates their strategic significance. As a result, sustained investment in pharmaceutical lipids is being supported by the expanding pipeline of poorly soluble active pharmaceutical ingredients.
Restraints
Complex Manufacturing and Regulatory Requirements for Liposomal and LNP-Based Pharmaceutical Lipids
The development of pharmaceutical lipids used in liposomal and lipid nanoparticle systems is being limited by complex technical and regulatory demands. These formulations require precise control of their structural and functional attributes. This increases development risk. Smaller manufacturers face higher entry barriers due to the sophisticated processes involved. The restraint is strengthened by the need for advanced characterization tools. These tools demand specialized skills and greater investment. As a result, significant delays occur in early-stage development, which raises overall project uncertainty.
Extensive quality characterization is required to ensure consistent performance of liposomal medicines. Parameters such as particle size, surface charge, lamellarity, and drug encapsulation must be measured with accuracy. These activities increase analytical burden and operational cost. According to regulatory frameworks, strict adherence to defined specifications is mandatory to achieve product approval. This creates pressure on companies to upgrade manufacturing infrastructure. Additional validation steps extend timelines. The overall impact is a slower development pathway for complex lipid-based dosage forms.
Advanced scientific expectations further intensify this restraint. According to PubMed Central, current reviews highlight that a Quality-by-Design approach has become standard for liposomal nano-pharmaceuticals. Study by multiple research groups indicates that systematic risk assessment and design-space evaluation are now integral parts of development. These requirements expand experimental workload. For example, formulation teams must evaluate each lipid component under varied process conditions. This significantly increases resource consumption and elevates production costs for pharmaceutical lipid-based systems.
The regulatory landscape reinforces these challenges by mandating high-resolution analytical methods and robust process documentation. For instance, the European Medicines Agency requires detailed evaluation of critical quality attributes using sophisticated instrumentation. These obligations demand skilled personnel and continuous process monitoring. As a result, operational complexity rises. Smaller firms struggle to meet these expectations due to limited budgets and technology access. The heightened regulatory burden therefore acts as a major restraint, reducing market participation and slowing innovation in pharmaceutical lipids.
Opportunities
Expansion of Pharmaceutical Lipids Driven by Growth in mRNA and RNA-Based Therapeutics
The opportunity for pharmaceutical lipids is expanding as the adoption of RNA-based modalities continues to rise. The advancement of mRNA and broader RNA therapeutics has increased the demand for high-performance delivery systems. Growth in clinical programs indicates that specialized lipids such as ionizable lipids, PEGylated lipids, phospholipids and high-purity cholesterol will remain essential. These components are considered critical for effective formulation, and the sustained expansion of RNA pipelines is expected to support long-term market demand for advanced lipid excipients.
The accelerating number of therapeutic candidates illustrates how delivery technologies are becoming a strategic priority. A 2025 mapping of the field identified more than 70 mRNA therapeutic programs in development. This expansion signals that lipid innovation will remain necessary to optimize stability, potency and manufacturability. The market outlook is strengthened by continuous investment in infectious diseases, oncology and rare disease pipelines, where delivery efficiency is viewed as a major determinant of clinical success.
Further momentum originates from vaccine development trends. The global vaccine R&D landscape, about 280 mRNA vaccine candidates were in progress by December 2024. Approximately 55% were at the preclinical stage and around 45% had entered clinical phases. This shift toward advanced formats suggests rising reliance on lipid-enabled delivery platforms. The growing clinical pipeline demonstrates sustained industrial commitment, creating favourable conditions for suppliers of pharmaceutical lipids.
Scientific literature reinforces the importance of lipids as foundational materials for RNA delivery. A study by PubMed Central reported that a large proportion of mRNA vaccines in clinical trials use lipid-based carriers such as liposomes and LNPs. These systems protect fragile RNA molecules and enhance cellular uptake. For example, LNP formulations were instrumental in enabling the first approved mRNA vaccines. This evidence highlights how pharmaceutical lipids occupy a central role in formulation science, supporting continuous opportunities as RNA technology progresses.
Trends
Advancements in Nanotechnology-Driven Lipid Systems and Strengthening Regulatory Oversight in Pharmaceutical Lipids
The pharmaceutical lipids market is experiencing a clear shift toward advanced nanotechnology-enabled systems. This movement is driven by the need for more efficient drug delivery platforms. The trend is supported by rising demand for lipid carriers that improve stability, targeting, and therapeutic performance. Growth is being reinforced by the expanding use of lipids in complex biologics and precision therapies. As a result, higher-value functional lipids are gaining strategic importance across multiple therapeutic classes.
A strong emphasis on nanomedicine has become visible as companies adopt liposomes, lipid nanoparticles, and other nanoscale systems. These platforms enhance bioavailability and therapeutic precision. According to recent scientific assessments, solid lipid nanoparticles, nanostructured lipid carriers, SMEDDS, and oral lipid formats now form an integrated technological landscape. Applications are expanding beyond conventional small molecules. The market is being shaped by the need for lipids that support safe and effective delivery of nucleic acids, peptides, and emerging biologic modalities.
A regulatory pull effect is also influencing market development. A horizon scanning study by the EMA and EU-Innovation Network, first released in February 2025 and updated in November 2025, emphasized the growing strategic importance of nano-enabled drug products. Continuous updates indicate sustained regulatory attention. For instance, oncology and infectious disease therapies were identified as major focus areas. This regulatory visibility is contributing to stronger quality expectations and more structured evaluation pathways for nanotechnology-based lipid systems.
Research progress is reinforcing the demand for next-generation lipid architectures. Study by multiple research groups has highlighted innovations that improve endosomal escape, cellular targeting, and overall safety. For example, newly proposed LNP design strategies aim to enhance therapeutic payload delivery while reducing toxicity. These advances point to a future in which pharmaceutical lipids function as engineered components rather than commodity excipients. This shift is positioning technologically advanced lipids as essential inputs for the expanding nanomedicine ecosystem.
Regional Analysis
In 2024, North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 33.5% share and holds US$ 1.4 Billion market value for the year. The region benefited from strong demand for advanced formulations. Steady growth in lipid-based drug delivery supported wider adoption. Rising focus on high-purity excipients strengthened its leadership. The presence of specialized manufacturing sites enhanced production efficiency. Increasing clinical activities also drove consistent uptake across major therapeutic segments.
Regional growth was supported by strong research activity. Continuous development in lipid nanoparticles improved application potential. Expanded use in oncology and metabolic disorders stimulated higher demand. The region maintained strict quality standards, which encouraged the use of premium lipid excipients. Advanced healthcare systems ensured smooth adoption of new technologies. Stable regulatory procedures increased confidence among developers. These factors contributed to sustained usage of lipid-enabled platforms across both early-stage and commercial drug programs.
North America’s dominance was influenced by strong collaboration between industry and research institutes. Rapid advances in mRNA therapies increased the need for specialized lipid components. Contract manufacturers added capacity to support complex formulations. Skilled technical expertise improved scale-up processes. Personalized treatments also encouraged the adoption of high-performance lipid systems. Supportive reimbursement policies strengthened product uptake. These conditions created a favorable environment that reinforced the region’s position in the pharmaceutical lipids market.
Future outlook for North America remained positive. Continuous innovation in lipid nanoparticle systems is expected to drive further expansion. More clinical trials will likely increase the use of lipid-based delivery platforms. The region’s robust regulatory environment will support safe integration of new technologies. Expanding investment in biotechnology is projected to stimulate ongoing product development. These factors suggest that North America will continue to hold a strong and influential role in the pharmaceutical lipids landscape.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherland
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- New Zealand
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
The pharmaceutical lipids market is shaped by suppliers that deliver high-purity excipients and advanced delivery components. Strong capabilities in GMP manufacturing and phospholipid chemistry support consistent adoption across injectable and oral formulations. Companies such as Lipoid GmbH and Gattefossé strengthen the market through expertise in natural phospholipids and lipid-based bioavailability enhancers. Their portfolios are used in liposomes, emulsions, and complex formulations. Growth has been supported by rising demand for safe, stable, and high-performance lipids in innovative drug delivery systems.
A significant share of market development has been driven by firms specializing in advanced and synthetic lipids. Players including Croda Pharma, Evonik Health Care, and Seqens support the expansion of nucleic acid delivery systems through ionizable, PEGylated, and custom lipids. These companies maintain strong GMP capabilities and invest in high-capacity plants. Their technologies are used in lipid nanoparticles and vaccines. The market benefits from their rigorous quality standards and sustained focus on enabling next-generation therapeutic platforms.
The competitive environment is further shaped by manufacturers that act as integrated partners for complex lipid programs. Organizations such as CordenPharma International GmbH maintain capabilities in custom lipid development, LNP formulation, and large-scale production. Their activities support mRNA platforms, gene therapies, and sterile applications. These competencies ensure high reliability of supply. Growth in advanced therapeutics has increased demand for their expertise. Their strong regulatory compliance and global manufacturing networks reinforce their strategic position within the market.
Additional contributors play important roles across research, specialty excipients, and structured lipids. Companies such as BASF SE, Seppic, ABITEC Corporation, Nippon Fine Chemical, and DuPont de Nemours Inc. supply lipid excipients for oral, topical, and parenteral formulations. Others, including Creative Biolabs, Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc., Precision NanoSystems, and VAV Life Sciences, support early-stage programs and formulation development. Their diverse portfolios strengthen supply resilience. Continued innovation in lipid chemistry and delivery systems is expected to support overall market expansion.
Market Key Players
- Lipoid GmbH
- Croda Pharma
- Evonik Health Care
- CordenPharma International GmbH
- Seqens
- VAV Life Sciences
- Gattefossé
- BASF SE
- Seppic
- Merck KGaA
- ABITEC Corporation
- Nippon Fine Chemical
- DuPont de Nemours Inc.
- Creative Biolabs
- Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc.
- Precision NanoSystems
Recent Developments
- In July 2024: Croda reports newly-launched proprietary lipid-based adjuvants (sampled into ~80 projects) and highlights its 2,000+ lipid/polymer portfolio for nucleic-acid delivery. In its H1/2024 results commentary Croda set out that its Life Sciences / Nucleic Acid Delivery business now offers a large portfolio of >2,000 lipids/polymers and that its newly launched proprietary lipid-based adjuvants had been sampled into about 80 customer projects — signalling commercial traction for its pharma lipid products and adjuvant supply chain.
- In Feb 2024: Launch of CordenPharma LNP “Starter Kits” (product launch for pharmaceutical lipids): CordenPharma launched LNP Starter Kits containing four key lipid types (ionizable lipid, helper/sterol, PEGylated lipid and other helper lipids) to help developers formulate and test lipid-nanoparticle (LNP) systems for mRNA and gene-therapy payloads — a product announcement dated 28 Feb 2024. The company also reported completing expansions of its GMP LNP manufacturing capability (Caponago, IT) around the same period.
- In Mar 2023: Evonik opens a new GMP “lipid launch” facility at Hanau (Germany) for clinical/small-scale commercial lipid supply.
Evonik opened a cGMP lipid launch facility at its Hanau site to supply customers with clinical and small-scale commercial quantities of pharmaceutical lipids (supporting development through launch). The Hanau facility complements Evonik’s lab and commercial production capabilities and targets lipid excipients and LNP building blocks used in mRNA/gene-delivery formulations.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) US$ 4.2 Billion Forecast Revenue (2034) US$ 7.1 Billion CAGR (2025-2034) 5.4% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, COVID-19 Impact, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Product (Triglycerides, Phospholipids, Sphingolipids, Sterols, Fatty Acids, Others), By Source (Plant-derived, Animal-derived, Synthetic), By Delivery System (Liposomes, Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs), Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN), Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC), Lipid Emulsions, Self-Emulsifying Systems (SEDDS/SMEDDS)), By Route of Administration (Parenteral, Oral, Topical, Inhalation), By Application (Small-Molecule Drugs & Vaccine Delivery, Biologics & Peptides, Nucleic-Acid Therapies, Parenteral Nutrition), By End-User (Pharmaceutical & Biopharmaceutical Companies, CDMOs, Academic & Research Institutes, Hospitals & Clinical Centers) Regional Analysis North America – The US, Canada, & Mexico; Western Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Portugal, Ireland, Austria, Switzerland, Benelux, Nordic, & Rest of Western Europe; Eastern Europe – Russia, Poland, The Czech Republic, Greece, & Rest of Eastern Europe; APAC – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia & New Zealand, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, & Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Colombia, Chile, Argentina, Costa Rica, & Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – Algeria, Egypt, Israel, Kuwait, Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, & Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Lipoid GmbH, Croda Pharma, Evonik Health Care, CordenPharma International GmbH, Seqens, VAV Life Sciences, Gattefossé, BASF SE, Seppic, Merck KGaA, ABITEC Corporation, Nippon Fine Chemical, DuPont de Nemours Inc., Creative Biolabs, Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc., Precision NanoSystems Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Pharmaceutical Lipids MarketPublished date: Nov 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Pharmaceutical Lipids MarketPublished date: Nov 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Lipoid GmbH
- Croda Pharma
- Evonik Health Care
- CordenPharma International GmbH
- Seqens
- VAV Life Sciences
- Gattefossé
- BASF SE
- Seppic
- Merck KGaA
- ABITEC Corporation
- Nippon Fine Chemical
- DuPont de Nemours Inc.
- Creative Biolabs
- Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc.
- Precision NanoSystems










