Global Off-Grid Remote Sensing Power System Market Size, Share Analysis Report By Type (Natural Gas, Fuel Cell, Solar Energy), By Application (Oil and Gas Industry, Weather Monitoring Stations, Wind Power Industry, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Jan 2026
- Report ID: 173484
- Number of Pages: 371
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
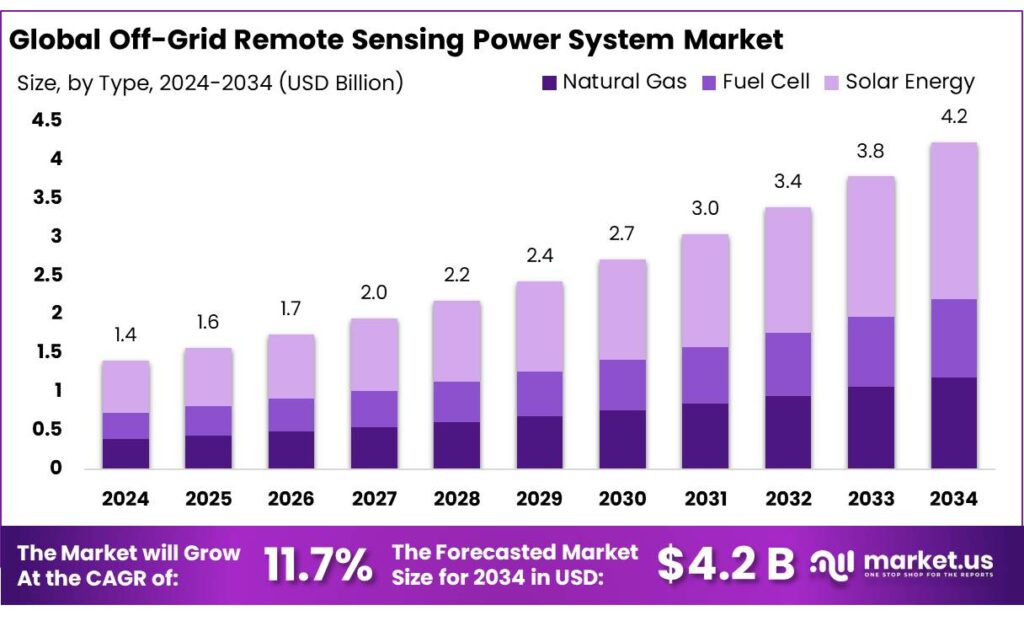
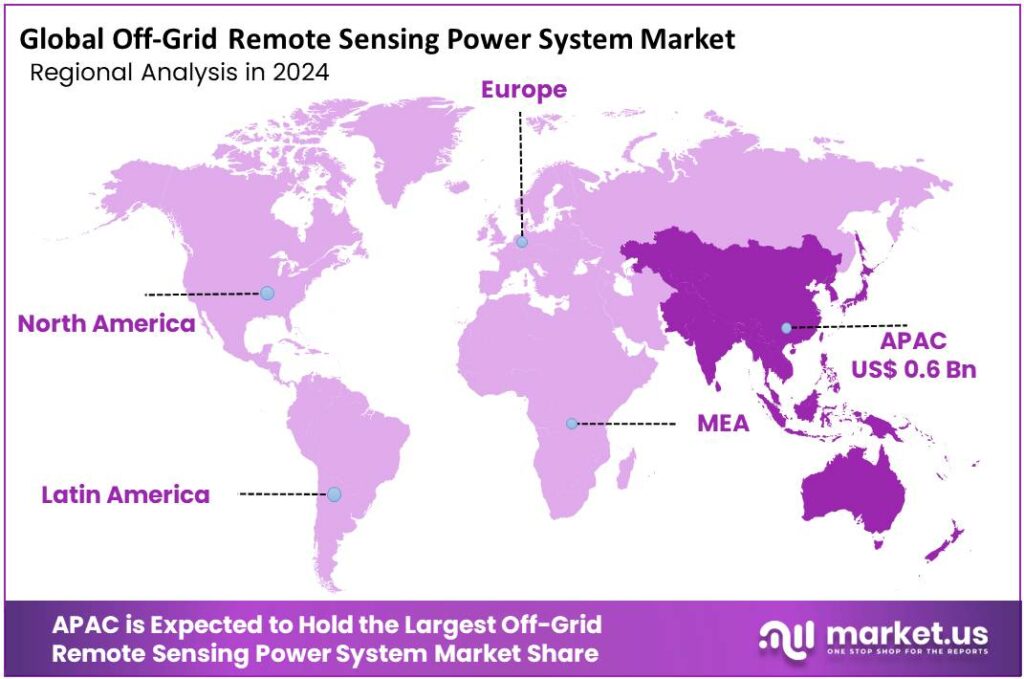
Global Off-Grid Remote Sensing Power System Market size is expected to be worth around USD 4.2 Billion by 2034, from USD 1.4 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 11.7% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024 Asia-Pacific held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 3.6% share, holding USD 0.6 Billion in revenue.
Off-grid remote sensing power systems are purpose-built energy packages that keep sensors, data loggers, gateways, and communication links running where grid power is unavailable or unreliable. In food and agriculture value chains, they typically support weather stations, soil and irrigation sensors, cold-room telemetry, livestock tracking, and storage monitoring. This matters because global food loss remains material—FAO estimates 13.3% of food is lost after harvest and before retail (latest estimate for 2023)—so better measurement and control at “last-mile” nodes is increasingly treated as an operational necessity, not a pilot project.
Industrial deployment is shifting from “single sensor + small panel” setups toward integrated edge power platforms: solar PV plus batteries, efficient charge controllers, low-power compute, and resilient connectivity. The industrial scenario is reinforced by broader electrification and cooling gaps. The IEA estimates around 750 million people still lacked access to electricity in 2023, concentrating demand for autonomous power solutions that can be installed quickly and maintained remotely. In parallel, SEforALL reports 1.2 billion people lack adequate access to cooling, a constraint that directly affects safe food storage and temperature-controlled logistics in hot regions.
Key driving factors cluster around reliability, cost of site visits, and the need to digitize perishable supply chains. Solar-first architectures are benefiting from the momentum of global PV scale-up: the IEA notes solar PV generation rose by 320 TWh in 2023, expanding the ecosystem of components and installers that off-grid system integrators depend on. The data layer is also expanding fast: GSMA Intelligence forecasts 38.7 billion IoT connections by 2030, which implies continued growth in distributed sensors that must be powered at the edge.
Government and trusted multilateral initiatives are strengthening the long-term industrial scenario. The EU’s space and Earth-observation infrastructure provides a public “data backbone” for remote sensing services; Copernicus sits within an EU Space Programme budget of €14.88 billion for 2021–2027. On the food-security side, the SOFI partners report around 733 million people faced hunger in 2023, underscoring the policy imperative for better monitoring, targeted support, and climate-risk management. Humanitarian logistics also signal scale: WFP reports it reached over 124 million people in 2024 and cites a need of US$13 billion to reach vulnerable populations, reinforcing why remote monitoring of routes, storage points, and local conditions matters in austere settings.
Key Takeaways
- Off-Grid Remote Sensing Power System Market size is expected to be worth around USD 4.2 Billion by 2034, from USD 1.4 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 11.7%.
- Solar Energy held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 48.2% share.
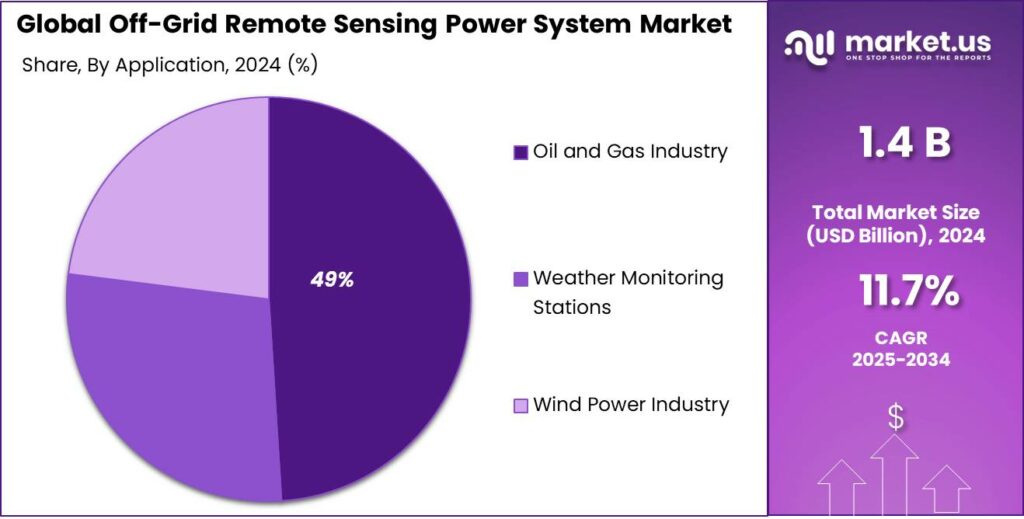
- Oil and Gas Industry held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 49.8% share.
- Asia-Pacific (APAC) region emerged as a dominant force in the off-grid remote sensing power system market, capturing around 43.6% of the global share and contributing an estimated USD 0.6 billion.
By Type Analysis
Solar Energy leads with 48.2% share due to its reliability and ease of use in remote locations.
In 2024, Solar Energy held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 48.2% share in the off-grid remote sensing power system market, mainly because it offers stable power without fuel dependency. Solar-based systems are widely used in remote sensing stations, weather monitoring units, border surveillance, and environmental data collection, where grid access is limited or unavailable. The dominance of this segment can be attributed to falling solar panel costs, improved energy storage integration, and low maintenance needs.
In 2025, adoption is expected to remain strong as governments and infrastructure agencies continue to favor clean and long-life power solutions for remote operations. Solar energy also performs well in harsh and isolated environments, ensuring uninterrupted data transmission and system uptime. Its ability to operate independently for long periods makes it a preferred choice for critical sensing applications, supporting steady growth of this segment without reliance on conventional power sources.
By Application Analysis
Oil and Gas Industry dominates with 49.8% share driven by critical monitoring needs in remote fields.
In 2024, Oil and Gas Industry held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 49.8% share in the off-grid remote sensing power system market, largely due to the high demand for continuous monitoring in isolated drilling and pipeline locations. Remote sensing systems are widely deployed across upstream and midstream operations to support leak detection, pressure monitoring, seismic activity tracking, and equipment health assessment. These sites often operate far from grid infrastructure, making off-grid power systems essential for reliable data collection.
In 2025, usage is expected to remain strong as energy operators focus on safety compliance, environmental monitoring, and operational efficiency. The ability of off-grid systems to deliver stable power in extreme climates, including deserts and offshore zones, further strengthens adoption. As exploration activities continue in hard-to-reach areas, the oil and gas sector is expected to retain its leading position, supported by the need for uninterrupted sensing and real-time data transmission.
Key Market Segments
By Type
- Natural Gas
- Fuel Cell
- Solar Energy
By Application
- Oil and Gas Industry
- Weather Monitoring Stations
- Wind Power Industry
- Others
Emerging Trends
Hybrid solar + satellite IoT sensing for food supply chains
One clear latest trend in off-grid remote sensing power systems is the move toward always-on monitoring that works beyond cellular coverage—especially for food production, storage, and humanitarian supply routes. Instead of building systems around a single network, more deployments now pair small solar PV + battery storage with low-power sensors and a hybrid communications layer. The pressure behind this is measurable—UNEP estimates 1.05 billion tonnes of food were wasted in 2022, about 19% of food available to consumers.
The power design itself is also changing. The newest trend is not “bigger panels,” but smarter energy budgeting: ultra-low-power electronics, duty-cycling, and edge processing that reduces how often a device transmits. That matters in agriculture, where sensing is closely tied to water decisions. FAO and UNESCO both highlight that agriculture accounts for roughly 70% of global freshwater withdrawals, which makes reliable field data a practical lever for water stewardship.
Food-loss prevention is shaping the monitoring targets, not just the technology. FAO notes that over 13% of food is lost in the supply chain before it reaches retail, and this loss is valued at over USD 400 billion annually in its latest estimates. Government and trusted public initiatives are reinforcing this direction by making Earth-observation and food-risk monitoring more operational. In Europe, Copernicus sits within the EU Space Programme, with a total budget of €14.88 billion for 2021–2027.
Drivers
Reliable Power for Food-System Monitoring in Remote Areas
One major driving factor for Off-Grid Remote Sensing Power Systems is the growing need to monitor food production, storage, and natural resources in places where grid electricity is weak or completely unavailable. Large parts of global agriculture still operate far from reliable power infrastructure. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), agriculture accounts for nearly 70% of global freshwater withdrawals, making it the single largest user of water worldwide.
Another strong push comes from the need to reduce food loss and waste across supply chains. The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) reported that 1.05 billion tonnes of food were wasted globally in 2022, representing about 19% of food available to consumers. A large share of these losses occurs in rural storage points, cold rooms, and transport corridors where electricity is unreliable.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) estimates that around 730 million people worldwide still lacked access to electricity in 2024, with a large share living in rural, agriculture-dependent regions. In these areas, extending grid power to every sensor location is economically unrealistic. As a result, food producers, cooperatives, and government agencies increasingly deploy self-powered sensing units using small solar panels and batteries. These systems reduce fuel use, avoid diesel generators, and allow long-term data collection with minimal maintenance.
Government and public-sector initiatives also reinforce this driver by promoting data-driven agriculture and climate resilience. The European Union’s Copernicus Programme supports satellite-based monitoring of crops, drought, and soil conditions under its space programme budget of €14.88 billion for 2021–2027. While satellites provide large-area insights, they depend on ground sensors for validation and local accuracy.
Restraints
High Upfront Cost and Maintenance Burden in Remote Food Zones
One major restraining factor for Off-Grid Remote Sensing Power Systems is the high upfront cost combined with ongoing maintenance challenges, especially in food-producing regions with limited financial and technical capacity. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), more than 80% of the world’s farms are smallholder operations, many operating on thin margins and limited access to credit.
Battery-related costs and reliability issues further restrict system scalability. Off-grid sensing systems rely heavily on energy storage to operate during nights, cloudy periods, or extreme weather. The International Energy Agency (IEA) notes that battery pack prices fell to around USD 139 per kWh in 2023, but replacement cycles in harsh outdoor environments remain short due to heat, dust, and humidity. In remote agricultural zones, batteries often need replacement every 3–5 years, adding recurring costs and logistical complexity.
Maintenance access is another practical constraint that slows adoption. Many off-grid sensing installations are located in fields, fisheries, forests, or rural cold-storage hubs that are difficult to reach. The World Bank estimates that nearly 2 billion people live in fragile or remote settings with weak infrastructure, where transport and technical services are inconsistent. In such areas, even simple issues like dust-covered solar panels, loose wiring, or sensor calibration errors can interrupt data flow for weeks.
Opportunity
Climate-Smart Irrigation and Water Stewardship at Scale
A major growth opportunity for Off-Grid Remote Sensing Power Systems is the fast-rising need for climate-smart irrigation and water management across remote farms and food-producing landscapes. Agriculture is still the world’s biggest water user, and that reality is pushing governments, food agencies, and agribusinesses to measure water use more closely. FAO states that agriculture accounts for about 70% of freshwater withdrawals worldwide, which means even small improvements in irrigation timing and field-level decisions can have an outsized impact.
This opportunity becomes even clearer in lower-income and rural regions where agriculture is the backbone of livelihoods, but power infrastructure is thin. The World Bank highlights that in low-income countries, water use in agriculture can reach 90% of all water withdrawals, reflecting just how tightly food production is tied to water access and water efficiency.
Food security pressure adds urgency, and it widens the addressable use cases beyond irrigation alone. The SOFI 2024 release notes that around 733 million people faced hunger in 2023—a reminder that better on-ground monitoring is not just a productivity play, but also a resilience and risk-management tool. When drought stress, delayed rains, or heatwaves hit, agencies and producers need timely field signals.
Government-backed Earth-observation and digital public infrastructure further strengthen this opportunity by making remote sensing more mainstream and easier to integrate. The European Commission lists a total EU Space Programme budget of €14.88 billion for 2021–2027, which includes Copernicus—one of the world’s largest sources of open Earth-observation data. Satellite insights are powerful, but they become more actionable when paired with reliable ground sensors that validate conditions on farms, canals, and watersheds.
Regional Insights
Asia-Pacific leads the Off-Grid Remote Sensing Power System Market with 43.60% share and approximately USD 0.6 Bn revenue by 2025, supported by rapid deployment of renewable-powered sensing solutions
In 2024–2025, the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region emerged as a dominant force in the off-grid remote sensing power system market, capturing around 43.6% of the global share and contributing an estimated USD 0.6 billion in revenue by 2025. This strong regional performance was largely driven by escalating investments in renewable energy infrastructure, government initiatives promoting rural electrification, and rising technological demand for robust sensing systems in agriculture, environmental monitoring, and infrastructure projects.
Countries such as China and India led adoption, where off-grid solutions powered by solar and hybrid systems support remote weather stations, wildlife monitoring, and smart agriculture deployments in areas beyond grid reach. According to broader market insights, APAC has been one of the fastest-growing regional markets for off-grid sensing power systems, bolstered by ongoing renewable energy expansion and digital transformation efforts across Southeast Asia and Oceania.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Siemens AG, a global engineering leader, supports off‑grid remote sensing power systems through its Smart Infrastructure and energy management solutions that ensure reliable power for remote monitoring and sensing sites. In 2024, the company reported €75.93 billion in revenue and sustained strong investments in renewable and hybrid power technologies relevant to off‑grid sensing systems.
Enphase Energy specialises in integrated solar and storage systems well suited for off‑grid remote sensing sites, using microinverter and energy storage technologies to ensure stable power independent of the grid. In 2024, the company continued to expand its customer base with advanced IQ System Controllers and modular battery systems, supporting widespread off‑grid adoption and positioning for further growth through 2025 as demand for reliable, renewable power systems rises.
ABB Ltd. works on off‑grid power conversion and hybrid energy solutions that support remote sensing systems with dependable energy delivery. In 2024, ABB advanced its renewable power electronics and storage technologies, with strategic moves such as acquiring Gamesa Electric’s power electronics business expected to close by 2025, enhancing its capabilities in power conversion for remote and hybrid solar applications.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Siemens AG
- Schneider Electric
- General Electric
- ABB Ltd.
- Enphase Energy
- SunPower Corporation
- Canadian Solar Inc.
- Tesla, Inc.
Recent Industry Developments
In 2025, Siemens continued growth with group revenue increasing to €78.9 billion, reflecting expansion of smart energy solutions that include hybrid microgrid and automation technologies capable of supporting autonomous power supplies in remote sensing installations.
In 2024, Schneider Electric posted €38.15 billion in annual revenue, with its energy management business showing strong growth and advanced solutions that support distributed and off‑grid power systems.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 1.4 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 4.2 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 11.7% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Type (Natural Gas, Fuel Cell, Solar Energy), By Application (Oil and Gas Industry, Weather Monitoring Stations, Wind Power Industry, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Siemens AG, Schneider Electric, General Electric, ABB Ltd., Enphase Energy, SunPower Corporation, Canadian Solar Inc., Tesla, Inc. Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Off-Grid Remote Sensing Power System MarketPublished date: Jan 2026add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Off-Grid Remote Sensing Power System MarketPublished date: Jan 2026add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Siemens AG
- Schneider Electric
- General Electric
- ABB Ltd.
- Enphase Energy
- SunPower Corporation
- Canadian Solar Inc.
- Tesla, Inc.










