Global Nickel Cobalt Manganese (NCM) Market By Product Type (NMC333 (33% Nickel, 33% Manganese, 33% Cobalt), NMC622 (60% Nickel, 20% Manganese, 20% Cobalt), NMC955 (90% Nickel, 5% Manganese, 5% Cobalt), Others, By End Use (Consumer Electronics, Automotive, Aerospace, Marine, Medical, Power, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Feb 2026
- Report ID: 177667
- Number of Pages: 223
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
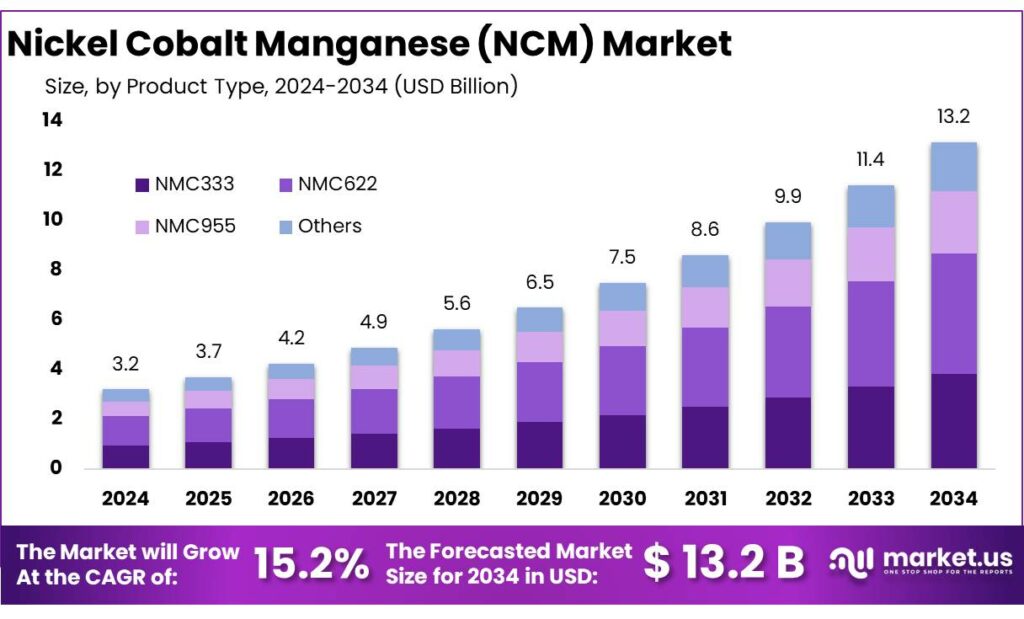
The Global Nickel Cobalt Manganese (NCM) Market is expected to be worth around USD 13.2 Billion by 2034, up from USD 3.2 Billion in 2024, and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 15.2% from 2025 to 2034. The North America segment maintained 49.6%, supporting a Psychedelic Mushrooms value of USD 1.5 Bn.
Nickel Cobalt Manganese (NCM) is a family of lithium-ion cathode chemistries used where manufacturers need high energy density, strong performance in cold weather, and longer driving range. Industrially, the NCM value chain links mining and refining of nickel, cobalt, and manganese, precursor and cathode active material (CAM) production, and cell manufacturing and battery pack assembly for EVs and stationary storage. Demand is ultimately anchored to electrification: the International Energy Agency notes that battery demand for the energy sector reached 1 TWh in 2024, with EV batteries alone rising to over 950 GWh in 2024.
The industrial scenario is characterized by fast capacity build-out but uneven geography. China remains central to cathode manufacturing and is described by the IEA as hosting more than three-quarters of installed NMC and other nickel-based chemistry capacity, shaping global pricing and technology diffusion. At the upstream level, supply is large but exposed to policy and operational shocks: USGS estimates global nickel mine production at ~3.7 million tons in 2024, while global cobalt mine production totaled ~290,000 tons in 2024. For manganese USGS reports world manganese mine production at ~20,000 thousand tons in 2024.
Key demand drivers include EV scale-up, cost declines, and supply-chain localization. BloombergNEF reported lithium-ion battery pack prices falling 20% in 2024 to $115/kWh, improving EV affordability and supporting higher-spec packs where NCM competes on range. On materials pull-through, the IEA quantified 2023 battery demand for critical metals at ~370 kt nickel, ~150 kt cobalt, and ~140 kt lithium, underscoring why NCM supply security is now treated as strategic industrial policy.
Government initiatives are increasingly shaping where NCM supply chains locate. The EU’s Critical Raw Materials Act sets 2030 benchmarks of 10% extraction, 40% processing, and 25% recycling within the EU, and limits dependence on any single third country to 65% for each strategic material at a relevant processing stage. In the United States, Treasury guidance for the EV clean-vehicle credit increases the “critical minerals” qualifying threshold to 60% (2025), 70% (2026), and 80% (from 2027)—incentivizing non-China sourcing and regional refining/cathode investment.
Key Takeaways
- Nickel Cobalt Manganese (NCM) Market is expected to be worth around USD 13.2 Billion by 2034, up from USD 3.2 Billion in 2024, and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 15.2%.
- NMC622 (60% Nickel, 20% Manganese, 20% Cobalt) held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 37.5% share.
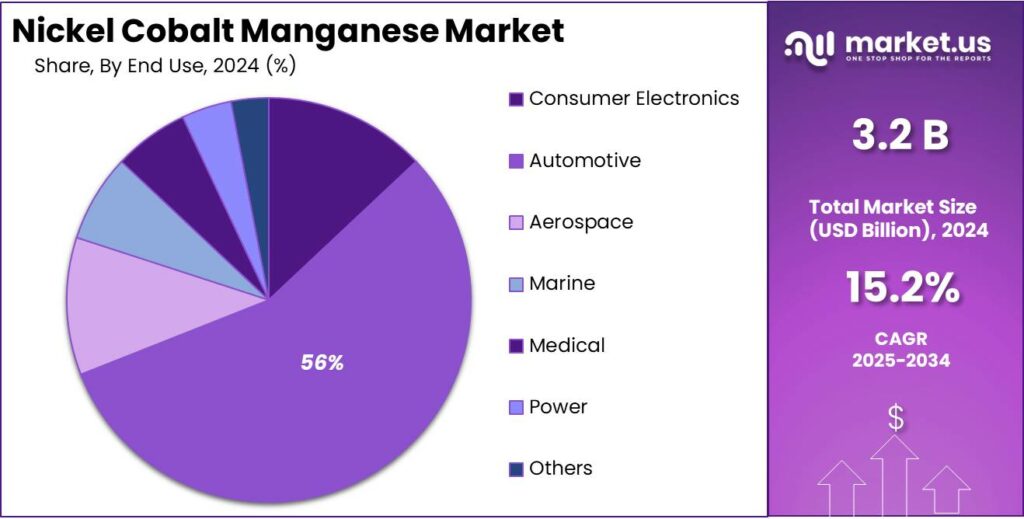
- Automotive held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 56.1% share.
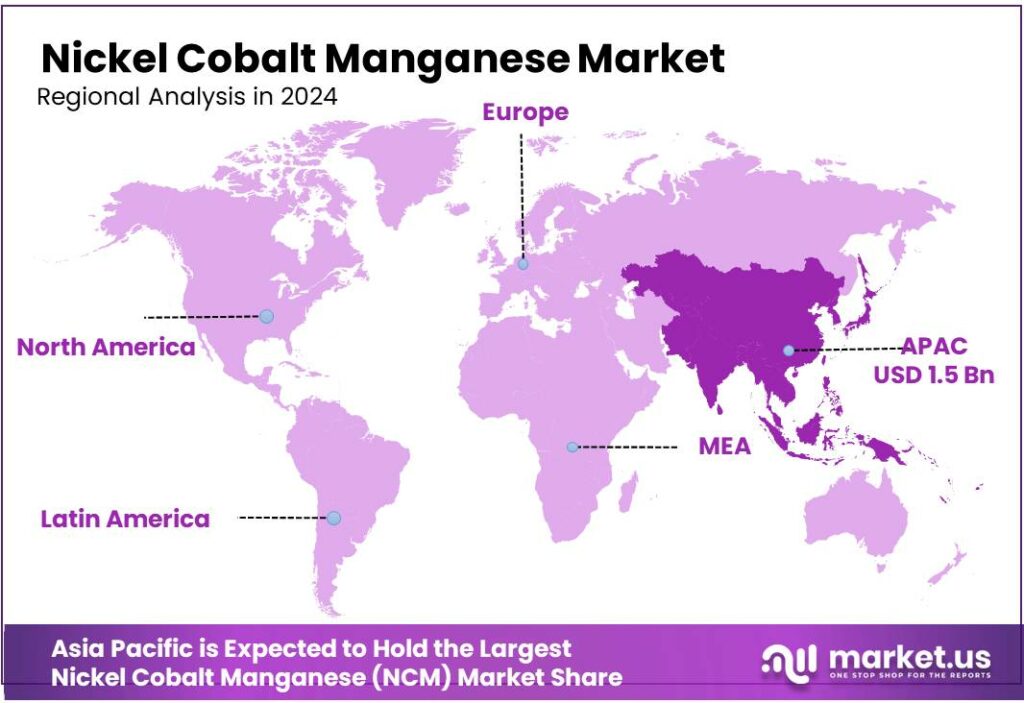
- North America dominates with 49.6% share 1.5 Bn, backed by EV demand and rapid battery.
By Product Type Analysis
NMC622 dominates with 37.5% share driven by balanced performance and cost efficiency
In 2024, NMC622 (60% Nickel, 20% Manganese, 20% Cobalt) held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 37.5% share. This chemistry has found a practical balance between energy density, safety, and cost, which has made it a preferred choice for many electric vehicle and battery pack manufacturers. Compared to higher-nickel variants, NMC622 offers relatively better thermal stability, while still delivering strong driving range performance.
At the same time, it reduces cobalt intensity compared to older NMC111 formulations, helping manufacturers manage raw material cost volatility and supply chain risks. Throughout 2024, several mid-range and premium electric vehicle models continued to rely on NMC622 cells because of their proven track record in durability and lifecycle stability.
By End Use Analysis
Automotive leads with 56.1% share as EV demand accelerates worldwide
In 2024, Automotive held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 56.1% share. The strong presence of Nickel Cobalt Manganese (NCM) batteries in electric passenger cars and commercial vehicles largely explains this leadership. Automakers across key regions continued to prioritize longer driving range, faster charging capability, and improved energy density—areas where NCM chemistry performs reliably.
Throughout 2024, many mid-range and premium electric vehicle models integrated NCM battery packs to meet consumer expectations for extended mileage and consistent performance in varied climate conditions. The automotive industry’s rapid electrification strategy, combined with stricter emission regulations, further reinforced the segment’s demand for high-performance cathode materials.
Key Market Segments
By Product Type
- NMC333 (33% Nickel, 33% Manganese, 33% Cobalt)
- NMC622 (60% Nickel, 20% Manganese, 20% Cobalt)
- NMC955 (90% Nickel, 5% Manganese, 5% Cobalt)
- Others
By End Use
- Consumer Electronics
- Automotive
- Aerospace
- Marine
- Medical
- Power
- Others
Emerging Trends
LFP’s rapid rise is reshaping where NCM fits, pushing NCM toward premium and “cleaner” supply chains
The clearest latest trend affecting Nickel Cobalt Manganese (NCM) is the fast expansion of lithium-iron-phosphate (LFP) batteries in mass-market EVs, which is changing how automakers choose chemistries. In 2024, global electric car sales exceeded 17 million units, taking EVs to more than 20% of total car sales, so chemistry decisions now move huge volumes. Against that backdrop, the International Energy Agency reports that in 2024, LFP batteries made up nearly half of the global EV battery market.
China is the main engine behind this shift, and the numbers show why the industry is paying attention. The IEA notes that LFP met nearly three-quarters of China’s domestic battery demand in 2024, and its share accelerated to 80% of batteries sold in November and December 2024. When a market of that size leans heavily into LFP, global supply chains react: automakers outside China feel price pressure, and battery makers look for clearer positioning. In practical terms, NCM is increasingly treated as the chemistry for vehicles that “need more”—longer range targets, higher speeds, heavier SUVs, or demanding duty cycles—while LFP expands strongly in cost-sensitive trims and high-volume models.
This trend is also feeding a second, related shift inside the NCM ecosystem: reducing cobalt exposure and improving traceability to meet tighter policy and customer requirements. Policy is no longer abstract here. The EU Batteries Regulation (Regulation (EU) 2023/1542) includes carbon-footprint obligations for EV batteries, and the consolidated legal text states that carbon footprint declaration shall apply from 18 February 2025. The European Commission’s Joint Research Centre is explicitly supporting the technical work for carbon-footprint rules under Article 7, signalling that reporting and verification expectations are becoming an operational reality for suppliers.
Drivers
Raw material supply challenges slow down NCM growth
One of the major restraining factors for the Nickel Cobalt Manganese (NCM) battery market is the unpredictability and limitations in the supply of key raw materials — especially nickel and cobalt. While NCM batteries are widely used in electric vehicles and energy storage systems because they offer good energy density and performance, the industry’s ability to scale depends heavily on steady and affordable access to high-quality nickel, cobalt and manganese. When these raw materials face production shortfalls, geopolitical risk, or price spikes, battery makers feel the effects immediately, and this can slow investment and production plans.
- According to the United States Geological Survey (USGS), global nickel mine production was about 3.7 million tonnes in 2024, yet only a fraction of that meets the low-impurity specifications required for EV batteries. This quality gap creates supply pressure because producers must either invest in new refining capacity or pay higher prices for battery-grade material.
Cobalt presents a similar challenge, though it is used in smaller quantities compared to nickel. The USGS reported global cobalt mine production at roughly 290,000 tonnes in 2024, with a large share coming from the Democratic Republic of Congo. While cobalt helps stabilize NCM battery chemistry and improve performance, its concentration in a small number of producing countries adds risk. Supply disruptions due to political instability, logistics issues or regulatory changes can cause price volatility.
Another aspect of raw material supply risk comes from manganese. Though manganese is more abundant than nickel or cobalt and has traditionally been used in steelmaking, only a subset of manganese production is refined to the purity required for battery cathodes. Global manganese mine output stood at about 20,000 thousand tonnes in 2024, mostly for ferrous applications rather than batteries. The gap between general manganese mining and the demand for battery-grade feedstock can create bottlenecks as NCM adoption grows.
Restraints
Cobalt concentration and compliance pressure restrain NCM expansion
A major restraining factor for Nickel Cobalt Manganese (NCM) is the heavy dependence on a narrow cobalt supply base, which creates cost volatility and compliance risk for battery and automaker supply chains. Cobalt is still used in NCM because it helps maintain cathode stability and performance, but sourcing remains highly concentrated. USGS data referenced in its cobalt commodity summary highlights how the market has long been dominated by the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) as the leading mining source, and that concentration keeps procurement teams cautious when planning multi-year NCM growth.
The scale of material needs also makes the risk feel real, not theoretical. USGS estimates global cobalt mine production at about 290,000 tonnes in 2024, a record level, yet the industry still treats supply security as fragile because so much volume originates from a limited set of geographies and operators. On the nickel side—another key NCM input—USGS estimated global nickel mine production at about 3.7 million tons in 2024, and noted that output trends can shift even when demand stays strong.
Policy is tightening this pressure, and it can act like a brake when supply chains are not yet ready. In the United States, the rules tied to the clean vehicle credit raise the bar over time. The Congressional Research Service summary explains that to qualify for the critical mineral portion of the credit, the minimum percentage increases from 50% in 2024 to 60% in 2025, 70% in 2026, and 80% thereafter. Separately, the Federal Register text on implementing clean-vehicle credit rules underscores how these “applicable percentage” thresholds are applied by calendar year, which forces manufacturers to re-work sourcing plans on a fixed schedule.
Europe is pushing in the same direction, which reinforces the constraint globally. The EU Critical Raw Materials Act sets 2030 benchmarks of 10% of annual consumption for extraction, 40% for processing, and 25% for recycling, and aims for no more than 65% dependence on a single third country for each strategic raw material at a relevant stage of processing.
Opportunity
Recycling-led “closed-loop” supply is a clear growth opportunity for NCM
One of the biggest growth opportunities for Nickel Cobalt Manganese (NCM) is scaling battery recycling into a reliable, local source of nickel and cobalt for new cathodes. NCM demand is tied to EV growth, but mining and refining constraints can slow expansions. Recycling changes that equation by turning end-of-life packs and factory scrap into usable feedstock that can be traced, priced more steadily, and sourced closer to cell plants.
The timing is attractive because EV batteries are moving into a volume phase. The IEA noted that in 2024, electric car sales rose 25% to 17 million, and annual battery demand surpassed 1 TWh. That scale matters for recycling because more gigawatt-hours in circulation eventually means more scrap today (from manufacturing yield and warranty returns) and more end-of-life material later. The same IEA outlook expects EV battery demand to reach more than 3 TWh in 2030, which implies a much larger installed base of packs feeding future recovery volumes.
Government action is actively pushing this opportunity from “nice to have” into “must build.” In the United States, DOE announced the selection of 8 projects for $44.8 million focused on lowering EV battery recycling costs—work that targets practical bottlenecks like transport, dismantling, and preprocessing. Looking into 2025, DOE’s Manufacturing & Energy Supply Chains office signaled it intends to issue a funding opportunity of up to $500 million to expand critical mineral processing and derivative battery manufacturing and recycling.
Industry is already moving from pilot scale toward meaningful throughput. Redwood Materials has stated it is processing 30,000 tons a year of end-of-life batteries and production scrap, with equipment expected to ramp to 60,000 tons (or 15 GWh) by the end of 2024.
Regional Insights
North America dominates with 49.6% share (1.5 Bn), backed by EV demand and rapid battery capacity build-out
North America is the dominating region, and North America 49.6% (1.5 Bn) reflects how strongly the U.S. and Canada are scaling electric mobility and the supporting battery supply chain. On the demand side, the U.S. market set a clear volume base in 2024, when EV sales reached a record 1.3 million units, up 7.3% year over year—keeping sustained pull for higher-energy chemistries such as Nickel Cobalt Manganese (NCM) in many long-range models. Canada strengthened the same trend: Statistics Canada reported over 264,000 zero-emission vehicles sold in 2024, valued at $17.3 billion, showing that adoption is broadening beyond early buyers and into mainstream replacement cycles.
On the supply side, North America’s NCM ecosystem is being reinforced by major cell-capacity announcements and policy-driven localization. The U.S. Department of Energy reported that by mid-2024, cumulative announced annual battery cell capacity in North America rose to nearly 1,400 GWh, which it noted is enough to supply about 14 million light-duty EVs annually—an important signal that cathode, precursor, and critical-mineral sourcing are being pulled into the region.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Samsung SDI closed 2024 with KRW 16.59 trillion in revenue and KRW 363.3 billion operating profit (battery + electronic materials footprint). The company’s battery business stays focused on high-performance cells for premium EVs and energy storage, where nickel-rich chemistries like NCM remain important for energy density and consistent output across climates.
BASF is a major upstream player for NCM through cathode active materials and recycling. BASF generated €65.3 billion in total sales in 2024 and has been building battery-materials scale, including a black-mass recycling plant in Germany with up to 15,000 tons/year processing capacity. Its Battery Materials platform supports NCM supply reliability for OEM-aligned chains.
Umicore is a key NCM cathode materials supplier in Europe. In 2024, it reported €3.5 billion in group revenues and €478 million adjusted EBIT. On production scale, Umicore’s Nysa cathode active material site targeted 40 GWh annual capacity in 2024, supporting EV customers seeking localized, traceable NCM supply in the region.
Top Key Players Outlook
- CATL
- Samsung SDI
- BASF SE
- Umicore
- Sumitomo Metal Mining Co., Ltd.
- Targray Technology International Inc.
- BMW Group
- General Motors
Recent Industry Developments
In 2024, CATL held about 37.9% of the global EV battery market, making it the world’s largest battery maker and a key buyer of cathode feedstocks like NCM for electric vehicles and energy storage systems.
In 2024, Samsung SDI’s battery division produced about 34 GWh of EV cell capacity, placing it among the top global battery makers, though still behind some of its larger rivals due to a 7.5% year-on-year drop in output.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 3.2 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 13.2 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 15.2% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Product Type (NMC333 (33% Nickel, 33% Manganese, 33% Cobalt), NMC622 (60% Nickel, 20% Manganese, 20% Cobalt), NMC955 (90% Nickel, 5% Manganese, 5% Cobalt), Others, By End Use (Consumer Electronics, Automotive, Aerospace, Marine, Medical, Power, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape CATL, Samsung SDI, BASF SE, Umicore, Sumitomo Metal Mining Co., Ltd., Targray Technology International Inc., BMW Group, General Motors Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Nickel Cobalt Manganese (NCM) MarketPublished date: Feb 2026add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Nickel Cobalt Manganese (NCM) MarketPublished date: Feb 2026add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- CATL
- Samsung SDI
- BASF SE
- Umicore
- Sumitomo Metal Mining Co., Ltd.
- Targray Technology International Inc.
- BMW Group
- General Motors










