Global Newborn Screening Market By Product (Instruments, Reagents) By Technology (Tandem Mass Spectrometry, Pulse Oximetry, Enzyme Based Assay, DNA Assay, Electrophoresis, Others) By Test Type (Dry Blood Spot Test, CCHD, Hearing Screen) Region and Companies – Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: June 2025
- Report ID: 150077
- Number of Pages: 394
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
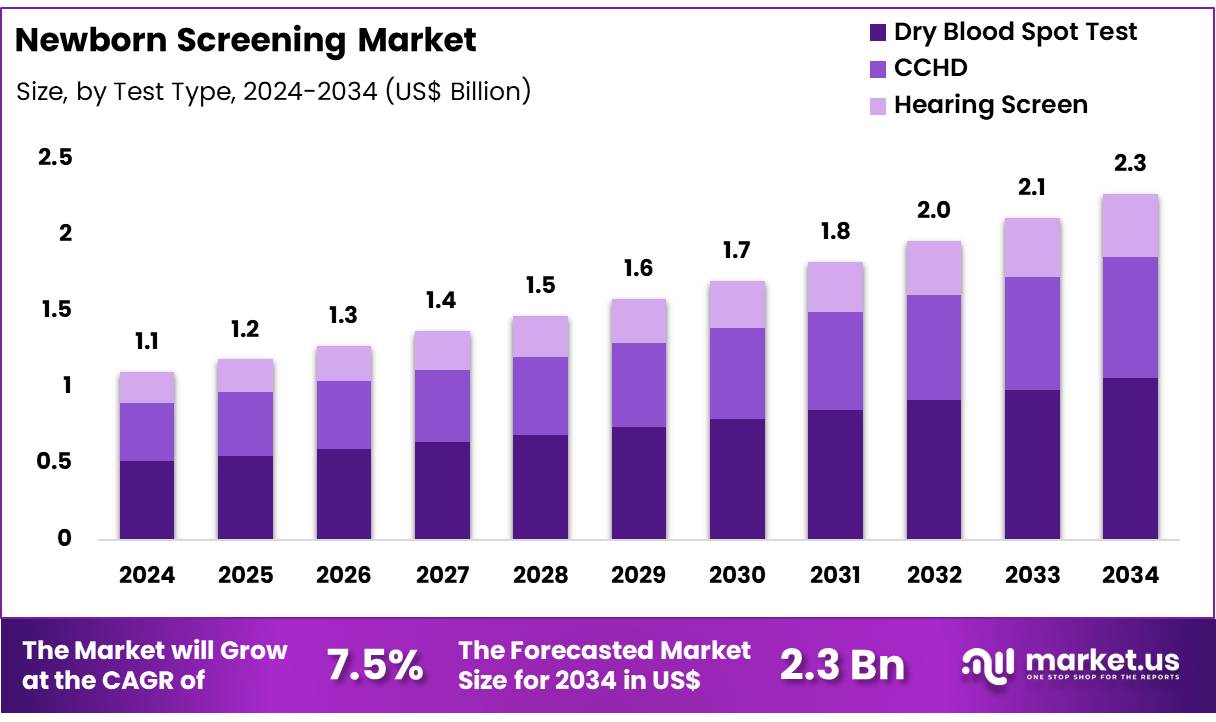
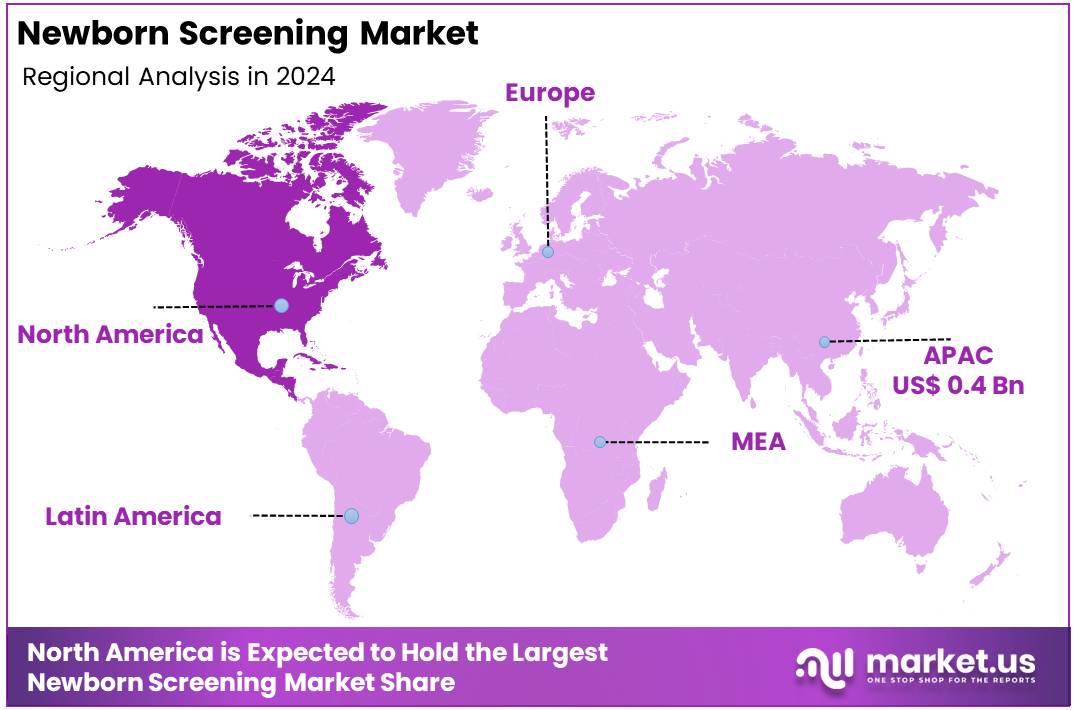
Global Newborn Screening Market size is expected to be worth around US$ 2.3 Billion by 2034 from US$ 1.1 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 7.5% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, Asia Pacific led the market, achieving over 37.2% share with a revenue of US$ 0.4 Billion.
The newborn screening market is experiencing steady growth, supported by public health funding, technological advances, and global health advocacy. Tandem mass spectrometry has significantly broadened screening capabilities, enabling the detection of multiple conditions from a single sample.
According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), universal screening is recommended for all infants to ensure early intervention. Similarly, the World Health Organization (WHO) stresses the importance of comprehensive screening programs to reduce infant morbidity and mortality.
Asia pacific dominates the market, attributed to robust healthcare infrastructure, standardized protocols, and regulatory support. Certified laboratories conduct these tests using validated methodologies. Results are promptly reported to healthcare professionals, allowing timely follow-up and treatment. In cases where disorders are identified, early therapies such as dietary interventions or medication are initiated to improve long-term outcomes.
Despite progress, the market faces challenges in developing regions, including limited program access and logistical issues in sample handling. However, there is growing opportunity in integrating point-of-care testing and digital tools, which can expand reach and improve real-time data management.
Screening programs continue to evolve, with national agencies updating test panels based on current evidence. These advancements have collectively saved thousands of lives and remain central to preventive pediatric healthcare worldwide.
Key Takeaways
- Market Size: Global Newborn Screening Market size is expected to be worth around US$ 2.3 Billion by 2034 from US$ 1.1 Billion in 2024.
- Market Growth: The market growing at a CAGR of 7.5% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
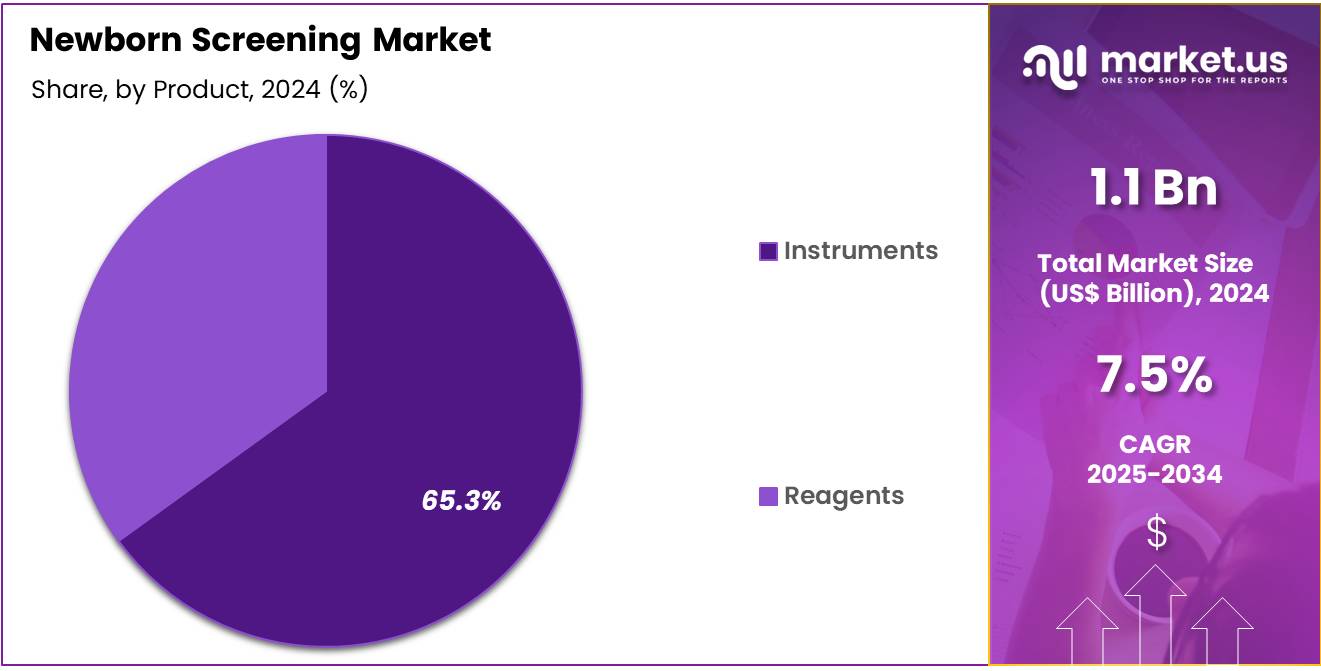
- Product Analysis: The instruments segment accounted for 65.3% of total revenue, reflecting the emphasis on advanced analytical platforms.
- Application Analysis: The tandem mass spectrometry segment is dominant with a 29.4% share.
- End-Use Analysis: In 2024, the newborn screening market is segmented by test type, with the dry blood spot (DBS) test leading at 46.7% of the total market share.
- Regional Analysis: In 2024, Asia Pacific led the market, achieving over 37.2% share with a revenue of US$ 0.4 Billion.
Product Analysis
In 2024, the newborn screening market’s product segmentation is characterized by the instruments and reagents categories. The instruments segment accounted for 65.3% of total revenue, reflecting the emphasis on advanced analytical platforms such as tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS), polymerase chain reaction (PCR) systems, and immunoassay analyzers.
These instruments enable accurate detection of metabolic disorders, hemoglobinopathies, and congenital hypothyroidism, with high throughput and automation reducing time-to-result and improving screening efficiency. The dominance of the instruments category can be attributed to ongoing technological innovations, increasing adoption of multiplex testing methodologies, and favorable regulatory initiatives by entities such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to standardize screening protocols.
Conversely, the reagents segment encompasses consumables such as assay kits, calibration standards, and quality control materials. Although representing a smaller share, the reagents category benefits from demand driven by testing schedules and expanding newborn screening panels. The growth potential within reagents is supported by emphasis on comprehensive panels and biomarker discovery programs.
Technology Analysis
Newborn screening technologies are categorized into tandem mass spectrometry, pulse oximetry, enzyme based assays, DNA assays, electrophoresis, and others. The tandem mass spectrometry segment is dominant with a 29.4% share, significantly driven by its high analytical sensitivity, ability to simultaneously detect multiple metabolic disorders, and support from standardized testing guidelines.
Pulse oximetry, with its noninvasive measurement of oxygen saturation, remains vital for early detection of critical congenital heart defects, owing to simplicity and low cost. Enzyme based assays are used for conditions such as phenylketonuria and galactosemia, leveraging colorimetric and fluorometric methods to quantify enzyme activity.
DNA assays, including PCR and next generation sequencing, enable precise identification of genetic mutations responsible for various inherited disorders. Electrophoresis techniques, such as isoelectric focusing and capillary electrophoresis, facilitate hemoglobinopathy screening. The others category encompasses emerging methods like immunoassays for biochemical markers and microfluidics platforms. Adoption of advanced technologies is encouraged by regulatory bodies to enhance screening accuracy and expand disorder panels.
Test Type Analysis
In 2024, the newborn screening market is segmented by test type, with the dry blood spot (DBS) test leading at 46.7% of the total market share. The dominance of DBS screening can be attributed to its minimal invasiveness, low sample volume requirements, and capacity for high-throughput processing. This method facilitates early detection of metabolic and endocrine disorders such as phenylketonuria and congenital hypothyroidism, enabling prompt intervention.
Critical congenital heart disease (CCHD) screening, typically performed using pulse oximetry, represents a growing segment due to increased adoption of standardized protocols in hospitals. Pulse oximetry is valued for its noninvasive nature and rapid bedside assessment, contributing to early diagnosis of life-threatening cardiac anomalies.
Hearing screening, encompassing otoacoustic emissions (OAE) and auditory brainstem response (ABR) tests, is another essential segment. These tests are performed before hospital discharge to identify sensorineural hearing loss, ensuring immediate referral for audiological evaluation. The remaining segment includes emerging modalities such as genetic and point-of-care assays, which are expected to gain traction as technology and reimbursement frameworks evolve.
Key Market Segments
By Product
- Instruments
- Reagents
By Technology
- Tandem Mass Spectrometry
- Pulse Oximetry
- Enzyme Based Assay
- DNA Assay
- Electrophoresis
- Others
By Test Type
- Dry Blood Spot Test
- CCHD
- Hearing Screen
Driving Factors
The expansion of newborn screening has been driven primarily by advancements in scientific and technological domains, coupled with sustained governmental support. Over the past six decades, innovations in biochemical methods, tandem mass spectrometry, and molecular diagnostics have enabled early detection of a wider spectrum of congenital disorders.
Simultaneously, federal and state funding initiatives such as those outlined in the Newborn Screening Saves Lives Reauthorization Act have fortified laboratory infrastructure and ensured uniformity in program implementation. Consumer advocacy and provider engagement have further stimulated programmatic growth by promoting awareness of rare disease identification and intervention.
Consequently, these factors collectively underpin the extensive reach of newborn screening, which now assesses over 98% of approximately four million U.S. newborns annually, yielding early treatment opportunities and significant reductions in morbidity and mortality.
Trending Factors
A salient trend in the newborn screening landscape is the gradual integration of genomic sequencing into public health protocols. Genomic newborn screening (gNBS) is being evaluated as a means to broaden the detection of childhood-onset conditions beyond traditional analytes. Pilot programs and feasibility studies have focused on delineating workflows, cost-effectiveness strategies, and ethical frameworks necessary for routine adoption.
Implementation enablers include existing laboratory capacities, interdisciplinary collaborations, and policy frameworks that support data sharing and follow-up services. However, barriers such as sequencing costs and public acceptability persist. Nonetheless, genomic approaches are anticipated to complement current methodologies, enhancing diagnostic yield and enabling personalized management plans in newborn populations.
Restraining Factors
Despite notable progress, capacity constraints and regulatory variability among states represent major restraints to program uniformity. Divergences in legislative authority have led to inconsistencies in mandated screening panels and follow-up protocols not all states possess the statutory framework required for comprehensive data collection.
Resource limitations such as shortages of skilled laboratory personnel and funding deficits have inhibited the expansion of specialized assays, including testing for conditions like critical congenital heart disease. Additionally, concerns regarding scalability of genomic methods and potential overload of confirmatory diagnostic services have prompted cautious deliberation by public health agencies. These factors collectively slow nationwide harmonization and may delay the introduction of novel screening targets.
Opportunity
The integration of emerging technologies, notably genomic sequencing, presents substantial opportunities to enhance the scope and impact of newborn screening. By augmenting traditional biochemical assays with next-generation sequencing, state programs can identify actionable variants linked to rare metabolic and genetic disorders.
Early identification can facilitate timely interventions, potentially improving long-term neurodevelopmental outcomes for approximately 14,000 infants diagnosed annually through existing frameworks. Expansion of educational initiatives and partnership models between public health laboratories and academic centers can streamline implementation, reduce per-sample costs, and address ethical considerations.
Furthermore, evolving reimbursement policies and federal grant provisions offer financial incentives for pilot projects, laying the groundwork for scalable, uniformly accessible genomic newborn screening across diverse jurisdictions.
Regional Analysis
In 2024, Asia Pacific held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 37.2% share and holding a market value of US$ 0.4 billion for the year. Growth in this region is supported by rising birth rates and expanding national healthcare programs. Government-backed screening initiatives in countries like India and China have boosted early diagnosis efforts for metabolic and genetic disorders. Moreover, increasing awareness and healthcare infrastructure upgrades are driving market expansion across Southeast Asia.
In contrast, North America remains a mature and technologically advanced market for newborn screening. The region accounted for a significant share in 2024 due to mandatory screening policies, especially in the United States. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), all states in the U.S. conduct screening for more than 30 core conditions.
Strong support from public health agencies, alongside high awareness among parents and healthcare providers, continues to strengthen market demand. The presence of advanced laboratory facilities and trained personnel also contributes to North America’s leadership in early diagnostic interventions for newborns.
Key Regions and Countries
North America
- US
- Canada
Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherland
- Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of APAC
Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
The newborn screening market is driven by a range of established and emerging players focusing on diagnostic technologies and assay development. These organizations are actively investing in research to improve the accuracy, speed, and cost-effectiveness of screening tests. A strong emphasis is placed on expanding test panels to include rare genetic and metabolic disorders.
Partnerships with public health authorities help ensure the integration of new screening protocols into national programs. Several players are also developing point-of-care testing tools to increase accessibility in remote and low-resource settings. Continuous innovation in tandem mass spectrometry, molecular assays, and data management systems supports their competitive positioning.
Moreover, strategic collaborations with hospitals and diagnostic laboratories further enhance market reach and service capacity, particularly in regions with rising demand for early newborn diagnostics.
Market Key Players
- Bio-Rad Laboratories
- Agilent Technologies
- Covidien plc
- Masimo
- Waters Corporation
- Natus Medical
- Trivitron Healthcare
- GE Lifesciences
- PerkinElmer Inc.
- AB SCIEX
Recent Developments
- Bio-Rad Laboratories (February 13, 2025): Bio-Rad announced a binding offer to acquire Stilla Technologies, a digital PCR developer, complementing its digital PCR portfolio and accelerating next-generation digital PCR solutions for clinical diagnostics and applied research. The transaction, expected to close by Q3 2025, will integrate Stilla’s Nio® systems—enabling advanced genetic tests, including liquid biopsy and infectious disease applications—into Bio-Rad’s QX Continuum™ roadmap.
- Agilent Technologies (May 01, 2025): Agilent released the Seahorse XF Flex Analyzer, a high-performance, 24-well metabolic analyzer designed to enhance cellular assays in clinical research and diagnostics. This launch bolsters Agilent’s liquid biopsy and genomics workflows by providing rapid, real-time metabolic data, which can improve throughput in laboratories performing newborn screening assays that require detailed cellular metabolism profiling.
- Masimo (May 06, 2025): Masimo reported Q1 2025 GAAP revenue of $372 million, driven by 10 % growth. The company highlighted that its Masimo SET® pulse oximetry, integrated with Patient SafetyNet™, significantly improved critical congenital heart disease screening in newborns. This contribution to neonatal care reinforced Masimo’s role in the newborn screening market, underpinning clinical outcomes and supporting expanded adoption of continuous monitoring solutions.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) US$ 1.1 Billion Forecast Revenue (2034) US$ 2.3 Billion CAGR (2025-2034) 7.5% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Product (Instruments, Reagents) By Technology (Tandem Mass Spectrometry, Pulse Oximetry, Enzyme Based Assay, DNA Assay, Electrophoresis, Others) By Test Type (Dry Blood Spot Test, CCHD, Hearing Screen) Regional Analysis North America-US, Canada, Mexico;Europe-Germany, UK, France, Italy, Russia, Spain, Rest of Europe;APAC-China, Japan, South Korea, India, Rest of Asia-Pacific;South America-Brazil, Argentina, Rest of South America;MEA-GCC, South Africa, Israel, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Bio-Rad Laboratories, Agilent Technologies, Covidien plc, Masimo, Waters Corporation, Natus Medical, Trivitron Healthcare, GE Lifesciences, PerkinElmer Inc., AB SCIEX Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- Bio-Rad Laboratories
- Agilent Technologies
- Covidien plc
- Masimo
- Waters Corporation
- Natus Medical
- Trivitron Healthcare
- GE Lifesciences
- PerkinElmer Inc.
- AB SCIEX










