Global Molecular Breeding Market Size, Share Analysis Report By Marker Type (Simple Sequence Repeats (SSR), Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNP), Expressed Sequence Tags (EST), Others), By Breeding Process (Marker-Assisted Selection (MAS), Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL) Mapping, Marker-Assisted Back-Crossing, Genomic Selection), By Trait Target (Yield Enhancement, Disease and Pest Resistance, Abiotic Stress Tolerance, Quality and Nutritional Traits) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Sep 2025
- Report ID: 159177
- Number of Pages: 210
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
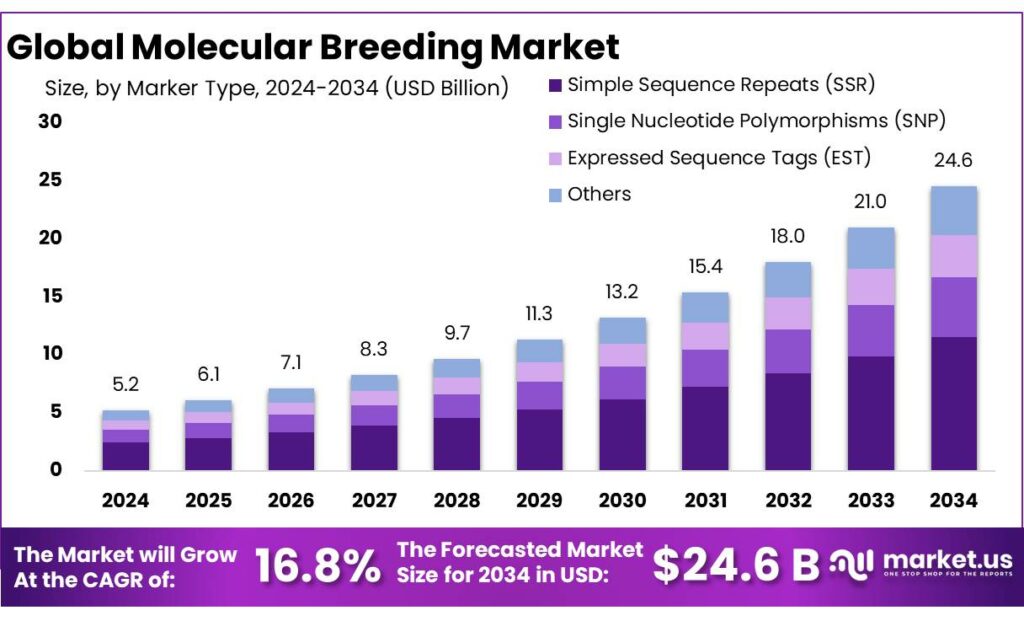
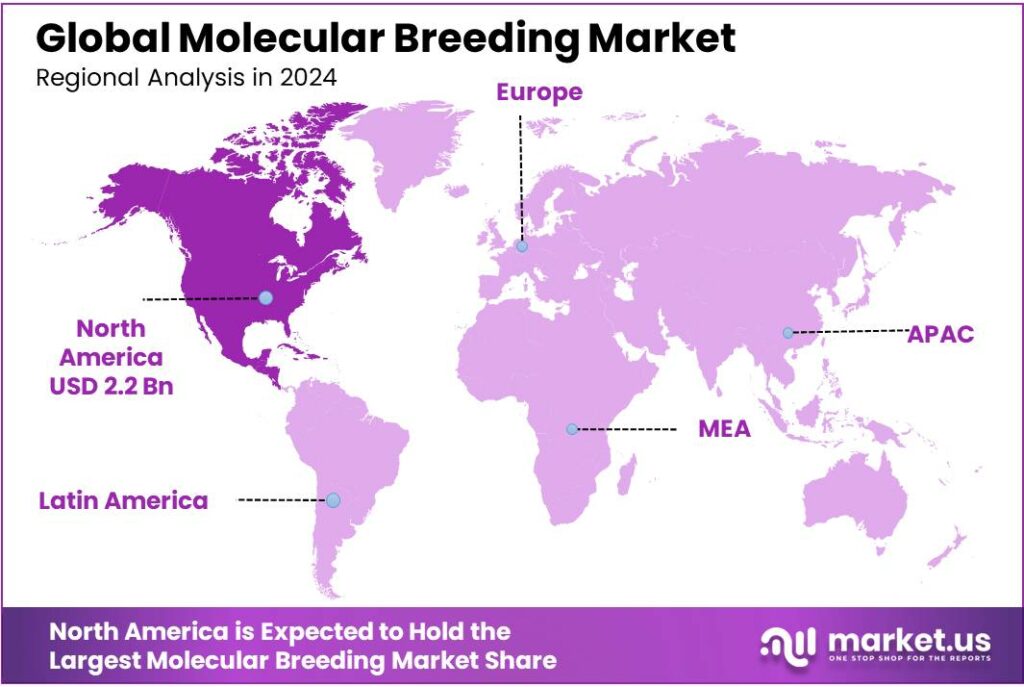
The Global Molecular Breeding Market size is expected to be worth around USD 24.6 Billion by 2034, from USD 5.2 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 16.8% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024 North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 43.80% share, holding USD 2.2 Billion in revenue.
Molecular breeding represents a transformative approach in agricultural biotechnology, integrating molecular biology with traditional breeding techniques to enhance crop traits such as yield, resistance to diseases and pests, and tolerance to abiotic stresses. This method employs molecular markers, quantitative trait loci (QTL) mapping, and gene editing tools like CRISPR-Cas9 to accelerate the development of superior crop varieties. In India, molecular breeding has led to the release of 74 improved varieties across seven crops, including rice, wheat, maize, and chickpea, demonstrating its significant impact on agricultural productivity.
In India, the molecular breeding sector is experiencing significant growth, supported by various government initiatives. The Department of Biotechnology (DBT) has allocated 10% of its annual budget to specialized programs in North East India, fostering research, education, and entrepreneurship. Furthermore, the DBT has endorsed the consolidation of two schemes into the Biotechnology Research Innovation and Entrepreneurship Development (Bio-RIDE) program, with a budget allocation of Rs. 9,197 crore (approximately USD 1.1 billion) for 2021-22 to 2025-26 under the 15th Finance Commission. These initiatives aim to enhance India’s competitiveness in biotechnology research, innovation, and industrial growth.
Government support is instrumental in driving the growth of molecular breeding. The DBT has allocated ₹9,197 crore (approximately $1.1 billion) under the Bio-RIDE scheme for the period 2021–2026, aimed at fostering biotechnology research and innovation. Additionally, the establishment of the National Speed Breeding Crop Facility at the National Agri-Food Biotechnology Institute (NABI) in Mohali underscores the government’s commitment to accelerating crop improvement through advanced breeding techniques.
Key Takeaways
- Molecular Breeding Market size is expected to be worth around USD 24.6 Billion by 2034, from USD 5.2 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 16.8%.
- Simple Sequence Repeats (SSR) held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 46.9% share of the molecular breeding market.
- Marker-Assisted Selection (MAS) held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 38.3% share of the molecular breeding market.
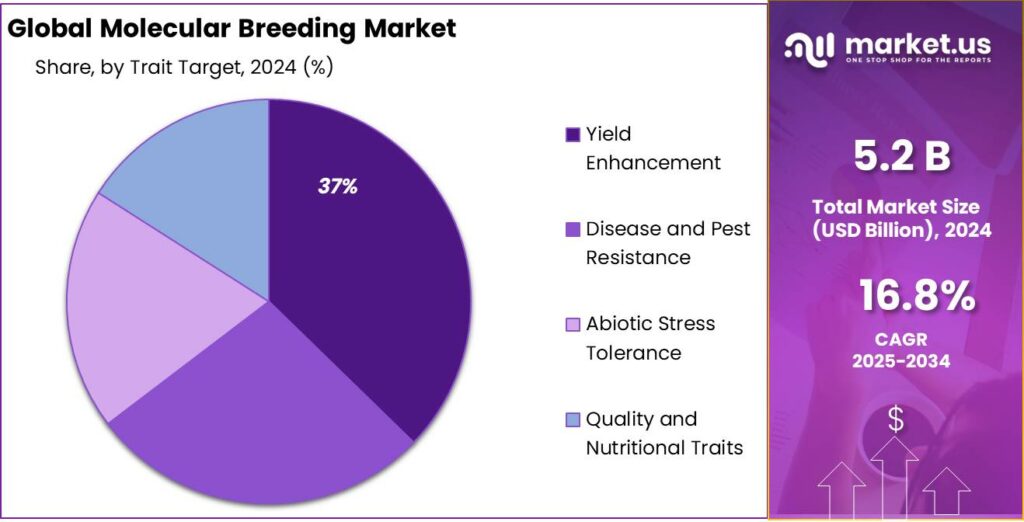
- Yield Enhancement held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 37.6% share of the molecular breeding market.
- North America held a dominant position in the molecular breeding market, capturing 43.80% of the market share, valued at approximately USD 2.2 billion.
By Marker Type Analysis
Simple Sequence Repeats (SSR) Dominates with 46.9% Share in 2024
In 2024, Simple Sequence Repeats (SSR) held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 46.9% share of the molecular breeding market. SSR markers are widely used in genetic research due to their high level of polymorphism, which makes them ideal for applications such as gene mapping, variety identification, and marker-assisted selection (MAS). This dominance can be attributed to SSR’s effectiveness in detecting genetic diversity across a wide range of crops and animals, particularly in those with limited genomic resources. The ability to detect numerous alleles with high reliability positions SSR as a preferred marker type for breeding programs focused on improving traits such as disease resistance, yield, and stress tolerance.
The demand for SSR markers has grown steadily over the years, driven by advancements in genetic research and the increasing adoption of molecular breeding technologies in both developed and emerging markets. In 2024, the widespread application of SSR markers in various crop species, including rice, maize, and wheat, has contributed significantly to their market dominance. The high accuracy and reproducibility of SSR markers make them an invaluable tool in both public and private breeding programs. Additionally, their ability to be used across different plant species without the need for specific sequence information further enhances their appeal. Given these advantages, SSR markers are expected to maintain a substantial share of the molecular breeding market in the coming years.
By Breeding Process Analysis
Marker-Assisted Selection (MAS) Leads with 38.3% Share in 2024
In 2024, Marker-Assisted Selection (MAS) held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 38.3% share of the molecular breeding market. MAS is a widely used technique that enables breeders to identify and select desirable traits at the genetic level, significantly speeding up the breeding process. By integrating molecular markers with traditional breeding methods, MAS allows for precise selection of traits such as disease resistance, drought tolerance, and improved yield without the need for extensive field testing or time-consuming backcrossing.
The growth of MAS is largely driven by its effectiveness in enhancing the efficiency of plant and animal breeding programs. In recent years, the technology has gained traction in both large-scale commercial agriculture and research-focused breeding programs. With the rise of global agricultural challenges, such as climate change and pests, MAS provides a faster and more reliable way to produce resilient and high-yielding varieties. In 2024, MAS was particularly prevalent in crops like maize, wheat, and soybean, where it is used to select for traits that directly impact productivity and market value.
By Trait Target Analysis
Yield Enhancement Dominates with 37.6% Share in 2024
In 2024, Yield Enhancement held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 37.6% share of the molecular breeding market. Yield enhancement is one of the most critical focus areas in molecular breeding, as global demand for food is rapidly increasing with the growing population. Through genetic improvements, breeding programs using molecular techniques such as MAS and genomic selection can significantly boost crop productivity, ensuring food security in the face of shrinking arable land and changing climate conditions.
The significant share of yield enhancement in 2024 can be attributed to the global need for more resilient and high-yielding crops that can withstand environmental stresses, such as droughts, extreme temperatures, and pests. In crops like maize, rice, and wheat, molecular breeding has successfully led to the development of varieties that are not only higher yielding but also more efficient in nutrient uptake and water usage. The focus on yield enhancement is particularly strong in regions with high agricultural dependency, where even small increases in crop yields can have significant economic and social benefits.
Key Market Segments
By Marker Type
- Simple Sequence Repeats (SSR)
- Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNP)
- Expressed Sequence Tags (EST)
- Others
By Breeding Process
- Marker-Assisted Selection (MAS)
- Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL) Mapping
- Marker-Assisted Back-Crossing
- Genomic Selection
By Trait Target
- Yield Enhancement
- Disease and Pest Resistance
- Abiotic Stress Tolerance
- Quality and Nutritional Traits
Emerging Trends
Speed Breeding for Accelerated Crop Improvement
A significant trend in molecular breeding is the adoption of speed breeding techniques to expedite the development of high-yielding, climate-resilient, and biofortified crop varieties. This approach aims to address the pressing challenges of food security, nutritional deficiencies, and climate change by reducing the time required to develop improved crop varieties.
In March 2024, the Union Minister of Science & Technology inaugurated the National Speed Breeding Crop Facility at the National Agri-Food Biotechnology Institute (NABI) in Mohali. This state-of-the-art facility is designed to accelerate the breeding process by utilizing controlled environments and advanced technologies, thereby reducing the time to develop new crop varieties from the conventional 8–10 years to just 2–3 years. The facility focuses on enhancing crop traits such as yield, disease resistance, and nutritional content, aligning with the government’s vision to double farmers’ income and promote agricultural sustainability.
Furthermore, the DBT’s Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC) has been actively supporting startups and small enterprises engaged in developing innovative agricultural solutions. Through initiatives like the Startup India Seed Fund Scheme (SISFS) and the e-YUVA Scheme, BIRAC provides seed funding, mentorship, and infrastructure support to emerging biotech companies. These programs aim to accelerate the commercialization of biotechnological innovations, including those related to speed breeding, thereby contributing to the growth of the biotechnology sector in India.
Drivers
Government Support and Strategic Initiatives
One of the most significant driving forces behind the growth of molecular breeding in India is the robust support from the government through strategic initiatives and substantial funding. The Department of Biotechnology (DBT), under the Ministry of Science and Technology, has been at the forefront of fostering biotechnology research and innovation in the country.
A landmark initiative is the Biotechnology Research Innovation and Entrepreneurship Development (Bio-RIDE) scheme, which consolidates various DBT programs to streamline efforts in biotechnology. For the period 2021–2026, the Indian government has allocated ₹9,197 crore (approximately $1.1 billion) under the Bio-RIDE scheme to bolster research and development, innovation, and entrepreneurship in the biotechnology sector
In addition to financial support, the government has established infrastructure to accelerate molecular breeding. In March 2024, the Union Minister of Science & Technology inaugurated the National Speed Breeding Crop Facility at the National Agri-Food Biotechnology Institute (NABI) in Mohali. This facility aims to expedite the development of crop varieties by enhancing the speed of breeding processes, thereby addressing the challenges of food security and climate resilience
Furthermore, the DBT has been instrumental in promoting public-private partnerships to translate research into practical applications. Through initiatives like the Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC), the government supports emerging biotechnology enterprises to undertake strategic research and innovation. This collaboration has led to the development of several high-yielding and climate-resilient crop varieties, contributing to increased agricultural productivity
Restraints
Regulatory and Public Perception Challenges
One of the most significant challenges hindering the widespread adoption of molecular breeding in India is the complex and often ambiguous regulatory landscape surrounding genetically modified (GM) crops. Despite advancements in biotechnology, the approval process for GM crops remains mired in delays and inconsistent policies, creating uncertainty among researchers, farmers, and investors.
A prominent example is the Dhara Mustard Hybrid-11 (DMH-11), a genetically modified mustard variety developed to enhance yield and reduce India’s dependence on edible oil imports. The development of DMH-11 spanned over 14 years and incurred an estimated cost of ₹70 crore (approximately $8.5 million). Field trials have demonstrated yield increases ranging from 19% to 40% over conventional varieties. However, despite these promising results, the Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) has not granted approval for its commercial cultivation, citing concerns over environmental impact and the potential for cross-pollination with wild mustard species.
The regulatory uncertainty is further compounded by the absence of a dedicated body like the Biotechnology Regulatory Authority of India (BRAI), which has been proposed multiple times since 2008 but has yet to be enacted. The lack of a centralized and transparent regulatory framework leads to fragmented decision-making, with different ministries and departments often taking conflicting stances on GM technology. This disjointed approach not only hampers the approval process but also erodes public trust in biotechnology advancements.
Public perception plays a crucial role in the acceptance of GM crops. In India, there is a significant level of skepticism and opposition to genetically modified organisms, driven by concerns over food safety, environmental impact, and ethical considerations. This apprehension is often fueled by misinformation and a lack of awareness about the scientific processes involved in genetic modification. The controversy surrounding GM mustard is a case in point, where public protests and media campaigns have intensified the debate, leading to a polarized view on the subject.
Opportunity
Biofortification through Molecular Breeding
One of the most promising avenues for molecular breeding in India is biofortification—the process of enhancing the nutritional quality of crops through genetic means. With the prevalence of malnutrition, especially among children and women, biofortified crops can play a pivotal role in addressing micronutrient deficiencies. The Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) has been at the forefront of this initiative, developing and releasing biofortified varieties across various crops.
As of 2022, ICAR has released 87 biofortified crop varieties, including 18 in the year 2021 alone. These varieties are enriched with essential nutrients such as iron, zinc, and vitamin A, aiming to combat deficiencies prevalent in the Indian population. For instance, the development of iron-rich rice and zinc-enriched wheat varieties has shown promising results in improving the nutritional intake of rural communities. These efforts are aligned with the government’s vision to enhance food security and public health through agricultural innovation.
The Department of Biotechnology (DBT) has also recognized the importance of biofortification and has allocated significant funds to support research in this area. Under the Bio-RIDE scheme, the government has committed ₹9,197 crore (approximately $1.1 billion) for the period 2021–2026 to promote biotechnology research and innovation. This funding is expected to accelerate the development of biofortified crops and facilitate their adoption among farmers and consumers.
Moreover, the establishment of the National Speed Breeding Crop Facility at the National Agri-Food Biotechnology Institute (NABI) in Mohali in March 2024 underscores the government’s commitment to enhancing the speed and efficiency of crop breeding processes. This facility aims to expedite the development of biofortified crop varieties, thereby contributing to the nation’s nutritional security.
Regional Insights
North America Dominates Molecular Breeding Market with 43.80% Share, Valued at USD 2.2 Billion in 2024
In 2024, North America held a dominant position in the molecular breeding market, capturing 43.80% of the market share, valued at approximately USD 2.2 billion. The region’s leadership is driven by its advanced agricultural infrastructure, strong research and development (R&D) capabilities, and significant investments in biotechnology.
The United States, in particular, plays a pivotal role in this dominance, with both private and public sectors heavily investing in genetic research and innovation. Government initiatives, such as the USDA’s National Institute of Food and Agriculture (NIFA), have dedicated millions of dollars to support molecular breeding technologies that aim to improve crop productivity, disease resistance, and environmental sustainability.
The North American market benefits from the adoption of cutting-edge technologies like CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing and marker-assisted selection (MAS), particularly in staple crops such as maize, soybeans, and wheat. These crops are vital to both regional and global food security, and molecular breeding offers significant improvements in yield and stress tolerance.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Slipstream Automation, based in New Zealand, specializes in providing automated services and support for organizations involved in Marker Assisted Selection (MAS) and other large-scale DNA extraction/genetic screening projects. Established in 2005, Slipstream offers a complete service from plant to data, managing up to 10,000 samples per week. Their expertise in automation development and molecular biology backgrounds enables fast and efficient conversion of manual protocols, enhancing the efficiency of molecular breeding processes.
DanBred P/S is a leading international pig breeding company, specializing in the development of high-performance breeding pigs. Their breeding program focuses on traits such as high fertility, large viable litters, outstanding feed conversion, low slaughter loss, and a high meat percentage. DanBred’s commitment to genomic selection ensures a 30% increase in genetic gain, providing pig producers worldwide with superior genetics for enhanced productivity and efficiency in pig production.
Charles River Laboratories is a global leader in providing comprehensive services to support the pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and agricultural industries. Their offerings include molecular biology services such as DNA sequencing, genotyping, and gene expression analysis, which are crucial for molecular breeding applications. With over 150 facilities worldwide, Charles River plays a pivotal role in accelerating the development of novel therapeutics and enhancing agricultural productivity through advanced molecular techniques.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Charles River Laboratories
- Eurofins Scientific
- DanBred P/S
- Intertek Group Plc
- Slipstream Automation
- Illumina Inc
- LGC Limited
- SGS Société Générale de Surveillance SA
- Lemna Tec GmbH
Recent Industry Developments
In 2024 Intertek Group Plc, revenue reached approximately USD 3.6 billion, driven in part by the increased demand for testing services in the agricultural biotechnology sector.
In 2024 Charles River Laboratories, saw strong growth in its life sciences division, with an estimated annual revenue of USD 4.8 billion, driven by the increasing demand for genetic testing and molecular breeding solutions.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 5.2 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 24.6 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 16.8% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Marker Type (Simple Sequence Repeats (SSR), Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNP), Expressed Sequence Tags (EST), Others), By Breeding Process (Marker-Assisted Selection (MAS), Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL) Mapping, Marker-Assisted Back-Crossing, Genomic Selection), By Trait Target (Yield Enhancement, Disease and Pest Resistance, Abiotic Stress Tolerance, Quality and Nutritional Traits) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Charles River Laboratories, Eurofins Scientific, DanBred P/S, Intertek Group Plc, Slipstream Automation, Illumina Inc, LGC Limited, SGS Société Générale de Surveillance SA, Lemna Tec GmbH Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- Charles River Laboratories
- Eurofins Scientific
- DanBred P/S
- Intertek Group Plc
- Slipstream Automation
- Illumina Inc
- LGC Limited
- SGS Société Générale de Surveillance SA
- Lemna Tec GmbH










