Global Zero Emission Buildings Market Size, Share Analysis Report By Energy Source (Solar Energy, Wind Energy, Geothermal Energy, Others), By Technology (On-site Renewable Generation Systems, Energy Storage Systems (ESS), Smart Grid Integration, Energy Management Systems (EMS), Others), By Element Type (Lighting, Walls And Roofs, Heating, Ventilation, And Air Conditioning (HVAC) Systems, Others), By Building Type (Residential, Commercial) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Dec 2025
- Report ID: 171988
- Number of Pages: 286
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
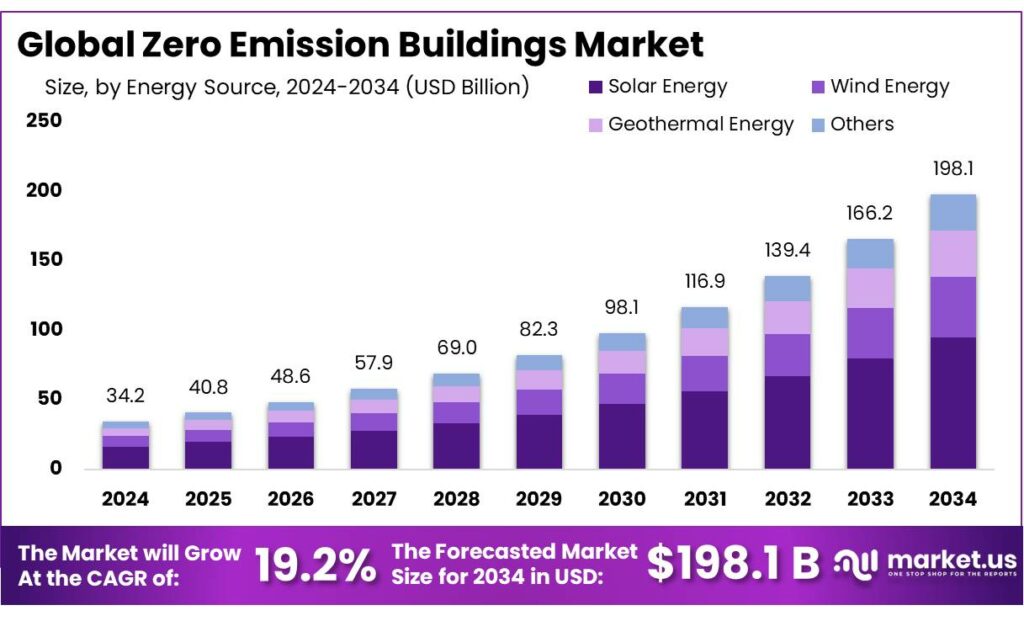
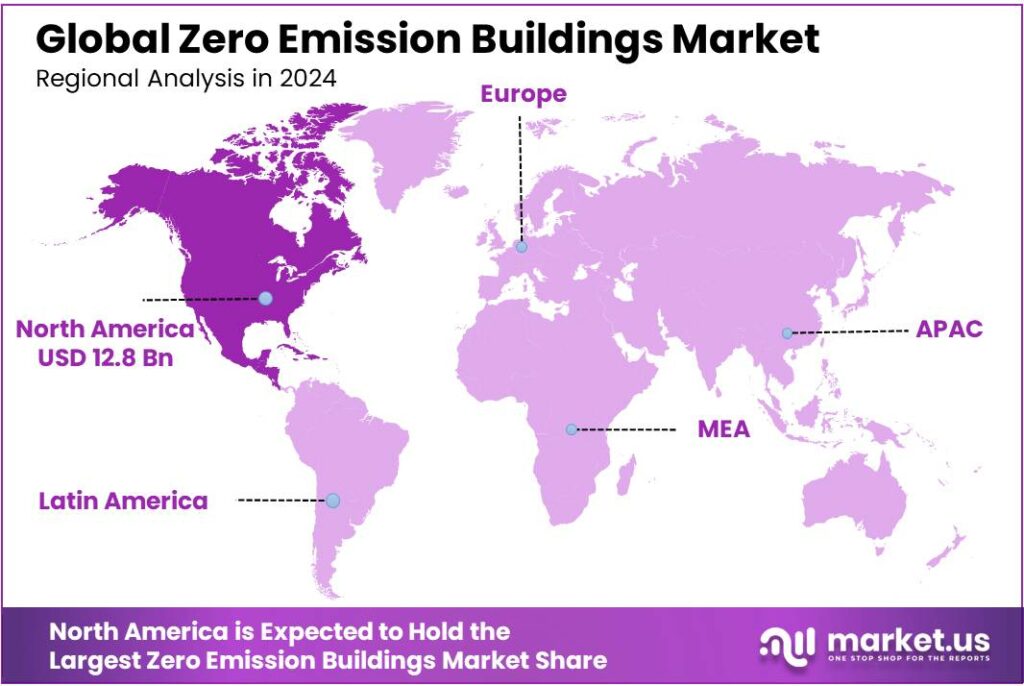
The Global Zero Emission Buildings Market size is expected to be worth around USD 198.1 Billion by 2034, from USD 34.2 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 19.2% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024 North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 37.5% share, holding USD 12.8 Billion in revenue.
Zero Emission Buildings (ZEBs) are moving from a “green premium” concept to an operating standard for new projects and major retrofits. In practical market terms, ZEBs are designed to eliminate operational on-site emissions while driving down total energy demand through envelope performance, controls, and high-efficiency electrified systems. This matters because building operations still account for around 30% of global final energy use and about 26% of global energy-related emissions.
Industry conditions are being shaped by the size of the problem and the maturity of available solutions. UNEP/GlobalABC reporting highlights that, in 2022, buildings were responsible for 34% of global energy demand and 37% of energy- and process-related CO₂ emissions—showing why policy and capital are concentrating on this sector.
Key driving factors are policy tightening, electrification economics, and the simple math of retrofit speed. The IEA’s net-zero pathway highlights that retrofit rates need to rise to around 2.5% per year by 2030—up from less than 1% today—to avoid locking in inefficient stock.
Governments are translating this into rules and standards. In the EU, the revised Energy Performance of Buildings framework makes zero-emission buildings the direction of travel for new construction and pushes requirements like “solar-ready” new buildings. At the same time, the IEA signals the scale of ambition: by 2030, all new buildings and about 20% of the existing building stock need to be “zero-carbon-ready” to stay aligned with net-zero trajectories.
Policy is now one of the strongest industrial accelerators. In the EU, the recast Energy Performance of Buildings Directive (EU/2024/1275) requires all new buildings to be zero-emission from 1 January 2028 for buildings owned by public bodies and from 1 January 2030 for all other new buildings.
- In the United States, tax incentives are actively shaping developer and contractor economics: the IRS describes the Section 179D commercial buildings deduction with values up to $1.00 per square foot for 50% energy savings. The IRS also states the 45L credit can be worth up to $5,000 per home for eligible builders of qualified energy-efficient homes.
- In India, the Bureau of Energy Efficiency’s ECBC 2017 positions compliant buildings at roughly 25% savings, with ECBC+ at 35%, and “Super ECBC” targeting 50% savings—creating a tiered pathway that supports both compliance and premium “high-efficiency” offerings.
Key Takeaways
- Zero Emission Buildings Market size is expected to be worth around USD 198.1 Billion by 2034, from USD 34.2 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 19.2%.
- Solar Energy held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 48.5% share.
- On-site Renewable Generation Systems held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 38.4% share.
- Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) Systems held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 39.1% share.
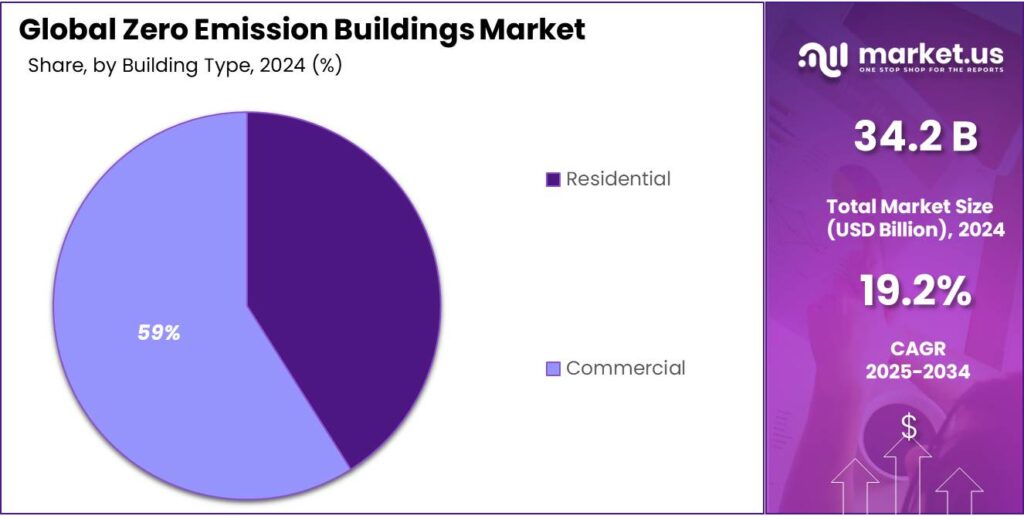
- Commercial held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 59.7% share.
- North America held a leading position in the zero emission buildings market in 2024, capturing a 37.5% share with an estimated market value of USD 12.8 billion.
By Energy Source Analysis
Solar Energy leads zero emission buildings with a 48.5% share due to clean power access and falling installation costs
In 2024, Solar Energy held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 48.5% share, as it remained the most widely adopted energy source for zero emission buildings across residential and commercial spaces. This leadership was supported by the ability of solar systems to generate clean electricity on-site, reducing dependence on grid power and lowering long-term energy costs. Building owners increasingly preferred solar energy because it integrates easily with rooftop designs and energy storage systems while supporting carbon reduction goals.
In 2025, adoption continued at a steady pace as policy support, net metering benefits, and improved panel efficiency encouraged new installations and retrofits. The strong share of solar energy reflected its practical role in helping buildings achieve near-zero or zero operational emissions while maintaining energy reliability.
By Technology Analysis
On-site renewable generation systems lead zero emission buildings with a 38.4% share due to energy independence and lower operating costs
In 2024, On-site Renewable Generation Systems held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 38.4% share, as building owners increasingly focused on producing clean energy directly at the point of use. These systems, which include rooftop solar panels and small wind setups, helped reduce reliance on external power grids while supporting zero emission targets. Demand was driven by the need for stable energy supply, long-term cost savings, and improved energy resilience.
In 2025, adoption remained strong as new building designs and retrofit projects integrated on-site generation to meet stricter energy efficiency standards. The segment’s leading share reflected its practical value in enabling buildings to control energy use while cutting operational emissions.
By Element Type Analysis
Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems lead zero emission buildings with a 39.1% share due to energy efficiency and indoor comfort benefits
In 2024, Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) Systems held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 39.1% share, as they remained essential for maintaining indoor comfort while minimizing energy consumption in zero emission buildings. The demand was driven by advancements in energy-efficient HVAC technologies, such as variable refrigerant flow systems, heat pumps, and smart thermostats, which optimize performance and reduce carbon emissions.
In 2025, adoption continued to grow as building codes and sustainability standards encouraged integrating high-performance HVAC solutions into new and retrofitted structures. The strong market share reflected the critical role of HVAC systems in balancing occupant comfort, operational efficiency, and compliance with environmental targets, making them a cornerstone of sustainable building design.
By Building Type Analysis
Commercial buildings lead zero emission construction with a 59.7% share due to high energy demand and sustainability focus
In 2024, Commercial held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 59.7% share, as offices, retail spaces, and institutional buildings increasingly adopted zero emission technologies to reduce operational costs and meet sustainability commitments. The high energy consumption of commercial facilities drove the integration of renewable energy, advanced HVAC systems, and on-site generation solutions to achieve near-zero carbon footprints.
In 2025, growth continued steadily as corporate policies, green building certifications, and regulatory incentives encouraged new and retrofitted commercial buildings to prioritize energy efficiency and emission reductions. The strong market share reflected the sector’s leadership in adopting innovative energy solutions while balancing operational needs and environmental goals.
Key Market Segments
By Energy Source
- Solar Energy
- Wind Energy
- Geothermal Energy
- Others
By Technology
- On-site Renewable Generation Systems
- Energy Storage Systems (ESS)
- Smart Grid Integration
- Energy Management Systems (EMS)
- Others
By Element Type
- Lighting
- Walls & Roofs
- Heating, Ventilation, And Air Conditioning (HVAC) Systems
- Others
By Building Type
- Residential
- Commercial
Emerging Trends
Growing Use of Grid-Interactive and Smart Energy Systems in Zero Emission Buildings
One of the most important recent trends in Zero Emission Buildings (ZEBs) is the increasing integration of grid-interactive technologies, including smart energy management systems, demand response, and energy storage. This trend is not just about cutting emissions—it is about buildings becoming active partners in energy systems, helping balance grids, lower costs, and improve reliability. As more countries push for electrification and clean power, smart buildings are emerging as key assets rather than passive energy consumers.
Traditionally, buildings were designed simply to meet heating, cooling, and lighting needs. That changed as renewable power expanded. Renewables like wind and solar are intermittent, meaning their output can swing with weather and time of day. Governments and grid planners now see buildings as flexibility resources. Smart ZEBs can adjust energy use in real time—shifting loads away from peak times, storing clean power when it is abundant, and reducing strain on the grid when it is tight. In the United States, the Department of Energy highlights that buildings account for around 75% of all electricity use, making them central to energy system flexibility.
In food-related industries, which often have high and variable energy loads, this trend is already visible. Cold storage warehouses, food processing facilities, and supermarkets are expensive to operate and sensitive to energy price volatility. Smart buildings for cold storage can pre-cool during times of low grid stress and then coast through peak hours, reducing overall costs and cutting emissions at the same time. The IEA notes that stationary batteries and flexible loads—like buildings—can reduce peak demand by up to 20% in some systems, which helps integrate more renewables without reliability risks.
Another dimension of this trend is the use of time-of-use electricity pricing and real-time energy data. Many utilities now offer dynamic pricing, where electricity costs more during high demand periods and less when renewable output is high. Smart ZEB systems are increasingly programmed to respond to these signals—charging heat pump thermal stores or EV chargers when prices are low and reducing load when prices spike. Governments and regulators in places like California, New York, and parts of Europe are expanding such pricing models precisely to unlock building flexibility.
Drivers
Stronger Building Policies and Carbon Targets Are Pushing Zero Emission Buildings Into the Mainstream
A major driver for Zero Emission Buildings is simple: governments and large institutions are now treating building emissions as a priority problem, and they are turning that priority into rules, timelines, and public programs. Buildings are no longer seen as “just real estate.” They are being measured like energy infrastructure, because the climate impact is large and visible. The IEA estimates that building operations account for about 30% of global final energy consumption and 26% of global energy-related emissions, with 8% coming from direct on-site emissions and 18% from the electricity and heat used in buildings.
That footprint creates pressure for action, and it explains why policy is moving faster than before. The UN-linked GlobalABC/UNEP reporting shows the buildings and construction sector still consumes roughly 34% of global energy demand and produces about 37% of energy- and process-related CO₂ emissions. When a sector is this big, even “small” improvements—better insulation, efficient cooling, electrified heating, tighter controls—add up to major national gains. This is why zero-emission building requirements are increasingly written into national and regional roadmaps, not left to voluntary pilots.
- Europe is a clear example of policy creating a pipeline. The European Commission notes that the revised Energy Performance of Buildings Directive (EU/2024/1275) entered into force on 28 May 2024 and must be transposed into national laws by 29 May 2026. In practice, this type of directive changes investment decisions across the value chain: developers, building owners, HVAC suppliers, insulation makers, and energy service firms all plan around compliance dates.
This policy pressure is also reinforced by corporate carbon commitments and capital markets. When firms are judged on emissions performance, buildings become one of the fastest areas to reduce operational emissions with proven tools. It is often easier to electrify heating and improve efficiency than to decarbonize certain industrial processes. As a result, zero-emission buildings are increasingly framed as a “low regret” move: they reduce exposure to future carbon rules, improve resilience to energy price shocks, and make portfolio reporting cleaner.
Restraints
High Upfront Retrofit Costs and Technical Complexity Slow Down Zero Emission Building Adoption
One major restraining factor for Zero Emission Buildings is the high upfront cost and technical difficulty of retrofitting existing buildings. While new buildings can be designed for zero emissions from the start, most of the real challenge lies in upgrading older stock. This matters because existing buildings dominate the global landscape. The UN Environment Programme confirms that about 80% of the buildings that will be in use by 2050 already exist today. This means climate targets cannot be met only with new construction; deep retrofits are essential, but they are expensive and complex.
Cost is the first and most visible barrier. According to the International Energy Agency, deep energy retrofits that align buildings with net-zero pathways often require capital investments two to three times higher than shallow efficiency upgrades. These costs come from insulation improvements, window replacement, electrified heating systems such as heat pumps, ventilation upgrades, electrical rewiring, and smart controls. Even when lifetime savings are strong, many owners struggle with the initial expense, especially small commercial owners and residential landlords.
Policy support helps, but it does not remove all barriers. For example, the European Union’s revised Energy Performance of Buildings Directive aims to accelerate renovation, yet Member States still face the practical challenge of financing millions of upgrades while protecting vulnerable households. The European Commission has acknowledged that renovation rates must at least double compared with historical levels to meet climate goals, a target that remains difficult under current cost structures.
Opportunity
Mass Renovation and Electrified Heating Programs Create the Biggest Growth Opportunity for Zero Emission Buildings
The strongest growth opportunity for Zero Emission Buildings is the same place the emissions problem is hiding: existing buildings and the heating systems inside them. Most countries can build a few showcase green projects every year, but the market scales when whole neighborhoods start renovating—better insulation, airtightness, efficient cooling, smart controls, and replacing fossil boilers with electric heat pumps. The climate case is big enough to keep policy support alive: the IEA estimates building operations use about 30% of global final energy and produce 26% of global energy-related emissions.
Europe shows how targets turn into demand. The European Commission’s Renovation Wave aims to renovate 35 million buildings by 2030 and “at least double” the annual rate of energy renovations. That is a huge pipeline for contractors, insulation suppliers, heat-pump brands, building automation firms, and energy service companies. What makes this opportunity practical is that renovation work is local: it creates steady business for regional installers, HVAC technicians, and civil contractors rather than relying on a single mega-project.
Electrified heating is the second engine behind this opportunity. Heat pumps are one of the most direct tools for cutting on-site fossil use in buildings. In 2022, global heat pump sales rose 11%, Europe added around 3 million new units, and in the United States heat pump purchases exceeded those of gas furnaces—signals that electrification can move from “early adopters” to mainstream when policy and prices align. Even with the 3% global sales dip in 2023, the IEA still frames heat pumps as a core building decarbonisation technology, and early data suggested a rebound in parts of 2024.
In the United States, the funding signals are also hard to ignore. The Inflation Reduction Act includes about $8.8 billion for two residential rebate programs—the Home Efficiency Rebates (HOMES) and the Home Electrification and Appliance Rebates (HEAR)—supporting measures like insulation, panel upgrades, wiring, and electric appliances such as heat pumps.
Regional Insights
North America dominates the zero emission buildings market with 37.5% share driven by strong sustainability policies
North America held a leading position in the zero emission buildings market in 2024, capturing a 37.5% share with an estimated market value of USD 12.8 billion, supported by robust regulatory frameworks, advanced technological adoption, and increasing investment in sustainable infrastructure. The region’s dominance is primarily driven by stringent building codes and energy efficiency standards in the United States and Canada, which encourage developers and building owners to integrate renewable energy systems, high-efficiency HVAC, and on-site generation solutions.
Commercial buildings in North America were particularly significant contributors, given their high energy demand and potential for operational savings through renewable integration. Residential adoption also gained momentum due to rising consumer awareness and financing programs supporting energy-efficient upgrades. Technologies such as solar panels, heat pumps, and smart energy management systems were widely implemented, allowing buildings to reduce grid dependence and carbon emissions while maintaining occupant comfort.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Johnson Controls International plc: Johnson Controls drives zero emission building adoption through its OpenBlue Net Zero Buildings solutions, helping customers cut emissions with energy-efficient systems and clean electrification. In 2024, it reduced absolute Scope 1 & 2 emissions by 43.8% since 2017 while investing 90% of R&D in climate technologies, supporting smarter and greener buildings globally.
Schneider Electric: Schneider Electric delivers digital energy and building management systems that can slash operational carbon emissions by up to 42% when combined with renewable and electrification strategies. The company commits to carbon neutral operations by 2025 and is a signatory to global Net Zero Carbon Buildings initiatives, advancing smart, efficient, and low‑emission building operations.
Bouygues Construction: Bouygues Construction focuses on sustainable building solutions that reduce lifecycle carbon impact and resource use. It has committed to cutting greenhouse gas emissions by 40% (Scope 1 & 2) and 30% (scope 3 intensity) by 2030 compared to 2021, while integrating low‑carbon materials and circular economy practices into its projects to support decarbonisation of buildings.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Johnson Controls International plc
- Bouygues Construction
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Tesla, Inc.
- Schneider Electric
- SunPower Corporation
- GreenTree Global.
- Turner Construction Company
- Siemens AG
- Skanska AB
Recent Industry Developments
In 2024, Bouygues Construction climate strategy set ambitious targets validated by the Science Based Targets initiative, including a 40% reduction in direct emissions and a 30% reduction in indirect emissions from its value chain compared with 2021, reflecting measurable commitments to decarbonise construction activities.
In 2024, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation reported several ZEB installations, including 1 small project under 300 m², 6 projects under 2,000 m², and 4 larger projects over 2,000 m², reflecting growing implementation of energy-saving solutions and on-site renewable integration.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 34.2 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 198.1 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 19.2% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Energy Source (Solar Energy, Wind Energy, Geothermal Energy, Others), By Technology (On-site Renewable Generation Systems, Energy Storage Systems (ESS), Smart Grid Integration, Energy Management Systems (EMS), Others), By Element Type (Lighting, Walls And Roofs, Heating, Ventilation, And Air Conditioning (HVAC) Systems, Others), By Building Type (Residential, Commercial) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italxy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Johnson Controls International plc, Bouygues Construction, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Tesla, Inc., Schneider Electric, SunPower Corporation, GreenTree Global., Turner Construction Company, Siemens AG, Skanska AB Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Zero Emission Buildings MarketPublished date: Dec 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Zero Emission Buildings MarketPublished date: Dec 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Johnson Controls International plc
- Bouygues Construction
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Tesla, Inc.
- Schneider Electric
- SunPower Corporation
- GreenTree Global.
- Turner Construction Company
- Siemens AG
- Skanska AB










