Global Tax Software Market Size, Share and Analysis Report By Component (Software, Services), By Deployment (Cloud-based, On-Premises), By Tax Type (Direct Tax, Indirect Tax), By End-User (Individual, Small Businesses, Large Enterprises, Accounting and Tax Firms, Other End-users), By Regional Analysis, Global Trends and Opportunity, Future Outlook By 2025-2034
- Published date: Dec. 2025
- Report ID: 172042
- Number of Pages: 275
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
- Report Overview
- Top Market Takeaways
- Role of Generative AI
- By Component
- By Deployment
- By Tax Type
- By End User
- Key Reasons for Adoption
- Benefits
- Usage
- Emerging Trends
- Growth Factors
- Key Market Segments
- Regional Analysis
- Opportunities
- Threats
- Key Challenges
- Competitive Analysis
- Future Outlook
- Recent Developments
- Report Scope
Report Overview
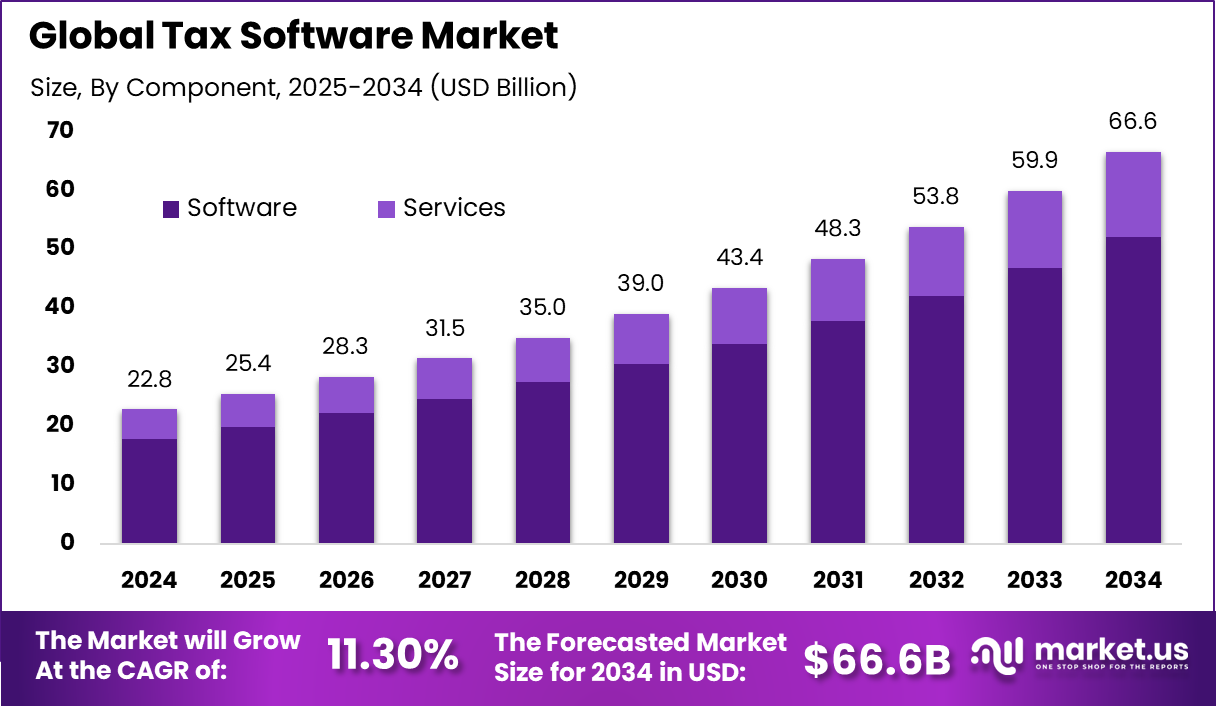
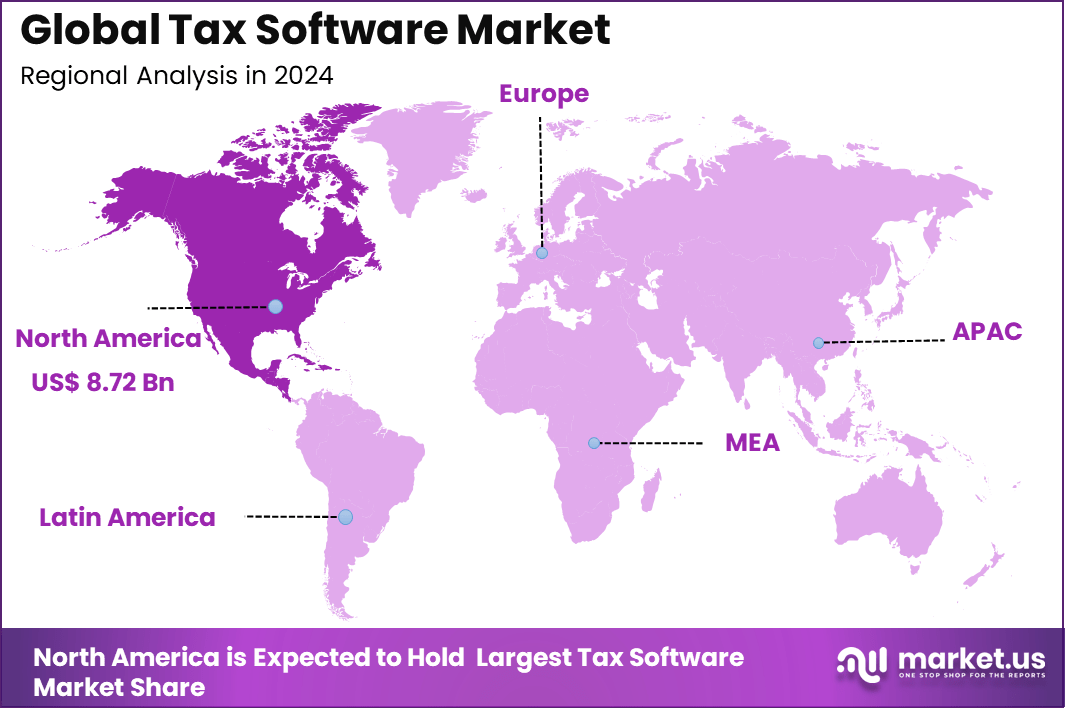
The Global Tax Software Market generated USD 22.8 billion in 2024 and is predicted to register growth from USD 25.4 billion in 2025 to about USD 66.6 billion by 2034, recording a CAGR of 11.30% throughout the forecast span. In 2024, North America held a dominan market position, capturing more than a 38.2% share, holding USD 8.72 Billion revenue.
The tax software market is experiencing notable transformation driven by widespread adoption of digital solutions that simplify complex tax compliance and reporting processes. Increasing regulatory complexity and the emphasis on automation have contributed to the integration of advanced technologies such as cloud computing and AI into tax platforms, enabling faster and more accurate tax operations for businesses and individual users.
The rising integration of digital systems reflects broader trends toward enhanced compliance and operational efficiency within financial workflows. This market is supported by increasing complexity of tax regulations, rising demand for automated financial workflows, and expanded use of digital tax reporting systems by government agencies. Enterprises and individual taxpayers prefer tax solutions that simplify compliance, lower risk, and integrate easily with accounting and financial systems.
The top driving factors for the tax software market are linked to growing regulatory complexity, increased focus on compliance, and the need for operational efficiency. Tax laws and reporting requirements change frequently, making it difficult for individuals and businesses to remain up to date. Automated tax software helps interpret evolving rules, apply deductions correctly, and reduce the risk of penalties associated with non-compliance.
Economic pressures and limited internal resources encourage organisations to adopt software that reduces manual workload and improves accuracy. The shift toward digital financial management and cloud-based solutions also supports tax software adoption by offering real-time updates and seamless integration with broader accounting systems.
Demand analysis shows that interest in tax software continues to rise as organisations and taxpayers seek scalable and cost-effective tools. Small and medium-sized enterprises, in particular, benefit from software that allows them to manage tax obligations without extensive in-house expertise. Large organisations rely on advanced tax solutions to handle multi-jurisdiction filings, transfer pricing issues, and consolidated reporting.
Top Market Takeaways
- By component, software took 78.3% of the tax software market, as it automates calculations and filings.
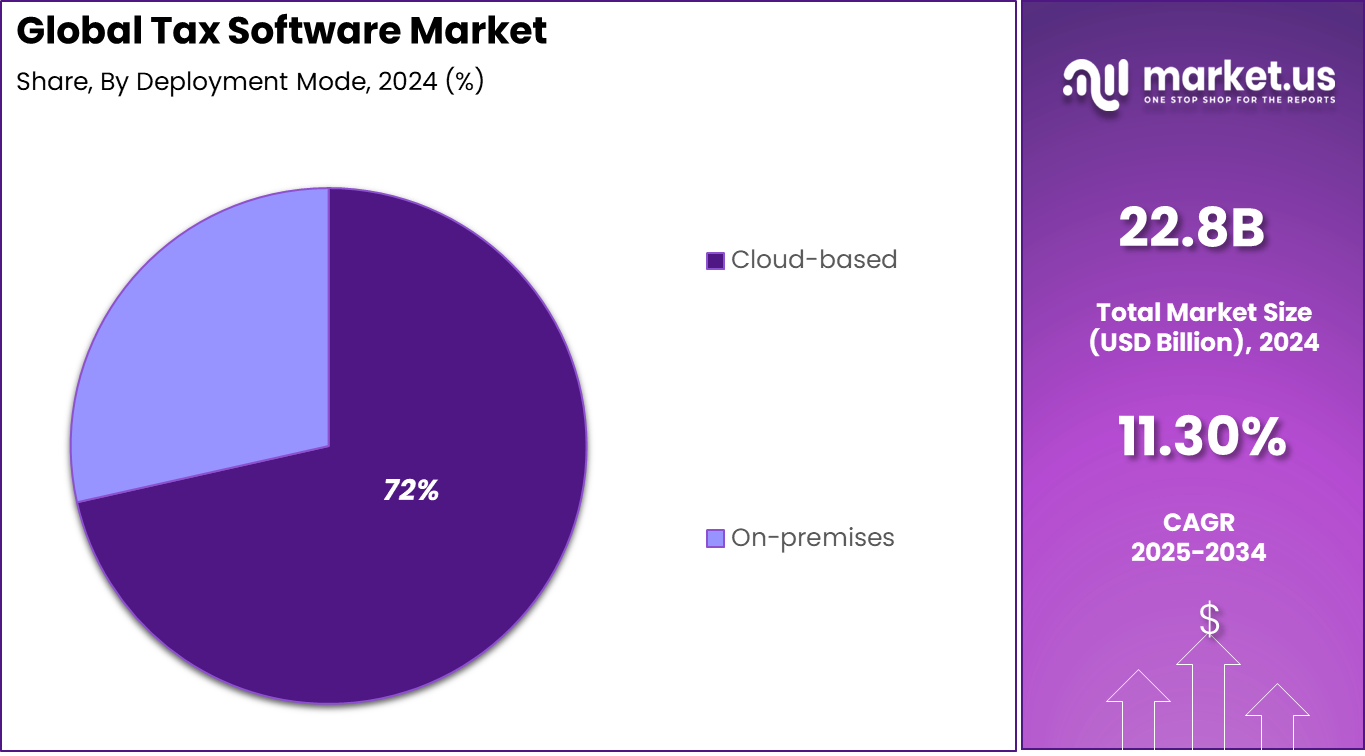
- By deployment, cloud-based SaaS solutions held 71.5% share, giving easy access and auto-updates.
- By tax type, indirect tax led with 56.4%, covering sales, VAT, and GST compliance.
- By end-user, large enterprises captured 53.81%, handling complex global tax needs.
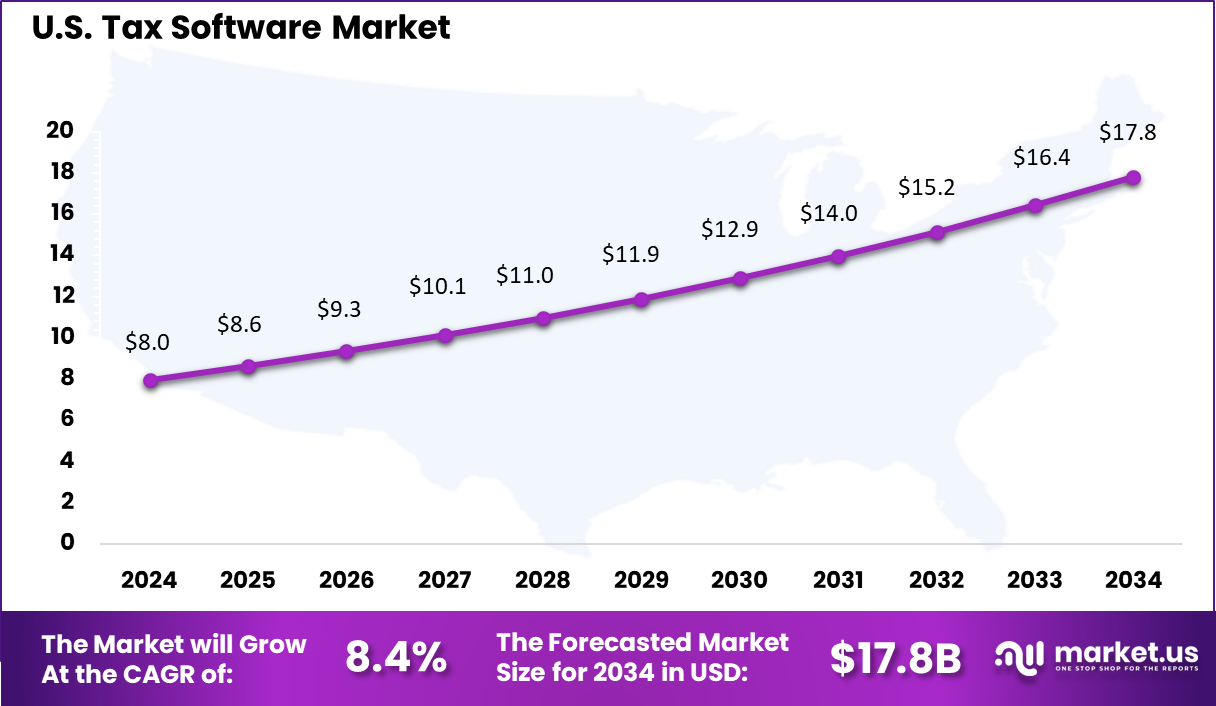
- North America had 38.2% of the global market, with the U.S. at USD 7.95 billion in 2025 and growing at a CAGR of 8.4%.
Role of Generative AI
Generative AI enhances tax software by automating data analysis, generating compliance reports, and interpreting complex regulations in real time. These tools process vast datasets to identify risks, simulate tax scenarios, and produce customized summaries of legal changes, reducing manual effort significantly. Professionals use them to streamline workflows, from document generation to predictive planning, marking a shift toward intelligent automation.
It also supports strategic functions like multi-jurisdictional filings and audit preparation by continuously monitoring global updates. It flags inconsistencies in financials and suggests optimizations, enabling faster decision-making. This integration positions AI as a core driver for efficiency gains in tax operations.
By Component
Software accounts for 78.3%, indicating that digital platforms are the core of tax management activities. These software solutions support tax calculation, filing, reporting, and compliance across multiple jurisdictions. Organizations rely on software to reduce manual errors and improve accuracy. Centralized systems also help manage complex tax rules.
The dominance of software is driven by increasing regulatory complexity and reporting requirements. Automated workflows help organizations meet deadlines efficiently. Software platforms also support updates when tax rules change. This ensures consistent compliance over time.
By Deployment
Cloud-based deployment holds 71.5%, reflecting strong preference for software delivered through online platforms. SaaS models allow users to access tax systems from multiple locations. This supports collaboration across finance and accounting teams. Cloud deployment also reduces the need for on-site infrastructure.
Adoption of cloud-based tax software is driven by ease of use and scalability. Organizations benefit from automatic updates and data backup. SaaS platforms also support integration with accounting and ERP systems. These factors continue to support widespread adoption.
By Tax Type
Indirect tax represents 56.4%, making it the leading tax type managed through tax software. Indirect taxes involve frequent transactions and complex rate structures. Software helps automate calculations across invoices and sales records. Accurate handling reduces compliance risk.
The growth of this segment is driven by increasing transaction volumes and regulatory oversight. Organizations rely on automation to manage changing tax rates. Tax software also supports audit readiness and reporting. This improves overall tax governance.
By End User
Large enterprises account for 53.81%, highlighting their significant use of tax software solutions. These organizations operate across multiple regions with complex tax obligations. Centralized software platforms help manage large data volumes. Consistent reporting is critical at this scale.
Adoption among large enterprises is driven by compliance and efficiency needs. Tax software helps standardize processes across business units. It also improves visibility into tax liabilities. Long-term operational control supports continued usage.
Key Reasons for Adoption
- The adoption of tax software is driven by the need to manage complex and frequently changing tax regulations.
- Manual tax calculations increase the risk of errors and compliance issues.
- Time constraints during filing periods encourage automation of tax processes.
- Digital recordkeeping requirements support the shift toward software-based solutions.
- Businesses seek standardized tax workflows across multiple jurisdictions.
Benefits
- Filing accuracy improves through automated calculations and built-in validation checks.
- Compliance risk is reduced by timely updates aligned with regulatory changes.
- Operational efficiency increases as repetitive tax tasks are automated.
- Audit readiness improves with organized and searchable tax records.
- Cost savings are achieved by reducing dependence on external tax consultants.
Usage
- Businesses use tax software to prepare and file corporate and indirect taxes.
- Individuals rely on these tools for personal income tax filing.
- Accounting firms use tax software to manage multiple client filings efficiently.
- Enterprises apply these solutions to handle multi-entity and cross-border taxation.
- Tax departments use the software for reporting, reconciliation, and compliance tracking.
Emerging Trends
Key Trend Description AI Auto Filing AI reads documents and files taxes accurately without manual errors. Cloud Real Time Cloud based tools update tax rules instantly and allow filing from anywhere. Blockchain Secure Tamper proof records reduce fraud risks and simplify audits. Mobile Tax Apps Mobile applications scan receipts and prepare tax returns quickly. Predictive Planning AI forecasts tax liabilities and identifies optimal saving opportunities. Growth Factors
Key Factors Description Complex Tax Rules Increasing regulations require advanced software to maintain compliance. Digital Shift Boom Businesses move online and adopt automated tax management tools. Remote Work Rise Accountants and finance teams file taxes remotely using cloud platforms. SME Tech Reach Small businesses adopt affordable tax software for regulatory compliance. Global Trade Grow Cross border transactions increase demand for multi country tax solutions. Key Market Segments
By Component
- Software
- Services
By Deployment
- Cloud-based
- On-Premises
By Tax Type
- Direct Tax
- Indirect Tax
By End-User
- Individual
- Small Businesses
- Large Enterprises
- Accounting and Tax Firms
- Other End-Users
Regional Analysis
North America accounted for 38.2% share, supported by high digital adoption in financial and accounting processes across individuals, small businesses, and large enterprises. Tax software has been widely used to manage complex tax rules, ensure accurate filings, and reduce compliance risks.
Demand has been driven by frequent regulatory updates, multi jurisdiction tax requirements, and the need for efficient reporting. The region’s strong penetration of cloud based financial tools has further supported adoption by simplifying access and updates.
The U.S. market reached USD 7.95 Bn and is projected to grow at an 8.4% CAGR, reflecting steady demand from individuals, professionals, and enterprises. Adoption has been driven by the complexity of federal, state, and local tax regulations, which require accurate and timely filing. Tax software has helped U.S. users reduce manual effort, improve calculation accuracy, and manage filing deadlines more effectively.
Key Regions and Countries
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Russia
- Netherlands
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Singapore
- Thailand
- Vietnam
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- South Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Rest of MEA
Opportunities
The Tax Software market offers strong opportunities as individuals and businesses look for easier ways to manage tax filing and compliance. Frequent changes in tax rules increase the need for software that can automate calculations and reduce manual errors.
Growing digital adoption by governments is encouraging electronic filing, which supports wider use of tax software. Small businesses and self employed professionals are also adopting these tools to save time and reduce dependence on external advisors.
Threats
The market faces threats related to data security and regulatory complexity. Tax software handles sensitive financial information, which makes it a target for cyber attacks. Any data breach can reduce trust and damage vendor reputation. Frequent regulatory changes also require continuous software updates, increasing development costs and operational pressure.
Another threat comes from strong competition and pricing pressure. Free or low cost tax filing options offered by governments or financial institutions can reduce demand for paid solutions. In some regions, low awareness of digital tax tools limits adoption. Complex user interfaces can also discourage non technical users, especially among older individuals.
Key Challenges
- Protecting sensitive financial and personal data
- Keeping software updated with changing tax laws
- Simplifying complex tax rules for users
- Integrating with accounting and payroll systems
- Managing user support during peak filing periods
Competitive Analysis
The competitive landscape of the tax software market is shaped by established tax preparation leaders, enterprise compliance providers, and cloud based accounting platforms. Intuit Inc., H&R Block Inc., Wolters Kluwer N.V., Thomson Reuters Corporation, Sage Group plc, and Xero Limited hold strong positions due to their wide user bases, trusted brand presence, and comprehensive tax and accounting capabilities.
These vendors serve both individual filers and businesses by offering integrated solutions that cover tax filing, reporting, and compliance across multiple jurisdictions. At the same time, companies such as Avalara Inc., Vertex Inc., Sovos Compliance LLC, ONESOURCE Indirect Tax, Stripe Tax through TaxJar, and TaxCloud compete strongly in indirect tax automation, helping businesses manage sales tax, VAT, and cross border compliance.
Competition is intensifying as demand grows for automation, accuracy, and real time compliance support. Vendors including TaxSlayer LLC, Drake Software LLC, TaxAct Inc., ClearTax, Canopy Tax Inc., Bluenose Analytics Inc., Quicko Infosoft Pvt Ltd, and IRIS Business Services Ltd. add pressure by focusing on affordability, ease of use, analytics, and regional tax expertise.
Top Key Players in the Market
- Intuit Inc.
- HandR Block Inc.
- Wolters Kluwer N.V.
- Thomson Reuters Corporation
- Sage Group plc
- Xero Limited
- Avalara Inc.
- Vertex Inc.
- Sovos Compliance LLC
- TaxSlayer LLC
- Drake Software LLC
- TaxAct Inc.
- Stripe Tax (TaxJar)
- ClearTax (Defmacro Software Pvt Ltd)
- Canopy Tax Inc.
- Bluenose Analytics Inc.
- ONESOURCE Indirect Tax
- Quicko Infosoft Pvt Ltd
- IRIS Business Services Ltd.
- TaxCloud
- Others
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the Tax Software market is expected to remain steady as individuals and businesses deal with complex tax rules and frequent regulatory updates. Tax software is being used to improve filing accuracy, reduce manual work, and ensure timely compliance across personal and corporate tax functions.
Growing digital reporting requirements from tax authorities are also supporting wider adoption. In the coming years, increased use of automation, cloud deployment, and data integration is likely to make tax preparation and compliance more efficient and reliable.
Recent Developments
- H&R Block Inc. focuses on expanding its small business offerings. In March 2025, it acquired Wave Financial for $398 million to enhance invoicing and accounting tools. The company also unveiled new features for the 2025 tax season in January. These steps strengthen its position in both consumer and professional tax services.
- In July 2025, Avalara obtained Platform Dematerialisation Partner accreditation from French tax authorities to support mandatory B2B e invoicing starting September 2026. This accreditation allows the company to combine indirect tax automation with certified e invoice exchange services, strengthening regulatory driven offerings and expanding its presence among French enterprises.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 22.8 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 66.6 Bn CAGR(2025-2034) 11.30% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue forecast, AI impact on Market trends, Share Insights, Company ranking, competitive landscape, Recent Developments, Market Dynamics and Emerging Trends Segments Covered By Component (Software, Services), By Deployment (Cloud-based, On-Premises), By Tax Type (Direct Tax, Indirect Tax), By End-User (Individual, Small Businesses, Large Enterprises, Accounting and Tax Firms, Other End-users) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Russia, Netherlands, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, New Zealand, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, Rest of Latin America; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – South Africa, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Intuit Inc., HandR Block Inc., Wolters Kluwer N.V., Thomson Reuters Corporation, Sage Group plc, Xero Limited, Avalara Inc., Vertex Inc., Sovos Compliance LLC, TaxSlayer LLC, Drake Software LLC, TaxAct Inc., Stripe Tax (TaxJar), ClearTax (Defmacro Software Pvt Ltd), Canopy Tax Inc., Bluenose Analytics Inc., ONESOURCE Indirect Tax, Quicko Infosoft Pvt Ltd, IRIS Business Services Ltd., TaxCloud, Others Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three license to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- Intuit Inc.
- HandR Block Inc.
- Wolters Kluwer N.V.
- Thomson Reuters Corporation
- Sage Group plc
- Xero Limited
- Avalara Inc.
- Vertex Inc.
- Sovos Compliance LLC
- TaxSlayer LLC
- Drake Software LLC
- TaxAct Inc.
- Stripe Tax (TaxJar)
- ClearTax (Defmacro Software Pvt Ltd)
- Canopy Tax Inc.
- Bluenose Analytics Inc.
- ONESOURCE Indirect Tax
- Quicko Infosoft Pvt Ltd
- IRIS Business Services Ltd.
- TaxCloud
- Others










