Global Static Var Compensator and STATCOM Market Size, Share, Growth Analysis By Type (Static Var Compensators, STATCOM), By End-User (Power Utilities, Industrial, Renewable Energy, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Nov 2025
- Report ID: 168276
- Number of Pages: 237
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
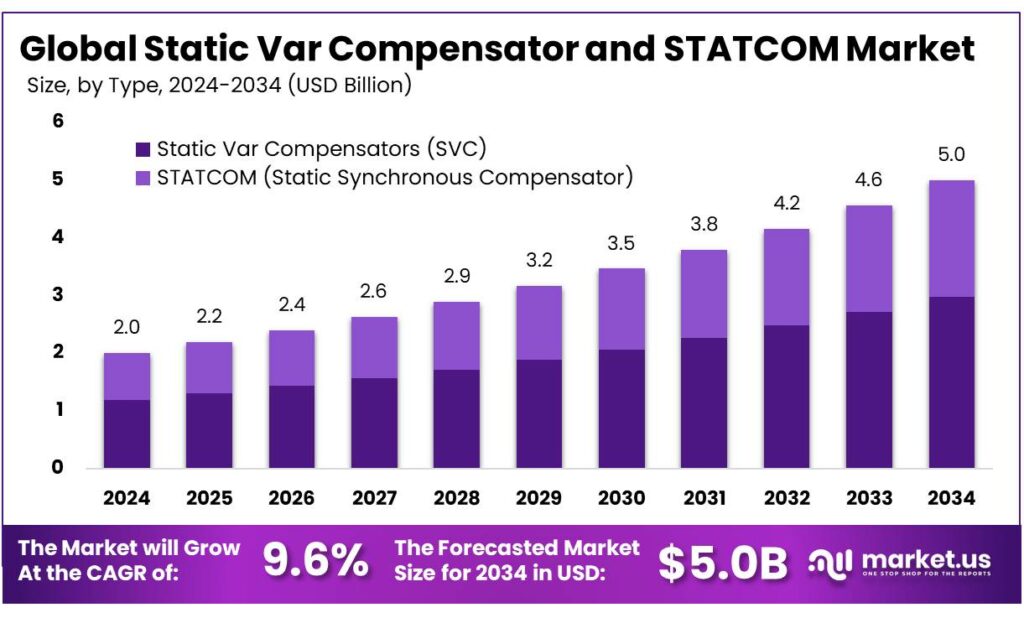
The Global Static Var Compensator and STATCOM Market size is expected to be worth around USD 5.0 Billion by 2034, from USD 2.0 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 9.6% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, North America held a dominan market position, capturing more than a 32.5% share, holding USD 3.2 Billion revenue.
Static Var Compensators (SVCs) and STATCOMs sit at the core of modern grid-stability strategies. SVCs are thyristor-based systems that inject or absorb reactive power on high-voltage AC networks to hold voltage within tight limits over long transmission lines. STATCOMs are the next generation: voltage-source-converter FACTS devices that provide very fast reactive current support and voltage regulation at the connection point.Together, they form a critical flexibility layer as grids become more dynamic and decentralized.
The industrial backdrop is a rapid build-out of transmission and distribution infrastructure. REN21 estimates global investment in power-grid infrastructure rose 5.3% in 2023 to about USD 310 billion, with the United States investing USD 86.5 billion and China USD 78.9 billion. An IEA grid study notes that dedicated transmission spending alone reached roughly USD 140 billion in 2023, within total energy investment of USD 2.8 trillion, of which USD 1.7 trillion went to clean energy.These figures signal sustained demand for high-performance reactive-power solutions in both new and upgraded lines.
The main structural driver for SVC and STATCOM adoption is the surge in variable renewables. IRENA reports global renewable power capacity reached about 4,448 GW in 2024, after a record annual addition of 585 GW. A separate analysis finds that clean energy met just over 40% of global electricity demand in 2024, with solar near 7%, wind above 8% and hydro around 14% of generation.
Policy commitments further underpin the opportunity. The IEA projects that by 2028 renewables will account for around 42% of global electricity generation, with wind and solar alone providing 25%. IRENA’s 1.5 °C roadmap suggests that annual renewable capacity additions would need to average roughly 1,066 GW per year from 2023–2050. Delivering and integrating this volume safely requires advanced voltage-control and congestion-management technologies, giving SVC and STATCOM suppliers a long growth runway in both mature and emerging grids.
National grid-investment programmes are already translating this need into concrete projects. In China, State Grid Corporation announced transmission investments of about USD 77 billion for 2023, and plans roughly USD 329 billion over the 2021–2025 14th Five-Year Plan; China Southern Power Grid adds around USD 99 billion, bringing total planned grid spending close to USD 442 billion. Such programmes typically bundle FACTS, SVC and STATCOM installations with new ultra-high-voltage corridors and regional interconnectors. Similar though smaller-scale incentives appear in US and EU grid-modernisation and resilience schemes.
Key Takeaways
- Static Var Compensator and STATCOM Market size is expected to be worth around USD 5.0 Billion by 2034, from USD 2.0 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 9.6%.
- Static Var Compensators (SVC) held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 59.8% share.
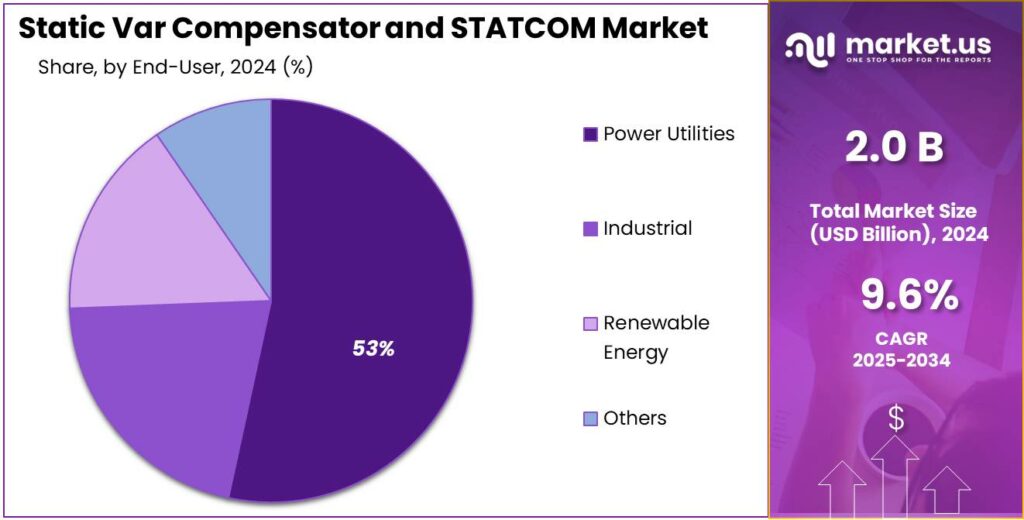
- Power Utilities held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 53.4% share.
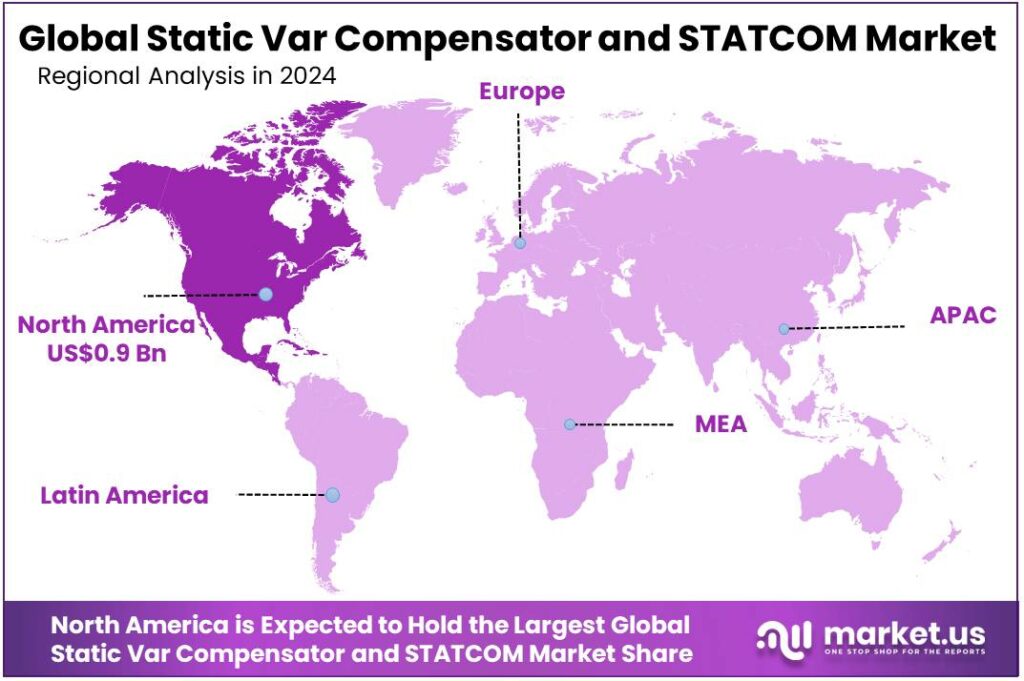
- North American region was observed to lead the Static Var Compensator (SVC) and STATCOM market, accounting for a dominant 45.90% share and an estimated regional value of USD 0.9 billion.
By Type Analysis
Static Var Compensators (SVC) dominate with 59.8% share driven by strong grid stability needs
In 2024, Static Var Compensators (SVC) held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 59.8% share. The strong uptake of SVC systems was supported by their widespread use in high-voltage transmission networks, where voltage stability and reactive power control continued to be critical.
The demand for SVC solutions was further strengthened by ongoing grid modernization programs across developing and developed regions, as utilities prioritized technologies capable of improving power quality and minimizing transmission losses. In 2025, the adoption of SVC systems is expected to remain steady as grid reinforcement projects expand and as power utilities focus on improving system reliability in response to rising electricity demand from industrial and renewable energy sources.
By End-User Analysis
Power utilities lead with 53.4% as they prioritized grid reliability and large-scale reactive power management.
In 2024, Power Utilities held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 53.4% share. This dominance was driven by continued investments in transmission and distribution networks where large-scale reactive power compensation was required to maintain voltage stability and reduce losses. Utility projects were favored because SVC and STATCOM installations were viewed as effective solutions for integrating renewable generation, managing peak loads, and improving overall system resilience.
Procurement was often influenced by long-term grid reinforcement plans and regulatory incentives that prioritized reliability and power quality. In 2025, utility demand was expected to remain substantial as network upgrade programs progressed and as the need to accommodate variable renewable output continued to shape investment decisions.
Key Market Segments
By Type
- Static Var Compensators (SVC)
- STATCOM (Static Synchronous Compensator)
By End-User
- Power Utilities
- Industrial
- Renewable Energy
- Others
Emerging Trends
Hybrid STATCOM–storage hubs and digital grids reshape VAR compensation
A clear latest trend for Static Var Compensators and STATCOMs is their shift from stand-alone voltage-control devices to part of hybrid “flexibility hubs” that combine power electronics, battery storage and digital control. Grid planners are no longer buying only reactive-power support; they are designing multi-service nodes that can manage voltage, congestion and short-term balancing in one place, especially around big renewable clusters and urban load pockets.
This change is closely tied to the boom in grid-scale batteries. REN21 reports that global battery storage capacity grew by 120% in 2023 to reach about 55.7 GW, with batteries accounting for 83% of all new utility-scale storage additions and pumped hydro still holding 179 GW of installed capacity. Source: REN21 – Renewables 2024 Global Status Report, Energy Storage module. As developers co-locate batteries with wind and solar plants, grid operators increasingly specify STATCOMs at the same node to provide fast fault current and voltage support that pure storage inverters alone may not deliver.
- According to REN21, global battery-storage investment rose 76.8% in 2023 to about USD 36.3 billion, with China investing USD 14.5 billion, the United States USD 9.6 billion and Germany USD 3.3 billion. Source: REN21 – Energy Storage module. These figures sit alongside rising grid investment and show that the money is moving toward flexible, electronics-rich infrastructure. For SVC and STATCOM suppliers, that means more projects where their systems are integrated from day one into storage plants, rather than added later as corrective measures.
Policy is reinforcing the trend. REN21 notes that by the end of 2023, 43 jurisdictions had specific energy-storage policies and 11 had explicit battery-storage targets. Source: REN21 – Energy Storage module. In parallel, the IEA’s Electricity Grids and Secure Energy Transitions report highlights that system-flexibility needs are set to double between 2022 and 2030, with at least 3,000 GW of renewable projects waiting in grid-connection queues, making grids a bottleneck. Source: IEA – Electricity Grids and Secure Energy Transitions.
Drivers
Rapid renewable growth and grid decarbonisation push SVC and STATCOM demand
A major driving force behind the Static Var Compensator (SVC) and STATCOM market is the fast growth of renewable electricity and the pressure to keep grids stable while cutting emissions. Wind and solar plants inject power that changes quickly with weather, which makes voltage control and reactive power support more critical at transmission and large distribution levels.
According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), the world added about 473 GW of new renewable power capacity in 2023, raising total renewable capacity by 13.9%, with renewables making up 86% of all new power additions that year. IRENA’s 2025 update shows another 585 GW added in 2024, taking global renewable capacity to 4,448 GW and accounting for over 90% of total power expansion. Such volumes force grid operators to invest in dynamic VAR devices so that voltage remains within safe limits as renewable output swings.
Policy commitments reinforce this trend. At COP28, more than 130 governments, including the EU, agreed to work towards tripling global installed renewable capacity to at least 11,000 GW by 2030. This creates a long pipeline of new renewable projects that must be connected to grids that were mostly designed around synchronous thermal plants, not inverter-based generation.
At the same time, grid investment is rising, but still needs to grow. The International Energy Agency (IEA) estimates that about USD 400 billion per year is currently spent on electricity grids worldwide, compared with roughly USD 1 trillion on generation assets. In its Net Zero by 2050 pathway, the IEA says annual clean-energy investment must more than triple to around USD 4 trillion by 2030
Restraints
High upfront cost and slow grid investment approvals limit SVC and STATCOM adoption
One major restraining factor for the Static Var Compensator (SVC) and STATCOM market is the high upfront capital cost, combined with slow grid-investment approvals. These systems are technically advanced and custom-engineered for each grid location, which makes utilities cautious, especially in cost-sensitive or regulated markets.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) explains that global electricity grid spending is currently around USD 400 billion per year, while it needs to rise to nearly USD 600 billion per year by 2030 just to keep pace with clean-energy expansion and electrification goals. When grid investment falls short, utilities often delay or scale down advanced technologies like STATCOMs and SVCs, choosing lower-cost or short-term solutions instead. This directly slows deployment, even when technical need is clear.
Cost pressure is strongest in developing economies. According to the World Bank, more than 70% of electricity network investment growth required this decade must occur in emerging and developing countries, yet many utilities in these regions face weak balance sheets and limited access to low-cost capital.
Another challenge is long approval and procurement timelines. Grid-scale projects involving FACTS devices often require environmental clearances, land permits, and multi-year regulatory reviews. The IEA notes that average transmission projects in advanced economies now take 5–10 years from planning to commissioning, even before adding power-electronics systems.
Opportunity
Digital-load growth and grid expansion open new roles for SVCs and STATCOMs
A big growth opportunity for Static Var Compensators and STATCOMs comes from how fast electricity demand is changing shape, not just growing in size. Electric vehicles, AI-heavy data centres and electrified industries are all clustering around specific nodes on the grid. That creates local voltage stress and reactive-power needs that traditional equipment cannot handle alone.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) estimates that global electricity demand will grow by about 3.3% in 2025 and 3.7% in 2026, among the highest rates seen in the last decade. Within that total, new loads are especially disruptive. In its Global EV Outlook 2025, the IEA reports that electric vehicles used around 180 TWh of electricity in 2024 and could reach roughly 780 TWh by 2030, more than a four-fold jump. Every fast-charging corridor or urban depot connected to the high-voltage network becomes a candidate site for STATCOM-based voltage support.
Data centres add another layer. The IEA’s Energy and AI analysis projects that total electricity use by data centres could rise to about 945 TWh by 2030, nearly double today and close to 3% of global electricity demand. Many of these facilities are concentrated in a few regions, which makes local voltage and flicker control critical. Utilities have started to specify dynamic VAR systems in grid-connection agreements for large clusters of cloud or AI infrastructure.
All of this sits on top of a historic wave of grid investment. The IEA notes that to stay on track for national climate targets, annual grid spending must nearly double to over USD 600 billion per year by 2030, with a strong focus on modern, digital distribution networks. A complementary assessment by the Global Renewables Alliance suggests cumulative grid investment of about USD 21 trillion by 2050, with yearly outlays exceeding USD 700 billion by 2030 to meet climate goals.
Regional Insights
North America dominates with 45.90% share (USD 0.9 Bn)
In 2024, the North American region was observed to lead the Static Var Compensator (SVC) and STATCOM market, accounting for a dominant 45.90% share and an estimated regional value of USD 0.9 billion. Market leadership in the region can be attributed to a concentrated programme of grid modernization, increased transmission investments, and utility-scale renewable integration projects that required rapid reactive power support and dynamic voltage control.
Regional incentives and tighter grid-code requirements accelerated replacement and upgrade cycles for older compensation equipment, and the rollout of HVDC interconnections further stimulated demand for fast-acting reactive power solutions. Project pipeline data showed that utility-scale wind and solar tie-ins, together with electrification of transport and industry, contributed to near-term capacity additions and sustained aftermarket service revenues. Supply chain resilience and local engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) capacity supported faster project execution times for large transmission projects, thereby reinforcing North America’s leading position.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Siemens AG is recognized for its comprehensive portfolio of grid technologies, including Static Var Compensators and STATCOM solutions tailored to transmission and utility needs. The company’s offerings are positioned toward high-voltage applications and are supported by local engineering and global manufacturing capabilities. Lifecycle services, system integration, and digital monitoring are provided to enhance asset reliability. Product development emphasizes modular design, scalability, and compliance with evolving grid codes to support renewable generation and stricter stability requirements, and extended warranty options globally.
General Electric provides Static Var Compensator and STATCOM systems engineered for flexible AC transmission and reactive power management across utility networks. Emphasis is placed on robust engineering, advanced power electronics, and adaptation to diverse grid environments. Predictive maintenance, digital diagnostics, and system-level consulting are offered to improve uptime and performance. Solutions are designed to facilitate renewable integration, manage transient events, and enable rapid response to voltage fluctuations while being supported by local project execution teams and comprehensive aftersales support worldwide.
Mitsubishi Electric supplies STATCOM and SVC solutions for large transmission networks and heavy industrial customers. Focus is placed on high-reliability power electronics, compact modular designs, and rigorous testing that meet strict grid standards. System engineering, local project management, and long-term service agreements are provided to ensure operational continuity. Products are targeted at scenarios requiring rapid dynamic reactive support, such as renewable tie-lines and HVDC converter stations, and are backed by regional manufacturing and spare parts logistics and extended field training.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Siemens AG
- General Electric (GE)
- Schneider Electric
- Mitsubishi Electric
- ABB Ltd.
- Eaton Corporation
- Toshiba Corporation
Recent Industry Developments
In 2024, Siemens (through its energy business Siemens Energy) continued to strengthen its position in grid-stabilization with reactive-power solutions like STATCOMs and SVC-PLUS systems. In its financial results for fiscal 2024, the company delivered overall revenue of €34.5 billion.
In 2024, ABB Ltd. continued to stand out as a global technology leader working to modernize electricity grids through reactive-power solutions such as STATCOM and SVC systems. Its overall revenue reached USD 32.9 billion in FY 2024, with a solid income-from-operations of USD 5,071 million (margin ~ 15.4%).
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 2.0 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 5.0 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 9.6% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Type (Static Var Compensators, STATCOM), By End-User (Power Utilities, Industrial, Renewable Energy, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Siemens AG, General Electric (GE), Schneider Electric, Mitsubishi Electric, ABB Ltd., Eaton Corporation, Toshiba Corporation Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Static Var Compensator and STATCOM MarketPublished date: Nov 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Static Var Compensator and STATCOM MarketPublished date: Nov 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Siemens AG
- General Electric (GE)
- Schneider Electric
- Mitsubishi Electric
- ABB Ltd.
- Eaton Corporation
- Toshiba Corporation










