Global Solar Battery Charger Market Size, Share Analysis Report By Product Type (Portable, Stationary), By Technology (Photovoltaic (PV) Solar Battery Chargers, Thin-Film Solar Battery Chargers, Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) Battery Chargers), By Application (Residential, Commercial, Industrial) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends, and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Dec 2025
- Report ID: 168687
- Number of Pages: 347
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
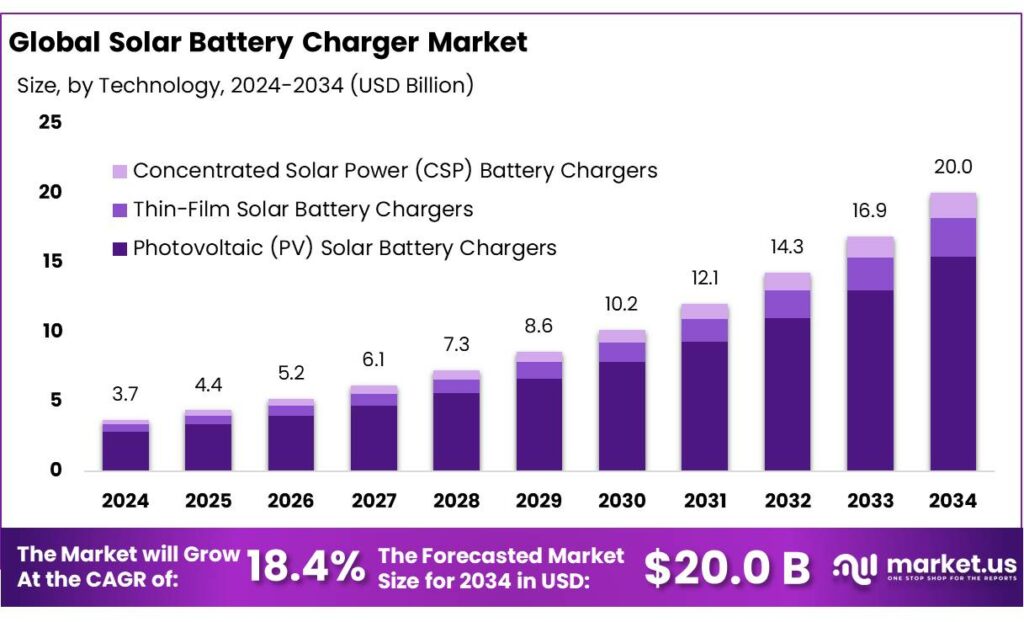
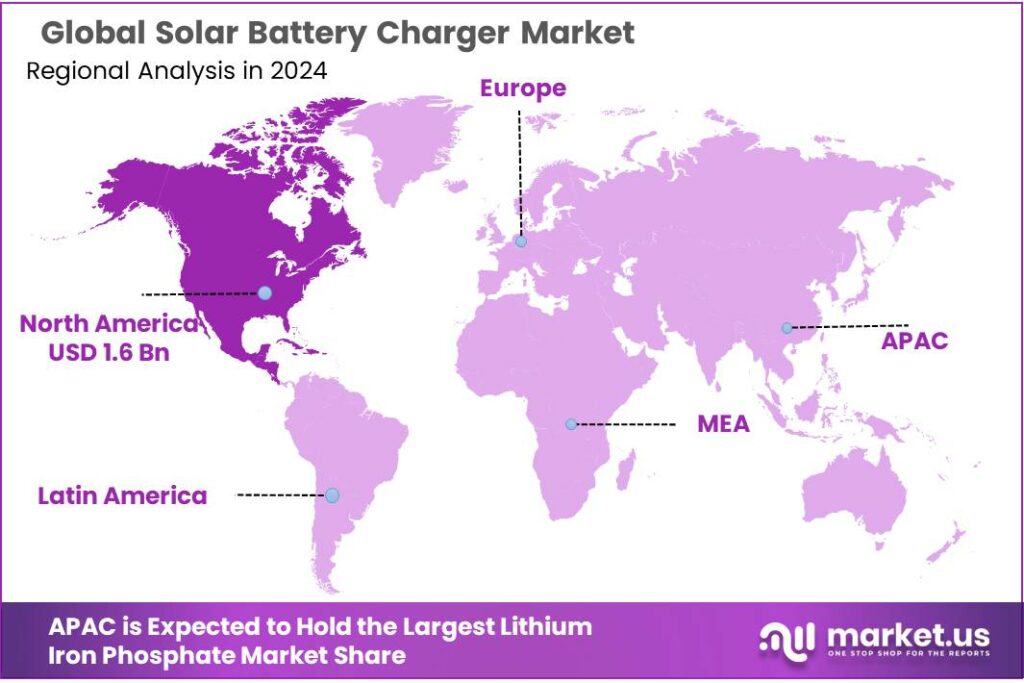
The Global Solar Battery Charger Market size is expected to be worth around USD 20.0 Billion by 2034, from USD 3.7 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 18.4% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 45.8% share, holding USD 1.6 Billion revenue.
Solar battery chargers sit at the intersection of solar PV, storage, and power electronics. They convert DC power from small modules or rooftop systems into controlled charging for lead-acid, lithium-ion or LiFePO₄ batteries used in consumer devices, off-grid solar home systems, telecom sites, vehicles and emerging portable power stations. As solar deployment accelerates and users expect reliable power anywhere, these chargers are becoming critical components of distributed and off-grid energy ecosystems.
- According to IEA PVPS, global solar PV cumulative capacity reached about 1.6 TW in 2023, up from roughly 1.2 TW in 2022, with around 407–446 GW of new systems commissioned. IRENA reports that renewables capacity grew by 585 GW in 2024, and solar alone added about 452 GW, taking solar PV capacity close to 1.865 TW. Each new rooftop or small C&I system typically integrates one or more charge controllers or hybrid inverter-chargers, expanding the addressable market for solar battery charger manufacturers.
Off-grid and rural electrification programs are another major demand pillar. The World Bank’s Lighting Global / IFC initiative estimates that off-grid solar solutions could deliver first-time electricity access to nearly 400 million, people by 2030, while GOGLA projects around 624 million people will rely on Tier-1+ off-grid solar solutions by that date. Every lantern, solar home system, or DC mini-grid requires integrated charge control, driving volume demand for low-cost, robust solar battery chargers designed for harsh environments and variable battery chemistries.
Residential rooftop and behind-the-meter storage trends further strengthen the industrial scenario. In the IEA Net Zero scenario, households relying on rooftop solar PV rise from about 25 million. today to more than 100 million by 2030. India’s Grid Connected Rooftop Solar Programme targets 40 GW of rooftop capacity, with the deadline extended to 2026, supported by subsidies of up to 40% for households under schemes such as PM Surya Ghar. In the United States, the federal Residential Clean Energy Credit allows homeowners to claim 30% of qualified solar and battery system costs through 2032. These policies directly stimulate sales of residential hybrid inverters and battery chargers that manage PV generation, storage, and backup loads.
- Policy-driven agricultural and micro-grid schemes are also important. India’s PM-KUSUM program aims to add about 34,800 MW, of solar capacity by March 2026, including 1.4 million, standalone solar pumps and 3.5 million grid-connected pumps. Each pump or feeder-level system uses dedicated solar charge controllers, creating sustained demand for higher-current industrial-grade chargers. Similar rural electrification and agricultural solar programs across Africa, Southeast Asia, and Latin America underpin a growing OEM market for local assemblers and global power-electronics suppliers.
Key Takeaways
- Solar Battery Charger Market size is expected to be worth around USD 20.0 Billion by 2034, from USD 3.7 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 18.4%.
- Portable held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 69.3% share of the solar battery charger market.
- Photovoltaic (PV) Solar Battery Chargers held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 77.2% share.
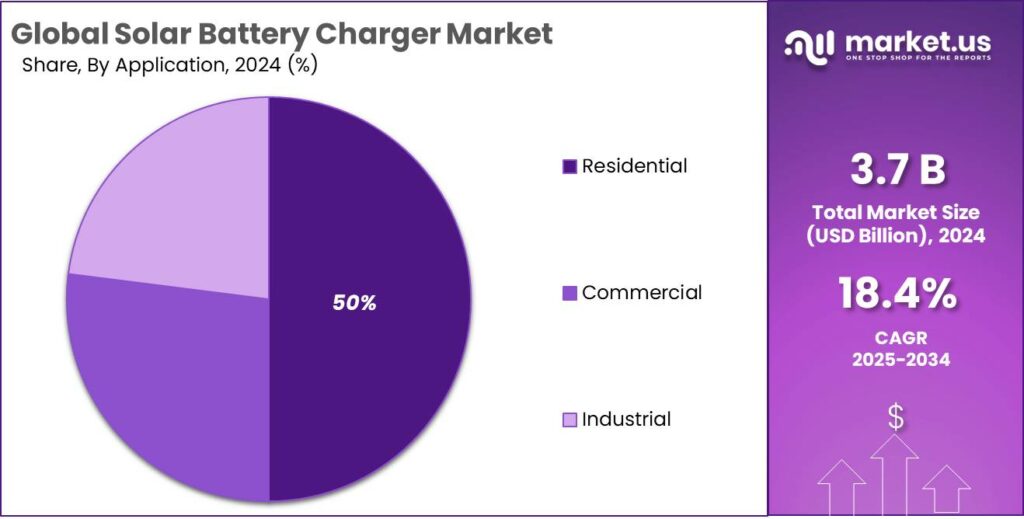
- Residential held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 49.9% share of the solar battery charger market.
- North American region accounted for a substantial 45.8% share of the global solar battery charger market, corresponding to approximately USD 1.6 billion.
By Product Type Analysis
Portable solar chargers lead with 69.3% share thanks to convenience and broad consumer adoption
In 2024, Portable held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 69.3% share of the solar battery charger market. This leadership can be attributed to the convenience of portable units, their suitability for off-grid and outdoor use, and strong uptake by individual consumers and small businesses. Portable chargers are commonly chosen because they offer simple installation, plug-and-play operation and lower upfront costs compared with fixed systems, which makes them attractive for camping, mobile work sites and backup power for small electronics.
In 2025, the portable segment is expected to remain the primary category as product designs are refined for higher efficiency and lighter weight, and as distribution through retail and online channels keeps expanding. The reliance on portability and ease of use will continue to underpin demand for this product type.
By Technology Analysis
Photovoltaic (PV) solar battery chargers dominate with 77.2% share due to efficiency and versatility
In 2024, Photovoltaic (PV) Solar Battery Chargers held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 77.2% share. This dominance is driven by the efficiency, reliability, and wide applicability of PV technology for converting sunlight into usable energy for battery charging. PV chargers are preferred in both residential and outdoor applications because they provide consistent performance, require minimal maintenance, and can be integrated with various battery types. In 2025, the PV segment is expected to maintain its leading position as technological improvements continue to enhance energy conversion efficiency and reduce costs, reinforcing its role as the primary choice for solar-powered battery solutions.
By Application Analysis
Residential applications lead with 49.9% share due to growing household adoption of solar solutions
In 2024, Residential held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 49.9% share of the solar battery charger market. The strong uptake is driven by increasing household interest in clean energy, off-grid backup solutions, and energy cost savings. Residential users prefer solar battery chargers for powering small appliances, mobile devices, and home backup systems, benefiting from simple installation and low maintenance. In 2025, demand in the residential segment is expected to continue growing as awareness of renewable energy solutions rises and technology improvements enhance efficiency and reliability, maintaining its leading position in the market.
Key Market Segments
By Product Type
- Portable
- Stationary
By Technology
- Photovoltaic (PV) Solar Battery Chargers
- Thin-Film Solar Battery Chargers
- Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) Battery Chargers
By Application
- Residential
- Commercial
- Industrial
Emerging Trends
Shift from Simple Lighting to Smart Food-Focused Solar Systems
A clear latest trend in solar battery chargers is their move from simple phone-charging or lantern systems to smart, food-focused solar solutions for farms, cold rooms and rural businesses. Instead of only powering light bulbs, today’s solar kits run water pumps, milk chillers, walk-in cold rooms and small processing equipment, all of which depend on reliable solar battery chargers to balance panels, batteries and growing loads.
Food and agriculture needs are driving this change. FAO warns that global food demand could rise by around 60% by 2050, putting heavy pressure on land, water and energy systems. At the same time, a joint UNEP–FAO report shows that lack of effective refrigeration causes the loss of about 526 million tonnes of food, or roughly 12% of total food production, every year. That lost food could feed hundreds of millions of people. This gap creates a huge push for solar-powered cooling and processing, and each of those solutions needs robust battery chargers at its heart.
- Renewable energy in agriculture is growing quickly. REN21 notes that the share of renewable energy in agriculture, forestry and fisheries reached 15.4% in 2021, up from 10.8% in 2011, and that around 55% of this renewable energy use is in the form of electricity. As of 2022, global capacity of off-grid solar water pumps for agriculture reached about 1,165 MW, with India alone accounting for roughly 1,083 MW, Bangladesh 49 MW and Ethiopia 17 MW. Every one of these pumps is paired with a solar charge controller or charger that keeps the system stable as sunlight and water demand change through the day.
Government policies in the water–energy–food nexus are reinforcing this trend. REN21’s agriculture factsheets highlight that policymakers are increasingly focusing on electrification of agricultural activities, including solar irrigation systems, as part of their climate and rural-development strategies. In India, for example, the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy reported that by October 2022, more than 152,000 stand-alone solar pumps had been installed under the PM-KUSUM programme, supported by central and state subsidies.
Drivers
Rising Off-Grid Electrification and Affordable Energy Access Needs
One of the strongest driving factors for the solar battery charger market is the rapid push for off-grid and decentralized electrification, especially in rural and low-income regions. According to the World Bank, nearly 685 million people globally still lacked access to electricity as of 2022, with over 75% of them living in Sub-Saharan Africa . In many of these regions, extending central grid infrastructure remains slow and costly, making standalone solar systems combined with battery chargers the most practical solution.
Solar battery chargers play a vital role in these systems by regulating power from photovoltaic panels to safely store energy in batteries. Organizations such as GOGLA, the global association for the off-grid solar industry, report that off-grid solar companies sold over 9.5 million solar products worldwide in 2023, ranging from solar lanterns to solar home systems with battery storage . Each of these systems depends on reliable and efficient charging electronics, directly increasing demand for solar battery chargers.
Government-backed rural electrification programs are accelerating this trend. For example, India’s PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana, launched in 2024, aims to equip 10 million households with rooftop solar systems, offering subsidies covering up to 40% of system costs for lower-capacity installations . While these systems are grid-connected, most include battery backup due to frequent power outages, creating strong pull-through demand for residential solar battery chargers and hybrid charge controllers.
- The government targets deployment of about 3.5 million solar-powered irrigation pumps by 2026 . These pumps typically operate with dedicated solar battery charging units to manage variable solar output and ensure consistent water supply. Similar programs exist across Africa, where the African Development Bank estimates that decentralized renewable energy solutions could serve 140 million people by 2030 through mini-grids and standalone systems .
The International Finance Corporation (IFC) committed more than USD 700 million in cumulative investments to off-grid solar projects across Asia and Africa by 2023, focusing on solar-plus-storage solutions for households and small businesses . Battery chargers are a core hardware component in these projects, as storage is essential for providing power during nighttime and cloudy periods.
Restraints
High Up-Front Cost and Affordability Barriers
Solar-battery systems, which include not just the charger but also panels, batteries, wiring and often installation, require a relatively big initial investment. According to a recent sector review by World Bank and ESMAP, a leading barrier for adoption of off-grid solar in many developing regions is exactly “low affordability.” People living on modest incomes — often in rural or remote communities — struggle to pay the upfront cost, even if the long-term benefits are substantial.
Even though battery storage costs have fallen significantly over the past decade (for example, lithium-ion battery prices dropped nearly 80% since 2010), the total cost of a full solar + charger + battery setup remains out of reach for many low-income households. For these households, such upfront costs often represent a substantial portion of their annual disposable income, making them hesitant or unable to adopt solar systems despite needing reliable electricity access.
Moreover, off-grid solar systems also require maintenance and periodic battery replacement — costs that are nontrivial for economically vulnerable communities. As noted in a broader review of hybrid renewable energy and storage deployment challenges, weaknesses such as capacity to maintain and service battery-based systems, and limited availability of spare parts in remote areas, act as real-world barriers to adoption and long-term reliability.
Even in places where governments and international agencies support electrification efforts — such as through subsidies, grants, or micro-financing — the high upfront capital still discourages many potential users. The need for affordable financing models, subsidies or pay-as-you-go schemes becomes critical to bridge the gap between cost and demand. Unfortunately, such support mechanisms are often insufficient, unevenly distributed, or poorly implemented, which constrains growth.
Opportunity
Solar-Powered Cold Chains and Food Systems as a Big Growth Wave
A powerful growth opportunity for solar battery chargers lies in solar-powered cold chains and food systems. Today, food loss is still shockingly high. The FAO and UNEP estimate that around 13.2% of food is lost in the supply chain after harvest, while another 19% is wasted at retail, food service and household level. In total, studies for FAO show that roughly 30% of cereals and 40–50% of root crops, fruits and vegetables never reach consumers. A huge part of this loss happens because farmers and traders lack reliable, affordable refrigeration and power.
A joint FAO–UNEP cold-chain report found that ineffective refrigeration leads to a loss of about 526 million tonnes of food every year, equal to around 12% of global production, and in 2017 less than 45% of food needing refrigeration was actually refrigerated. At the same time, UNEP notes that food loss and waste are responsible for roughly 8–10% of global greenhouse-gas emissions. These figures show how big the prize is if we can power more cold rooms, milk chillers, fish storage and village-level processing with clean energy.
- Across agriculture, forestry and fisheries, REN21 reports that renewables already supplied about 15.4% of energy use in 2021, up from 10.8% in 2011. Within this, electricity is crucial: around 55% of renewable energy used in agriculture came from electricity, and by 2022 there were roughly 1,165 MW of off-grid solar water pumps, with India alone accounting for about 1,083 MW. All of these systems depend on robust solar charge controllers and battery chargers to manage variable sunlight and keep pumps and auxiliary loads running.
Government and international initiatives are now pushing this direction. UNEP’s Cold Chain Database and Modelling initiative, run with the Global Food Cold Chain Council, helps countries map their cold-chain gaps and plan investment in efficient, climate-friendly systems that reduce food loss and emissions. Many of these solutions will be off-grid or grid-interactive solar systems that rely on advanced battery chargers, including MPPT-based controllers and hybrid charger-inverters. Development banks and climate funds increasingly see cold chains as a “triple win”: lower food loss, higher farmer income, and lower diesel use.
Regional Insights
North America leads with 45.8% share, valued at USD 1.6 billion in 2024 thanks to high adoption of solar charging devices and strong renewable interest
In 2024, the North American region accounted for a substantial 45.8% share of the global solar battery charger market, corresponding to approximately USD 1.6 billion in regional market value. This dominance is supported by widespread consumer awareness, established distribution networks, and strong demand for portable and residential‑use solar chargers — especially in the United States and Canada, where outdoor recreation, emergency preparedness, and sustainable energy adoption remain high.
The high share in 2024 was also driven by adoption across a variety of use cases — from camping, travel and off-grid power needs to backup charging solutions for small electronics and remote work. Manufacturers targeting North America have particularly emphasized portability, convenience, and compatibility with common consumer devices, which aligns with user preferences for plug‑and‑play solar charging solutions.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Anker Innovations is a leading consumer electronics brand that offers portable solar battery chargers alongside power banks and charging accessories. In 2024, the company recorded revenue: USD 1.8 billion, with employees: ~3,200 globally. Anker’s solar chargers are designed for portability, reliability, and compatibility with multiple devices, targeting outdoor enthusiasts and emergency-preparedness users.
Goal Zero specializes in solar energy solutions, including portable solar panels, battery chargers, and complete off-grid kits. In 2024, the company achieved estimated revenue: USD 230 million, serving outdoor, residential, and emergency-preparedness markets. Goal Zero focuses on user-friendly, durable solar battery chargers with integrated battery storage and modular expansion, supporting portability for camping, travel, and disaster scenarios.
RavPower, a subsidiary of Sunvalley Group, is known for high-performance charging solutions, including solar battery chargers and power banks. In 2024, estimated revenue reached USD 145 million, with employees: ~650. RavPower’s solar chargers are designed for fast energy conversion, portability, and broad device compatibility.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Anker
- Goal Zero
- RavPower
- EcoFlow
- Jackery
- Voltaic Systems
- YOLK
- Solar Technology International
- Letsolar
- Hanergy
Recent Industry Developments
In 2024, Anker Innovations reported a total revenue of ¥24.71 billion CNY (≈ USD 3.43 billion), growing 41.1% compared with the previous year. Among its business segments, the charging and energy‑storage division — which includes solar battery charger and renewable‑energy solutions — recorded ¥12.67 billion CNY in sales, accounting for roughly half of total revenue.
In 2024 Jackery, had sold over 5 million units worldwide (since 2018), a milestone that highlights its wide consumer acceptance and global reach.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 3.7 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 20.0 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 18.4% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Product Type (Portable, Stationary), By Technology (Photovoltaic (PV) Solar Battery Chargers, Thin-Film Solar Battery Chargers, Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) Battery Chargers), By Application (Residential, Commercial, Industrial) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Anker, Goal Zero, RavPower, EcoFlow, Jackery, Voltaic Systems, YOLK, Solar Technology International, Letsolar, Hanergy Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Solar Battery Charger MarketPublished date: Dec 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Solar Battery Charger MarketPublished date: Dec 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Anker
- Goal Zero
- RavPower
- EcoFlow
- Jackery
- Voltaic Systems
- YOLK
- Solar Technology International
- Letsolar
- Hanergy










