Global Sodium Propionate Market Size, Share Analysis Report By Grade (Food-grade, Pharmaceutical-grade), By Form (Powder, Liquid), By Function (Preservatives, pH Regulators, Flavor Enhancers, Mold Inhibitors, Antimicrobial Agents, Others), By End-use (Pharmaceuticals, Food And Beverages, Agriculture, Cosmetics And Personal Care, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends, and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Oct 2025
- Report ID: 161566
- Number of Pages: 241
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
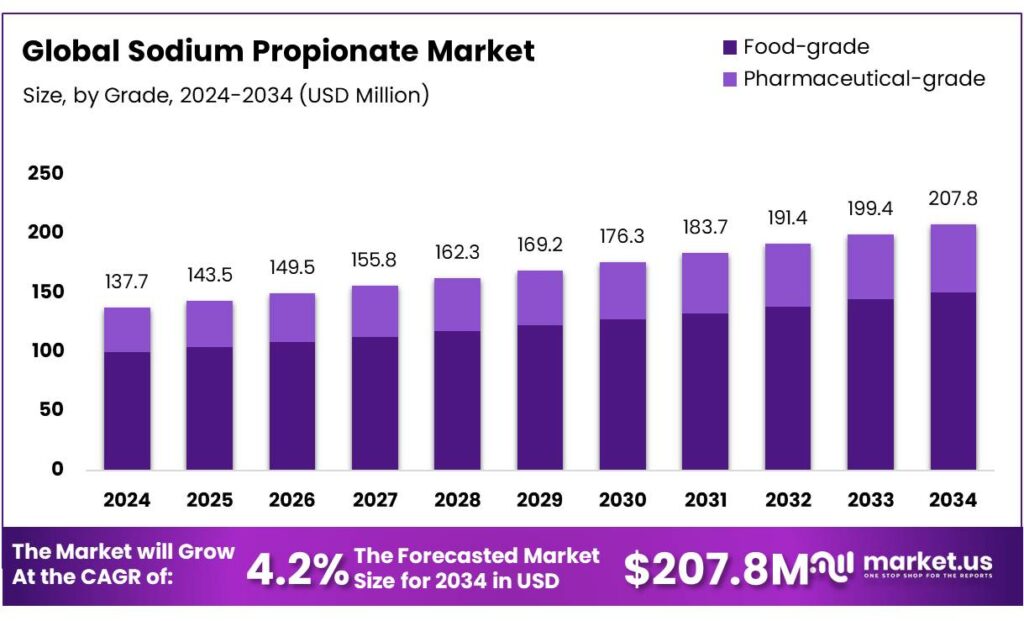
The Global Sodium Propionate Market size is expected to be worth around USD 207.8 Million by 2034, from USD 137.7 Million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 4.2% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024 North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 38.9% share, holding USD 53.5 Million in revenue.
Sodium propionate (E281; INS 281) is a widely used antimicrobial preservative for bakery and dairy systems, valued for inhibiting mold growth while preserving dough performance and crumb quality. In the United States it is affirmed as GRAS and permitted “with no limitation other than current good manufacturing practice” for use as an antimicrobial and flavoring agent, anchoring regulatory certainty for formulators across breads, rolls, buns, and related products.
Industrial demand is tied closely to bakery throughput and the broader cereals complex. The FAO estimates 2024 global wheat production at 787 million tonnes, underscoring a large and relatively steady flour-to-bread pipeline in which propionates are standard shelf-life tools. USDA’s Foreign Agricultural Service places 2023/24 wheat output at 792.3 million tonnes, reinforcing the scale of applications where preservative efficacy translates into reduced waste and longer distribution windows.
Policy and standards trends continue to support safe, effective use. FDA’s bakery standards explicitly allow calcium propionate without the general 0.25-parts-per-100-parts-flour limit for certain calcium salts—an approach consistent with the longstanding view of propionates’ technological need in bread molds. Australia–New Zealand’s risk assessments similarly note permissibility of propionates across breads, bakery and flour products, helping regional producers align with international practice.
Cost dynamics for propionate producers are sensitive to energy markets because propionic acid synthesis and downstream neutralization are energy-intensive. In the EU, industrial natural gas prices eased to €0.0616/kWh in H1 2024, before a modest uptick to €0.0624/kWh in H2 2024, supporting margin repair across chemical value chains. The IEA similarly documents the trajectory of 2020–2024 industrial gas prices in top EU markets, a key variable for operating rates at acid and salt plants.
Key Takeaways
- Sodium Propionate Market size is expected to be worth around USD 207.8 Million by 2034, from USD 137.7 Million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 4.2%.
- Food-grade held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 72.4% share of the global sodium propionate market.
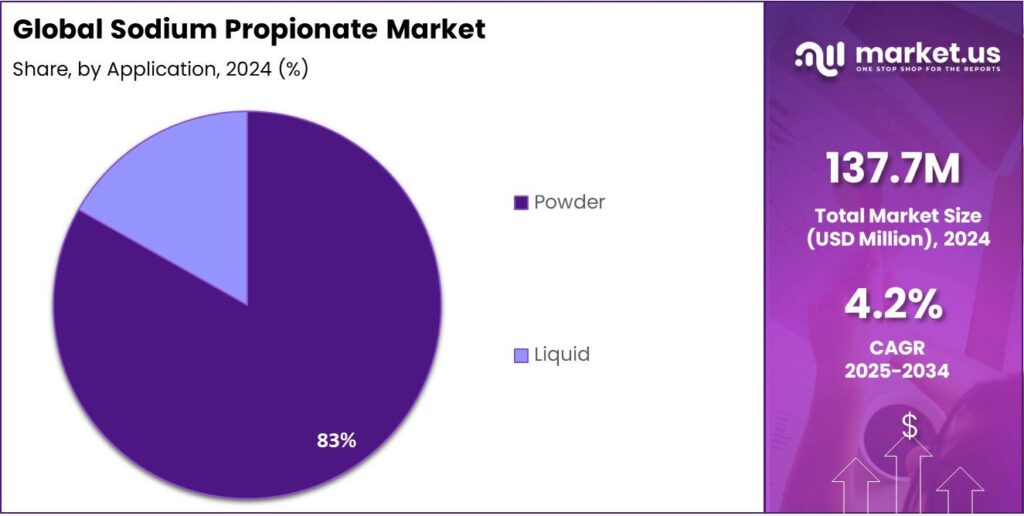
- Powder held a dominant market position, capturing more than an 83.2% share of the global sodium propionate market.
- Preservatives held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 44.8% share of the global sodium propionate market.
- Food & Beverages held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 56.4% share of the global sodium propionate market
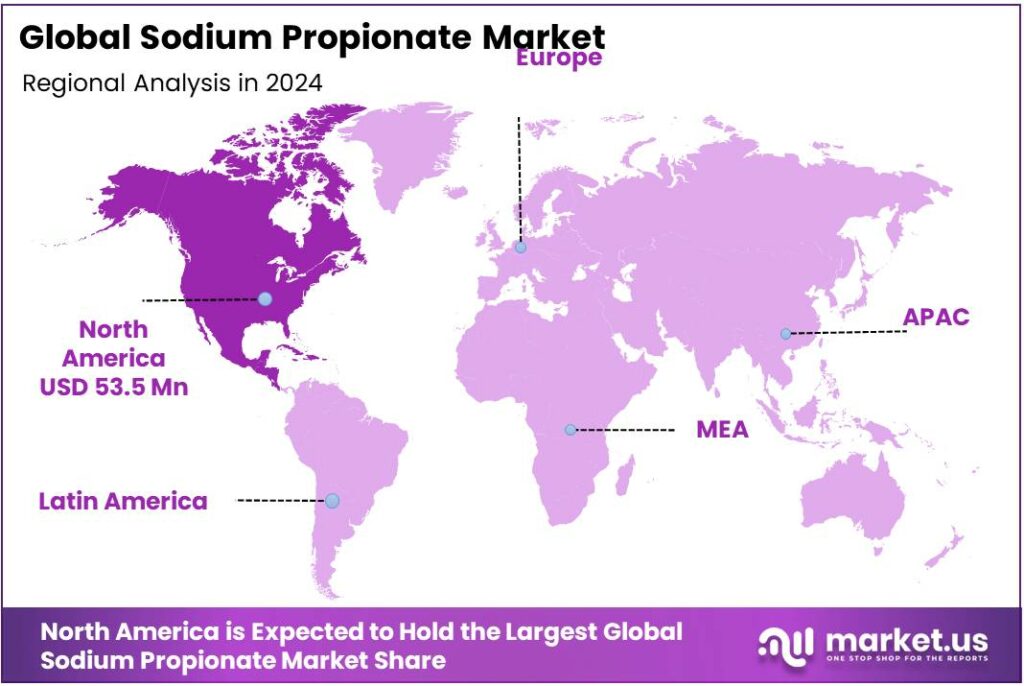
- North America held a dominant position in the global sodium propionate market, capturing approximately 38.9%, equating to a market value of $53.5 million.
By Grade Analysis
Food‑grade dominates with 72.4% share due to its essential role in safe and long-lasting food products.
In 2024, Food-grade held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 72.4% share of the global sodium propionate market by grade. This strong position is driven by the widespread use of sodium propionate as a preservative in bakery products, dairy items, and processed foods, where it effectively prevents mold and bacterial growth, ensuring extended shelf life and product safety. The preference for food-grade quality reflects increasing regulatory compliance and consumer demand for safe, high-purity additives.
The food-grade segment continued to see robust adoption as processed food consumption grew across North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific. Manufacturers prioritized food-grade sodium propionate due to its ease of handling, consistent performance, and approval by international food safety authorities, which minimizes risk in large-scale production.
By Form Analysis
Powder Form dominates with 83.2% owing to its high stability and ease of use in food and feed applications.
In 2024, Powder held a dominant market position, capturing more than an 83.2% share of the global sodium propionate market by form. The dominance of the powder form is mainly attributed to its superior solubility, long shelf life, and easy blending properties, which make it ideal for applications in bakery, dairy, and animal feed industries. Its ability to mix evenly in dry formulations has made it the preferred choice among food processors and feed manufacturers worldwide.
Demand for powdered sodium propionate continued to grow steadily, supported by increased production of packaged and processed foods that require moisture-resistant preservatives. Powdered sodium propionate offers easier handling, storage, and transportation compared to liquid forms, which further strengthens its market position. The consistent performance and lower contamination risks associated with the powder variant have encouraged large-scale adoption, especially in developing economies experiencing industrial expansion in food manufacturing and livestock nutrition.
By Function Analysis
Preservatives lead the market with 44.8% share, driven by growing demand for extended shelf life in food and feed products.
In 2024, Preservatives held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 44.8% share of the global sodium propionate market by function. This leadership is primarily attributed to the compound’s proven effectiveness in preventing mold and bacterial growth in baked goods, dairy items, and processed meats. Sodium propionate’s strong antimicrobial properties make it a trusted preservative for ensuring food safety and maintaining product freshness during extended storage and distribution.
The preservative function continued to expand as food manufacturers increasingly prioritized clean and safe production processes that comply with international safety standards. The rising consumption of packaged and ready-to-eat foods across Asia-Pacific, Europe, and North America reinforced the demand for reliable preservatives, strengthening sodium propionate’s position in this segment. The compound’s versatility also supports its use in animal feed preservation, further broadening its industrial relevance.
By End-use Analysis
Food & Beverages lead the market with 56.4% share owing to rising demand for safe and long-lasting packaged food products.
In 2024, Food & Beverages held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 56.4% share of the global sodium propionate market by end-use. This dominance is largely due to the compound’s widespread application as a preservative in bakery products, dairy items, confectionery, and processed foods. Sodium propionate effectively prevents the growth of mold and bacteria, helping manufacturers extend product shelf life and maintain quality during storage and transport—key factors in the growing packaged food sector.
The Food & Beverages segment continued to strengthen its position, supported by the steady rise in processed food consumption and increased emphasis on food safety regulations worldwide. As urbanization accelerates and consumer lifestyles become more convenience-oriented, the demand for bakery and ready-to-eat items has surged, directly contributing to higher usage of sodium propionate in food formulations. The compound’s approval by global food safety authorities has also encouraged its use across international food supply chains.
Key Market Segments
By Grade
- Food-grade
- Pharmaceutical-grade
By Form
- Powder
- Liquid
By Function
- Preservatives
- pH Regulators
- Flavor Enhancers
- Mold Inhibitors
- Antimicrobial Agents
- Others
By End-use
- Pharmaceuticals
- Food & Beverages
- Agriculture
- Cosmetics & Personal Care
- Others
Emerging Trends
Clean Label And Additive Transparency Becoming Mainstream
One of the clearest trends reshaping the sodium propionate space today is how strongly consumers are demanding clean labels and ingredient transparency. The push isn’t small or niche anymore — it’s fast becoming normal, meaning that sodium propionate, typically listed on ingredient panels as “sodium propionate” or “E 281,” faces fresh pressures to adapt, blend, or be hidden behind more consumer-friendly narratives.
In fact, surveys show a vast majority of consumers feel strongly about clean labels. For example, a 2024 Clean Label Insights Study found that 81% of shoppers consider it important to purchase foods labeled “clean label.” Similarly, a U.S. consumer survey revealed that 83% of consumers are already familiar with or have heard of the term “clean label.”
Beyond the marketing angle, regulators are shining more light on additive disclosures and enhancing requirements for consumer understanding. In the EU, Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 requires additives to be declared clearly, often by name or E-number, so nothing can be hidden from labels. That regulatory clarity makes additives exposed to shopper scrutiny.
At the same time, public institutions and sustainability goals continue to reinforce the narrative of reducing waste and improving food system transparency. The UNEP Food Waste Index 2024 reports that about 1.05 billion tonnes of food were wasted in 2022, i.e. 19% of the food available to consumers.
These attitudes are influencing how new food products are launched. In global product development data, nearly one in three new products now carry some sort of clean label claim (e.g. “no additives/preservatives,” “clean ingredients,” etc.). Among these claims, the “no additives or preservatives” label is one of the most prominent, used in about 15% of the new product launches.
Drivers
The Urgent Need to Reduce Food Waste
One of the most compelling forces behind the demand for sodium propionate is the global push to limit food waste and spoilage. When you think of bakeries, packaged breads, tortillas or buns sitting on shelves, every extra day they stay fresh means fewer discarded loaves—and that’s where preservatives like sodium propionate are critical.
- According to the UNEP Food Waste Index Report 2024, about 1.05 billion tonnes of food was wasted in 2022—roughly 19% of all food made available to consumers. Households alone accounted for 60 percent of that waste, while 28% was attributed to food service and 12% to retail.
Food companies prefer solutions that align with sustainability goals, so if a preservative helps meet waste-reduction targets, it becomes more attractive. The economics of waste reduction often outweigh the added cost: for many retailers and bakeries, discarding spoiled goods is a direct hit to margins.
Bakery chain produces 100,000 loaves a day, even a 1 % reduction in spoilage thanks to better preservation could save 1,000 loaves per day. Over a year, that’s hundreds of thousands of loaves, not only reducing waste but also recovering cost and margin.
That policy backdrop directly increases the importance of efficient, approved preservatives. Sodium propionate is effective against molds and certain bacteria in moist, baked goods, allowing products to last longer under standard distribution and storage conditions. Each additional day of shelf life can translate into lower spoilage rates, fewer returns, and lower waste losses—making the investment in the additive more compelling, especially in regions with weaker cold chains.
Restraints
The Rising “Clean Label” Pressure from Consumers
In recent years, one of the strongest headwinds against the broader adoption of sodium propionate has come from the consumer shift toward “clean label” foods. In plain terms, many people now prefer products with short, natural-sounding ingredient lists rather than chemical names or numbers—especially when it comes to preservatives. That desire is being felt by food companies everywhere, pushing them to look for alternatives or reduce synthetic additives.
Across the globe, studies suggest this is no niche trend. For instance, a global clean label report indicates that nearly one in two (≈ 50%) consumers recently bought more fresh or less processed foods, and many are actively reducing products with ingredients perceived as “artificial,” such as synthetic preservatives. Because sodium propionate, although approved and safe at regulated doses, still registers as a chemical preservative on labels (often as “E 281” or “sodium propionate”), it becomes a target in a consumer-driven backlash.
Regulators, too, are watching labels more closely. In the European Union, for instance, the Regulation (EC) 1333/2008 strictly controls how additives can be used and demands transparency in labeling. If public sentiment shifts, enforcement or further restrictions could follow in some markets. Already, food labeling laws in many countries force manufacturers to list preservatives by name or E-number. That means unwillingness among consumers to see “E 281” or “sodium propionate” can influence buying behavior directly.
Major retailers are committing to reduce additives. For example, Walmart in the U.S. announced plans to remove synthetic food colors and 30 other additives (including some preservatives) from its private-label products by January 2027. Though not all of those are sodium propionate specifically, the move signals a wider push.
Opportunity
Expansion via Food Waste Reduction & Shelf-Life Extension
One of the biggest growth opportunities for sodium propionate lies in its role as a practical tool in the fight against food loss and waste. In many parts of the world, food spoilage is a structural problem—products, especially high-moisture items like bread, pastries, and fresh baked goods, can spoil or mold before reaching consumers. If sodium propionate can be integrated in a way that safely stretches shelf life, it becomes part of a solution rather than just another additive.
Globally, the scale of the food waste problem is staggering. The UNEP Food Waste Index Report 2024 estimates that 1.05 billion tonnes of food were wasted in 2022, representing 19% of food available to consumers, in addition to losses earlier in the supply chain. Meanwhile, FAO and related studies suggest that 14% of food is lost between harvest and retail, and 17% is wasted in retail, food service and by consumers. Because food waste also contributes 8-10% of global greenhouse gas emissions, there is increasing policy, consumer, and corporate pressure to reduce it.
Governments and public agencies are acting. For example, the EU has committed to SDG Target 12.3, which aims to halve per‐capita food waste in retail and consumer sectors by 2030. The U.S. EPA has a National Strategy for Reducing Food Loss and Waste, targeting prevention and better recycling of organics as part of climate and sustainability goals. National food donation and loss-waste strategies are being adopted in several countries to incentivize better handling, storage, and preservation of surplus food.
From a business perspective, even modest improvements in shelf life translate into meaningful gains. Suppose a bakery chain distributing fresh bread across a wide region manages to extend shelf life by one extra day across 100,000 units—that could result in tens of thousands fewer spoiled loaves each week. Over a year, the cost savings, improved margins, and reduced waste disposal burdens add up.
Regional Insights
North America leads with 38.9% share, valued at $53.5 million in 2024, driven by high demand in food preservation and animal feed sectors.
In 2024, North America held a dominant position in the global sodium propionate market, capturing approximately 38.9%, equating to a market value of $53.5 million. This significant share is primarily attributed to the robust demand for sodium propionate in the food and beverage industry, where it serves as an effective preservative to extend shelf life and maintain product quality. The increasing consumption of convenience foods, including baked goods and processed meats, has further propelled the need for such preservatives.
Additionally, the animal feed sector in North America has been a substantial contributor to the market’s expansion. Sodium propionate is utilized to inhibit mold growth in feed, thereby enhancing its stability and nutritional value. The growing awareness among livestock producers about the benefits of using preservatives in feed has led to increased adoption of sodium propionate.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Prathista, based in India, positions itself strongly in food ingredients, API (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients), and feed supplements, producing additives via advanced fermentation and sustainable practices. It offers natural food ingredient solutions that promote clean-label formulations and improved shelf life, reflecting growing global demand. The company holds certifications aligning with WHO and FSSAI guidelines. In 2025 it expanded its fermentation capacity (announced capacity ~135,000 L) to meet rising demand in food preservation and livestock feed systems.
Krishna Chemicals, headquartered in Ahmedabad, India, supplies food-grade sodium propionate (≥98–99% purity, CAS 137-40-6) and related propionates. Their product is a fine white/off-white powder with low impurities (iron, heavy metals etc.), moisture <5%, and conforms to typical preservative quality specifications. The firm is active domestically and exports, offering standard packaging (25 kg) and timely delivery. Its positioning is strong in price-sensitive markets and local supply chains where regulatory compliance (food safety) is required.
Macco Organiques, based in Canada with operations in the Czech Republic, is a longstanding manufacturer of high-purity inorganic and organic mineral salts, including sodium propionate. The company operates under GMP Q7, FSSC 22000 food safety system, with FDA and Health Canada registrations. It supplies dust-free, food- and pharmaceutical-grade propionates in powder/granular forms widely used in infant nutrition, IV/dialysis solutions, and food preservation. Their facility supports large production volumes, exports to over 80 countries, and strong reputation in quality, regulatory compliance, and customer service.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Prathista Industries Ltd.
- Jainex Specialty Chemicals
- Dr. Paul Lohmann GmbH KG
- Krishna Chemicals
- Macco Organiques Inc.
- Titan Biotech Ltd
- Foodchem International Corporation
- Rishi Chemicals Work Pvt. Ltd.
- Niacet Corporation
Recent Industry Developments
In 2024, the firm expanded its fermentation capacity to 135,000 litres, enhancing the ability to produce organic and fermented salts for food-grade applications.
In 2024 Macco Organiques Inc, offered sodium propionate in FCC-grade agglomerate form, characterized by a purity range of 99.0% to 100.5% on an anhydrous basis, with a maximum water content of 1.0%. The product complies with stringent specifications, including a pH range of 8.0 to 10.5, and low levels of impurities such as iron.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 137.7 Mn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 207.8 Mn CAGR (2025-2034) 4.2% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Grade (Food-grade, Pharmaceutical-grade), By Form (Powder, Liquid), By Function (Preservatives, pH Regulators, Flavor Enhancers, Mold Inhibitors, Antimicrobial Agents, Others), By End-use (Pharmaceuticals, Food And Beverages, Agriculture, Cosmetics And Personal Care, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Prathista Industries Ltd., Jainex Specialty Chemicals, Dr. Paul Lohmann GmbH KG, Krishna Chemicals, Macco Organiques Inc., Titan Biotech Ltd, Foodchem International Corporation, Rishi Chemicals Work Pvt. Ltd., Niacet Corporation Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- Prathista Industries Ltd.
- Jainex Specialty Chemicals
- Dr. Paul Lohmann GmbH KG
- Krishna Chemicals
- Macco Organiques Inc.
- Titan Biotech Ltd
- Foodchem International Corporation
- Rishi Chemicals Work Pvt. Ltd.
- Niacet Corporation










