Global Grapeseed Oil Market Size, Share Analysis Report By Extraction Process (Mechanically By Pressing, Chemically Extracted, Others), By Application (Food Industry, Personal Care And Cosmetics, Supplements And Healthcare, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Dec 2025
- Report ID: 170404
- Number of Pages: 364
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
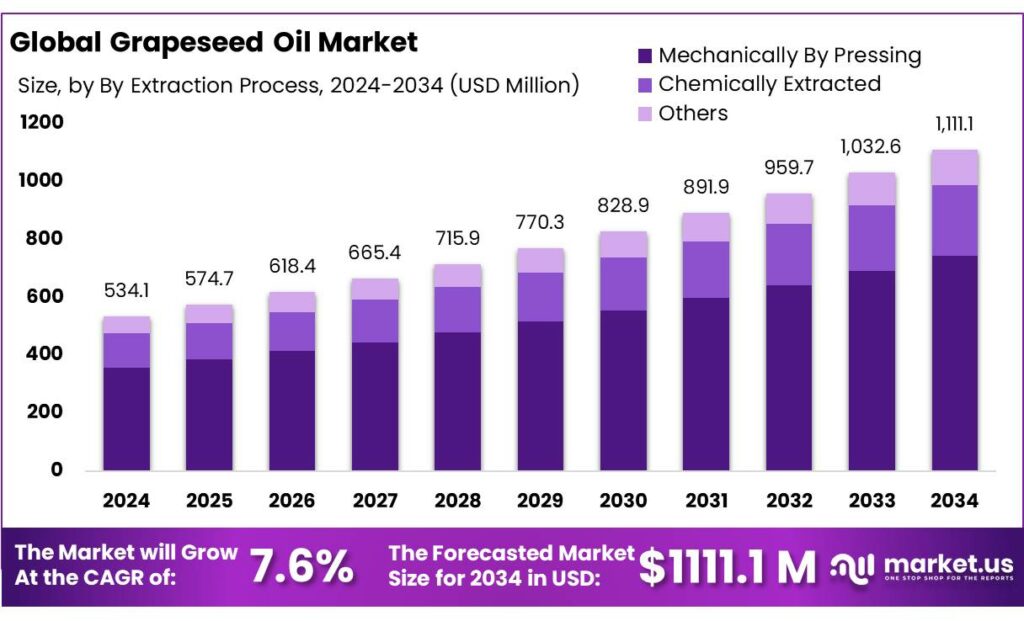
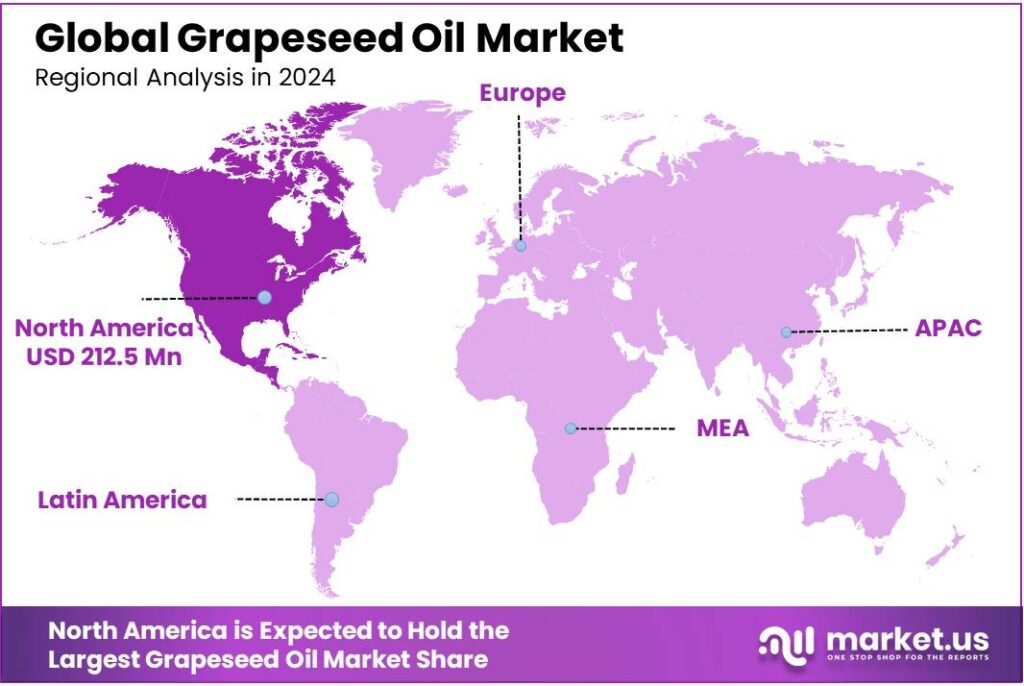
The Global Grapeseed Oil Market size is expected to be worth around USD 1111.1 Million by 2034, from USD 532.1 Million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 7.6% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 39.80% share, holding USD 212.5 Million revenue.
Grapeseed oil is a specialty edible oil produced by pressing grape seeds—an input that mainly comes from the wine value chain. That linkage matters because the available raw material follows vineyard area, grape crush volumes, and winery by-product handling economics. The International Organisation of Vine and Wine (OIV) estimates global vineyard surface area at 7.1 million hectares in 2024, while global wine production in 2024 is estimated at 225.8 million hectolitres—described as the lowest level in over 60 years—reflecting climate volatility and disease pressure that ripple into downstream by-products.
From an industrial scenario standpoint, the vine-and-wine sector remains the biggest upstream anchor. The International Organisation of Vine and Wine (OIV) estimated global wine production at 225.8 million hectolitres in 2024, down 4.8% versus the prior year, while global wine consumption was estimated at 214.2 million hectolitres in 2024 (down 3.3%). These climate- and demand-linked swings matter because they influence how much grape marc and seeds flow into secondary processing streams such as oil extraction.
Demand drivers are split between functionality and positioning. From a formulation standpoint, grapeseed oil is naturally high in polyunsaturated fats; one peer-reviewed summary reports 61–73% linoleic acid, 14–25% oleic acid, and overall 85–90% unsaturated fatty acids. This supports use in salad oils, dressings, and blended oils, while also fitting cosmetic emollient applications where light texture and “plant-derived” sourcing are valued.
At the same time, broader vegetable-oil market signals influence pricing and substitution: FAO’s monitoring has shown notable volatility in vegetable oil markets, and in February 2025 FAO-reported vegetable-oil prices were up 29.1% year-on-year in a widely cited market update—an environment that often pushes brands to diversify oil inputs and optimize blends.
- In the U.S., government statistics show how volatile the raw-material pipeline can be at the regional level. USDA’s California Final Grape Crush Report recorded 1,970,643 tons of grapes crushed in 2023. A separate USDA Pacific Region press release reported the 2024 California crush at 2,918,158 tons, down 25.2% from the 2023 crush of 3,899,631 tons. For grapeseed oil producers, this kind of shift can affect contracting, seed pricing, and plant utilization.
Key Takeaways
- Grapeseed Oil Market size is expected to be worth around USD 1111.1 Million by 2034, from USD 532.1 Million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 7.6%.
- Mechanically By Pressing held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 67.2% share.
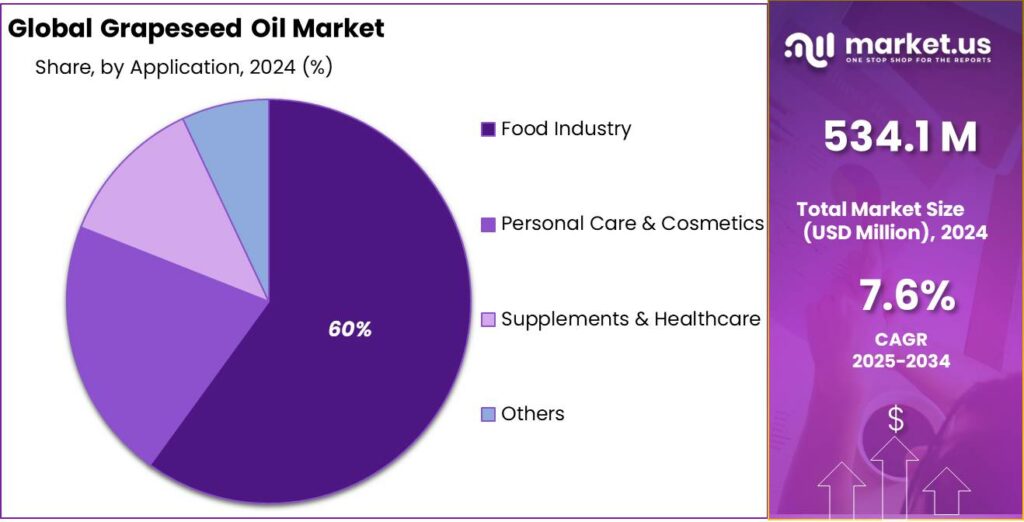
- Food Industry held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 59.8% share in the grapeseed oil market.
- North America accounted for a substantial portion of global grapeseed oil consumption, representing a 39.80% share and a market volume of 212.5 million.
By Extraction Process Analysis
Mechanical pressing leads with 67.2% driven by natural processing and clean oil quality
In 2024, Mechanically By Pressing held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 67.2% share in the global grapeseed oil market, supported by strong demand for naturally extracted and chemical-free edible oils. This extraction method was widely preferred as it preserves the oil’s light taste, nutritional profile, and antioxidant content without the use of solvents. In 2024, food manufacturers and household consumers showed higher trust in mechanically pressed grapeseed oil due to its clean-label appeal and suitability for cooking, salad dressings, and cosmetic applications.
Looking into 2025, this segment is expected to maintain its leading position as health awareness continues to rise and consumers increasingly favor minimally processed oils, reinforcing mechanical pressing as the preferred extraction process within the market.
By Application Analysis
Food industry dominates with 59.8% due to wide use in everyday cooking and food processing
In 2024, Food Industry held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 59.8% share in the grapeseed oil market, driven by its broad use across household cooking and commercial food preparation. Grapeseed oil was widely used for frying, baking, salad dressings, and ready-to-eat food products due to its high smoke point and neutral flavor. In 2024, food processors favored grapeseed oil for its stability and ability to enhance product shelf life without altering taste.
Moving into 2025, demand from the food industry is expected to remain strong as consumers continue to prefer light, plant-based oils with perceived health benefits, supporting the segment’s sustained leadership in overall market consumption.
Key Market Segments
By Extraction Process
- Mechanically By Pressing
- Chemically Extracted
- Others
By Application
- Food Industry
- Personal Care & Cosmetics
- Supplements & Healthcare
- Others
Emerging Trends
Functional and Health-Oriented Usage Across Food and Personal Care
A powerful trend shaping the grapeseed oil landscape today is how people are choosing foods and products that feel better for the body and connect back to broader health lifestyles. In simple terms, more people are thinking about not just what they eat, but how the ingredients in their food and personal care products affect their health and wellbeing — and grapeseed oil fits right into that picture.
In many communities, consumers are increasingly aware that eating oils high in healthy fats and natural antioxidants can support heart health, balance inflammation, and offer more nutritional value than traditional options. Grapeseed oil is naturally high in polyunsaturated fats, with about 69.6% linoleic acid, a desirable fatty acid associated with heart health when consumed in balanced diets. That simple fact helps grapeseed oil stand out in kitchens where people aim to cook and eat more consciously.
This health orientation is not just at home. Across the food world — from restaurants to health-focused cafes — chefs are experimenting more with grapeseed oil because of its neutral flavor and high smoke point, around 216 °C, which makes it practical for a wide range of cooking styles including frying, roasting, and dressings. These cooking attributes marry well with public interest in oils that do double duty — they can be healthy and functional in dynamic culinary settings.
Policy and government guidance also subtly support this trend. Public health recommendations from authorities like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and other trusted institutions continue to highlight the benefits of unsaturated fats over high saturated fat choices for heart health. These kinds of recommendations boost confidence in oils such as grapeseed oil that deliver mostly unsaturated fats in well-regulated, food-safe forms. Seed oils in general are recognized as safe by FDA and public health bodies, even as some social narratives push conflicting messages online — something nutrition scholars and experts increasingly push back against.
Drivers
Rising Demand for Sustainable, Health-Focused and Circular Food Products
One of the biggest reasons grapeseed oil is gaining real momentum in food and allied industries is that people and companies alike are increasingly choosing food products that are both health-oriented and environmentally responsible. This isn’t just a marketing slogan — it reflects real consumption habits and broader food system goals shared by consumers, food processors, and governments.
At its core, grapeseed oil embodies two important trends: health consciousness among consumers and resource efficiency within the food industry. On the consumer front, grapeseed oil is valued for its nutritional profile, especially its high polyunsaturated fat content and natural antioxidants, which support heart health and overall well-being. This aligns with healthier diets that people are actively adopting globally. In fact, grapeseed oil contains roughly 69.6% polyunsaturated fats (linoleic acid), making it significantly rich in essential fatty acids compared with many other vegetable oils — a fact that food scientists and nutrition advocates often use when discussing healthier cooking oil alternatives.
On the sustainability side, grapeseed oil comes from waste, which is increasingly important when leaders, brands, and regulators talk about food waste and circular use of resources. After grapes are pressed for wine or juice, the remaining seeds would otherwise be discarded. Instead, these seeds are now repurposed to produce edible oil. This helps reduce environmental burden and supports industry goals to valorize by-products instead of treating them as waste. For example, food waste is a massive global problem — the European Union alone wastes an estimated 153 million tonnes of food each year, prompting policies and industry action plans to reduce waste and repurpose by-products wherever possible.
This convergence of health and sustainability is also reflected in how the market is evolving. While not specific to grapeseed oil, broader food industry data on food waste and valorization provides context: nearly one-third of all food produced globally is lost or wasted, according to the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). Governments and food system stakeholders are actively pursuing strategies to bring that number down, including by promoting circular economy models where by-products like grape seeds are turned into value-added ingredients.
Restraints
Unstable Raw Material Supply and Shelf-Life Sensitivity Limit Scale
A major restraint for grapeseed oil is that its raw material supply is tied to grape processing and wine production, which can swing sharply from year to year. When vineyards face climate stress, disease pressure, or economic pullbacks, the flow of grape seeds tightens and prices can move quickly.
The International Organisation of Vine and Wine (OIV) reported global wine production of 225.8 million hectolitres in 2024, down 4.8% versus 2023, and described it as the lowest level in over 60 years. In the same reporting cycle, global vineyard surface area fell to about 7.1 million hectares. For grapeseed oil producers, these numbers matter because less wine and fewer vineyards generally mean fewer seeds available for extraction, making long-term supply contracts harder to secure at stable costs.
This constraint is visible even in large food processing economies. USDA agricultural research notes that the U.S. produces over 150 thousand metric tons of dried grape seeds each year, containing about 13–19% oil, generated as a by-product from processing roughly 5.8 million metric tons of grapes. That sounds big, but it also shows the bottleneck: grapeseed oil supply depends on a much larger primary industry (grapes/wine/juice). If grape crushing volumes drop or shift to different product mixes, grapeseed availability changes, and oil plants must either run below capacity or source seeds from farther away—raising logistics and handling costs.
The second part of this restraint is quality and stability. Grapeseed oil is naturally high in polyunsaturated fatty acids, with linoleic acid commonly reported at 68.10–78.18 g per 100 g of oil across analyzed samples. This nutritional profile is attractive, but it also makes the oil more prone to oxidation if processing, storage, packaging, or distribution are not tightly controlled. In practical terms, oxidation can mean faster development of off-odors and shorter shelf stability—issues that food manufacturers take seriously because they can affect taste, returns, and brand trust.
Opportunity
Upcycling Winery By-Products into Premium, Traceable Oils
A major growth opportunity for grapeseed oil is simple: it turns a large, unavoidable by-product from grape processing into a sellable, higher-value food ingredient. Every time grapes are crushed for wine or juice, seeds are left behind. Those seeds can either become a cost or become an input for oil, meal, and other extracts.
This “use everything” approach is becoming more attractive as food companies tighten sustainability goals and as policymakers push harder to reduce food waste and improve resource efficiency. The scale of the upstream system is still huge: global wine production in 2024 was 225.8 million hectolitres, which means grape processing volumes remain large even in a weak year.
The U.S. is a practical example of how big the feedstock pool can be when it is organized well. USDA’s Agricultural Research Service notes that the United States produces over 150 thousand metric tons of dried grape seeds each year, containing about 13–19% oil, as a by-product of processing about 5.8 million metric tons of grapes.
Policy is another strong tailwind for this “by-product to ingredient” model. The European Commission notes that the 2025 amendment of the Waste Framework Directive introduced binding food waste reduction targets for Member States to achieve by 2030: 10% reduction in processing and manufacturing and 30% (per capita) reduction jointly at retail and consumption stages.
Finally, there is room to link grapeseed oil growth to the bigger global push to cut food losses and waste. FAO has long highlighted that roughly one-third of food produced for human consumption is lost or wasted globally—about 1.3 billion tonnes. Ingredients that use existing by-products—without demanding extra farmland—are increasingly attractive to brands that want practical sustainability.
Regional Insights
North America leads with 39.80% (212.5 Mn) driven by strong culinary and personal-care demand
In 2024, North America accounted for a substantial portion of global grapeseed oil consumption, representing a 39.80% share and a market volume of 212.5 million (units/revenue as applicable), supported by well-established foodservice channels, growing retail penetration, and significant demand from cosmetics and personal-care manufacturers. The region’s preference for light, neutral-flavoured oils suitable for frying, baking and dressings underpinned household and industrial adoption, while a parallel uptake in skincare formulations reinforced commercial volumes.
Distribution was concentrated in organized retail and e-commerce, which together improved product availability and encouraged premium and private-label launches. Culinary attributes such as a high smoke point and neutral taste strengthened grapeseed oil’s selection for high-heat and value-added applications. Regulatory alignment and quality standards in the United States and Canada supported traceability and labelling that appealed to health-conscious buyers.
In 2024, manufacturers in the region focused on fortification, clean-label claims and sustainability messaging to differentiate offerings and drive repeat purchase; product innovation was directed at value-added blends and smaller-format convenience packs for urban consumers. Looking into 2025, market momentum was expected to continue as demand from food processors and personal-care formulators remained resilient, and as trade flows adjusted to supply-side developments in European and domestic seed production. The region therefore served as a dominant market and a strategic test bed for new grapeseed oil formats and marketing approaches.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
ConnOils LLC, based in the United States, is a key supplier of grapeseed and other specialty vegetable oils for foodservice and industrial applications. In 2024, the company produced ~80,000 tons of oils, focusing on high-quality, cold-pressed, and refined products. Employing ~350 staff, ConnOils emphasizes sustainable sourcing, consistent supply, and compliance with food safety standards.
Gustav Heess GmbH, based in Germany, specializes in vegetable oils including grapeseed oil, catering to culinary, industrial, and cosmetic applications. In 2024, it processed ~150,000 tons of vegetable oils with a focus on high-quality cold-pressed methods. Employing ~600 staff, the company emphasizes natural extraction and consistent supply reliability. Gustav Heess GmbH’s distribution network spans Europe and parts of Asia, offering refined and unrefined grapeseed oils.
Pietro Coricelli, an Italian edible oil company, produces grapeseed oil for culinary and industrial applications. In 2024, it processed ~100,000 tons of oils annually, focusing on quality, traceability, and Mediterranean-style branding. With ~450 employees, the company serves domestic and international markets, emphasizing cold-pressed and refined oil options. Its grapeseed oil is popular for frying, salad dressings, and bakery products.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Tampieri Group
- Borges Mediterranean Group
- Gustav Heess GmbH
- Olitalia S.R.L.
- Pietro Coricelli
- ConnOils LLC
- Aromex Industry
- Oilseeds International Ltd.
- Oleificio Salvadori
- Sophim
- Jan K. Overweel Limited
Recent Industry Developments
In 2024, Pietro Coricelli, one of Italy’s longstanding edible oil producers founded in 1939, continued its growth trajectory with a record €415 million in turnover and over 62 million litres of oil sold, reflecting a 25% increase from the previous year and solidifying its commercial strength in Mediterranean and international markets.
In 2024, Gustav Heess GmbH continued to be recognized as a reputable supplier of vegetable oils, including grapeseed oil, within the broader edible and specialty oils market. Founded in 1897 and headquartered in Leonberg, Germany, the company operates with more than 150 employees across its European and international facilities, delivering over 50,000 tons of high‑quality vegetable oils annually to food, cosmetic, and pharmaceutical industries.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 534.1 Mn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 1111.1 Mn CAGR (2025-2034) 7.6% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Extraction Process (Mechanically By Pressing, Chemically Extracted, Others), By Application (Food Industry, Personal Care And Cosmetics, Supplements And Healthcare, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Tampieri Group, Borges Mediterranean Group, Gustav Heess GmbH, Olitalia S.R.L., Pietro Coricelli, ConnOils LLC, Aromex Industry, Oilseeds International Ltd., Oleificio Salvadori, Sophim, Jan K. Overweel Limited Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- Tampieri Group
- Borges Mediterranean Group
- Gustav Heess GmbH
- Olitalia S.R.L.
- Pietro Coricelli
- ConnOils LLC
- Aromex Industry
- Oilseeds International Ltd.
- Oleificio Salvadori
- Sophim
- Jan K. Overweel Limited










