Global Energy Storage Battery for Microgrid Market Size, Share, Growth Analysis By Product Type (Lithium-ion Batteries, Flow Batteries, Lead-acid Batteries, Nickel-cadmium Batteries, Others), By Technology (Battery Management Systems, Thermal Management Systems, Energy Management Systems), By Application (Renewable Energy Integration, Grid Stability, Backup Power, Peak Shaving, Others), By End User (Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Utility) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Nov 2025
- Report ID: 167666
- Number of Pages: 204
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
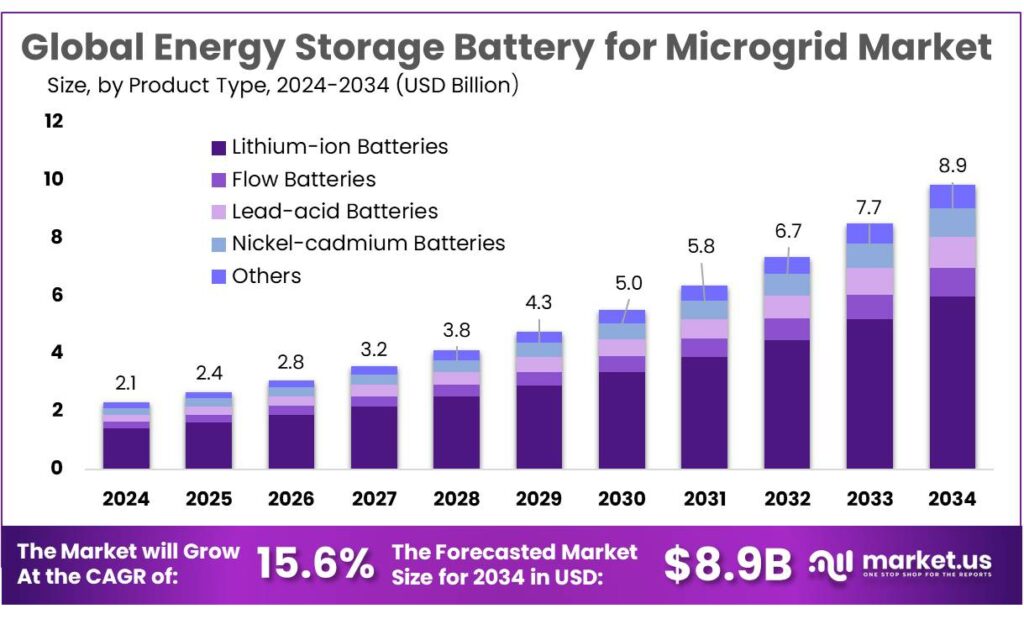
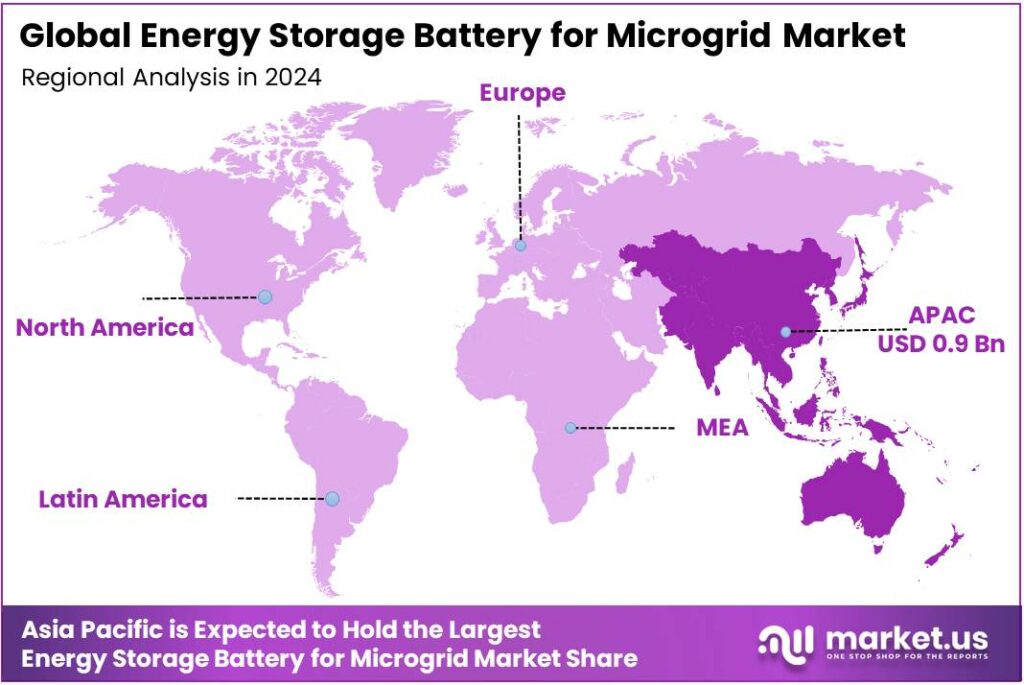
The Global Energy Storage Battery for Microgrid Market size is expected to be worth around USD 8.9 Billion by 2034, from USD 2.1 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 15.6% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, APAC held a dominan market position, capturing more than a 43.90% share, holding USD 0.9 Billion revenue.
Energy storage batteries for microgrids sit at the intersection of decentralised power, resilience, and renewable integration. Microgrids are local energy systems that can island from the main grid and rely heavily on batteries to balance variable solar, wind, and critical loads. Globally, grid-scale battery capacity reached 55.7 GW in 2023, up 120% in just one year, underscoring how fast storage is scaling to support such distributed systems.
At system level, decarbonisation targets are creating a structural pull for microgrid-scale batteries. IRENA estimates that renewable power capacity must more than triple from 3,382 GW in 2022 to 11,174 GW by 2030 in its 1.5°C scenario. To integrate this surge without compromising reliability, the IEA projects the world will need about 1,300 GW of battery storage by 2030. A meaningful slice of that capacity will be embedded in microgrids serving campuses, industrial parks, data centres, and remote communities.
The industrial scenario is shifting from pilot projects to portfolio deployment. In the United States, microgrid capacity is expected to rise from 4.4 GW in 2022 to 10 GW by end-2025, supported by a federal pledge of USD 7.6 billion for grid innovation and state-level schemes such as California’s USD 200 million Microgrid Incentive Program. A 2018 NREL study for the U.S. DOE found typical microgrids cost USD 2–5 million per MW of generation, highlighting why batteries—whose costs have fallen sharply—are central to making projects bankable.
Policy and social-equity programmes are an important driver for storage batteries in community microgrids. The U.S. DOE’s Energy Storage for Social Equity (ES4SE) initiative began with USD 9 million in support and has since awarded about USD 3.7 million in project-development assistance to selected communities, specifically to pair storage with resilient local energy systems. In 2025, the Community Microgrid Assistance Partnership (C-MAP) pilot cohort was announced with 14 projects across 35 towns and villages, creating a clear pipeline of battery-centric microgrids for rural and Indigenous communities.
Key Takeaways
- Energy Storage Battery for Microgrid Market size is expected to be worth around USD 8.9 Billion by 2034, from USD 2.1 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 15.6%.
- High-Density Polyethylene held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 67.2% share of the Energy Storage Battery for Microgrid Market.
- Battery Management Systems held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 48.9% share in the Energy Storage Battery for Microgrid Market.
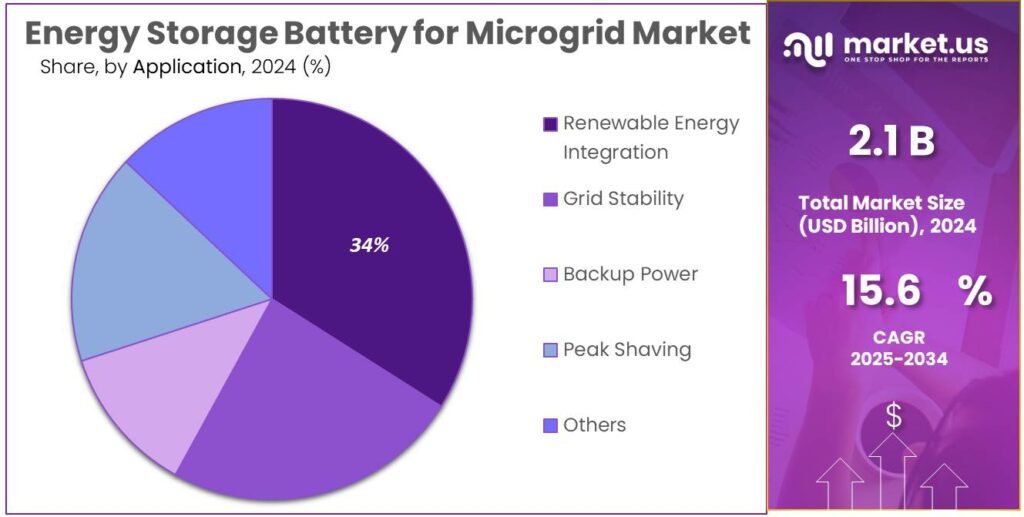
- Renewable Energy Integration held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 34.1% share in the Energy Storage Battery for Microgrid Market.
- Utility held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 38.5% share in the Energy Storage Battery for Microgrid Market.
- APAC emerged as the dominant region in the Energy Storage Battery for Microgrid Market, holding 43.90% of global share and an estimated regional value of USD 0.9 billion.
By Product Type Analysis
Lithium-ion Batteries dominate with a strong 67.2% share in 2024 due to efficiency and longer service life.
In 2024, High-Density Polyethylene held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 67.2% share of the Energy Storage Battery for Microgrid Market under the product type segment of lithium-ion batteries. The strong position of lithium-ion technology in microgrid storage systems reflects its balance of long cycle life, compact storage capacity, and high round-trip efficiency. In many microgrid deployments, lithium-ion systems deliver discharge efficiencies above 90%, making them an attractive choice for regions adopting solar-plus-storage or wind-hybrid microgrid structures.
By 2025, the role of lithium-ion batteries in microgrids continues expanding, supported by growing investments in decentralized energy systems, industrial backup power, and remote electrification. Many microgrids in communities, campuses, and industrial parks prefer lithium-ion solutions because they offer scalable power, predictable maintenance, and compatibility with advanced battery-management systems. Their adaptability to temperature variations and the ability to maintain stable discharge even under fluctuating loads further strengthens their role in the sector.
By Technology Analysis
Battery Management Systems lead the segment with a solid 48.9% share, driven by reliability and safety needs.
In 2024, Battery Management Systems held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 48.9% share in the Energy Storage Battery for Microgrid Market under the technology category. Their strong demand comes from the growing need to protect high-value battery assets, improve efficiency, and ensure safe charging and discharging cycles within microgrid environments. As microgrids increasingly integrate renewable energy like solar and wind, the role of battery management systems becomes essential to balance energy flow, prevent overheating, detect failures early, and extend overall system life.
The market in 2025 shows continued reliance on Battery Management Systems as microgrids expand from pilot sites to commercial and community-level infrastructure. Many project developers prioritize BMS-equipped systems because they provide real-time monitoring, predictive diagnostics, and performance optimization. The shift toward automation, digital control, and remote monitoring further strengthens the demand for advanced BMS solutions in both off-grid and grid-connected microgrids.
By Application Analysis
Renewable Energy Integration leads the segment with a strong 34.1% share due to rising clean power adoption.
In 2024, Renewable Energy Integration held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 34.1% share in the Energy Storage Battery for Microgrid Market under the application segment. This strong demand reflects the rapid deployment of solar, wind, and hybrid renewable systems that require energy storage to ensure grid stability. As more regions aim to reduce carbon emissions and replace fossil-based backup systems, batteries paired with renewable microgrids become essential for maintaining consistent power during fluctuating generation periods. Storage helps smooth output, maintain voltage balance, and deliver energy when sunlight or wind availability drops.
By 2025, the focus on clean energy continues growing across industries, public institutions, and remote communities. Many organizations see renewable-powered microgrids as a long-term solution for both sustainability and energy independence. With increasing installation of distributed solar rooftops, community wind hubs, and hybrid clean power systems, the need for storage becomes even more critical. Batteries help store excess daytime energy and release it during peak consumption periods, creating a stable and predictable energy flow.
By End User Analysis
Utility end-use dominates with a solid 38.5% share, driven by grid stability and resilience priorities.
In 2024, Utility held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 38.5% share in the Energy Storage Battery for Microgrid Market by end-user category. This leadership reflects the rising need for utilities to modernize power distribution, support renewable energy growth, and enhance resilience against outages. As many electrical grids face increasing instability from fluctuating renewable energy inputs, extreme weather, and aging infrastructure, utilities are turning to battery-enabled microgrids to maintain reliability and service continuity. The storage systems allow utilities to manage peak loads, perform frequency balancing, and operate isolated energy zones when required.
By 2025, the role of utilities becomes even more central as decentralized clean energy models gain momentum. Many utilities are shifting from traditional centralized power delivery to flexible distributed networks where localized energy storage supports better demand management. Microgrids equipped with advanced batteries help utilities integrate solar and wind assets more efficiently, avoid energy curtailment, and reduce operating costs over time. The move toward digital grid operations and automated control further supports adoption.
Key Market Segments
By Product Type
- Lithium-ion Batteries
- Flow Batteries
- Lead-acid Batteries
- Nickel-cadmium Batteries
- Others
By Technology
- Battery Management Systems
- Thermal Management Systems
- Energy Management Systems
By Application
- Renewable Energy Integration
- Grid Stability
- Backup Power
- Peak Shaving
- Others
By End User
- Residential
- Commercial
- Industrial
- Utility
Emerging Trends
Sustainable food cold chains are turning solar-battery microgrids into a new normal
One of the clearest new trends for energy storage batteries in microgrids is their use in sustainable food cold chains. Instead of being sold only as “power products”, batteries are now packaged as part of complete cold-chain solutions for farmers, fisheries, and food processors. The idea is simple: use solar-plus-battery microgrids to keep cooling and processing equipment running all day and night, even in places with weak or no grid.
The food side of this story is huge. FAO’s SDG 12.3 data show that 13.3% of all food produced is lost after harvest at farm, transport, storage, wholesale and processing stages in 2023.UNEP and FAO further estimate that around 14% of food is lost and 17% is wasted across the chain, enough to feed about 1 billion people in a world where 811 million people are hungry and 3 billion cannot afford a healthy diet. For governments, food companies, and donors, this is no longer just a statistic – it is a call to redesign infrastructure, and that is where microgrids with batteries come in.
Cold chains are at the centre of this trend. A joint UNEP–FAO–IIR–IRENA assessment finds that 526 million tonnes of food, about 12% of global production, are lost every year because of inadequate refrigeration.In 2017, only 45% of food that required refrigeration worldwide was actually refrigerated, leaving more than half of the potential cold-chain market still open. Rather than extend diesel-based cooling, many pilots now link efficient refrigeration directly to solar-battery microgrids, so that cold rooms, milk chillers and fish stores keep running during the night and through power cuts.
At the same time, the mini-grid sector itself is scaling, which creates a natural highway for battery deployment. A World Bank analysis shows that to power about 490 million people by 2030, the world will need more than 217,000 solar mini-grids, requiring around USD 127 billion in cumulative investment.Many of these mini-grids are planned for rural Africa and South Asia, where agriculture and food processing are the main local businesses. As developers look for stable, income-generating loads, cold rooms, grain mills, oil presses and small food factories become prime anchor customers, locking in demand for multi-hour battery storage.
Drivers
Decarbonising Food Chains and Cutting Food Loss Are Powering Microgrid Storage
A major force behind energy storage batteries for microgrids is the urgent need to clean up and modernise the food and agriculture value chain. Energy and food systems are now seen as one connected challenge, not two separate sectors. IRENA and FAO estimate that about 30% of the world’s energy is consumed within agri-food systems, and that energy use is responsible for roughly one-third of agri-food greenhouse gas emissions.
Pressure is also rising on the climate side. FAO’s latest assessment shows agrifood systems emitted 16.2 billion tonnes of CO₂-equivalent in 2022, an increase of 10% since 2000, while still accounting for about one-third of total human-made emissions. Governments know they cannot meet their climate targets unless farms, fisheries and food processing plants switch to cleaner, more efficient power. Microgrids with battery storage allow rural cooperatives, mills, pack-houses and cold rooms to run on solar or hybrid systems without worrying about clouds, storms or evening peaks.
Food loss is another powerful driver. FAO’s SDG-12.3 tracking shows that in 2023 around 13.3% of all food produced globally was lost after harvest during transport, storage, wholesale and processing. An earlier FAO analysis suggested that roughly one-third of food was lost or wasted along the chain. A big share of this loss in low- and middle-income countries comes from weak cold chains, unreliable electricity and diesel costs that are too high for small actors. Battery-backed microgrids can power cold rooms, milk chillers and processing lines through the night, directly attacking this structural loss.
Finally, there is a strong access dimension. A World Bank-led SDG7 review reports that around 666 million people still lacked electricity in 2023, even though almost 92% of the world’s population had access overall. Many of those without power live in farming and fishing communities where food losses and climate risks are highest. New World Bank and government programmes now explicitly fund mini-grids and cold-storage infrastructure for agriculture, irrigation and processing, positioning battery-equipped microgrids as a core development tool rather than a niche technology.
Restraints
High Upfront Costs and Weak Finance Slow Microgrid Batteries for Food Systems
A joint UNEP–FAO study shows that lack of effective refrigeration leads to the loss of 526 million tonnes of food a year, equal to about 12% of global production. Yet, even with losses on this scale, many farmers, cooperatives and traders still struggle to finance basic cold rooms, let alone battery-backed microgrids.
The same report notes that around 14% of food produced for people is lost before it reaches the consumer, and another 17% is wasted, in a world where 811 million people are hungry and 3 billion cannot afford a healthy diet. FAO and partners estimate that post-harvest losses reduce the income of 470 million smallholder farmers by up to 15%, mainly in developing countries. These communities could benefit directly from microgrids with batteries powering cold chains, mills and processing, but tight margins make it very hard to take on new capital-intensive energy assets.
Cooling gaps highlight why high costs are such a brake. UNEP reports that in 2017 only 45% of food that needed refrigeration actually had it, and again links lack of refrigeration to the same 526 million tonnes, or 12% of global food output being lost. In Kenya, a recent SEforALL study estimates that about 40% of food is lost each year because of poor storage and supply-chain inefficiencies, while roughly 25% of people face hunger or food insecurity.
World Bank analysis on cold chains in Rwanda’s tomato sector makes this even more concrete. The country produces about 97,400 tonnes of tomatoes, but around 49% is lost along the value chain, and at the farm and market stages there is no cold storage available. The same paper notes that only about 5% of firms in the food and agriculture sector have any cold storage at all.
On the energy side, technology costs are falling but remain a hurdle once you add financing and rural risk. REN21 reports that average lithium-ion battery pack prices dropped to about USD 139 per kWh in 2023, mainly driven by electric vehicles. However, NREL modelling for utility-scale systems still shows four-hour battery storage costs in the range of USD 245–403 per kWh in 2030, before considering project-level risk premiums.
Opportunity
Sustainable food cold chains open a powerful microgrid battery opportunity
One of the most promising growth opportunities for energy storage batteries in microgrids lies in making food systems cleaner and more reliable. FAO’s latest SDG 12.3 data show that 13.3% of all food produced globally was lost after harvest in 2023 along the chain from farm to processing and wholesale.Much of that loss is linked to weak or non-existent cold chains and unstable power. Every time a country decides to tackle food loss with modern, decentralised cold and processing infrastructure, it effectively creates new demand for microgrids and the batteries that stabilise them.
The cold chain gap is huge, and so is the opportunity. A joint UNEP–FAO–IRENA technical brief estimates that lack of effective refrigeration directly leads to 526 million tonnes of food being lost each year, about 12% of global food production.UNEP notes that in 2017 only 45% of food that required refrigeration actually had it, meaning more than half of the potential cold chain market is still untapped.
The human side of this story is just as strong. UNEP and FAO highlight that current food loss and waste is enough to feed around one billion people, in a world where 811 million people are hungry and over 3 billion cannot afford a healthy diet. Battery-backed microgrids can power cold rooms for vegetables, milk chillers, fish storage and small processing plants in villages and peri-urban areas.
Public financial flows are starting to line up with this need, which strengthens the growth outlook. A recent global mini-grids market report, using World Bank deal data, records USD 700 million already committed across 217 mini-grid investment projects.A separate World Bank handbook on mini-grids estimates that achieving large-scale access could mobilise about USD 127 billion in cumulative investment by 2030, much of it in rural and agrifood-linked systems.
Regional Insights
APAC leads the Energy Storage Battery for Microgrid Market with a 43.9% share, valued at USD 0.9 Billion
In 2024, APAC emerged as the dominant region in the Energy Storage Battery for Microgrid Market, holding 43.90% of global share and an estimated regional value of USD 0.9 billion. This leadership is closely linked to the region’s aggressive renewable energy build-out and rapid electrification. Countries such as China, India, Japan, South Korea, and several ASEAN economies are combining solar and wind additions with distributed microgrid projects to improve grid stability and support remote or islanded communities.
Across Asia, the scale of the underlying power transition is striking. IRENA reports that Asia accounted for over half of global renewable power capacity in 2023, with China alone adding tens of gigawatts of solar and wind each year, creating natural demand for battery storage to manage variability and peak loads. Governments in India and Southeast Asia are also promoting microgrids for villages, industrial parks, and commercial complexes, where batteries provide backup, frequency support, and better use of rooftop solar. Public programmes targeting rural electrification, resilience against extreme weather, and diesel displacement further accelerate storage uptake.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Beacon Power Systems — Beacon Power’s technology is focused on high-cycle, short-duration kinetic (flywheel) storage used for frequency regulation and fast grid services. Deployments have included a 20 MW plant (200 Series 400 flywheels) providing sub-second response for market ancillary services, demonstrating value in fast-response microgrid and grid-stabilization use cases where high cycle life and low-degradation are prioritized.
EnerSys — EnerSys supplies industrial battery chemistries and energy-storage products targeted to C&I, telecom and utility microgrids; product lines include flooded, VRLA and advanced TPPL batteries with typical cycle lives up to ~1,500 cycles for select ranges. Recent strategic moves include acquisitions to expand lithium and portable power capabilities and industry awards recognizing energy-storage product innovations, reinforcing its position in industrial and mission-critical microgrid deployments.
ABB Ltd. — ABB’s energy-storage portfolio is positioned as a factory-built, pre-tested offering for BESS and microgrids, enabling faster deployment and higher safety. Modular solutions and digital control are offered under ABB Ability™, with integrated power conversion, grid controls and BESS-as-a-service partnerships to optimise asset value. Recent partnerships target AI-enabled optimisation and BESS-as-a-service deployments.
Top Key Players Outlook
- ABB Ltd.
- AEG Power Solutions BV
- Beacon Power Systems
- EnerSys
- General Electric Co.
- GS Yuasa International Ltd.
- Hitachi Ltd.
- LG Corp.
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd.
- Panasonic Holdings Corp.
Recent Industry Developments
General Electric reported approximately 53,000 employees as of December 31, 2024, a workforce that supports engineering, field services and lifecycle contracts required by complex microgrid rollouts.
ABB has already delivered automation solutions covering more than 10 GW of renewables in India, including solar, wind and BESS assets, by August 2024.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 2.1 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 8.9 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 15.6% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Product Type (Lithium-ion Batteries, Flow Batteries, Lead-acid Batteries, Nickel-cadmium Batteries, Others), By Technology (Battery Management Systems, Thermal Management Systems, Energy Management Systems), By Application (Renewable Energy Integration, Grid Stability, Backup Power, Peak Shaving, Others), By End User (Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Utility) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape ABB Ltd., AEG Power Solutions BV, Beacon Power Systems, EnerSys, General Electric Co., GS Yuasa International Ltd., Hitachi Ltd., LG Corp., Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd., Panasonic Holdings Corp. Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Energy Storage Battery for Microgrid MarketPublished date: Nov 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Energy Storage Battery for Microgrid MarketPublished date: Nov 2025add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- ABB Ltd.
- AEG Power Solutions BV
- Beacon Power Systems
- EnerSys
- General Electric Co.
- GS Yuasa International Ltd.
- Hitachi Ltd.
- LG Corp.
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd.
- Panasonic Holdings Corp.










