Global Chloroform Market Size, Share Analysis Report By Grade (Technical Grade, Alcohol Stabilized Grade, Fluorocarbon Grade), By Application (Solvent, Intermediates, Reagent, Others), By End-User (Pharmaceutical, Agrochemical, Chemical Industry, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Nov 2025
- Report ID: 163970
- Number of Pages: 299
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
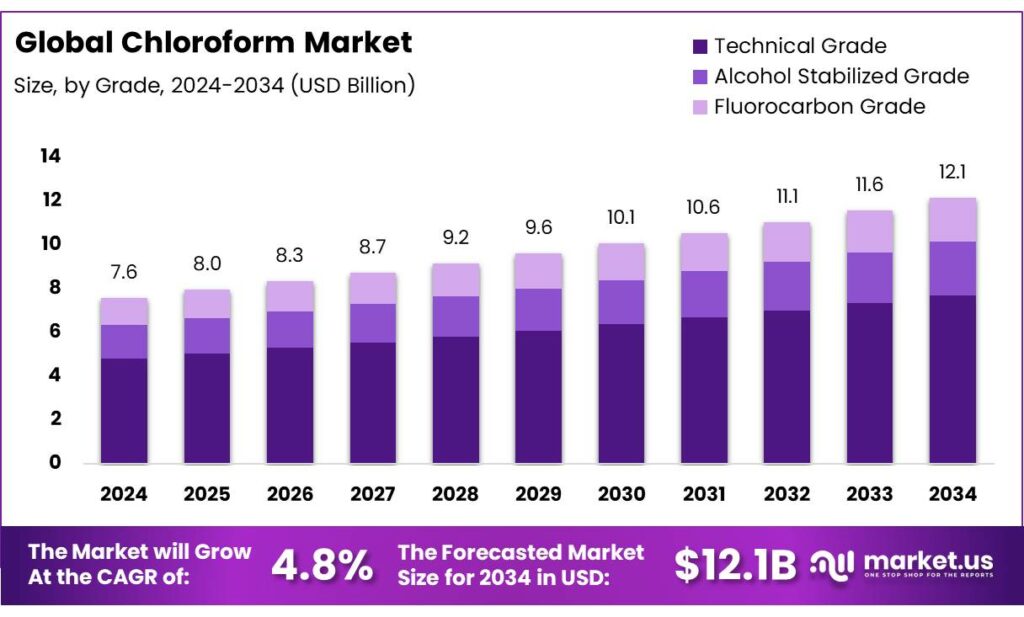
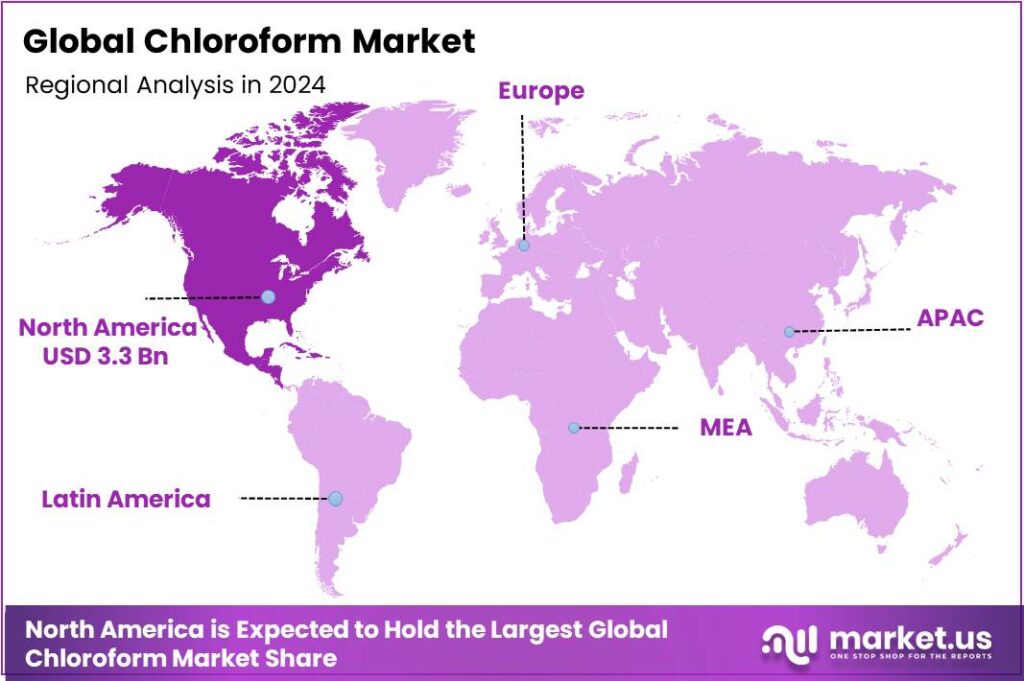
The Global Chloroform Market size is expected to be worth around USD 12.1 Billion by 2034, from USD 7.6 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 4.8% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024 North America held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 43.8% share, holding USD 3.3 Billion in revenue.
Chloroform (trichloromethane, CHCl₃) is a high-volume chlorinated solvent and a critical feedstock for fluorochemicals, especially HCFC-22 used to make PTFE and related polymers. The scientific community estimates more than 1,600 kilotonnes (Gg) of chloroform are used annually as feedstock for HCFC-22 production, and emissions associated with this feedstock use are comparable to solvent-use emissions—underscoring its industrial scale and atmospheric significance.
The current industrial scenario is tightly linked to the refrigeration, air-conditioning and fluoropolymer value chains. UNEP assessments indicate ~1.2 million tonnes of HCFC-22 were produced in 2022, largely for feedstock applications, which cascades into sizeable upstream demand for chloroform. In the United States alone, EPA’s Chemical Data Reporting shows national chloroform production volume in 2019 was 250–500 million pounds, reflecting its enduring role across chemicals and pharmaceuticals.
On the public-health compliance side, drinking-water standards drive monitoring and treatment choices: WHO lists a guideline value of 0.3 mg/L for chloroform, while the U.S. EPA regulates total trihalomethanes at 80 μg/L, shaping utilities’ disinfection strategies that can influence chloroform by-product formation.
Key driving factors include downstream cooling demand and fluoropolymer growth, alongside regulatory pressure to curb by-products and unintended emissions. The IEA estimates space cooling and fans account for nearly 20% of electricity used in buildings globally, signalling long-run pull for refrigerant-related supply chains even as technologies transition, which indirectly sustains HCFC-22 feedstock flows where permitted and, therefore, chloroform demand.
Policy controls are also sharpening: UNEP/TEAP analysis reports a global HFC-23-to-HCFC-22 production emission ratio near 1.20% for 2022–2023, intensifying abatement expectations at HCFC-22 plants and reinforcing cleaner feedstock stewardship upstream.
Policy-led transitions open two avenues. First, feedstock re-balancing: many Article-5 (developing) countries follow step-downs of 35% (2020), 67.5% (2025) and 97.5% (2030) before full phase-out, sustaining short-term HCFC-22 service demand while accelerating shifts to HFC/HFO and non-fluorinated cooling options—encouraging chloroform producers to pivot toward high-purity solvent grades for pharma/agrochemical synthesis and to invest in abatement for by-product streams.
Key Takeaways
- Chloroform Market size is expected to be worth around USD 12.1 Billion by 2034, from USD 7.6 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 4.8%.
- Technical Grade held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 63.5% share of the global chloroform market.
- Solvent application held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 43.8% share of the global chloroform market.
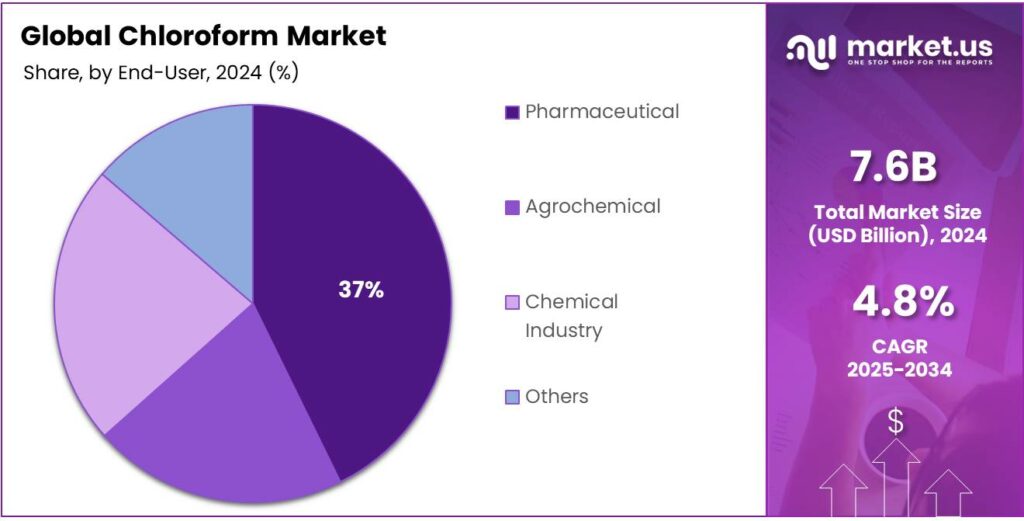
- Pharmaceutical end-user segment held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 37.4% share of the global chloroform market.
- North America dominated the global chloroform market, accounting for over 43.8% share and valued at approximately USD 3.3 billion.
By Grade Analysis
Technical Grade leads the Chloroform Market with 63.5% share in 2024 due to its wide industrial use
In 2024, Technical Grade held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 63.5% share of the global chloroform market. The dominance of this segment is mainly attributed to its extensive use across chemical manufacturing, pharmaceutical intermediates, and laboratory applications. Technical grade chloroform is widely preferred in industrial processes because of its high purity levels, cost-effectiveness, and consistent chemical stability. It serves as a crucial raw material in the production of refrigerants, agrochemicals, and dyes, where precise composition and performance reliability are essential.
The growing consumption of technical grade chloroform in developing economies such as China, India, and South Korea has further strengthened its market presence. In 2025, the segment is expected to witness steady demand growth supported by rising pharmaceutical manufacturing and expanding chemical exports in Asia-Pacific. The compound’s role in the synthesis of intermediates like chlorodifluoromethane, used in refrigerant production, continues to anchor its industrial relevance. Moreover, regulatory guidelines that encourage quality control in bulk chemical manufacturing have favored the adoption of technical grade over lower-grade variants.
By Application Analysis
Solvent application dominates the Chloroform Market with 43.8% share in 2024 driven by its extensive industrial usage
In 2024, Solvent application held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 43.8% share of the global chloroform market. This leadership is primarily due to the compound’s strong solvency power and its wide acceptance in various industrial and laboratory processes. Chloroform is extensively used as a solvent in pharmaceuticals, paints and coatings, adhesives, and extraction processes, where its ability to dissolve a wide range of organic compounds provides significant operational efficiency. Its compatibility with many chemical formulations has made it a preferred choice for large-scale production environments.
The segment continues to benefit from the growing need for efficient solvents in the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and specialty chemicals. In 2025, the solvent application is expected to maintain steady growth as emerging economies expand their manufacturing capacity in pharmaceutical and agrochemical sectors. Industrial adoption has been further supported by the consistent demand for high-performance cleaning and extraction agents, particularly in controlled and well-regulated settings.
By End-User Analysis
Pharmaceutical sector dominates the Chloroform Market with 37.4% share in 2024 owing to its essential role in drug manufacturing
In 2024, Pharmaceutical end-user segment held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 37.4% share of the global chloroform market. The growth of this segment is primarily supported by the compound’s critical use as an intermediate and solvent in the synthesis of various active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and intermediates. Chloroform is widely employed in the production of anesthetics, antibiotics, and other pharmaceutical compounds due to its strong solvency and high chemical purity. Its controlled application in laboratory and industrial drug formulation processes has made it an indispensable material in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
The rising demand for healthcare products and the expansion of drug production facilities in regions such as India, China, and the United States have further accelerated the consumption of chloroform within the pharmaceutical sector. In 2025, this end-user segment is expected to witness steady growth driven by increasing R&D activities and the rising focus on efficient chemical synthesis methods. The compound’s ability to facilitate purification and extraction processes in pharmaceutical research continues to enhance its market relevance.
Key Market Segments
By Grade
- Technical Grade
- Alcohol Stabilized Grade
- Fluorocarbon Grade
By Application
- Solvent
- Intermediates
- Reagent
- Others
By End-User
- Pharmaceutical
- Agrochemical
- Chemical Industry
- Others
Emerging Trends
Food cold-chains pivot to stewardship first refrigeration
A clear, recent trend shaping chloroform’s context is how food cold-chains are upgrading refrigeration while enforcing tighter stewardship of legacy systems. The FAO and UNEP put the problem in stark numbers: the lack of effective refrigeration directly causes 526 million tons of food production loss—about 12% of the global total—each year. That is food that could nourish people if it stayed cold from farm to market.
Developing countries could save another 144 million tons annually if they reached developed-country levels of cold-chain access. Those figures are pushing governments and food companies to expand cold storage and reefer logistics, but to do it with better refrigerant management and lower leakage.
Alongside this, the food system’s “silent” baseline persists: around 14% of all food is lost between post-harvest and retail, before consumers even see it. That loss is a daily nudge to keep existing cooling equipment running reliably while new, more efficient plants are built. In practice, it means service teams are trained to minimize leaks, recover refrigerant, and document chain-of-custody—behaviours that keep legacy HCFC-22 systems compliant during the transition window.
Energy realities are reinforcing this stewardship trend. The International Energy Agency notes that energy demand for space cooling has risen about 4% per year since 2000, and the stock of residential air conditioners reached >1.5 billion units in 2022. Without stronger efficiency action, cooling electricity use could more than triple by 2050. For food operators, that means a very large installed base of vapor-compression systems that must be maintained carefully—tightening the focus on leak reduction, refrigerant recovery, and certified servicing even as fleets shift to lower-GWP options.
Drivers
Food safety testing keeps chloroform relevant
The scale of modern food monitoring makes this practical dependence matter. In the European Union’s most recent coordinated survey, authorities analyzed 110,829 samples for pesticide residues in 2022—a record volume, up about a quarter from 2021. Of these, 96.3% were within legal limits, but the workload behind those numbers—sampling, extraction, and confirmation—was immense, and it leans on well-established solvent protocols in many labs. Rising sample counts don’t just show safer food; they signal persistent throughput that keeps chloroform in purchasing lists for method-bound steps.
The United States shows similar momentum. FDA’s regulatory pesticide monitoring in FY 2022 analyzed 3,030 samples. Compliance was high—96.2% for domestic and 89.5% for imported foods—but the testing machine that produces these numbers runs every single day, across a sprawling variety of commodities. Labs prize reproducible, codified methods; when a validated chapter specifies chloroform—especially for total fat or difficult matrices—buyers stay with what regulators know and auditors expect.
Global rule-making deepens this pull. The Codex Alimentarius—jointly managed by FAO and WHO—now lists 6,453 maximum residue limits (MRLs) and 63 extraneous maximum residue limits across pesticide–commodity combinations. Each new tolerance invites more method validation, proficiency testing, and surveillance—work that, in many laboratories, still involves chloroform in specific extraction or clean-up steps because those steps are written into validated procedures. When the rulebook grows, method-bound solvent demand grows with it.
Government-led expert reviews add another nudge. In 2024, the Joint FAO/WHO Meeting on Pesticide Residues (JMPR) evaluated 37 pesticides and recommended new or revised MRLs. Every such cycle pushes labs to update methods, re-validate recoveries, and run more comparisons—again favoring entrenched solvent systems when performance and regulatory familiarity are critical.
Restraints
Regulatory phase-out pressure on refrigerants and downstream impact
One major restraining factor for the chloroform market lies in the regulatory tightening around its key downstream application—the production of HCFC‑22 (also known as R-22), which is used in refrigeration and air-conditioning systems including cold-chain infrastructure for food. Many food-industry stakeholders rely on refrigerated storage and transport, but as older refrigerant systems face mandated retirements, the precursor demand (i.e., chloroform) is squeezed accordingly.
For example, in the United States, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency states that from 1 January 2020, production and import of HCFC-22 must end, and however remaining systems must rely on recovered or recycled stock rather than new supply. In parallel, in the European Union, legislation made it illegal to use virgin HCFCs to service refrigeration and air-conditioning equipment after 1 January 2010, and from 1 January 2015 use of any HCFC for servicing in many applications was prohibited.
Moreover, the food sector’s own cold-chain growth is creating pressure to replace older refrigeration systems with newer, lower-GWP refrigerants—thus reducing the servicing demand for HCFC-22. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) jointly reported that roughly 12% of global food production is lost annually because of lack of effective refrigeration, pointing to the size of cold-chain investment needed. At the same time, those investments increasingly favour next-gen refrigerants, which bypass HCFC-22 entirely.
In India, for instance, the HPMP (HCFC Phase-out Management Plan) Stage I report shows that in 2005 the total consumption of HCFC-22 in the refrigeration and air-conditioning (RAC) sector was 6,640 metric tonnes for new equipment plus 2,214 metric tonnes for servicing of existing equipment. With HCFC-22 consumption shrinking over time under treaty obligations, the indirect impact flows upstream to chloroform as feedstock.
For chloroform producers, the upshot is clear: while end-use growth in the food cold-chain is robust, the associated refrigerant pathway that uses chloroform is being squeezed by regulation. This mismatch creates risk—capacity built for legacy feedstock demand may become underutilised, and project viability rests on ability to pivot. The transition cost is real: retrofitting or replacing old systems may mean older refrigerants are phased out altogether, reducing servicing demand permanently.
Opportunity
Food cold-chain retrofits during the transition window
A clear growth opportunity for chloroform lies in the “service tail” of food cold-chains—keeping legacy HCFC-22 systems running safely and legally while countries expand refrigerated storage and transport. The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and UNEP estimate that the lack of effective refrigeration directly causes 526 million tons of food production loss each year, roughly 12% of the global total—losses that cold-chain expansion is meant to curb.
As that expansion rolls through emerging markets, a large installed base of HCFC-22 equipment still requires compliant refrigerant servicing; because HCFC-22 is produced from chloroform, this creates a predictable, near-term demand niche for producers who operate under strict stewardship. Meanwhile, FAO’s broader accounting shows about 14% of food is lost between post-harvest and retail, underscoring the scale of cold-chain build-out—and the interim need to keep existing systems reliable to avoid spoilage.
Governments are moving money and rules in the same direction: more cold-chain capacity and stricter refrigerant management. In India, the Ministry of Food Processing Industries continues to fund integrated cold-chain and value-addition infrastructure under national schemes that connect farms to markets; recent updates fold the Cold Chain Scheme under the PM-SAMPADA/PM-SKY umbrella to cut wastage and strengthen perishable logistics.
Importantly, the same FAO-UNEP assessment notes that developing countries could save an additional 144 million tons of food annually if they reached developed-country levels of cold-chain infrastructure—signaling how much servicing and retrofit work will occur before fleets are fully converted to next-generation refrigerants.
Policy guardrails shape the opportunity’s contours. Under the Montreal Protocol, HCFCs are being phased out, with Article-5 (developing) countries progressing through staged cuts toward 2030 and beyond; national HCFC Phase-out Management Plans (HPMPs) pair consumption caps with guidance on safe servicing and eventual conversion.
Regional Insights
North America leads the Chloroform Market with 43.8% share valued at USD 3.3 billion in 2024
In 2024, North America dominated the global chloroform market, accounting for over 43.8% share and valued at approximately USD 3.3 billion. The region’s strong position is primarily supported by its advanced chemical manufacturing infrastructure, stringent quality standards, and high demand from the pharmaceutical and healthcare industries. The United States remains the largest contributor, driven by extensive use of chloroform as an intermediate in the production of refrigerants, anesthetics, and other specialty chemicals. According to data from the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), the chemical manufacturing sector contributed over USD 438 billion to the national GDP in 2024, reflecting the region’s robust industrial output.
The widespread adoption of chloroform in pharmaceutical synthesis and laboratory applications continues to support market expansion in North America. The region’s strong R&D investments in biotechnology and drug formulation have further enhanced chloroform’s demand as a reliable solvent and process chemical. Additionally, government initiatives promoting clean manufacturing technologies and responsible chemical handling—such as the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) compliance standards under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA)—have fostered safer and more efficient production processes.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Shin-Etsu Chemical leverages fluorochemicals and vinyl integration, supporting steady chloroform use as feedstock and solvent. Strengths include process know-how, high-purity specifications, and reliable logistics across Asia, Europe, and the Americas. Customer ties span HCFC-22/PTFE intermediates and pharmaceutical synthesis, backed by rigorous stewardship and compliance. HCFC phase-downs are a structural overhang, yet portfolio balance and disciplined capex cushion cycles. Strategically, Shin-Etsu advances low-emission operations, heat-recovery projects, and diversification into specialty grades aligned with servicing needs in food cold-chains and refrigeration assets.
FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical focuses on high-purity laboratory and electronic-grade chloroform, supplying analytical labs, pharma R&D, and quality control. Strengths include rigorous specifications, lot traceability, and dependable distribution in Japan and exports. Volumes are modest versus industrial feedstocks, yet margins are attractive and customer stickiness high. Strict compliance, packaging safety, and documentation requirements protect reputation. As HCFC chains evolve, Wako’s specialty positioning, micro-contaminant control, and service culture provide resilient demand anchored in validated methods, reference materials, and semiconductor wet-chemistry applications.
Henan GP Chemicals is a China-based distributor and exporter of solvents and intermediates, including chloroform, serving customers across Asia, Africa, the Middle East, and Eastern Europe. Value lies in sourcing breadth, flexible packaging, competitive pricing, and responsive logistics. Strengths include document handling and consolidating shipments for smaller buyers. Risks involve hazardous-goods regulation, documentation scrutiny, and currency volatility. To sustain growth, the firm prioritizes supplier qualification, compliance knowledge, and partnerships supporting safe handling, leak-tight transfers, and availability during refrigerant transition cycles.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Olin Corporation
- Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd.
- Tokuyama Corporation
- FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation
- Henan GP Chemicals Co., Ltd.
- Meru Chem Pvt. Ltd.
- Arihant Chemicals
- Ideal Chemicals
Recent Industry Developments
In FY2023 Tokuyama, reported ¥341.9 billion consolidated net sales, with Chemicals accounting for 33% of sales—showing the materiality of basic chemicals in the portfolio.
Henan GP Chemicals Co., Ltd. acts primarily as a distributor and trader of industrial and specialty chemicals—including solvents relevant to the chloroform chain—in China and abroad. According to its public profile, the company services about 2,000 customers worldwide and offers over 1,000 different chemical products.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 7.6 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 12.1 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 4.8% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Grade (Technical Grade, Alcohol Stabilized Grade, Fluorocarbon Grade), By Application (Solvent, Intermediates, Reagent, Others), By End-User (Pharmaceutical, Agrochemical, Chemical Industry, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Olin Corporation, Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd., Tokuyama Corporation, FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation, Henan GP Chemicals Co., Ltd., Meru Chem Pvt. Ltd., Arihant Chemicals, Ideal Chemicals Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- Olin Corporation
- Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd.
- Tokuyama Corporation
- FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation
- Henan GP Chemicals Co., Ltd.
- Meru Chem Pvt. Ltd.
- Arihant Chemicals
- Ideal Chemicals










