Global BIPV Modules Market Size, Share Analysis Report By Technology (Crystalline Silicon, Thin Film, Others), By Installation Type (Rooftop, Façade, Glazing, Others), By Application (Residential, Commercial, Industrial), By End-Use (New Construction, Retrofit) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Dec 2025
- Report ID: 170527
- Number of Pages: 385
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
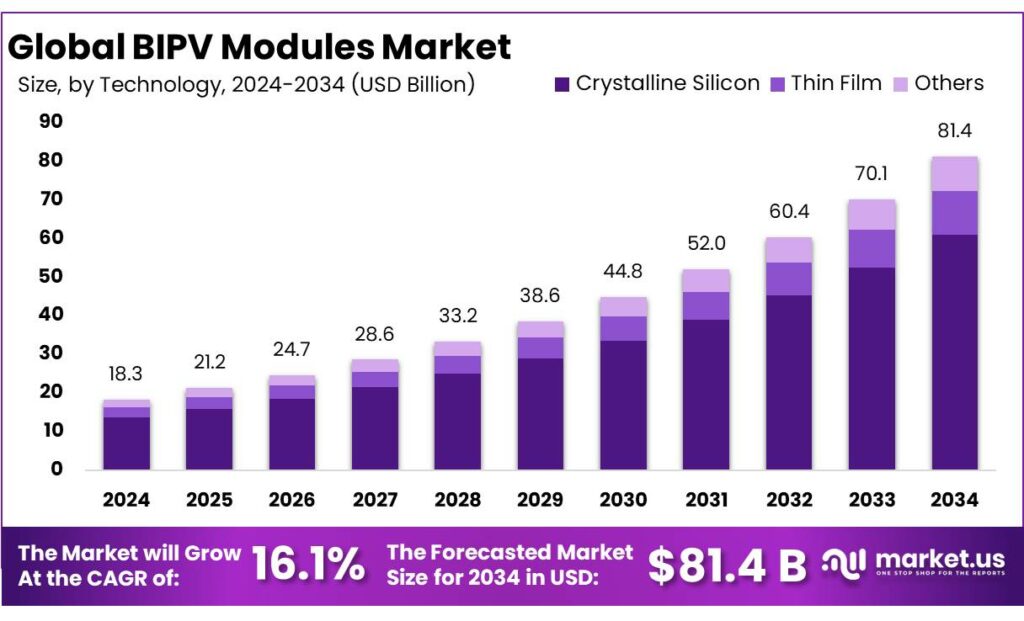
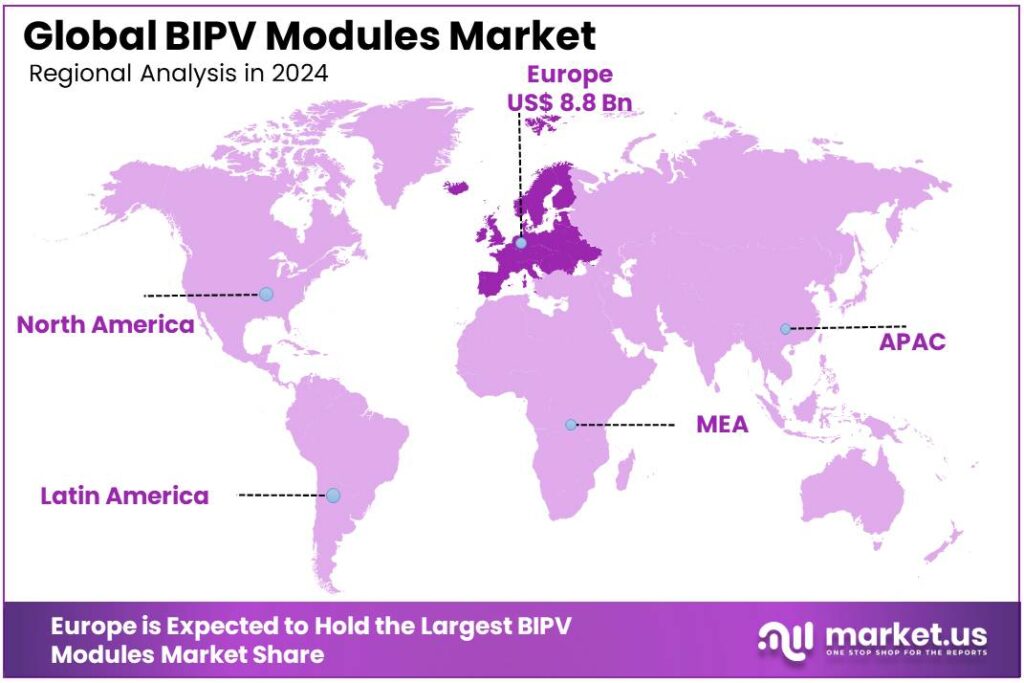
The Global BIPV Modules Market size is expected to be worth around USD 81.4 Billion by 2034, from USD 18.3 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 16.1% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, Europe held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 48.30% share, holding USD 8.8 Billion revenue.
Building-Integrated Photovoltaic (BIPV) modules are solar PV products designed to replace conventional building envelope elements—such as roofs, façades, skylights, balustrades, and shading—while also generating electricity. In market terms, BIPV sits at the intersection of solar manufacturing, construction materials, and high-performance building design, with projects typically led by a mix of PV brands, façade/roofing contractors, architects, and EPCs. The macro pull is clear: building operations account for about 30% of global final energy consumption and 26% of global energy-related emissions.
Industrially, the BIPV scenario is being shaped by two parallel shifts. First, solar itself has become a mainstream power source: at the beginning of 2024, more than 1.6 TW of PV systems were operational, producing over 2,135 TWh—about 8.3% of global electricity demand. Second, buildings are moving from “efficiency only” to “efficiency + onsite generation,” because the buildings and construction sector still consumes around 32% of global energy and contributes about 34% of global CO₂ emissions (2023). In this context, BIPV is increasingly positioned as a design-integrated compliance and decarbonization tool rather than an optional add-on.
Key driving factors are largely policy-led and economics-enabled. In Europe, the revised Energy Performance of Buildings Directive (EU/2024/1275) entered into force on 28 May 2024 and must be transposed into national law by 29 May 2026, reinforcing renovation momentum and higher building performance expectations. In parallel, the EU “Solar Rooftop Standard” timeline targets solar deployment on new non-residential/public buildings from 2027, existing non-residential buildings under major renovation by 2028, and new residential buildings from 2030. These milestones support BIPV because they expand the addressable surface area where “PV as building fabric” can compete.
- Government initiatives are critical enablers. At the international level, the International Energy Agency’s PVPS Task 15 workplan (2024–2027) aims to address barriers and foster a supportive innovation framework for BIPV deployment. National policies — including incentives, building codes, and subsidies — complement these frameworks, especially in regions pursuing smart city and green building objectives.
- In India, broader solar manufacturing support policies such as the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme for high-efficiency solar PV modules with an outlay of ₹24,000 crore are expanding domestic solar module capacity and indirectly benefiting BIPV supply chains, generating ~43,000 jobs by late 2025.
Key Takeaways
- BIPV Modules Market size is expected to be worth around USD 81.4 Billion by 2034, from USD 18.3 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 16.1%.
- Crystalline Silicon held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 74.8% share.
- Rooftop held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 49.9% share.
- Large held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 43.2% share.
- New Construction held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 67.1% share.
- Europe held a commanding position in the building-integrated photovoltaics market, accounting for 48.30% of regional share and representing an estimated USD 8.8 billion.
By Technology Analysis
Crystalline Silicon dominates with a 74.8% share, supported by proven performance and long-term reliability
In 2024, Crystalline Silicon held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 74.8% share. This leadership was driven by its high energy efficiency, stable output in diverse climatic conditions, and long operational life, which made it the preferred choice for building-integrated photovoltaic (BIPV) applications. The technology was widely adopted across commercial buildings, offices, and high-end residential projects where performance and visual integration were both important.
In 2024, demand remained strong due to large-scale urban construction and green building regulations favoring reliable solar solutions. Moving into 2025, the segment continued to benefit from gradual cost optimization, improved cell efficiency, and strong acceptance among architects and developers, reinforcing its dominant role within the BIPV modules market.
By Installation Type Analysis
Rooftop leads with a 49.9% share, driven by easy integration and growing urban adoption
In 2024, Rooftop held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 49.9% share. This leadership was supported by the widespread use of rooftop spaces in residential, commercial, and institutional buildings, where BIPV modules were installed without altering building footprints. Rooftop systems were preferred due to lower installation complexity, faster project timelines, and better control over energy generation at the point of use.
During 2024, supportive building energy codes and rising electricity costs encouraged rooftop BIPV adoption. In 2025, steady growth continued as urban renovation projects and net-zero building targets increased the use of rooftop-integrated solar solutions, maintaining the segment’s strong position in the overall BIPV modules market.
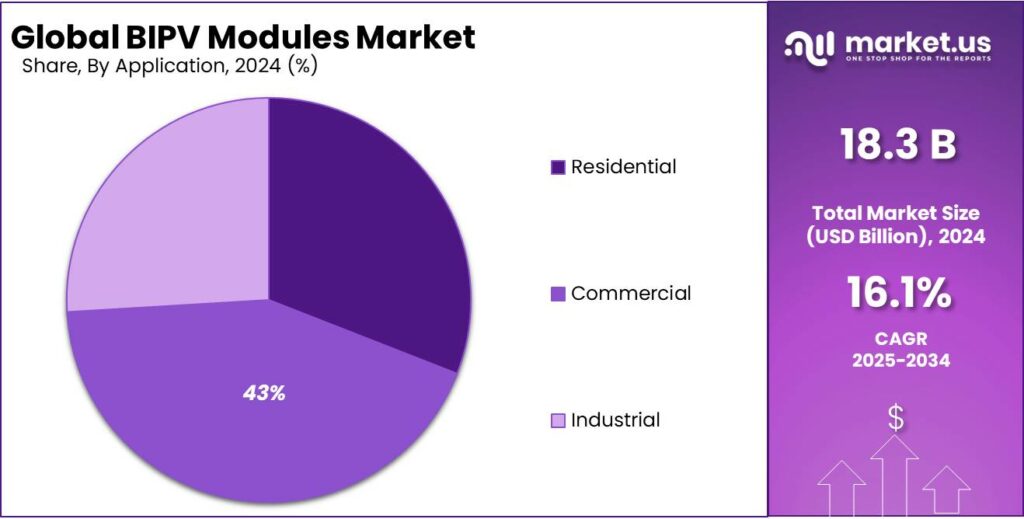
By Application Analysis
Large commercial buildings lead with a 43.2% share, supported by scale advantages and higher energy demand
In 2024, Large held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 43.2% share. This dominance was mainly driven by the high energy needs of large commercial buildings such as shopping malls, airports, corporate offices, and convention centers, where BIPV modules were integrated into roofs, façades, and glass surfaces. Large projects allowed better cost distribution and faster payback, making BIPV a practical choice.
During 2024, sustainability mandates and green certification requirements increased adoption across major commercial developments. In 2025, demand remained stable as new large-scale commercial projects and retrofitting of existing buildings continued to support the strong position of this segment in the BIPV modules market.
By End-Use Analysis
New construction leads with a 67.1% share, driven by early design integration and energy-efficient building trends
In 2024, New Construction held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 67.1% share. This dominance was supported by the ability to integrate BIPV modules directly into building designs at the planning stage, which reduced additional structural costs and improved visual appeal. Developers favored new construction projects as BIPV systems could replace conventional building materials while generating on-site power.
During 2024, stricter energy efficiency standards and green building certifications increased adoption in newly developed residential and commercial projects. In 2025, the segment maintained strong momentum as urban expansion and net-zero construction targets continued to support the use of BIPV modules in new buildings.
Key Market Segments
By Technology
- Crystalline Silicon
- Thin Film
- Others
By Installation Type
- Rooftop
- Façade
- Glazing
- Others
By Application
- Residential
- Commercial
- Industrial
By End-Use
- New Construction
- Retrofit
Emerging Trends
Solar Energy Integration Beyond Electricity — Linking BIPV Growth with Renewable Use in Food and Agriculture
One of the most interesting trends shaping the future of Building-Integrated Photovoltaic (BIPV) modules today is how solar energy is increasingly becoming part of broader systems that connect energy, food production, and sustainability. This trend doesn’t just live in the realm of clean electricity — it’s part of a deeper shift where governments, farmers, businesses and even food industries are seeing solar power as a tool for resilience, cost savings and environmental improvement.
Governments and international organisations have been encouraging solar deployment not only to power homes but to support food systems and agriculture. For example, the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) teamed up to produce a framework aimed at accelerating renewable energy use across agri-food chains, linking energy access directly to food systems resilience and sustainable development. This collaboration highlights that renewable energy — including solar photovoltaics — plays a role in agriculture, food processing, rural electrification and related supply chains.
In practical terms, these intersections mean that solar PV — the technology at the heart of BIPV — is gaining familiarity and trust across sectors that were once only marginal consumers of solar power. For example, research into solar energy applications in dairy and food processing shows that solar thermal and PV solutions are being explored to reduce dependence on traditional fuels, given that many of these processes are energy intensive. While these solar solutions are not BIPV in themselves, this trend of food and agriculture embracing PV technology helps create broader acceptance and awareness of solar power viability.
- According to the most recent IRENA report, global solar photovoltaic (PV) employment reached approximately 7.1 million jobs in 2023, representing about 44% of the total renewable energy workforce worldwide. Another example of solar integration affecting food and sustainability can be seen in companies like Grupo Bimbo, a major global food producer. While not directly a BIPV example, the company has embraced renewable energy by installing distributed solar generation systems with a capacity of 25 MW across its facilities, avoiding significant CO₂ emissions annually.
Drivers
Policy and Government Renewable Energy Initiatives
Across countries, governments are not simply encouraging solar installations — they are setting clear targets and frameworks for renewable energy adoption. For example, India’s National Solar Mission, which is one of its flagship renewable initiatives, set out ambitious goals for solar power deployment by states and cities. Initially launched to push solar generation capacity, this mission ultimately helped India reach a monumental milestone of 100 GW of installed solar power capacity by March 2025 as part of its broader clean energy planning. This target was part of a phased approach designed to boost solar deployment across rooftops, building facades, and utility systems.
- On the ground, this has materialized into real impacts. In the Indian Union Territory of Chandigarh alone, over 11,300 government buildings now have solar panels installed — including rooftop systems on schools, offices, and health facilities — demonstrating how policy cascades into execution at scale. While not all of these are strictly BIPV systems today, they reflect how solar adoption has become part of government building norms — which lays the groundwork for even more integrated solutions like BIPV.
Similarly, building performance codes are enabling more energy-efficient infrastructure. The Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC) in India, for instance, is shaping how commercial buildings are designed to save energy. Andhra Pradesh recently led the nation by approving 786 ECBC-compliant buildings, the most in any state, which doesn’t just promote efficiency but creates a regulatory environment where integrated solar solutions like BIPV become not just attractive but part of compliance.
Government initiatives don’t operate in isolation either. They often bring financial incentives, tax breaks, and subsidy frameworks that reduce upfront costs, making the switch to integrated photovoltaics more affordable for builders and property owners. When a community sees solar powering public libraries, schools, and offices, it helps shift public perception — solar isn’t an add-on, it’s part of the future.
Restraints
High Upfront Costs and Limited Solar Adoption in Buildings Slow BIPV Growth
One of the most meaningful restraining factors holding back the widespread use of BIPV modules is the high upfront installation cost, especially in countries where solar adoption in buildings is still developing. Even though governments push renewable energy, the reality on the ground is that many buildings—both public and private—still struggle to integrate solar systems due to financial and structural barriers. This slows down the natural shift toward BIPV, which requires even higher investment than conventional rooftop solar.
- A clear example comes from India’s rooftop solar landscape. Despite the country’s strong renewable energy ambitions, rooftop solar adoption has been much slower than expected. The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) reported that India had installed only ~11 GW of rooftop solar capacity by 2023, far below potential, largely due to financial and bureaucratic constraints that discourage households and small businesses.
High initial expenses are not the only issue. Building integration requires professional design, electrical configuration, structural reinforcement, and certified installers. These steps add cost and time, especially for older buildings. A good example comes from public infrastructure: the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), India, highlighted that while over 11,300 government buildings in Chandigarh installed solar systems, the installations occurred mostly on rooftops—not as BIPV systems—because retrofitting façades involves architectural approvals and significantly higher budgets.
The same concern appears in energy-efficiency programs. The Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC) aims to make commercial buildings more sustainable, yet even with policy support, only 786 buildings in Andhra Pradesh have been able to comply so far—showing how difficult it is for developers to meet efficiency norms that often require additional cost-intensive features.
Opportunity
Rising Solar Adoption and Government Clean Energy Momentum
One of the strongest growth opportunities for Building-Integrated Photovoltaic (BIPV) modules today comes from the broader shift toward solar adoption supported by government clean energy efforts. This isn’t just a technical trend—it reflects how societies are thinking differently about energy, buildings, and sustainability. More solar on rooftops and in communities primes the environment for BIPV to go mainstream, especially as building owners begin seeing integrated photovoltaics not as a luxury, but as a smart investment for long-term energy costs and carbon reduction.
- For instance, under the PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana, nearly 23.96 lakh households have installed rooftop solar systems so far, enabling millions of people to produce clean electricity right where they live. This number shows that when government support aligns with citizen interest, solar technology becomes far more widespread. BIPV stands on the shoulders of this momentum, because as rooftop installations become normal, the next logical step for builders and homeowners is considering integrated solar solutions like BIPV that blend directly into building design.
Beyond individual and government buildings, national clean energy progress has been remarkable. India, according to official data backed by the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), has installed over 27,200 MW of solar power capacity as part of its clean energy portfolio, contributing to overall renewable capacity that reached more than 132,800 MW by November 2025. This reflects sustained policy focus and investment in solar energy that creates a fertile environment for integrated solar applications—including BIPV—because the infrastructure, regulatory frameworks, and workforce skills are growing in tandem.
- According to data from the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), the renewable energy sector supported about 13.7 million jobs in 2022, with around 4.9 million jobs specifically in solar photovoltaic (PV) work. These employment figures signal that solar isn’t just a niche technology—it is a major economic engine providing livelihoods and spurring innovation worldwide. As the solar PV workforce grows, so does the pool of experts capable of designing, installing, and maintaining more complex systems like BIPV.
Regional Insights
Europe leads the BIPV market with 48.3% share and an $8.8 Bn market in 2024, supported by mature demand and regulatory backing.
In 2024, Europe held a commanding position in the building-integrated photovoltaics market, accounting for 48.30% of regional share and representing an estimated USD 8.8 billion in value. This dominance can be attributed to strong policy drivers that have encouraged renewable integration into buildings and to a well-established construction sector that is able to absorb higher-value integrated solutions. Adoption was concentrated in Western Europe where energy-efficiency regulations and green building expectations led to greater specification of BIPV for façades, roofs and glazing.
Moving into 2025, Europe’s share was expected to remain significant as new regulations and building standards kept BIPV attractive for developers seeking compliance and aesthetic value, even as project timelines and incentive structures were monitored closely by stakeholders. Overall, Europe’s market structure in 2024 combined regulatory support, concentrated demand in mature economies, and sizable project pipelines to produce the region’s dominant position.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Avancis GmbH is a key innovator in thin-film BIPV modules, mainly based on CIS technology. In 2024, the company operated manufacturing capacity of over 100 MW annually, supplying façade-integrated solar solutions across Europe. Its modules typically deliver efficiency levels above 15%, supporting large commercial buildings focused on architectural design and long service life.
Hanergy Holding Group Limited is a major thin-film solar producer with strong presence in BIPV. In 2024, the company maintained thin-film manufacturing capacity above 1 GW, supporting large-scale building integration projects. Hanergy’s BIPV products are widely used in commercial roofs and façades across Asia and Europe.
Belectric Holding GmbH is active in integrated solar and energy infrastructure, including BIPV systems. In 2024, the company had delivered more than 500 MW of solar installations globally, with a growing share from building-integrated projects. Its strength lies in turnkey solutions for large commercial and industrial developments.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Avanics GmbH
- Heliatek GmbH
- AGC Solar
- Belectric Holding GmbH
- Hanergy Holding Group Limited
- Ertex Solar
- Solaria
- Onyx Solar
Recent Industry Developments
In 2024, Hanergy’s BIPV offerings included modules with power ratings such as 43–153 Wp for integrated wall and roof components, and smaller integrated tiles with ranges around 9.8–30 Wp, showing how the company tailors thin-film products for diverse architectural requirements.
In 2024, Heliatek achieved a major milestone when its latest generation of HeliaSol organic solar films earned IEC 61215 certification, confirming durability and quality for mainstream solar use — a key validation as the company pushes its flexible modules into commercial and industrial BIPV markets.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 18.3 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 81.4 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 16.1% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Technology (Crystalline Silicon, Thin Film, Others), By Installation Type (Rooftop, Façade, Glazing, Others), By Application (Residential, Commercial, Industrial), By End-Use (New Construction, Retrofit) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Avanics GmbH, Heliatek GmbH, AGC Solar, Belectric Holding GmbH, Hanergy Holding Group Limited, Ertex Solar, Solaria, Onyx Solar Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- Avanics GmbH
- Heliatek GmbH
- AGC Solar
- Belectric Holding GmbH
- Hanergy Holding Group Limited
- Ertex Solar
- Solaria
- Onyx Solar










