Global Battery Management Market Size, Share, Growth Analysis By Battery Type (Lithium-Ion Based, Lead-Acid Based, Nickel Based, Flow Batteries), By Topology (Centralized, Distributed, Modular), By Type (Stationary, Mobile), By Application (Automotive, Consumer Electronics, Energy, Defense, Others), By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034.
- Published date: Nov 2025
- Report ID: 167520
- Number of Pages: 279
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
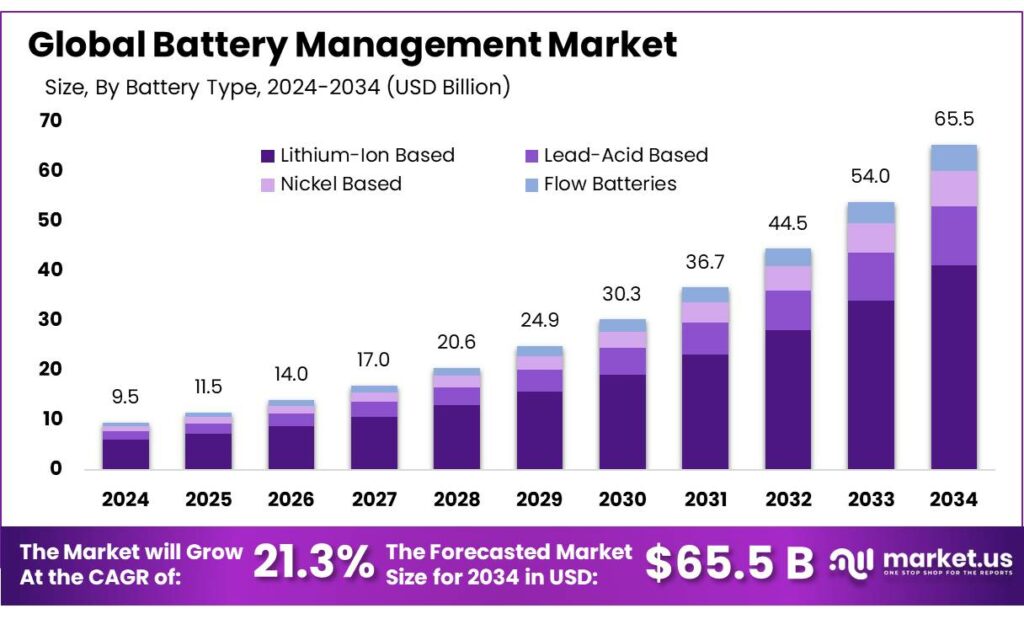
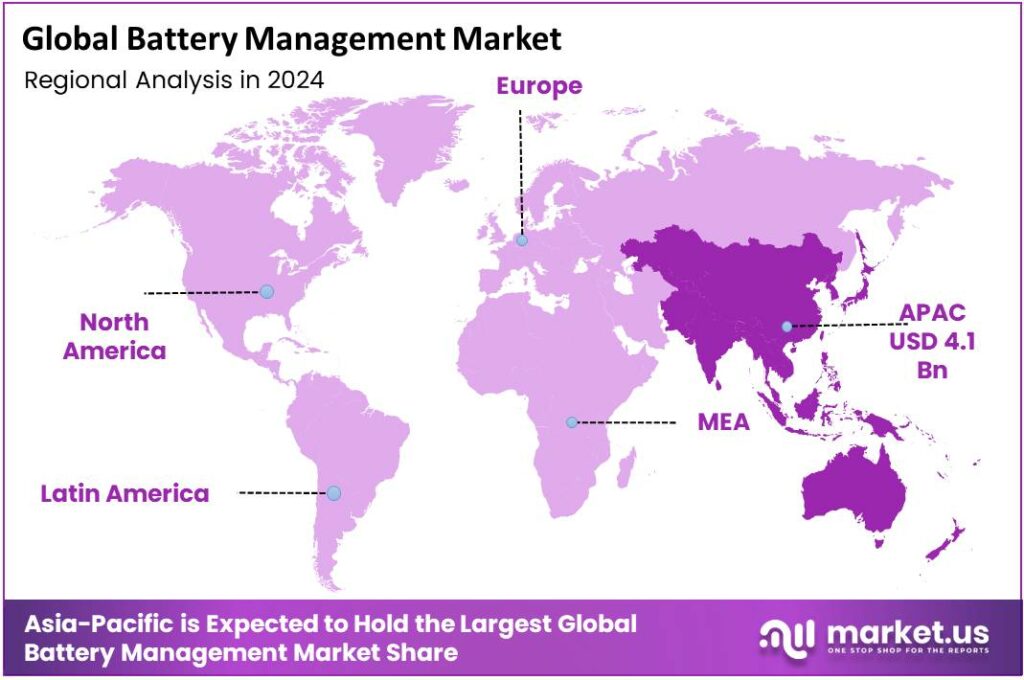
The Global Battery Management Market size is expected to be worth around USD 65.5 Billion by 2034, from USD 9.5 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 21.3% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024, Asia Pacific held a dominan market position, capturing more than a 43.8% share, holding USD 4.1 Billion revenue.
Battery management systems (BMS) have moved from a niche electronics function to a core layer of the global energy and mobility infrastructure. As electrification accelerates, batteries are scaling across electric vehicles, grid-scale storage, industry and buildings.
Each of these deployments relies on BMS hardware and software to monitor cell health, control safety and optimise performance. The International Energy Agency (IEA) estimates that in 2023 there were nearly 45 million electric vehicles on the road worldwide and over 85 GW of battery storage operating in the power sector, underscoring how deeply batteries are now embedded in modern energy systems.
The overall industrial context is defined by rapid growth in renewables and electrified transport. IEA’s Global EV Outlook 2024 reports that almost 14 million new electric cars were registered in 2023, bringing the global electric-car stock to about 40 million and marking a 35% year-on-year increase in sales compared with 2022.
In parallel, data compiled from IRENA statistics show that global renewable power capacity reached about 3,864.52 GW by the end of 2023, with renewables providing roughly 83% of global net power additions that year. In 2024 alone, IRENA estimates that renewable capacity expanded by a record 585 GW, a 15.1% increase that lifted total renewable capacity to around 4,448 GW. Each new electric vehicle and each megawatt of variable renewable generation increases demand for robust battery packs and sophisticated BMS architectures.
Policy and planning frameworks are reinforcing this trajectory. The IEA’s Renewables 2024 analysis finds that the world is on track to add more than 5,500 GW of new renewable capacity between 2024 and 2030, almost three times the increase seen in the 2017–2023 period.
A separate IEA special report warns that tripling global renewable capacity by 2030 will require around 1,500 GW of battery storage, highlighting the central role of storage and, by extension, BMS in delivering climate goals. In Europe, the European Commission projects that total energy-storage capacity will need to exceed 200 GW by 2030, up from roughly 89 GW in 2024, with electrochemical storage providing about 128 GW / 300 GWh of that increase.
Government and regulatory initiatives are shaping market architecture. The European Union’s Battery Regulation (Regulation (EU) 2023/1542) imposes lifecycle, traceability and sustainability obligations that will affect BMS data-logging and end-of-life handling.
National industrial programmes and funding are also influential. India’s ACC programme was approved with an allocation of INR 18,100 crore (~USD 2.16 billion) to build domestic cell capacity targeting large GWh-scale manufacturing. Meanwhile, the U.S. Department of Energy announced about USD 43 million in targeted battery funding to improve safety and strengthen manufacturing resilience.
Key Takeaways
- Battery Management Market size is expected to be worth around USD 65.5 Billion by 2034, from USD 9.5 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 21.3%.
- Lithium-Ion Based held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 62.9% share in the Battery Management System market.
- Centralized held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 42.3% share in the Battery Management System (BMS) market.
- Stationary held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 58.7% share in the Battery Management System market.
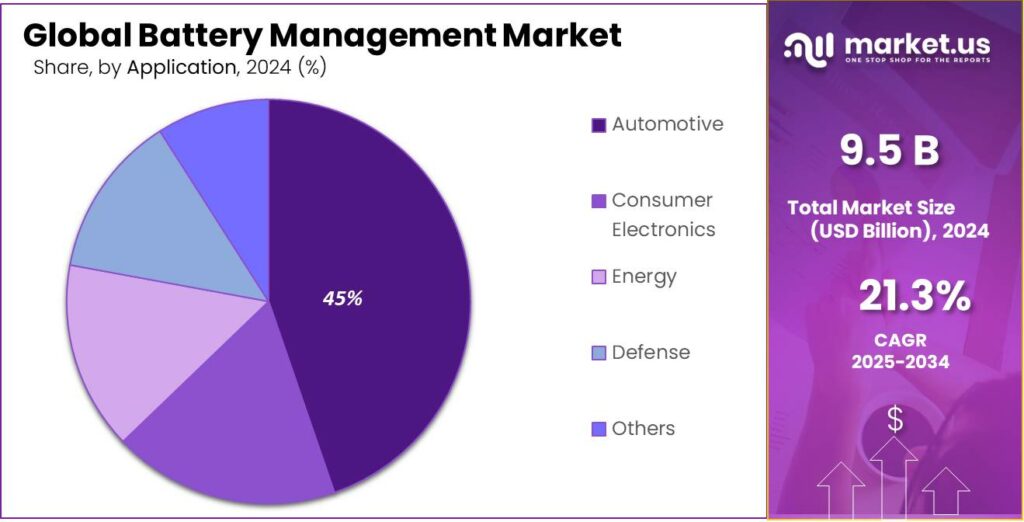
- Automotive held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 44.5% share in the Battery Management System market.
- Asia Pacific region dominated the battery-management systems (BMS) space, capturing approximately 43.8% of global market share with a market size of around USD 4.1 billion.
By Battery Type Analysis
Lithium-Ion Based batteries lead with a strong 62.9% share, supported by rapid adoption in EVs and energy storage systems.
In 2024, Lithium-Ion Based held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 62.9% share in the Battery Management System market. The rise of electric vehicles, consumer wearables, drones, and residential ESS (Energy Storage Systems) has played a key role in helping lithium-ion stay ahead of other chemistries. In simple terms, industries now prefer lithium-ion because it offers higher energy density, longer charging cycles, and better performance consistency.
Throughout 2024, many governments and industries continued expanding incentives and production capacity for lithium-ion technology, especially across EV manufacturing in regions like Europe, North America, China, and India. As EV adoption increased, the demand for intelligent Battery Management Systems grew, because these systems help maintain safety, prevent overheating, and improve charging behavior in lithium-ion packs.
By Topology Analysis
Centralized topology leads the market with 42.3% share, driven by simplicity and cost-efficient integration.
In 2024, Centralized held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 42.3% share in the Battery Management System (BMS) market. Many manufacturers continue choosing centralized architecture because it offers a straightforward design, easier battery monitoring, and lower wiring complexity compared to distributed approaches. The cost advantage also plays a major role, especially in applications like e-bikes, small EVs, consumer electronics, and handheld equipment where compact battery packs are standard.
During 2024, industries working with lithium-ion batteries increased adoption of centralized topology due to quicker installation and lower component count. For smaller and medium-sized battery packs, centralized systems remain practical because all monitoring and balancing logic stays in a single control unit. This makes maintenance and calibration easier and avoids the need for multiple circuit boards or communication modules.
By Type Analysis
Stationary systems lead the market with 58.7% share, supported by rising energy storage and grid modernization demand.
In 2024, Stationary held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 58.7% share in the Battery Management System market. This growth is closely linked to the increasing deployment of grid-scale energy storage, residential backup systems, and commercial microgrids. As renewable power such as solar and wind continues expanding globally, stationary battery systems are becoming essential for balancing supply fluctuations and improving energy reliability.
Demand strengthened from both public and private sectors as organizations focused on stabilizing power networks and improving resilience during peak load conditions. Stationary systems also grew in industrial segments where uninterrupted energy is necessary, such as hospitals, telecom infrastructure, and data centers. Battery management systems are essential in these installations because they monitor cell health, prevent thermal events, and improve operational efficiency across long-duration battery usage.
By Application Analysis
Automotive leads with a strong 44.5% share, driven by rapid EV adoption and advancing battery technologies.
In 2024, Automotive held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 44.5% share in the Battery Management System market. This momentum is mainly shaped by the rising manufacturing of electric vehicles, hybrid vehicles, and plug-in hybrids across global markets. Automakers continued to increase investments in battery-powered platforms throughout 2024 as countries strengthened emission standards, making efficient battery monitoring, safety control, and thermal management essential.
Battery management systems play a key role in automotive applications because they directly influence vehicle safety, charging performance, and driving range. As electric vehicle battery packs become larger and more complex, reliable monitoring of voltage, temperature, and cell balance becomes necessary to protect battery health and extend lifecycle performance. This helped the automotive segment maintain its clear lead during 2024.
Key Market Segments
By Battery Type
- Lithium-Ion Based
- Lead-Acid Based
- Nickel Based
- Flow Batteries
By Topology
- Centralized
- Distributed
- Modular
By Type
- Stationary
- Mobile
By Application
- Automotive
- Consumer Electronics
- Energy
- Defense
- Others
Emerging Trends
Data-driven cold chains are turning batteries and smart management into a core food-system technology.
A clear latest trend in the Battery Management market is the rise of data-driven, battery-backed food cold chains. Food systems are under pressure to cut emissions and waste, while keeping prices stable. UNEP Finance Initiative notes that food systems are responsible for at least one-third of global greenhouse-gas emissions, once farming, processing and packaging are included.
- In 2025, FAO highlighted that 13.3% of total food production is lost between harvest and retail, equal to about 1.31 billion tonnes of food every year. UNEP and FAO also estimate that around 14% of food is lost before retail and another 17% is wasted at retail and household level. Food that spoils because power failed in a cold store or truck is now seen as an avoidable climate and cost problem, not just “operational risk”.
The cold chain itself is a big energy and emissions source. A joint UNEP–FAO report explains that the global food cold chain is responsible for around 4% of total greenhouse-gas emissions, once you include both refrigeration equipment and food loss due to lack of cooling. The International Institute of Refrigeration estimates that refrigeration equipment uses about 20% of global electricity and contributes roughly 7.5–10% of energy-related CO₂ emissions. In the food industry alone, refrigeration can account for around 35% of electricity consumption.
Government and multilateral initiatives reinforce this digital cold-chain trend. The UNEP–FAO flagship report Sustainable Food Cold Chains: Opportunities, Challenges and the Way Forward calls for cleaner, more efficient cold chains and highlights the role of low-carbon energy solutions. At the same time, UNFCCC estimates that food loss and waste account for 8–10% of annual global greenhouse-gas emissions, almost five times aviation’s emissions. This has pushed several countries to include cold-chain and food-loss measures in their 2025 climate plans, indirectly supporting investment in batteries and BMS as enabling technologies.
Drivers
Rising energy-hungry food chains are pushing strong demand for smarter battery management systems.
One major driving factor for the Battery Management market is the growing need for reliable and efficient power in the global food and cold-chain industry. Modern food production, processing, storage, and retail depend heavily on refrigeration, pumps, controls, and digital systems that cannot afford power interruptions. The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) estimates that the food sector accounts for around 30% of the world’s total energy consumption and roughly 22% of total greenhouse-gas emissions, underlining how energy-intensive this industry has become.
- Food loss is another powerful part of this story. In 2025, FAO reported that about 13.3% of global food production – equal to 1.31 billion tonnes – is lost between harvest and retail. Other UN and FAO analyses show that roughly 14% of food is lost post-harvest and a further 17% is wasted at retail, food service, and household level.
Cooling itself is a heavy energy user inside the food system. Studies show that cooling and freezing alone can account for around 30% of the electricity consumption in the food sector. At a global level, the food cold chain – including refrigeration technologies and food loss related to missing cold capacity – is responsible for about 4% of total greenhouse-gas emissions. The International Institute of Refrigeration estimates that refrigeration, excluding heat pumps, represents close to 20% of global electricity consumption.
Government and multilateral initiatives since 2024 and into 2025 reinforce this driver. The UN’s focus on food loss and waste – highlighted each year on the International Day of Awareness of Food Loss and Waste – explicitly calls for better infrastructure, including reliable cold chains and cleaner energy solutions. FAO and partner governments are promoting “sustainable food cold chains,” encouraging countries to modernize refrigeration, reduce emissions, and cut waste.
Restraints
Critical-Mineral Supply and Supply-Chain Constraints
A principal restraint on the rapid deployment of advanced Battery Management Systems (BMS) is the constrained and uneven supply of critical battery raw materials — notably lithium and cobalt — which raises costs, causes production bottlenecks and forces manufacturers to prioritise cell supply over added-value systems such as sophisticated BMS integration. Global lithium production grew but remained tightly matched to demand: worldwide lithium production rose to ~240,000 tonnes in 2024, up about 18% from 2023, yet demand for battery-grade compounds continues to place intense pressure on upstream processing and refining capacity.
Cobalt supply dynamics add another layer of risk because output is geographically concentrated. The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) remains the dominant source of mined cobalt; large new operations have pushed global mine and refinery production higher, but reliance on one region creates vulnerability to political, social and logistical disruption. Recent industry reports showed record increases in mine production but also emphasised that a small number of projects supply a disproportionate share of refined output, intensifying the potential for short-term shocks to ripple through the battery value chain.
Government responses both mitigate and expose the constraint. On one hand, public programmes and defence-led investments have been used to secure domestic refining and reclaim value locally — for example, targeted grants and incentives to develop refining capacity in North America and Europe have been announced to reduce dependence on a single region. Such steps can relieve BMS firms over the medium term but do not erase short-term scarcity. (Example: reported government-backed investments in North American cobalt refining capacity).
Opportunity
Cold-chain modernization in food systems creates a powerful new growth path for battery management.
A major growth opportunity for the Battery Management market lies in the rapid modernization of food cold chains and agrifood energy systems. Today, food production, processing, transport, and waste are under intense pressure to cut emissions and reduce losses. FAO estimates that agrifood systems now account for about one-third of total human-made greenhouse gas emissions, once you include everything from farm activities to processing, retail, and disposal.
Cold chains are at the heart of this opportunity. UNEP and FAO report that the food cold chain is responsible for around 4% of total global greenhouse gas emissions when you combine emissions from cooling equipment and from food loss caused by lack of refrigeration. Research also shows that cooling and freezing alone can account for about 30% of electricity use in the food sector. At the same time, FAO data indicate that roughly 14% of all food produced is lost between harvest and retail, mainly due to poor storage and transport, while additional losses occur later at retail and consumer level.
Policy direction is moving in the same line. International initiatives on food loss and waste, such as the SDG 12.3 target to halve food waste and significantly reduce food loss by 2030, are pushing governments to upgrade storage and logistics. Many National Cooling Action Plans and green-cold-chain programs from agencies like UNIDO and UNEP highlight the need for energy-efficient, low-carbon cooling.
For battery-management suppliers, food systems offer two types of growth. First, there is the straightforward equipment demand from new cold-chain projects and retrofit programs in 2024 and 2025, especially in developing countries trying to cut post-harvest losses.
Regional Insights
Asia Pacific leads with 43.8% share (~USD 4.1 billion) in the Battery Management market.
In 2024, the Asia Pacific region dominated the battery-management systems (BMS) space, capturing approximately 43.8% of global market share with a market size of around USD 4.1 billion, reflecting its strength across electric-vehicle (EV), grid storage and industrial applications. The region’s dominance is supported by several converging factors: China’s massive EV deployment, India’s accelerating electrification policies, and Southeast Asia’s push toward renewables and storage infrastructure.
China, which leads in battery manufacturing and EV adoption, plays a major role in this regional story. For example, recent data show that China’s exports of battery energy-storage systems surged by about 24% year-on-year during the first nine months of 2025, signalling strong manufacturing momentum in the region.
Moreover, in the stationary storage market the Asia Pacific battery-energy-storage system (BESS) market was valued at around USD 48.62 billion in 2024, signalling the scale of investments underpinning BMS demand. Since batteries and their management are integral to both mobility and stationary storage, the APAC region’s large BESS build-out supports the high share for BMS.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Elithion, Inc. — Elithion has been developing lithium-ion battery management systems (BMS) since 2008 and supplies modular BMS hardware and software for large-format packs used in stationary, EV and telecom applications; the company’s off-the-shelf and custom solutions emphasise cell monitoring, balancing and safety features to extend pack life and simplify integration for system integrators and microgrid projects.
Analog Devices, Inc. — Analog Devices provides a broad portfolio of battery-management ICs, cell monitors, and system reference designs for automotive and industrial BMS applications; its offerings include wired and wireless BMS architectures, software tools, and development kits aimed at accurate state-of-charge estimation, cell balancing and functional-safety compliance for EV and ESS integrators.
Lithium Balance A/S — Lithium Balance (LiTHIUM Balance) delivers compact, modular BMS products (e.g., c-BMS24 / c-BMS24X and s-BMS families) targeted at automotive, commercial and stationary applications, with engineered focus on high SOC accuracy, multi-cell monitoring and scalable communication for up to 1000V systems; the product line supports both OEMs and system integrators seeking ready-to-use BMS modules.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Elithion, Inc.
- Johnson Matthey
- Analog Devices, Inc.
- Lithium Balance A/S
- NXP Semiconductor N.V.
- Nuvation
- Texas Instruments Incorporated
- Leclanché SA
- Eberspaecher Vecture Inc.
- Infineon Technologies AG
Recent Industry Developments
31 March 2024 Johnson Matthey, the company reported total revenue of £12,843 million and an underlying operating profit of £410 million for continuing operations.
Analog Devices, Inc. (ADI) has carved a strong niche in the battery-management space, especially by supplying key analog and mixed-signal components used in BMS for electric vehicles and stationary storage systems. In fiscal 2024 (ended Nov 2 2024), ADI reported an annual revenue of USD 9.4 billion.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 9.5 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 65.5 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 21.3% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Battery Type (Lithium-Ion Based, Lead-Acid Based, Nickel Based, Flow Batteries), By Topology (Centralized, Distributed, Modular), By Type (Stationary, Mobile), By Application (Automotive, Consumer Electronics, Energy, Defense, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Elithion, Inc., Johnson Matthey, Analog Devices, Inc., Lithium Balance A/S, NXP Semiconductor N.V., Nuvation, Texas Instruments Incorporated, Leclanché SA, Eberspaecher Vecture Inc., Infineon Technologies AG Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- Elithion, Inc.
- Johnson Matthey
- Analog Devices, Inc.
- Lithium Balance A/S
- NXP Semiconductor N.V.
- Nuvation
- Texas Instruments Incorporated
- Leclanché SA
- Eberspaecher Vecture Inc.
- Infineon Technologies AG










