Global Automotive Carbon Fiber Composites Market Size, Share and Report Analysis By Propulsion (Internal Combustion Engine, Battery Electric Vehicles, Hybrid Electric Vehicles, Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles, Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles), By Fiber Type (Carbon Fiber, Glass Fiber, Hybrid Hiber), By Resin Type (Epoxy Resin, Polyester Resin, Vinyl Ester Resin), By Application (Structural Assembly, Powertrain Components, Interiors, Exteriors, By Vehicle Type (Passenger Car, Commercial Vehicle) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Feb 2026
- Report ID: 178161
- Number of Pages: 325
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
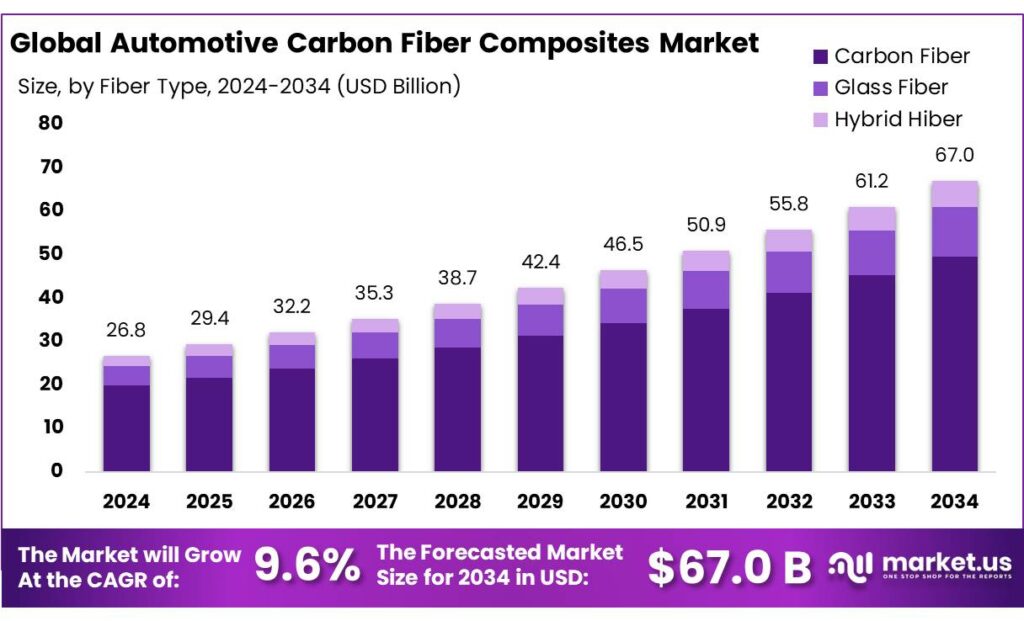
The Global Automotive Carbon Fiber Composites Market is expected to be worth around USD 67.0 Billion by 2034, up from USD 26.8 Billion in 2024, and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 9.6% from 2025 to 2034. The Asia Pacific segment maintained 48.6%, supporting a Automotive Carbon Fiber Composites value of USD 13.0 Bn.
Automotive carbon fiber composites are moving from niche supercars and motorsport into higher-volume vehicle programs as OEMs chase mass reduction without sacrificing crash performance, stiffness, or corrosion resistance. This shift is closely tied to the broader electrification cycle: the International Energy Agency expects electric car sales in 2025 to exceed 20 million units, representing more than one-quarter of global car sales, which raises the premium on lightweight structures that protect range and enable downsized powertrains.
Industrial conditions are improving, but still constrained by cost, cycle time, and capacity planning. On the supply side, major fiber producers continue to add nameplate capacity in regions close to automotive and energy customers; for example, Toray’s Abidos expansion increases annual capacity from 5,000 to 6,000 metric tons to support European demand. At the same time, profitability pressure remains visible in some carbon-fiber value chains as end-markets rebalance and competition intensifies; SGL Carbon reported its Carbon Fibers business unit sales declining to €209.8 million in 2024 (from €224.9 million in 2023), highlighting the importance of mix and disciplined program selection.
Key demand drivers combine regulation, performance economics, and platform redesign. Regulators are tightening fleet emissions expectations while markets accelerate zero-emission adoption; the European Commission notes that zero-emission vehicles reached 14.5% of new car registrations in 2024, and that Regulation (EU) 2019/631 as revised sets a 100% CO₂ reduction target for new cars and vans from 2035. In parallel, energy-efficiency math continues to justify lightweighting where it can be manufactured at scale: the U.S. Department of Energy cites that a 10% vehicle weight reduction can improve fuel economy by 6%–8%, a relationship that also supports EV range optimization and battery right-sizing.
Key Takeaways
- Automotive Carbon Fiber Composites Market is expected to be worth around USD 67.0 Billion by 2034, up from USD 26.8 Billion in 2024, and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 9.6%.
- Internal Combustion Engine held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 39.5% share.
- Liquid Automotive Carbon Fiber Composites held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 74.1% share.
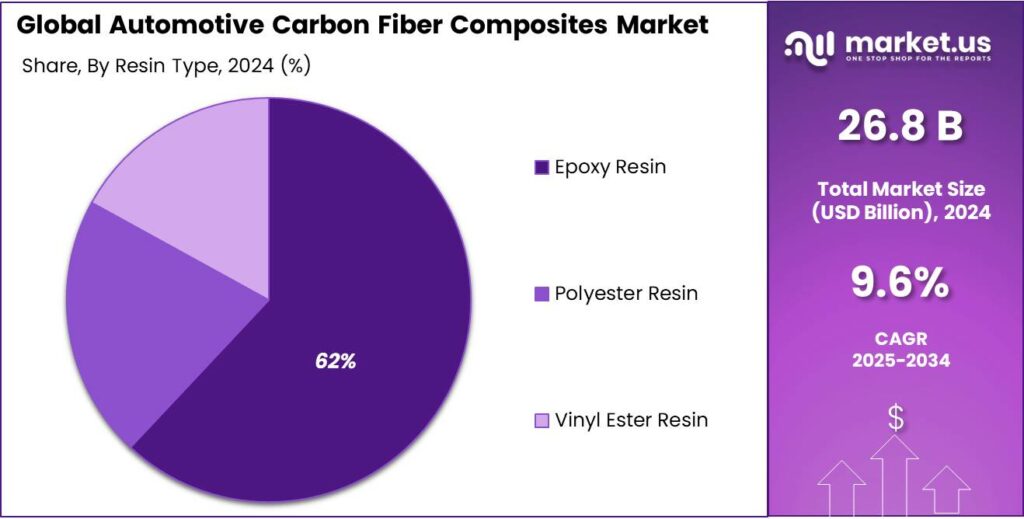
- Epoxy Resin held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 62.7% share.
- Structural Assembly held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 43.4% share.
- Passenger Car held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 79.9% share.
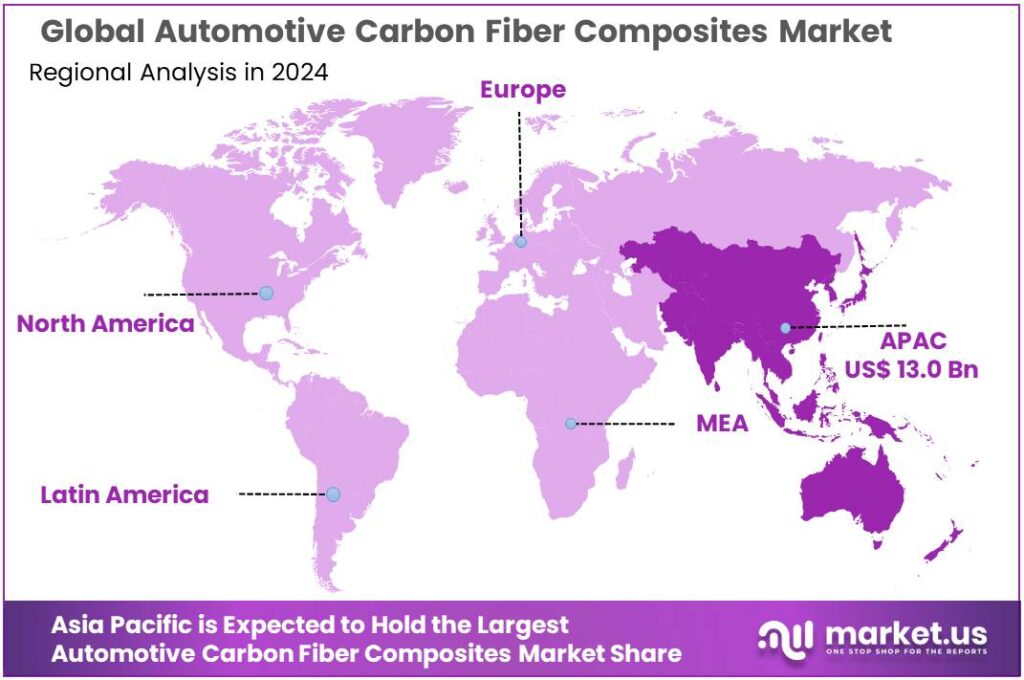
- Asia Pacific emerged as the dominating region in the automotive carbon fiber composites market, accounting for 48.6% share and reaching USD 13.0 Bn.
By Propulsion Analysis
Internal Combustion Engine leads with 39.5% share driven by established production scale and structural lightweighting needs
In 2024, Internal Combustion Engine held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 39.5% share. This leadership was largely supported by the continued global production of gasoline and diesel vehicles across Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and parts of Europe where conventional powertrains still represent a major portion of annual vehicle output. Automakers increasingly integrated carbon fiber composites into ICE platforms to meet tightening emission standards while preserving engine performance and driving dynamics. Lightweight structural parts such as hoods, roof panels, trunk lids, and drive shafts have been key application areas, helping manufacturers offset the weight of safety reinforcements and comfort features.
By Fiber Type Analysis
Liquid Automotive Carbon Fiber Composites dominate with 74.1% share due to manufacturing flexibility and faster cycle times
In 2024, Liquid Automotive Carbon Fiber Composites held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 74.1% share. This strong position was mainly supported by the growing preference for liquid molding processes such as resin transfer molding and compression molding, which allow better control over fiber placement and resin flow. Automakers increasingly adopted liquid composite systems for structural and semi-structural parts because they offer improved surface finish, reduced void content, and compatibility with automated production lines.
By Resin Type Analysis
Epoxy Resin dominates with 62.7% share driven by high strength and durability
In 2024, Epoxy Resin held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 62.7% share. This strong position was mainly supported by epoxy’s superior mechanical strength, excellent bonding capability, and high resistance to heat and chemicals. Automotive manufacturers widely prefer epoxy-based carbon fiber composites for structural components because they deliver long-term durability and stable performance under stress. Parts such as chassis reinforcements, roof structures, and load-bearing panels often rely on epoxy systems to ensure safety and stiffness while reducing overall vehicle weight.
By Application Analysis
Structural Assembly leads with 43.4% share supported by lightweight body integration demand
In 2024, Structural Assembly held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 43.4% share. This leadership was mainly driven by the increasing use of carbon fiber composites in load-bearing and safety-critical vehicle structures. Automakers are integrating carbon fiber into body-in-white components, roof frames, pillars, cross members, and chassis reinforcements to reduce overall vehicle weight while maintaining structural rigidity. The demand is particularly strong in premium passenger vehicles and high-performance models, where strength-to-weight ratio is a key design priority.
By Vehicle Type Analysis
Passenger Car dominates with 79.9% share driven by premium and performance demand
In 2024, Passenger Car held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 79.9% share. This strong position was mainly supported by the widespread use of carbon fiber composites in luxury, sports, and premium passenger vehicles where lightweight performance and design flexibility are key priorities. Automakers increasingly integrated carbon fiber components such as roof panels, hoods, trunk lids, and structural reinforcements to enhance fuel efficiency and driving dynamics. The passenger car segment benefits from higher production volumes compared to commercial vehicles, which allows better cost absorption for advanced materials.
Key Market Segments
By Propulsion
- Internal Combustion Engine
- Battery Electric Vehicles
- Hybrid Electric Vehicles
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles
By Fiber Type
- Carbon Fiber
- Glass Fiber
- Hybrid Hiber
By Resin Type
- Epoxy Resin
- Polyester Resin
- Vinyl Ester Resin
By Application
- Structural Assembly
- Powertrain Components
- Interiors
- Exteriors
By Vehicle Type
- Passenger Car
- Commercial Vehicle
Emerging Trends
Recycled Carbon Fiber Moves From Pilots To Production-Ready Parts
A major latest trend in automotive carbon fiber composites is the fast rise of recycled carbon fiber as a practical, near-term route to scale composites beyond a few premium models. Automakers and tier suppliers are increasingly treating recycled fiber not as a sustainability “nice-to-have,” but as a way to solve two real problems at once: cost pressure and end-of-life expectations. Instead of relying only on virgin continuous fiber for high-end structures, manufacturers are qualifying recycled carbon fiber formats—often chopped or reclaimed fiber combined with liquid resin systems—for repeatable parts where weight savings still matter, but the business case has to be tighter.
Government-backed work is pushing this shift from experimentation to scale. Washington State University reported a $2 million U.S. Department of Energy research award to develop an eco-friendly approach to using recycled carbon fiber in car components. That matters because DOE-linked projects typically target the hard issues that slow adoption—repeatable mechanical performance, resin compatibility, and process stability—so suppliers can meet automotive quality requirements. In parallel, policy signals keep the demand-side pressure high. The European Commission states the EU fleet-wide CO₂ target for new cars and vans is 0 g CO₂/km, pointing to the long-term direction of travel for the industry.
What makes this trend “current” is that it lines up with what large food-and-beverage-linked fleets are already doing on the vehicle side. PepsiCo’s fleet decarbonization update says that in 2024 it deployed 50 Class 8 Tesla Semi trucks and over 500 Ford E-Transit electric vans across its enterprise. As more delivery fleets electrify, the industry becomes more sensitive to vehicle mass, because weight can affect range, payload planning, and operating efficiency on fixed routes.
Drivers
Lightweighting pressure from fleet decarbonization rules is the key demand driver
One major driving factor for automotive carbon fiber composites is the push to cut vehicle emissions by taking weight out of the structure without sacrificing safety or stiffness. Regulators are making that pressure unavoidable. In Europe, the policy direction is clear: from 2035 onward the EU fleet-wide CO₂ target for new cars and vans is 0 g CO₂/km, which forces automakers and their suppliers to rethink materials across platforms, not just in niche performance models.
This same pressure is now coming from the “real economy” of everyday distribution, including food and beverage logistics. Large food and retail operators run enormous vehicle fleets, and their decarbonization choices influence what OEMs build at scale. PepsiCo’s public fleet update shows how quickly heavy and light commercial vehicles are shifting: in 2024 the company expanded electric fleet deployments by adding 50 Class 8 Tesla Semi trucks and over 500 Ford E-Transit electric vans across its operations.
Retail logistics further underlines the scale of the demand signal. Walmart describes its private fleet as having 9,000 tractors and more than 15,000 drivers, a footprint large enough that even small efficiency gains can translate into meaningful fuel or energy savings across routes. As food and beverage move through these networks, fleet operators look for equipment that can haul more per trip, run longer between charges, and meet tightening local air-quality rules. That practical need feeds back into OEM product planning, pushing for lighter and more durable materials in vehicles built for high utilization.
- Government and trusted technical sources also reinforce why lightweighting remains central. The U.S. Department of Energy notes that a 10% reduction in vehicle weight can improve fuel economy by about 6%–8%, which helps explain why automakers keep investing in lightweight materials even when cost pressure is high.
Restraints
High material and processing costs remain the biggest barrier to wider adoption
One major restraining factor for automotive carbon fiber composites is their high material and production cost compared to conventional steel and aluminum. While carbon fiber delivers excellent strength-to-weight performance, its price structure makes it difficult to scale across mass-market vehicles. The U.S. Department of Energy has openly acknowledged this challenge, noting that reducing carbon fiber production cost is essential for broader automotive use and setting a long-term technical target of $5 per pound to make carbon fiber viable for high-volume vehicle manufacturing.
The issue becomes even more visible when viewed through the lens of large-scale food and retail logistics fleets. These industries operate on tight operating margins and prioritize vehicle affordability and lifecycle cost. Walmart, for example, operates a private fleet of 9,000 tractors and works with more than 15,000 drivers, reflecting the massive scale at which vehicle procurement decisions are made.
Similarly, PepsiCo reported in 2024 that it added 50 Tesla Semi trucks and over 500 Ford E-Transit electric vans to its fleet as part of its decarbonization strategy. Even as electrification grows, fleet managers must balance sustainability goals with procurement budgets. The integration of carbon fiber composites into high-volume commercial vehicles would significantly increase upfront cost, especially when combined with already expensive battery systems in electric trucks and vans. For fleet operators focused on return on investment, durable steel and aluminum structures still offer a more predictable cost profile.
Government research initiatives reinforce that affordability is central to material transition. The Department of Energy continues to fund research into low-cost precursor materials and faster manufacturing cycles to reduce production expenses associated with carbon fiber. However, scaling advanced composite production requires capital-intensive facilities, controlled curing environments, and specialized tooling, all of which add to per-unit cost.
Opportunity
Recycled carbon fiber for high-volume fleet vehicles is a clear growth opportunity
One major growth opportunity for automotive carbon fiber composites is the shift from “premium-only” parts toward recycled carbon fiber solutions that can fit the economics of high-volume vehicles, especially those used in food and grocery distribution. The key idea is simple: if recycled carbon fiber can be supplied at consistent quality, it can unlock wider use in semi-structural and reinforcement parts where automakers need weight savings but cannot justify virgin fiber costs.
Government-backed work is already pushing this direction. Washington State University reported a $2 million U.S. Department of Energy research award aimed at developing an eco-friendly approach to using recycled carbon fiber in car components. That kind of funded work matters because it targets the bottlenecks that have slowed adoption: reliable reclaimed fiber quality, resin compatibility, repeatable mechanical performance, and scalable processing that can be integrated into automotive production.
The same opportunity aligns with what fleet operators in the food ecosystem are already doing. PepsiCo stated that in 2024 it expanded electric fleet deployments by deploying 50 Class 8 Tesla Semi trucks and over 500 Ford E-Transit electric vans across its enterprise. For companies like this, every kilogram saved can translate into practical operational benefits—more payload flexibility, better range stability on fixed routes, and less energy consumed per delivery cycle.
Scale in food logistics makes this even more compelling. Walmart’s own fleet footprint is massive, and the company notes it operates 9,000 tractors and more than 15,000 drivers. When vehicle purchases happen at that scale, automakers have an incentive to develop materials and processes that can deliver both performance and predictable cost—exactly where recycled carbon fiber can shine. If recycled composite solutions can be standardized for common vehicle parts, OEMs can offer lighter vehicles without pushing purchase prices into premium-only territory.
Regional Insights
Asia Pacific dominates automotive carbon fiber composites with 48.6% share, supported by its large vehicle manufacturing base and fast adoption of lightweight materials.
In 2024, Asia Pacific emerged as the dominating region in the automotive carbon fiber composites market, accounting for 48.6% share and reaching USD 13.0 Bn, as the region combines the world’s highest vehicle output with accelerating electrification and premiumization. China remains the primary volume engine: the China Association of Automobile Manufacturers reported 31.436 million vehicle sales in 2024, with production also above 31 million, reinforcing strong demand for lightweight structural solutions used in passenger cars and performance variants.
Alongside China, India continues to expand manufacturing depth and export capability; the Government of India shows total automobile exports rising from 4,496 units in 2023–24 to 5,356 units in 2024–25, indicating a broader production and supply ecosystem that can absorb advanced materials over time.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Toray is one of the largest upstream suppliers in carbon fiber, prepregs, and composite materials used in lightweight vehicle parts. The group is headquartered in Tokyo, Japan, employs 48,140 people (Toray 6,995; Japan subs 10,432; overseas subs 30,713), and had 306 subsidiaries/affiliates as of March 31, 2024. Its paid-in capital is ¥147,873,030,771, and it was established in January 1926. In its carbon fiber composite materials segment, Toray reported ¥290.5 billion revenue.
Hexcel is a major producer of carbon fiber, prepregs, honeycomb, and engineered core materials that also translate into high-performance transport applications. In 2024, the company delivered $1.903 billion in sales, with $202.9 million in free cash flow and $2.03 adjusted earnings per share. As of December 31, 2024, Hexcel employed 5,894 full-time employees and contract workers (3,120 in the U.S. and 2,774 internationally). Its executive offices are listed at Two Stamford Plaza, Stamford, CT 06901.
SGL Carbon supplies carbon fibers and composite solutions used in mobility and industrial end markets, with a footprint anchored in Germany. For FY2024, SGL Carbon reported €539.0 million in sales. The company reported 4,511 total employees (headcount) as of December 31, 2024. Its head office is listed as Söhnleinstrasse 8, 65201 Wiesbaden, Germany. These figures reflect a focused composites business operating alongside graphite solutions, with demand sensitivity tied to automotive and industrial production cycles in Europe and North America.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Toray Industries Inc.
- Hexcel Corporation
- Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation
- SGL Carbon SE
- Teijin Ltd
- BASF SE
- Solvay SA
- Hyosung Advanced Materials
- Dow
- Aksa
- Nippon Graphite Fiber Corporation
Recent Industry Developments
In 2024, Hexcel reported strong financial traction with full-year net sales of about $1.903 billion and free cash flow of approximately $203 million, underpinned by its broad product range that includes carbon fiber reinforcements, honeycomb core, prepregs and resin systems used for lightweight structures.
In FY2024, Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation reported ¥4,407.4 billion in consolidated sales revenue and ¥298.4 billion in core operating income, showing the financial scale behind its advanced materials investment, while its workforce stood at 63,258 employees as of March 31, 2025 and it listed 528 subsidiaries and affiliates.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 26.8 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 67.0 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 9.6% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Propulsion (Internal Combustion Engine, Battery Electric Vehicles, Hybrid Electric Vehicles, Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles, Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles), By Fiber Type (Carbon Fiber, Glass Fiber, Hybrid Hiber), By Resin Type (Epoxy Resin, Polyester Resin, Vinyl Ester Resin), By Application (Structural Assembly, Powertrain Components, Interiors, Exteriors, By Vehicle Type (Passenger Car, Commercial Vehicle) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Toray Industries Inc., Hexcel Corporation, Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation, SGL Carbon SE, Teijin Ltd, BASF SE, Solvay SA, Hyosung Advanced Materials, Dow, Aksa, Nippon Graphite Fiber Corporation Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Automotive Carbon Fiber Composites MarketPublished date: Feb 2026add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Automotive Carbon Fiber Composites MarketPublished date: Feb 2026add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Toray Industries Inc.
- Hexcel Corporation
- Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation
- SGL Carbon SE
- Teijin Ltd
- BASF SE
- Solvay SA
- Hyosung Advanced Materials
- Dow
- Aksa
- Nippon Graphite Fiber Corporation










