Global Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer Rebars Market Size, Share, And Enhanced Productivity By Resin Type (Polyester, Vinyl Ester, Ероху, Others), By Diameter (< 10mm, 10-20 mm, and > 20 mm), By Manufacturing Type (Compression Molding, Injection Molding, Resin Transfer Molding, Filament Winding, By Tensile Strength (Low Strength (< 1000 MPa), High Strength (>1000 MPa), By Application (Highways, Bridges And Buildings, Marine Structure And Waterfront, Water Treatment Plants, Others), By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends, and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Feb 2026
- Report ID: 177133
- Number of Pages: 205
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
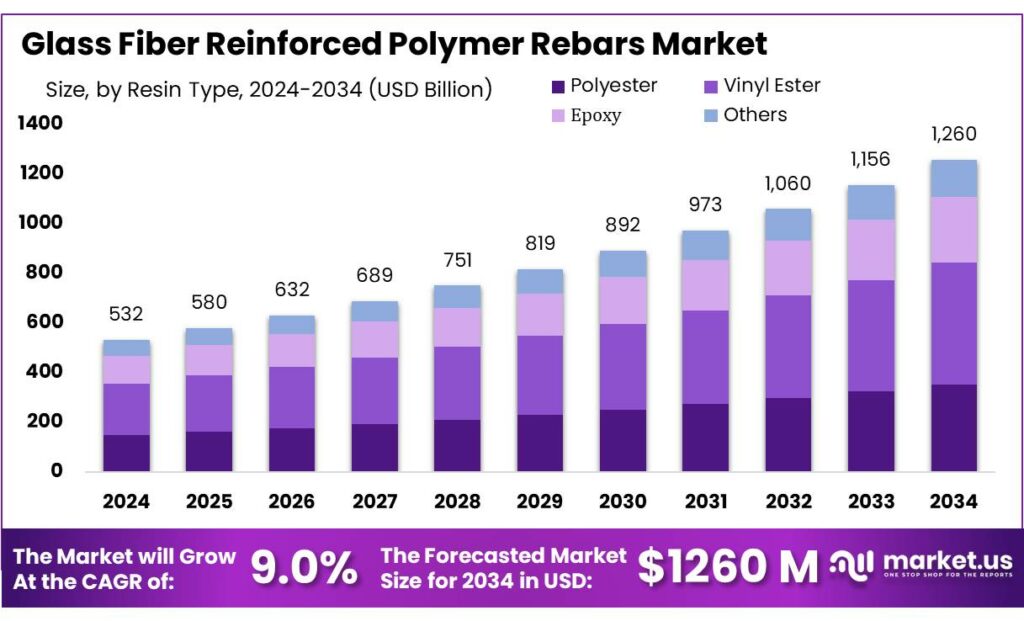
The Global Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer Rebars Market is expected to be worth around USD 1260 Million by 2034, up from USD 532 Million in 2024, and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 9.0% from 2025 to 2034. The North America segment maintained 36.1%, supporting a Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer Rebars value of USD 192.0 Mn.
Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer (GFRP) rebars are non-metallic reinforcement bars used in concrete where steel’s corrosion risk, electromagnetic interference, or weight becomes a design constraint. In practice, they are positioned as a durability-led alternative for assets expected to face chloride exposure, aggressive chemicals, or long wet–dry cycles. The broader industrial scenario is being shaped by the rising cost of maintaining aging concrete infrastructure, where corrosion is a root cause of lifecycle overruns.
- AMPP/NACE estimates the global cost of corrosion at about US$2.5 trillion, roughly 3.4% of global GDP, and indicates that applying available corrosion control practices could reduce these costs by 15–35%, implying potential annual savings of US$375–875 billion.
A key adoption accelerator is the transition from “pilot use” to codified design pathways. In the U.S., the publication and growing reference use of ACI CODE-440.11-22 is frequently cited by specifiers as a practical milestone because it standardizes structural design requirements for concrete reinforced with GFRP bars, lowering approval friction for public owners and large contractors.
In parallel, infrastructure programs are expanding the pipeline of bridge and rehabilitation work where owners are increasingly open to corrosion-resistant solutions: the U.S. Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act authorizes USD 1.2 trillion for transportation and infrastructure spending, including US$550 billion toward new investments and programs. The Federal Highway Administration’s Bridge Investment Program also reports bridge grants announced to date totaling US$930 million across 31 projects in 24 states, reinforcing near-term concrete repair and replacement activity where durability materials can be value-justified.
Demand pull is also visible in food-linked infrastructure that routinely operates in corrosive or hygiene-critical conditions—cold stores, processing plants, and temperature-controlled logistics—where moisture, washdowns, and salts can accelerate steel reinforcement degradation. FAO has estimated that roughly one-third of food produced for human consumption is lost or wasted, about 1.3 billion tonnes annually, keeping policy and capital focused on strengthening storage and supply-chain reliability. In the U.S., FSIS notes it monitors about 7.1 thousand establishments, underscoring the scale of regulated meat/poultry/egg facilities where resilient floors, drains, and utility corridors are essential.
Key Takeaways
- Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer Rebars Market is expected to be worth around USD 1260 Million by 2034, up from USD 532 Million in 2024, and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 9.0%.
- Vinyl Ester held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 39.8% share.
- 10–20 mm held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 49.9% share.
- Filament Winding held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 42.4% share.
- High Strength (>1000 MPa) held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 67.7% share.
- Automotive held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 36.3% share.
- North America dominates the GFRP Rebars Market with 36.1%, valued at 192.0 Mn, as durability priorities rise.
By Resin Type Analysis
Vinyl Ester leads the GFRP Rebars Market with a strong 39.8% share in 2024
In 2024, Vinyl Ester held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 39.8% share, reflecting its strong acceptance across infrastructure, marine, and industrial construction projects. This segment’s leadership is mainly driven by the material’s superior corrosion resistance, high bond strength with concrete, and stable performance under harsh temperature cycles.
Many public infrastructure upgrades undertaken in 2024 preferred Vinyl Ester–based GFRP rebars due to their ability to extend structural lifespan without the maintenance burden associated with steel reinforcement. The material’s chemical stability also made it a natural choice for wastewater plants, desalination facilities, and industrial flooring systems, where durability expectations continue to rise year after year.
By Diameter Analysis
10–20 mm diameter leads the GFRP Rebars Market with a solid 49.9% share in 2024
In 2024, 10–20 mm held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 49.9% share, mainly because this diameter range fits the structural needs of most medium-to-heavy concrete applications. Construction teams preferred this size for bridge decks, foundations, retaining walls, and industrial flooring, where balanced strength, easy handling, and reliable bonding with concrete are essential.
The size also aligns well with typical design codes used in public infrastructure, making it the practical choice for long-span durability projects. Throughout 2024, many municipal and highway upgrades continued shifting toward corrosion-resistant reinforcement, and the 10–20 mm category became the default due to its compatibility with standard rebar spacing and load-bearing requirements.
By Manufacturing Type Analysis
Filament Winding leads the GFRP Rebars Market with a strong 42.4% share in 2024
In 2024, Filament Winding held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 42.4% share, mainly because this manufacturing method offers exceptional control over fiber alignment, producing rebars with superior tensile strength and consistent quality. The process became the preferred choice across major infrastructure and industrial projects in 2024, as it delivers highly reliable reinforcement designed to withstand corrosive environments and heavy structural loads. Engineers favored Filament Winding for its precision, which supports uniform mechanical properties across every batch, helping reduce material variability and ensuring predictable long-term performance in concrete applications.
By Tensile Strength Analysis
High Strength (>1000 MPa) leads the GFRP Rebars Market with a commanding 67.7% share in 2024
In 2024, High Strength (>1000 MPa) held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 67.7% share, reflecting the construction industry’s growing shift toward reinforcement materials capable of handling demanding loads with long-term reliability. This segment gained rapid traction in 2024 as public infrastructure projects, including bridges, coastal defenses, and industrial foundations, increasingly required reinforcement that could endure both mechanical stress and corrosive conditions.
The superior tensile capacity of >1000 MPa rebars offered engineers a dependable solution to reduce structural weight while maximizing safety margins. As durability expectations rose across new projects, this strength class became the preferred choice for designs targeting long service life with minimal repair cycles.
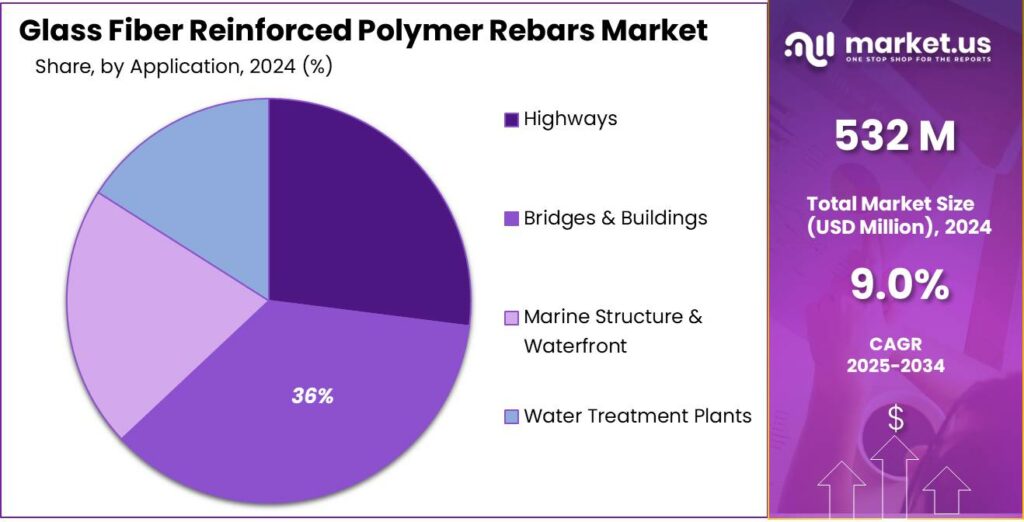
By Application Analysis
Automotive segment leads the GFRP Rebars Market with a steady 36.3% share in 2024
In 2024, Automotive held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 36.3% share, driven by the sector’s increasing shift toward lightweight, corrosion-resistant materials that can withstand high vibration and long operating cycles. Automotive manufacturers began integrating GFRP rebars into specialized tooling, structural supports, and production-line infrastructure where conventional steel reinforcement underperforms in moisture-prone or chemically exposed environments.
Throughout 2024, the push for more durable plant facilities and lightweight structural elements supported steady adoption, especially in regions expanding EV manufacturing and component processing units where clean, non-corrosive reinforcement is preferred to maintain operational continuity.
Key Market Segments
By Resin Type
- Polyester
- Vinyl Ester
- Ероху
- Others
By Diameter
- < 10mm
- 10-20 mm
- and > 20 mm
By Manufacturing Type
- Compression Molding
- Injection Molding
- Resin Transfer Molding
- Filament Winding
By Tensile Strength
- Low Strength (< 1000 MPa)
- High Strength (>1000 MPa)
By Application
- Highways
- Bridges & Buildings
- Marine Structure & Waterfront
- Water Treatment Plants
- Others
Emerging Trends
GFRP rebars are moving from “special projects” to code-led, spec-ready reinforcement
One of the clearest latest trends in Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer (GFRP) rebars is the shift toward code-based adoption—meaning owners and engineers are no longer treating GFRP as a niche material that needs fresh justification on every job. Instead, more projects are using GFRP through recognized design rules and repeatable specifications. A key signal is the release and growing reference of ACI CODE-440.11-22 by the American Concrete Institute, which sets requirements for structural concrete reinforced with GFRP bars. The code is identified as ACI CODE-440.11-22 and became effective September 2, 2022.
This code-led approach is gaining attention because asset owners are under pressure to reduce corrosion-driven repair cycles. The Association for Materials Protection and Performance (AMPP) highlights the scale of the corrosion problem, estimating the global cost of corrosion at about US$2.5 trillion, roughly 3.4% of global GDP, and noting that corrosion control practices could reduce costs by 15–35%, implying US$375–875 billion in potential annual savings. Those numbers are increasingly used in internal business cases to justify durable reinforcement choices, especially for structures exposed to water, chlorides, and chemicals.
The same “durability-first” thinking is showing up in food-linked construction, which matters because many food facilities operate in wet, chemical-cleaning environments where reinforced concrete faces long-term stress. The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) estimates that roughly one-third of food produced for human consumption is lost or wasted globally, amounting to about 1.3 billion tonnes each year. This keeps policymakers and operators focused on upgrading cold storage, processing, and logistics facilities—buildings that need to stay online with minimal structural disruption.
Drivers
Corrosion-proof infrastructure spending is pushing GFRP rebars forward, with food logistics adding extra demand pressure.
A major driving factor for Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer (GFRP) rebars is the urgent need to cut corrosion-related repairs in concrete assets that stay wet, salty, or chemically exposed. Corrosion is not a “small maintenance issue”—it is a global cost problem that owners can measure in real money. AMPP (formerly NACE) estimates the global cost of corrosion at about US$2.5 trillion, equal to roughly 3.4% of global GDP, and notes that applying available corrosion control practices could reduce costs by 15–35%, implying potential annual savings of US$375–875 billion.
In the U.S., the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act authorizes US$1.2 trillion for transportation and infrastructure spending, including US$550 billion in “new” investments and programs. When bridges, decks, and rehabilitation packages expand, reinforcement choices naturally get reviewed—especially in regions with de-icing salts, marine exposure, or aggressive groundwater. In these settings, corrosion-resistant reinforcement supports longer service intervals and fewer disruptive closures, which owners often value more than a small material cost difference.
FAO has long highlighted the scale of food efficiency pressure, estimating roughly one-third of food produced for human consumption is lost or wasted globally—about 1.3 billion tonnes per year. That reality keeps attention on better cold storage, processing sites, and logistics reliability, where structural downtime can quickly turn into product loss. In the U.S. alone, USDA’s FSIS indicates there are about 7,100 federally inspected establishments and roughly 7,500 frontline workers, showing how large the regulated processing footprint is and how important dependable facilities are to daily operations.
In 2025, the same driver remains strong, but it becomes more operational: owners want reinforcement that helps avoid shutdowns, not just reduce rust stains. Cold-chain policy support also continues to expand. For example, India’s government communications around the Integrated Cold Chain and Value Addition Infrastructure scheme point to a budget increase to ₹6,520 crore, signaling ongoing emphasis on cold-chain strengthening where durable building materials reduce maintenance interruptions.
Restraints
High upfront cost remains a major restraint, especially for food-related and public infrastructure budgets
A significant restraining factor for Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer (GFRP) rebars is their higher initial cost, which often becomes a barrier for public project owners, food-processing facilities, and small-scale industrial builders who operate under tight budgets. While GFRP brings long-term savings, many decision-makers still frame reinforcement choices around upfront expenditure rather than lifecycle value. This cost sensitivity becomes more visible in sectors such as food logistics and cold-chain construction, where margins can be thin and capital planning is usually conservative.
The food industry itself operates with notable financial pressure because global food loss remains extremely high. The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) reports that 1.3 billion tonnes of food are lost or wasted every year—about one-third of all food produced globally—highlighting how inefficiencies already strain resources across the sector. When companies must invest heavily in refrigeration, hygiene systems, and safety compliance, the idea of spending more on reinforcement materials—even if durable—can feel difficult to justify in the short term. For smaller operators, additional structural cost becomes a hurdle that delays or reduces adoption of GFRP rebars.
Regulated food-processing environments also face major operational oversight. The Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSIS) monitors around 7,100 inspected establishments across the United States. These facilities require frequent cleaning, chemical washdowns, and temperature control—all conditions where GFRP would outperform steel. Government budgets, while supportive of infrastructure growth, also demonstrate how allocation pressures limit immediate adoption of premium materials. India’s updates to the Integrated Cold Chain and Value Addition Infrastructure Scheme outline allocations of ₹6,520 crore, directed largely toward capacity building rather than pushing adoption of advanced building materials.
Opportunity
Cold-chain expansion is a clear growth opportunity for GFRP rebars
One major growth opportunity for Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer (GFRP) rebars is the steady buildout of cold-chain and food-processing infrastructure, where concrete structures face constant moisture, chemicals, and washdowns. These facilities depend on floors, drains, loading bays, and utility corridors that must stay reliable under harsh operating conditions. In many of these environments, steel reinforcement can become a long-term weakness because corrosion risk rises when concrete stays wet or is exposed to salts and cleaning agents.
The food system is actively pushing for better storage and handling because waste remains extremely high. The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) estimates that about one-third of food produced for human consumption is lost or wasted globally—around 1.3 billion tonnes every year.
This opportunity becomes even clearer when you look at how large the regulated processing footprint is. In the U.S., the USDA Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSIS) states there are approximately 7,100 federally inspected establishments. That number represents thousands of facilities where hygiene-driven cleaning is routine and wet environments are common—exactly the kind of setting where owners start valuing materials that reduce long-term structural problems.
Government initiatives are also supporting this pathway. In India, the government’s press note on PMKSY indicates the total allocation rising to ₹6,520 crore, and it also mentions ₹500 crore to support 50 Multi-Product Food Irradiation Units under the Integrated Cold Chain and Value Addition Infrastructure component. This matters for GFRP rebars because cold-chain investments do not stop at equipment; they bring new concrete construction and upgrades—processing zones, chilled storage, distribution centers, and supporting utilities. These are long-life assets where corrosion resistance can translate into fewer repairs over time.
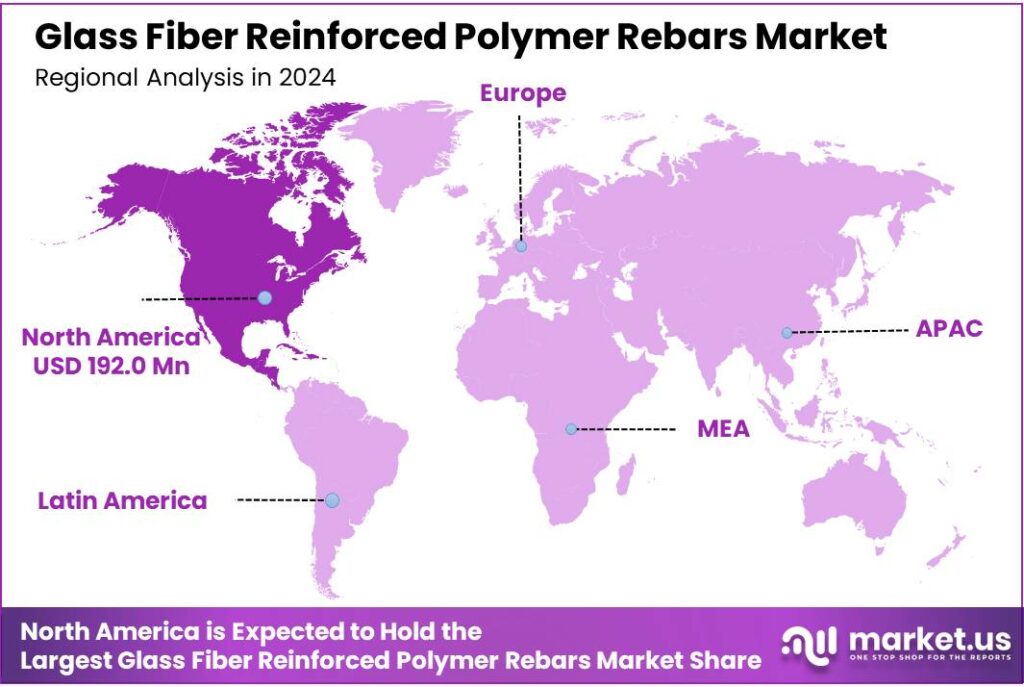
Regional Insights
North America dominates the GFRP Rebars Market with 36.1%, valued at 192.052 Mn, as durability priorities rise.
In 2024, North America remained the most influential region for Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer (GFRP) rebars, backed by a steady pipeline of bridge rehabilitation, coastal protection, and water-adjacent construction where corrosion is a daily engineering concern. The region’s leadership is closely tied to how owners evaluate long-life performance: corrosion is no longer treated as routine wear-and-tear, but as a measurable financial drain. AMPP highlights the global cost of corrosion at about US$2.5 trillion (around 3%+ of global GDP) and notes that applying corrosion control practices could reduce costs by 15–35%, implying US$375–875 billion in potential annual savings—numbers that increasingly strengthen the business case for non-corrosive reinforcement.
The industrial scenario is also helped by clearer design pathways. American Concrete Institute published ACI CODE-440.11-22, which gives engineers and reviewers a code-based route to specify GFRP bars with fewer approval delays, supporting repeat procurement rather than one-off pilots. On the demand side, public infrastructure spending continues to keep projects moving: the Government Finance Officers Association summarizes the U.S. Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act as authorizing US$1.2 trillion, including US$550 billion in new investments and programs.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Röchling – In 2024, the company reported annual sales of €2,592 million and a workforce of 11,681 people operating across 83 locations in 25 countries. These scale indicators matter because GFRP rebar adoption often follows larger construction-material supply chains that can support consistent quality and delivery performance across regions.
Dextra Group – Dextra states it was established in 1983 and is headquartered in Bangkok, Thailand. In a published company interview note, it cites around US$130 million in revenues, nearly 900 employees, and operations in 55+ countries—useful signals of global reach for supplying FRP solutions into multi-country infrastructure programs.
Sireg S.p.A. – The Sireg Group traces its origin to 1936 and operates from Arcore (MB), Milan area, with a listed address at Via del Bruno 12, 20862. Its Italian tax IDs are published for group entities, including P.IVA IT 09263030968 (Geotech) and P.IVA IT 08936400962 (Hydros), signaling formal multi-entity operations supporting engineered civil solutions.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Rochling
- Sireg S.P.A.
- Pultrall Inc.
- Armastek
- Dextra Group
- FRT TUF-BAR
- SKD Composites
- Pultron Composites
- Schock Bauteile GmbH
- Kodiak Fiberglass Rebar
- ARC Insulations & Insulator Ltd.
Recent Industry Developments
In 2024, Röchling reported group annual sales of €2,592 million, with 11,681 employees across 83 locations in 25 countries—scale that matters for infrastructure customers who prefer stable, multi-site partners when qualifying advanced materials and components.
In 2024, Sireg’s composite bars were selected for the reconstruction of the Fontanamare-Gonnesa bridge in Italy, using GFRP reinforcement estimated to have a service life twice as long as steel, illustrating real-world trust in its products.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 532 Mn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 1260 Mn CAGR (2025-2034) 9.0% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Resin Type (Polyester, Vinyl Ester, Ероху, Others), By Diameter (< 10mm, 10-20 mm, and > 20 mm), By Manufacturing Type (Compression Molding, Injection Molding, Resin Transfer Molding, Filament Winding, By Tensile Strength (Low Strength (< 1000 MPa), High Strength (>1000 MPa), By Application (Highways, Bridges And Buildings, Marine Structure And Waterfront, Water Treatment Plants, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Rochling, Sireg S.P.A., Pultrall Inc., Armastek, Dextra Group, FRT TUF-BAR, SKD Composites, Pultron Composites, Schock Bauteile GmbH, Kodiak Fiberglass Rebar, ARC Insulations & Insulator Ltd. Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer Rebars MarketPublished date: Feb 2026add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer Rebars MarketPublished date: Feb 2026add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Rochling
- Sireg S.P.A.
- Pultrall Inc.
- Armastek
- Dextra Group
- FRT TUF-BAR
- SKD Composites
- Pultron Composites
- Schock Bauteile GmbH
- Kodiak Fiberglass Rebar
- ARC Insulations & Insulator Ltd.










