Global Coconut Yogurt Market Size, Share Analysis Report By Form (Dairy Coconut Yogurt, Non-Dairy Coconut Yogurt), By Product Type (Plain Coconut Yogurt, Flavored Coconut Yogurt, Greek-style Coconut Yogurt) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Oct 2025
- Report ID: 162738
- Number of Pages: 393
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
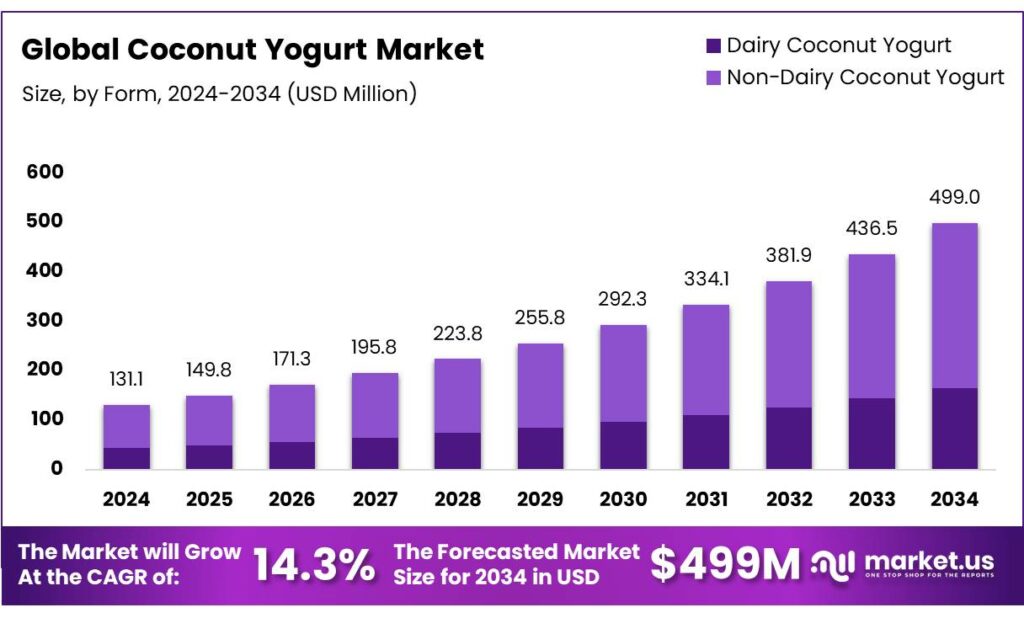
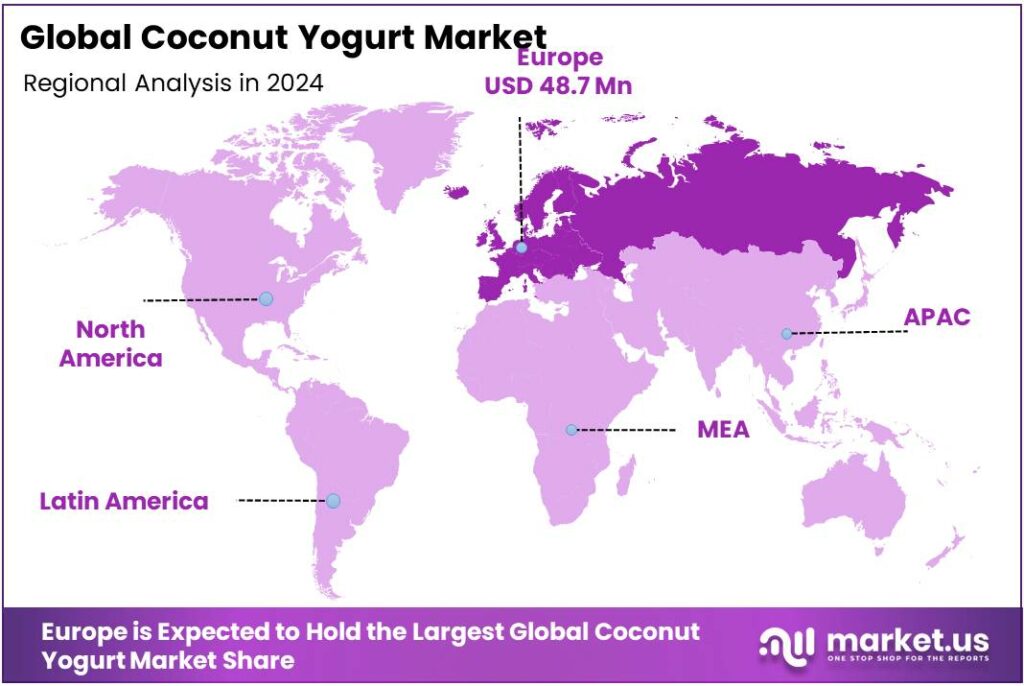
The Global Coconut Yogurt Market size is expected to be worth around USD 499.0 Million by 2034, from USD 131.1 Million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 14.3% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024 European held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 37.2% share, holding USD 48.7 Million in revenue.
Coconut yogurt—fermented coconut milk or cream with live cultures—sits at the intersection of dairy-alternative foods and resource-sensitive processing. From a supply standpoint, coconuts are abundant yet geographically concentrated: FAO’s latest statistical briefs indicate global coconut output has hovered around ~65 million tonnes over the past decade, underscoring stable raw-material availability for processors building long-term contracts in Southeast and South Asia.
Agri-food systems account for ~31–34% of global anthropogenic GHG emissions, keeping plant-based formats like coconut yogurt in the conversation for lower-impact diets relative to ruminant dairy. Meat and dairy together are linked to ~14.5% of emissions, a benchmark that continues to shape retailer and brand decarbonization targets.
Industrial production typically uses UHT coconut base, homogenization, inoculation, and refrigerated distribution. Energy use and cold chains are material: peer-reviewed analyses estimate ~30% of the food sector’s electricity goes to cooling/freezing, a cost and emissions lever for yogurt makers investing in high-efficiency compressors, heat recovery, and demand-response.
- In parallel, the IEA reports energy-related CO₂ emissions at 36.8 Gt (2022) and 37.4 Gt (2023), keeping pressure on processors and retailers to cut Scope 2/3 through procurement of lower-emission electricity and insulation upgrades across depots.
Policy and labeling frame market access. In the United States, FDA modernized the yogurt standard of identity with an effective date of April 14, 2023 and a compliance date of January 1, 2024—clarifying dairy definitions and driving plant-based players to continue using “yogurt alternative” or similar terms and to tighten cultures, sugars, and fortification disclosures. In the EU, the European Court of Auditors’ 2024 review flagged gaps and delays in food-labelling rules, reinforcing the need for precise claims on plant origin and nutrients in non-dairy products sold across the single market.
Key driving factors include lactose-free and vegan adoption, Asian coconut supply depth, and government attention to coconut value chains. India—an important origin for coconut base—reported 15.329 million tonnes of coconuts and 2.333 million hectares under cultivation in 2023–24, highlighting raw-material security for domestic and export-oriented processors; parliamentary disclosures reinforce ongoing public programs supporting productivity and replanting.
- Volatility remains a watch-out: coconut-oil markets saw global prices reach ~$2,990/ton in 2025, reflecting weather and tree-age dynamics that can tighten desiccated coconut and cream inputs for yogurt lines.
Key Takeaways
- Coconut Yogurt Market size is expected to be worth around USD 499.0 Million by 2034, from USD 131.1 Million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 14.3%.
- Non-Dairy Coconut Yogurt held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 67.3% share of the global coconut yogurt market.
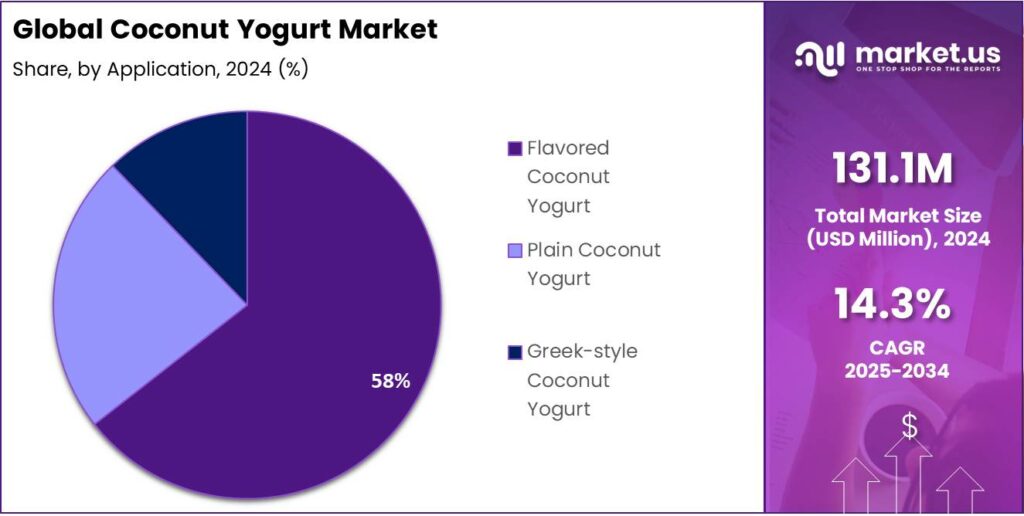
- Flavored Coconut Yogurt held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 58.8% share of the overall coconut yogurt market.
- European region held a 37.20% share USD 48.7 million of the global coconut-yogurt Market.
By Form Analysis
Non-Dairy Coconut Yogurt dominates with 67.3% share driven by growing vegan and lactose-intolerant consumers
In 2024, Non-Dairy Coconut Yogurt held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 67.3% share of the global coconut yogurt market. The segment’s strong performance was primarily supported by rising consumer preference for plant-based, lactose-free alternatives, as awareness regarding digestive health and animal welfare continued to grow. The demand for non-dairy yogurt products, particularly those made from coconut milk, has been increasing in both developed and emerging markets due to their creamy texture, natural flavor, and nutritional benefits, including medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) that support energy metabolism.
In 2025, the market for non-dairy coconut yogurt is expected to expand further as plant-based diets gain mainstream acceptance across North America, Europe, and the Asia Pacific region. The segment’s growth is also supported by the increasing number of product innovations, such as probiotic-enriched and low-sugar formulations, catering to health-conscious consumers. Retailers and foodservice operators are also widening their product offerings, contributing to the steady rise in consumption.
By Product Type Analysis
Flavored Coconut Yogurt dominates with 58.8% share driven by consumer preference for taste variety and indulgence
In 2024, Flavored Coconut Yogurt held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 58.8% share of the overall coconut yogurt market. The strong demand for flavored variants was influenced by the growing consumer shift toward indulgent yet healthy food options. Flavors such as vanilla, strawberry, mango, and blueberry have gained popularity due to their familiar taste profiles and ability to mask the natural tanginess of coconut yogurt, appealing to a wider audience. The increasing adoption of flavored non-dairy yogurt among millennials and urban consumers has also accelerated market expansion, particularly across supermarkets and online retail platforms.
The flavored coconut yogurt segment is projected to maintain its dominance, supported by product innovation and rising consumption of ready-to-eat breakfast and snack items. Manufacturers are focusing on clean-label ingredients, natural fruit extracts, and reduced sugar formulations to meet evolving consumer expectations for both taste and nutrition. The availability of seasonal and regionally inspired flavors is further strengthening the segment’s growth, attracting repeat purchases.
Key Market Segments
By Form
- Dairy Coconut Yogurt
- Non-Dairy Coconut Yogurt
By Product Type
- Plain Coconut Yogurt
- Flavored Coconut Yogurt
- Greek-style Coconut Yogurt
Emerging Trends
Nutrient-Smart plant yogurt low sugar, live cultures, school-ready
Coconut yogurt is leaning hard into “nutrient-smart” design: low sugar, live cultures that aid lactose digestion, more protein and calcium, and labels ready for public-meal programs. Sugar is the first pivot. The World Health Organization recommends keeping free sugars below 10% of energy, and suggests 5% (~25 g/day) for extra benefits; these numbers are now widely used by buyers and retailers as guardrails for category resets. In the U.S., the Food and Drug Administration places the Daily Value for added sugars at 50 g/day and requires “Added Sugars” and % DV on every label—pushing coconut yogurt toward unsweetened or lightly sweetened cups and drinkables.
The second leg of the trend is culture science. Europe’s food-health rulebook allows a specific claim—“live yogurt cultures improve lactose digestion”—when the product contains ≥10^8 CFU of the traditional starters. Per gram at consumption. Brands are aligning processes and QC to meet this threshold, because it speaks directly to shoppers who struggle with lactose but want the yogurt experience. The audience is large: experts estimate ~68% of the world’s population has lactose malabsorption, which helps explain why coconut-based, dairy-free cultured products keep gaining shelf space.
A third, fast-moving element is “school-ready” formulation. The U.S. Department of Agriculture finalized 2024 updates to school-meal standards, and is phasing in stricter limits—most notably the first-ever caps on added sugars in school meals—over school years beginning 2025–26 and beyond. This creates a clear brief for coconut yogurt: keep added sugars low, manage saturated fat, and fortify responsibly so products earn a place on menus. In Europe, the EU School Fruit, Vegetables and Milk Scheme allocates €220.8 million per school year, giving compliant products a predictable route into classrooms via national procurers; discussions have even emphasized EU-sourced inputs, sharpening attention to traceable, rules-aligned supply.
Drivers
Lactose-free eating is going mainstream
A single, powerful force is pushing coconut yogurt forward: the large share of people who cannot comfortably digest lactose and are turning to dairy-free foods. The U.S. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) notes that about 68% of the world’s population has lactose malabsorption—people who do not absorb lactose well after infancy—which directly lifts demand for non-dairy cultured products such as coconut yogurt. In the scientific literature, a global meta-analysis covering 62,910 participants from 89 countries estimated lactose malabsorption at 68% (95% CI 64–72%), confirming the scale and geographic breadth of this need.
Supply depth is another enabler. FAO statistics show coconuts have maintained ~65 million tonnes of global production over the past decade, giving processors confidence to sign longer contracts for coconut cream and milk bases. Major origins are backing the crop: India’s Coconut Development Board, a statutory body under the Government of India, details integrated schemes for production, replanting and value-addition that strengthen raw-material security for food manufacturers.
- Energy and climate goals are reinforcing this shift. Food companies face pressure to cut value-chain emissions; positioning more plant-based options is one lever. The International Energy Agency reports that global energy-related CO₂ emissions reached 37.4 Gt in 2023, up 1.1% year-on-year—figures that keep Scope 2/3 reductions on executive agendas and nudge portfolios toward lower-impact offerings, including coconut yogurt.
The combination of very high global lactose malabsorption (≈68%), regulatory clarity on yogurt standards in a major market, steady ≈65 Mt coconut supply supported by government programs in key origins, and ongoing 37.4 Gt energy-sector emissions that corporations seek to curb, all pull in the same direction. For coconut yogurt makers, this means a durable demand base, smoother compliance, secure inputs, and a sustainability narrative that aligns with retailer and brand commitments—clear reasons why lactose-free eating is the category’s defining growth driver.
Restraints
Nutrition and labelling scrutiny
Coconut yogurt faces a real headwind from nutrition rules and shopper concerns about saturated fat and added sugar. The World Health Organization (WHO) advises that saturated fat should provide no more than 10% of daily calories for everyone aged two and older. On a 2,000-calorie diet, that’s about 22 g/day. WHO also urges keeping free sugars below 10% of energy, with a further cut to 5% (≈25 g/day) for extra health benefits. These clear numerical targets make high-SFA and sweetened products harder to justify in school meals, hospitals, and retailer “healthy choice” sets.
The coconut base itself is under the microscope. USDA-linked nutrition data show ~42.7 g of saturated fat per cup (226 g) of canned coconut milk—the ingredient many brands ferment into coconut yogurt. That single cup already doubles the WHO daily limit example above, before any sugars are added. While recipes and fat levels vary by brand, the underlying fact remains: coconut fat is mostly saturated. The American Heart Association notes coconut oil is ~82% saturated fat, reinforcing why dietitians flag caution for frequent consumption without careful portion control.
Sugar adds another constraint. WHO’s intake cap pushes manufacturers toward unsweetened or lightly sweetened recipes, yet fermenting a low-protein, plant-fat matrix into a product that still tastes indulgent often leads to added sugars. The U.S. FDA requires “Added Sugars” in grams and % Daily Value on every Nutrition Facts label, and the agency reiterates the Dietary Guidelines recommendation to keep added sugars below 10% of calories. This visibility raises the bar for coconut yogurt to hit flavor targets without tripping red lines in retailer nutrition profiling or wellness programs.
There is also a nutrient-density hurdle versus dairy. Many consumers buy yogurt for protein, calcium, and vitamin D. Standard dairy yogurts naturally deliver meaningful protein, whereas coconut-based yogurts are typically much lower unless fortified or blended with legumes. U.S. NIH guidance pegs adult calcium needs at 1,000–1,200 mg/day, making reliable calcium fortification essential for a plant-based yogurt to compete on bone-health credentials. Fortification is not universally mandated, so nutrient levels can vary widely across coconut yogurt labels, adding friction for nutrition buyers in healthcare, schools, and fitness retail.
Opportunity
Win school And public-meal channels with compliant, fortified coconut yogurt
In the United States, the National School Lunch Program serves ~29.7 million students each day across 95,000+ schools, a scale that can make or break a category when menus change. In Europe, the EU’s School Fruit, Vegetables and Milk Scheme provides €220.8 million per school year to distribute qualifying items and fund nutrition education, creating steady, rules-based demand for compliant products. Coconut yogurt can fit these channels as a lactose-free, allergy-aware option—provided brands hit the numbers policy makers care about.
Winning these procurements also requires meeting nutrient expectations. A yogurt that contributes to protein and calcium targets will score better with dietitians and menu planners. FDA’s Interactive Nutrition Facts resources peg the Daily Value for protein at 50 g/day, a useful benchmark when designing single-serve portions. Fortification policy guardrails matter too: FDA’s fortification Q&A outlines when and how voluntary fortification can be used to make claims, helping brands add calcium and vitamin D responsibly to match dairy benchmarks without over-fortifying.
Standards are tightening in ways that favor better plant-based formulations. USDA’s 2024 rulemaking for school nutrition is effective July 1, 2024, with phased changes beginning as early as SY 2025–26, signaling stricter limits and clearer expectations for menu items. At the product label level, FDA guidance tells consumers to keep added sugars <10% of daily calories.
Regional Insights
Europe leads strongly with 37.20% share and approximately USD 48.7 million value
In 2024, the European region held a 37.20% share USD 48.7 million of the global coconut-yogurt segment, establishing itself as the dominating market for this category. This dominance can be attributed to a combination of factors: high consumer awareness of dairy-free alternatives, well-developed retail and e-commerce infrastructure, and a regulatory environment favourable to plant-based innovation.
The mature yoghurt-consumption culture in countries such as Germany and the United Kingdom has eased the shift toward coconut-based options, while increasing concerns about lactose intolerance and environmental sustainability have further accelerated uptake.
For instance, national retail data from Germany indicate that in 2023 the plant-based yoghurt category grew in unit terms by 5.5% to 134 million units, and price/volume dynamics suggest consumers are willing to pay a premium for non-dairy variants.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Danone – In 2024, Danone strengthened its position in the coconut yogurt segment through its brands like Silk and So Delicious, emphasizing plant-based and dairy-free innovation. The company reported over EUR 27.6 billion in total revenue in 2024, with plant-based products contributing a growing share. Danone focuses on clean-label ingredients, sustainability, and nutritional balance, aiming for 85% of its portfolio to meet healthy nutrition standards by 2025. Its investment in R&D and wide retail distribution make it a global leader in coconut yogurt.
Chobani LLC – Chobani expanded its plant-based product portfolio in 2024 with Fair Trade Certified coconut yogurt lines. Its coconut-based range, containing cultured coconut blends and probiotics, caters to health-conscious and vegan consumers. The company reported total revenues of around USD 2.5 billion in 2024, driven by strong U.S. retail sales and growing international distribution. Chobani’s sustainable sourcing and commitment to non-GMO ingredients have positioned it as a trusted name in the non-dairy yogurt segment.
COYO – Founded in Australia, COYO specializes in organic coconut yogurt, emphasizing probiotic-rich and allergen-free formulations. Its products are available in over 5,000 retail outlets across Australia, the UK, and the U.S. In 2024, the company focused on expanding production capacity to meet global demand. COYO’s success lies in its commitment to natural, vegan-certified, and gluten-free ingredients, making it a premium choice for consumers seeking clean-label coconut yogurt alternatives.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Danone
- Chobani LLC
- The Coconut Collaborative
- COYO
- So Delicious Dairy Free
- Daiya Foods Inc.
- Alpro
- Silk (Danone North America)
- Kite Hill
- Harmless Harvest
- Nancy’s Probiotic Foods
- Rebel Kitchen
- Hudson River Foods
- Pure Harvest Smart Farms
Recent Industry Developments
In 2024, the UK-based brand secured £1.5 million in Series B funding to accelerate its transition from niche start-up to mainstream plant-based leader.
Chobani LLC, a U.S.-based leader in the yogurt sector, has steadily expanded its presence in the coconut-based non-dairy yogurt segment. In 2024 the company introduced its coconut-based yogurt line made from cultured coconut blends that contain fewer grams of sugar than competing non-dairy options—about 4 g less per 5.3-oz serving.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 131.1 Mn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 499.0 Mn CAGR (2025-2034) 14.3% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Form (Dairy Coconut Yogurt, Non-Dairy Coconut Yogurt), By Product Type (Plain Coconut Yogurt, Flavored Coconut Yogurt, Greek-style Coconut Yogurt) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Danone, Chobani LLC, The Coconut Collaborative, COYO, So Delicious Dairy Free, Daiya Foods Inc., Alpro, Silk (Danone North America), Kite Hill, Harmless Harvest, Nancy’s Probiotic Foods, Rebel Kitchen, Hudson River Foods, Pure Harvest Smart Farms Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- Danone
- Chobani LLC
- The Coconut Collaborative
- COYO
- So Delicious Dairy Free
- Daiya Foods Inc.
- Alpro
- Silk (Danone North America)
- Kite Hill
- Harmless Harvest
- Nancy’s Probiotic Foods
- Rebel Kitchen
- Hudson River Foods
- Pure Harvest Smart Farms










