Global Battery Manufacturing Equipment Market Size, Share Analysis Report By Battery Type (NCA, NMC, LFP, LMO, LCO, LTO), By Machine Type (Mixing Machines, Coating And Drying Machines, Calendering Machines, Slitting Machines, Electrode Stacking Machines, Assembling And Handling Machines, Formation And Testing Machines), By Application (Automotive, Renewable Energy, Consumer Electronics, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Jan 2026
- Report ID: 172938
- Number of Pages: 215
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
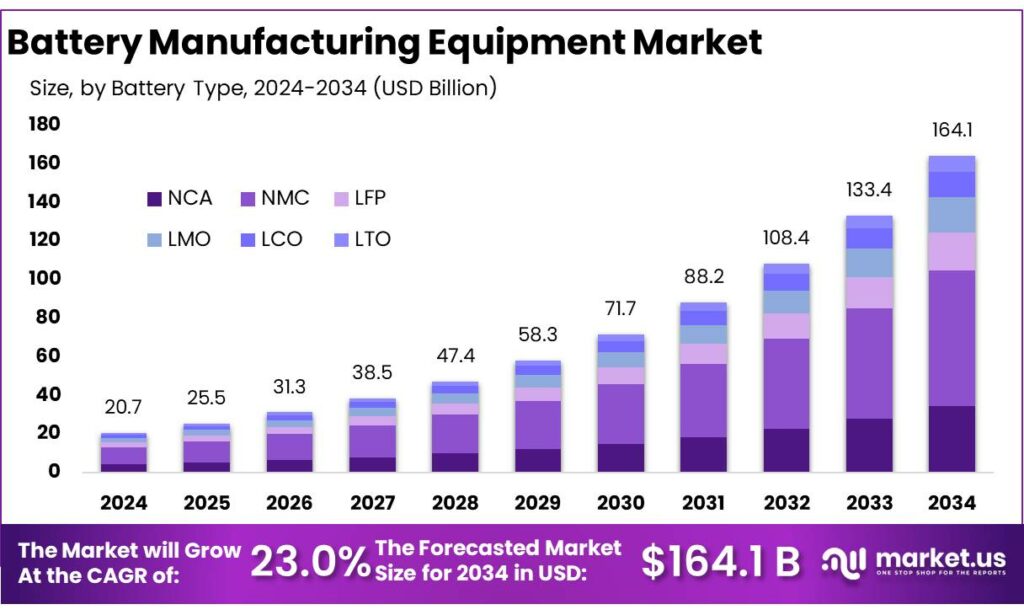
The Global Battery Manufacturing Equipment Market size is expected to be worth around USD 164.1 Billion by 2034, from USD 20.7 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 23.0% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. In 2024 Asia-Pacific (APAC) held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 43.8% share, holding USD 9 Billion in revenue.
Battery manufacturing equipment refers to the integrated set of machines and process lines used to turn active materials into finished lithium-ion cells—typically through mixing and coating, calendaring, slitting, stacking/winding, electrolyte filling, sealing, formation/aging, end-of-line testing, and pack/module assembly. As cell formats diversify and factories scale from pilot lines to multi-GWh the equipment market increasingly rewards suppliers that can deliver high-throughput automation, tighter quality control, and lower scrap rates—because battery yield, not just nameplate capacity, determines unit economics in a cost-competitive supply chain.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) notes that in 2024 global electric car sales rose about 25% to 17 million, and annual battery demand surpassed 1 terawatt-hour (TWh) for the first time—an inflection point that directly expands the installed base of new cell plants and the need for turnkey production equipment. At the same time, the IEA highlights how manufacturing capacity has been ramping quickly: in 2023, battery manufacturing reached about 2.5 TWh, adding 780 GWh of capacity versus the prior year—evidence of how rapidly new “gigafactory” lines are being ordered, installed, and qualified.
Key driving factors for battery manufacturing equipment demand include cost pressure and productivity needs, quality and safety requirements, and policy-led localization. On cost, the IEA reports the average battery pack price for a battery-electric car fell below USD 100 per kWh, a widely watched threshold that encourages broader EV adoption and intensifies competition among cell makers—pushing them toward higher-speed coaters, improved drying efficiency, and advanced inline inspection to protect margins.
Government initiatives are also shaping equipment roadmaps and factory investment decisions. In the United States, the Department of Energy’s Battery Materials Processing Grants program is advertised at USD 3 billion in total funding, explicitly aimed at strengthening domestic battery materials processing and expanding manufacturing capability—supporting project pipelines that typically pull through equipment orders for scaling and qualification.
In Europe, policy is tightening around circularity and strategic autonomy: the EU Council’s Net-Zero Industry Act infographics highlight lithium recovery targets of 50% by 2027 and 80% by 2030, which is expected to accelerate recycling-linked capacity and the specialized equipment needed for black-mass processing, materials recovery, and quality assurance.
In the United States, the Department of Energy reports it has awarded USD 1.82 billion to 14 projects under battery manufacturing and recycling grants to build and expand commercial-scale facilities across materials, components, and manufacturing. In the European Union, the Net-Zero Industry Act sets the aim that EU manufacturing capacity for strategic net-zero technologies approaches or reaches at least 40% of annual deployment needs by 2030, supporting investment visibility for domestic battery supply chains.
Key Takeaways
- Battery Manufacturing Equipment Market size is expected to be worth around USD 164.1 Billion by 2034, from USD 20.7 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 23.0%.
- NMC held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 42.9% share.
- Coating & Drying Machines held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 27.5% share.
- Automotive held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 66.1% share in the Battery Manufacturing Equipment Market.
- Asia-Pacific (APAC) region emerged as the most dominant segment in the Battery Manufacturing Equipment Market, securing a commanding 43.80% regional share USD 9 billion in revenue.
By Battery Type Analysis
NMC type batteries dominate with 42.9% share in 2024 due to balanced performance and broad applicability.
In 2024, NMC held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 42.9% share in the Battery Manufacturing Equipment Market by battery type of NMC. The segment’s strong performance was driven by its balanced energy density and cost profile, which made it the preferred choice across multiple manufacturing applications. During 2025, the NMC equipment segment continued to sustain its leading position as demand for high-performance lithium-ion batteries grew, supported by increased investments in electric vehicle production and energy storage systems.
By Machine Type Analysis
Coating & Drying Machines lead with 27.5% share in 2024 as key enabler of electrode quality and production efficiency.
In 2024, Coating & Drying Machines held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 27.5% share in the Battery Manufacturing Equipment Market by machine type. The segment’s strength was driven by its essential role in forming uniform electrode layers, which directly influenced cell performance and reliability. During 2025, the demand for Coating & Drying Machines remained robust as manufacturers focused on improving throughput and reducing material wastage in high-volume production lines.
By Application Analysis
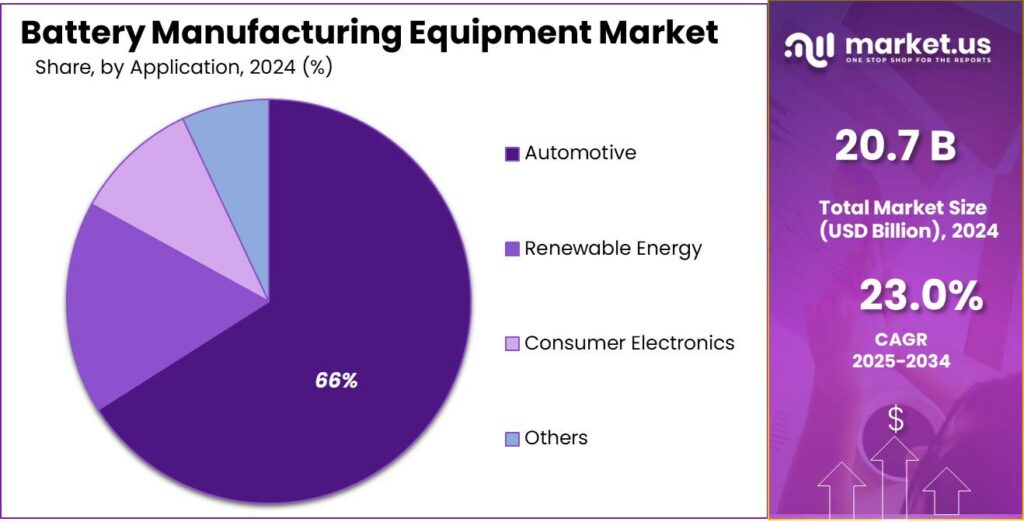
Automotive leads with 66.1% share in 2024 driven by strong EV and hybrid vehicle production demand.
In 2024, Automotive held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 66.1% share in the Battery Manufacturing Equipment Market by application. The automotive segment’s leadership was supported by the rapid growth of electric and hybrid vehicle manufacturing, which required sophisticated equipment for large-scale battery assembly. As the industry progressed into 2025, the reliance on battery manufacturing equipment for automotive applications remained significant, reflecting continued expansion of production facilities and upgrades in automation technologies.
Key Market Segments
By Battery Type
- NCA
- NMC
- LFP
- LMO
- LCO
- LTO
By Machine Type
- Mixing Machines
- Coating & Drying Machines
- Calendering Machines
- Slitting Machines
- Electrode Stacking Machines
- Assembling & Handling Machines
- Formation & Testing Machines
By Application
- Automotive
- Renewable Energy
- Consumer Electronics
- Others
Emerging Trends
Dry-Electrode and Low-Energy Coating Lines Gain Momentum
A clear latest trend in battery manufacturing equipment is the push toward dry-electrode or lower-energy electrode production, because traditional wet coating and drying is one of the biggest cost and energy hotspots inside a cell factory. In a standard lithium-ion line, slurry is coated onto foil and then sent through long drying ovens, often followed by solvent recovery. As factories scale, the footprint, energy bill, and permitting complexity of these drying and recovery systems become hard to ignore, so equipment buyers are increasingly asking for processes that reduce or remove these steps.
Independent technical literature helps explain why this is becoming a priority. A 2024 peer-reviewed review reports that electrode drying can consume ~27% of the total energy required for lithium-ion cell production, and it also notes other studies that assign drying an even larger share, in the 47%–48% range. Even if the exact share varies by factory design and assumptions, the direction is consistent: drying is a major energy sink, and a major lever for improvement. This reality is changing equipment roadmaps. Manufacturers are looking for shorter drying sections, better heat recovery, improved humidity control, and more efficient solvent capture systems, because these upgrades can lower operating cost while helping stabilize quality.
Solvent recovery itself is another reason the equipment mix is changing. A widely cited study on cathode drying and solvent recovery found that the drying and recovery process can impose an energy demand of roughly ~10 kWh per kg of NMP solvent, underscoring why plants using NMP have strong incentives to optimize or avoid it where possible. This is where dry-electrode equipment enters the conversation. Dry-electrode approaches aim to form an electrode film without solvent, which can remove large parts of the oven and recovery train.
Drivers
EV Growth Forces Rapid Gigafactory Equipment Investment
One major driving factor for battery manufacturing equipment is the speed at which electric-vehicle demand is expanding, and how quickly cell makers must build or upgrade factories to keep up. When EV sales rise sharply, battery makers cannot rely on gradual, step-by-step capacity additions. They are pushed toward large “next factory” decisions—new coating lines, additional stacking/winding machines, more formation racks, and higher-speed end-of-line testing—because missing supply windows can mean losing long-term customer contracts.
Public, trusted data shows why this pressure is intense. The International Energy Agency (IEA) reports that annual battery demand in the energy sector reached 1 TWh in 2024, a historic milestone, and that demand for EV batteries alone grew to over 950 GWh—about 25% higher than in 2023. In practical factory terms, that kind of demand jump translates into more shifts, more lines, and more emphasis on automation—because manual or semi-manual steps struggle to keep pace while maintaining consistent quality.
Cost pressure strengthens the same equipment “upgrade cycle.” The IEA notes that the average battery pack price for a battery-electric car dropped below USD 100 per kWh in 2024, a level often associated with wider cost competitiveness. When prices fall, producers must protect margins through throughput and yield. That usually means better coating uniformity, better calendaring control, improved drying and solvent recovery, more precise stacking/winding alignment, and more reliable formation systems.
Government initiatives add another layer of momentum by encouraging domestic manufacturing buildouts that require new toolsets. In the United States, the Department of Energy’s Battery Manufacturing and Recycling Grants program is structured around USD 3 billion in grant funding to strengthen domestic manufacturing and recycling capability. In the European Union, the Net-Zero Industry Act sets a goal for net-zero manufacturing capacity to meet at least 40% of the EU’s annual deployment needs by 2030, sending a long-term signal that supports additional factory investment.
Restraints
Profitability Uncertainty Delays New Line Purchases
One major restraining factor for battery manufacturing equipment is profitability uncertainty, which makes cell makers slow down, postpone, or cancel factory expansions—especially when price competition is intense. Battery plants are expensive to build and even harder to ramp up. If a producer is not confident it can sell cells at a margin that justifies the investment, it often delays buying big-ticket tools such as coaters, calenders, stackers/winders, electrolyte filling systems, formation racks, and end-of-line inspection equipment. In plain terms, equipment orders rise quickly during optimism, but they can pause just as quickly when companies worry about returns.
Trusted industry analysis shows why this pressure has grown. The International Energy Agency (IEA) notes that global battery manufacturing capacity reached 3 TWh in 2024, and that the next five years could see another tripling of capacity if all announced projects are built. A pipeline that large can create a “build now, compete later” situation, where too many factories chase the same customers.
The IEA reports that the average price of a battery pack for a battery-electric car dropped below USD 100 per kWh in 2024. When pack prices fall, manufacturers must produce more efficiently to stay profitable. That usually means better yields and better automation—but it also means some producers hesitate to spend until they are sure demand and pricing will hold. Falling input prices can also signal a fast-changing market: the IEA highlights that lithium prices dropped by more than 85% from their peak in 2022.
Europe is a clear example of how profitability concerns can restrict equipment momentum. The IEA states that many battery producers in Europe are postponing or cancelling expansion plans due to uncertainty about future profitability, and it notes that production costs in the region are about 50% higher than in China.
Opportunity
Grid-Scale Storage Boom Opens New Equipment Demand
One major growth opportunity for battery manufacturing equipment is the fast rise of stationary energy storage for power grids. Unlike EVs, grid batteries are bought by utilities, renewable project developers, and commercial sites that need dependable backup and flexible power. As more solar and wind connect to the grid, storage becomes a practical tool to smooth peaks, avoid curtailment, and provide fast response services. That creates a new and growing pool of battery orders, and every new order eventually turns into demand for more electrode lines, cell assembly tools, formation systems, and testing equipment.
Trusted international data shows the direction clearly. The International Energy Agency (IEA) reports that over 40 GW of battery storage capacity was added in the power sector in 2023, which was double the previous year’s increase. The IEA also notes that 65% of these additions were utility-scale projects and 35% were behind-the-meter systems.
The same story is visible in demand forecasts. The IEA’s Global EV Outlook 2024 indicates stationary storage will lift battery demand to around 400 GWh in the Stated Policies Scenario and 500 GWh in the Announced Pledges Scenario by 2030. Even though EVs remain the biggest driver, stationary storage is large enough to influence factory planning.
This opportunity is strengthened by the overall scale-up of batteries worldwide. The IEA notes that annual battery demand surpassed 1 TWh in 2024, while electric car sales rose 25% to 17 million the same year. When demand grows at this pace, manufacturers need not only more factories, but also better tools that shorten ramp-up time and reduce scrap. In real plants, the “hidden cost” is often yield loss during early production. That is why equipment upgrades—inline inspection, better drying control, smarter formation protocols—become attractive investments, especially when markets like grid storage can add new volume without depending on a single automaker platform cycle.
Regional Insights
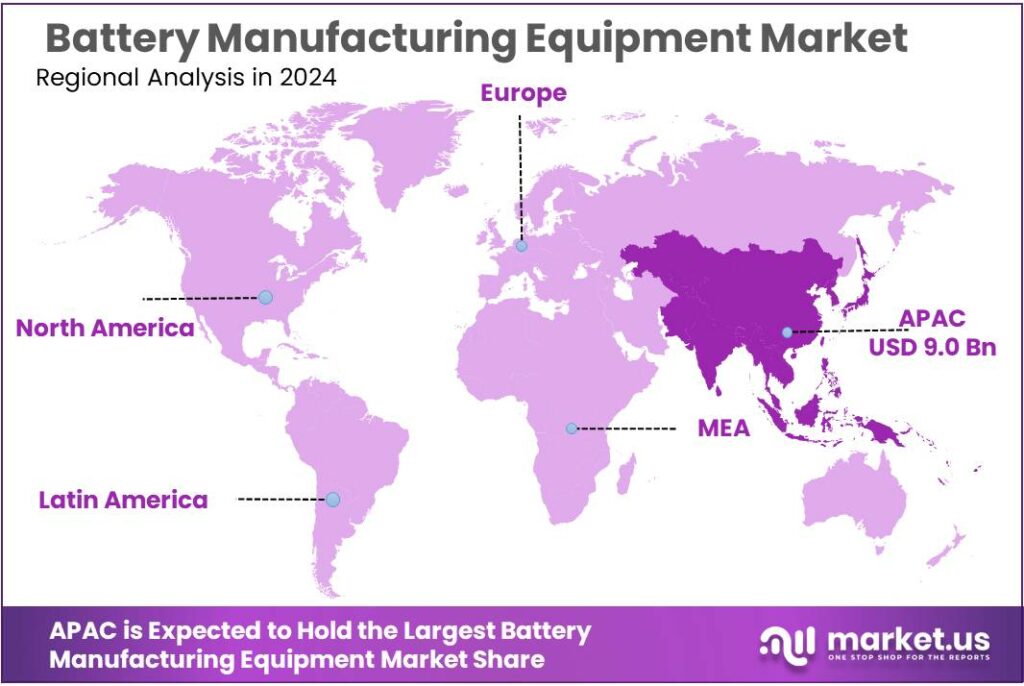
APAC leads strongly with 43.80% share and $9 Bn revenue in 2024 due to robust battery production infrastructure and EV ecosystem.
In 2024, the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region emerged as the most dominant segment in the Battery Manufacturing Equipment Market, securing a commanding 43.80% regional share and generating approximately $9 billion in revenue. This leadership was underpinned by well-established manufacturing ecosystems in China, South Korea, and Japan, where extensive battery production capacity and supportive industrial policies accelerated capital investment into manufacturing equipment. China alone accounts for a significant portion of global battery production and export activity, reinforcing APAC’s central role in the global supply chain and attracting both domestic and foreign equipment suppliers.
The year-on-year trend into 2025 indicates that APAC maintained its competitive edge, supported by continued expansion of gigafactories and advanced battery plants designed to meet surging demand from electric vehicle and energy storage sectors. Government incentives in major APAC economies aimed at electrification and energy transition further strengthened equipment procurement, particularly in coating, cell assembly, and formation systems. As EV sales in China, Japan, and South Korea continued to rise, the demand for battery manufacturing machinery to support high-volume production remained robust.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
Manz AG is a leading engineering firm specialising in automated battery production lines for lithium-ion and next-generation cells. It focuses on modular electrode coating, cell assembly, and formation systems that support scalable electric vehicle and energy storage manufacturing, with reported revenues of €249 million in 2023, reflecting its strong industrial footprint and broad global presence.
Nordson Corporation is a global precision technology provider with about $2.69 billion in revenue in 2024, offering a range of dispensing, coating, and inspection equipment tailored for battery manufacturing. Its machines support adhesive application, fluid handling, measurement and quality control in EV, stationary energy, and consumer battery production.
AMETEK, Inc. is a diversified manufacturer with approximately $6.94 billion in revenue in 2024, delivering precision instruments and electromechanical devices that are integrated into battery equipment for process control, testing, and monitoring, contributing reliability and automation support across production stages.
Top Key Players Outlook
- Manz AG
- Bühler AG
- Nordson Corporation
- ULVAC, Inc.
- Applied Materials, Inc.
- AMETEK, Inc.
- Ecopro BM Co., Ltd.
- Komax Holding AG
- GEA Group AG
- Sakamura Machine Co., Ltd.
Recent Industry Developments
In 2024 Manz AG faced a challenging market environment, with total Group revenues expected to be between €170 million and €180 million, down from previous years, and demand in the battery cell equipment market weakening, leading to strategic adjustments including the planned divestment of its battery cell production equipment business in early 2025.
In 2024, Nordson reported robust overall performance with annual revenues of $2.7 billion, marking a steady increase from prior years and reflecting diversified demand across industrial and technology segments, a foundation that also supported its battery-related equipment offerings.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 20.7 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 164.1 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 23.0% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Battery Type (NCA, NMC, LFP, LMO, LCO, LTO), By Machine Type (Mixing Machines, Coating And Drying Machines, Calendering Machines, Slitting Machines, Electrode Stacking Machines, Assembling And Handling Machines, Formation And Testing Machines), By Application (Automotive, Renewable Energy, Consumer Electronics, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape Manz AG, Bühler AG, Nordson Corporation, ULVAC, Inc., Applied Materials, Inc., AMETEK, Inc., Ecopro BM Co., Ltd., Komax Holding AG, GEA Group AG, Sakamura Machine Co., Ltd. Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF)  Battery Manufacturing Equipment MarketPublished date: Jan 2026add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample
Battery Manufacturing Equipment MarketPublished date: Jan 2026add_shopping_cartBuy Now get_appDownload Sample -
-
- Manz AG
- Bühler AG
- Nordson Corporation
- ULVAC, Inc.
- Applied Materials, Inc.
- AMETEK, Inc.
- Ecopro BM Co., Ltd.
- Komax Holding AG
- GEA Group AG
- Sakamura Machine Co., Ltd.










