Global Acrylate Esters Market Size, Share Analysis Report By Type (Methyl Acrylate, Ethyl Acrylate, Butyl Acrylate, 2-EH Acrylate, Others), By Application (Surface Coatings, Adhesives and Sealant, Plastic Additives, Textiles, Others) , By Region and Companies - Industry Segment Outlook, Market Assessment, Competition Scenario, Trends, and Forecast 2025-2034
- Published date: Oct 2025
- Report ID: 161431
- Number of Pages: 258
- Format:
-
keyboard_arrow_up
Quick Navigation
Report Overview
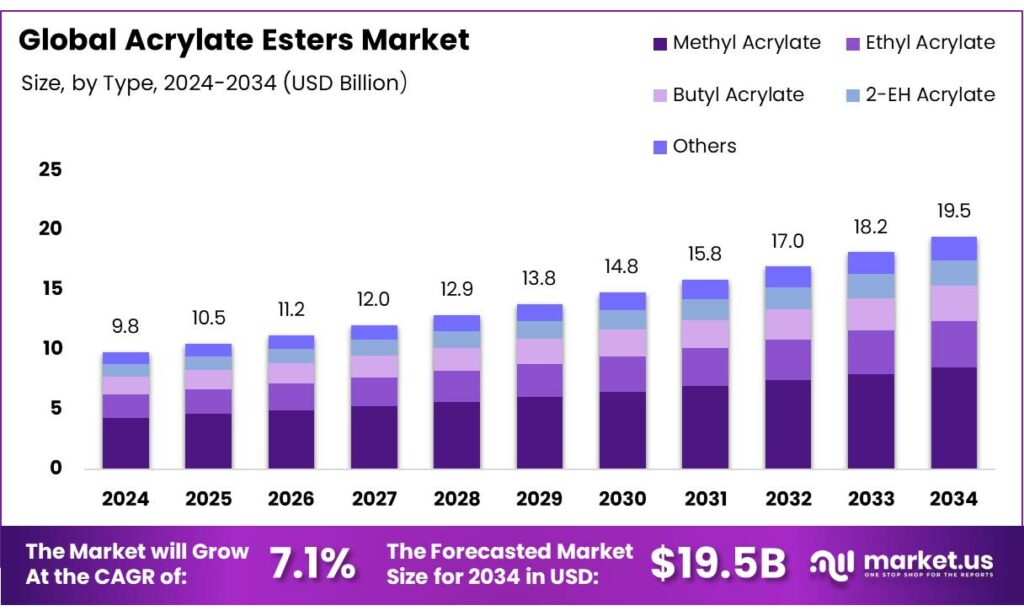
The Global Acrylate Esters Market size is expected to be worth around USD 19.5 Billion by 2034, from USD 9.8 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 7.1% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034.
Acrylate esters (or acrylic acid esters) are key chemical intermediates produced by esterification of acrylic acid (or its derivatives) with alcohols such as methanol, ethanol, butanol, or 2-ethylhexanol. They serve as monomers or comonomers in acrylate and methacrylate polymers, contributing desirable properties like adhesion, flexibility, weatherability, and clarity. In the typical value chain, crude acrylic acid (CAA) is oxidized from propylene, and about half of the CAA stream is converted to acrylate esters, while the remaining portion is purified to glacial acrylic acid (GAA) for further downstream derivatives.
Key drivers of growth include regulatory pressure to reduce volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in coatings, pushing shifts toward waterborne or high-solids acrylic formulations. The push for sustainability and green chemistries is also stimulating interest in bio-based acrylic acid and ester routes. Additionally, supply-side investments in integrated acrylic production (acid + ester + derivatives) help reduce costs and enhance supply stability. For example, in India, a large integrated acrylics and oxo-alcohol plant was inaugurated with an investment of Rs 5,894 crore (≈ USD 700+ million) to produce acrylic acid, butyl acrylate and associated units, improving local access to key monomers and reducing import dependence.
The chemical sector is recognized as the largest industrial energy consumer globally and ranks third in direct CO₂ emissions among industries. Within the chemical sector, electricity typically accounts for ~ 14% of total energy consumption. In the realm of sustainable transition, the International Energy Agency (IEA) notes that primary chemicals output is expected to increase from ~ 719 Mt in 2022 to ~ 861 Mt by 2030 under current trajectories—indicating growing scale and related emissions pressure. The chemical sector is also estimated to represent about 5% of global greenhouse gas emissions, which imposes regulatory and carbon constraint pressures on acrylate ester producers.
Key Takeaways
- Acrylate Esters Market size is expected to be worth around USD 19.5 Billion by 2034, from USD 9.8 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 7.1%.
- Methyl Acrylate held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 43.9% share of the global acrylate esters market.
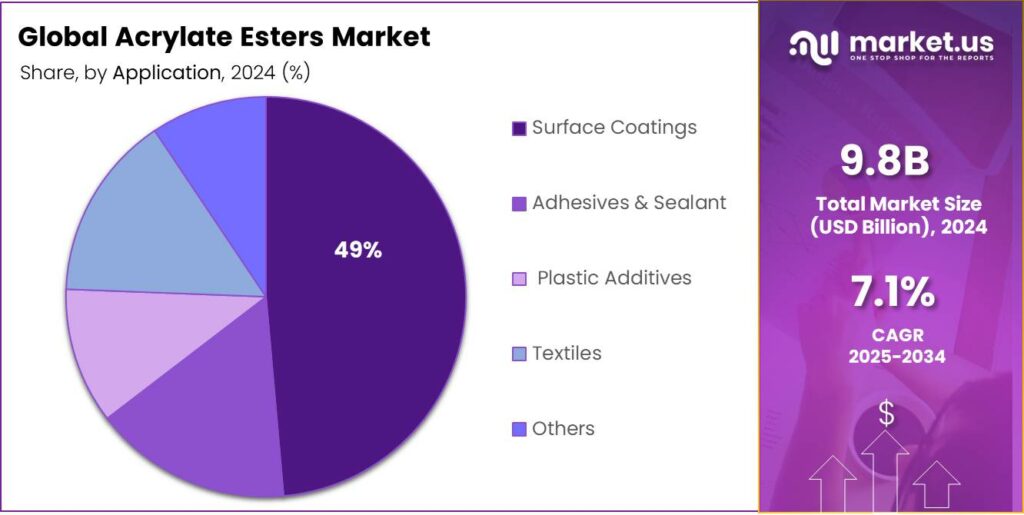
- Surface Coatings held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 48.6% share of the global acrylate esters market.
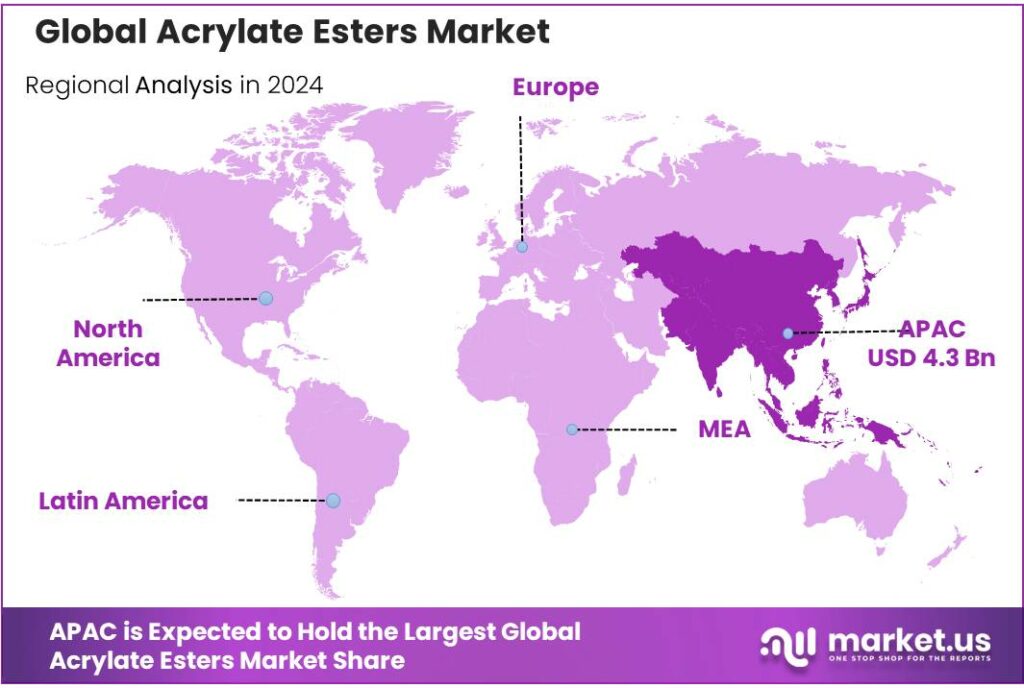
- Asia-Pacific (APAC) region emerged as the dominant market for acrylate esters, capturing a substantial 43.9% share, equating to an estimated value of USD 4.3 billion.
By Type Analysis
Methyl Acrylate dominates with 43.9% share in 2024 due to its versatile applications and high demand
In 2024, Methyl Acrylate held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 43.9% share of the global acrylate esters market. This strong performance can be attributed to its extensive use in the production of adhesives, coatings, and textiles, where its properties of clarity, hardness, and chemical resistance are highly valued. The chemical’s excellent polymerization characteristics make it a preferred choice for manufacturers seeking reliable and high-performance materials.
The demand for Methyl Acrylate has shown steady growth, particularly in regions with expanding construction and automotive sectors, where high-quality polymers are increasingly required. Its adaptability to various formulations, including waterborne and UV-curable products, further reinforces its market leadership. Additionally, Methyl Acrylate’s efficiency in producing specialty polymers has driven its uptake in industrial applications, cementing its position as a cornerstone segment in the acrylate esters market for 2024 and into 2025.
By Application Analysis
Surface Coatings lead with 48.6% share in 2024 due to high demand in protective and decorative applications
In 2024, Surface Coatings held a dominant market position, capturing more than a 48.6% share of the global acrylate esters market. This strong performance is driven by the growing need for durable, weather-resistant, and aesthetically appealing coatings across industries such as construction, automotive, and furniture. Acrylate esters in surface coatings provide excellent adhesion, flexibility, and resistance to UV radiation, chemicals, and abrasion, making them highly suitable for both industrial and decorative purposes.
The rising focus on infrastructure development and renovation projects worldwide has further contributed to the increasing demand for high-performance surface coatings. In addition, manufacturers are increasingly adopting eco-friendly, low-VOC formulations based on acrylate esters, aligning with environmental regulations and sustainability goals. The segment’s consistent growth in 2024 and projected demand into 2025 reflect its essential role in enhancing product durability and performance across multiple end-use industries.
Key Market Segments
By Type
- Methyl Acrylate
- Ethyl Acrylate
- Butyl Acrylate
- 2-EH Acrylate
- Others
By Application
- Surface Coatings
- Adhesives & Sealant
- Plastic Additives
- Textiles
- Others
Emerging Trends
Smart & Active Packaging Gains Traction in Food Industry
One of the most exciting shifts lately is the rise of smart and active packaging in the food sector—and this holds real promise for acrylate esters, especially those formulated for responsive or functional behavior. Smart packaging means the package not only protects but also senses, indicates, or even responds to changes (e.g. spoilage, gas levels). Active packaging refers to materials that actively interact (scavenging oxygen, releasing preservatives, moisture control) to extend shelf life.
The demand for smarter food packaging is being driven by rising concerns about food safety, waste, and transparency. Around the world, 42% of consumers have said they are willing to pay more for packaging that helps preserve the quality of food. That’s a strong signal to packaging developers to add intelligence and functionality. Also, regulatory pressure and food safety norms push brands to adopt packaging that can better prevent spoilage, detect contamination, or signal freshness.
In recent years, research has demonstrated real technical feasibility. One study built a battery-free, stretchable smart packaging system that includes gas sensors and controlled release of active compounds. They used it to monitor fish freshness and trigger release of antioxidants/antimicrobials when needed, extending shelf life up to 14 days. This kind of packaging blends electronics, sensors, and controlled chemistry. For acrylate esters, this opens doors: they can be engineered as adhesive or barrier layers that also embed sensor functions or controlled release features.
Governments and regulators are beginning to catch up. For example, many nations now look beyond banning single-use plastics to requiring transparency in packaging (e.g. indicating shelf life, recyclability, or safety properties). A review on global sustainable food packaging regulations notes that increasing mandates are pushing packaging innovation toward greener, active, and intelligent systems. In the EU, new laws are targeting packaging waste reduction and requiring that all packaging be recyclable by 2030.
Drivers
Growth in Packaged & Processed Food Industry Stimulating Demand for Advanced Packaging Materials
One of the strongest drivers for acrylate esters is the fast growth of the packaged and processed food industry, because acrylate esters (used in coatings, adhesives, barrier films, sealants) play a key role in food packaging materials. As the packaged food market expands, demand for higher-performance, safe, and durable packaging solutions rises—boosting the need for acrylate-based materials.
Governments in many countries are also pushing initiatives to strengthen food value chains, reduce waste, and upgrade packaging to improve food safety and shelf life. For instance, in India, the government is driving a major push in food processing—at the World Food India 2025 summit, global and domestic firms committed Rs 1.02 lakh crore in investments in India’s food processing sector. Such initiatives, by improving infrastructure, cold chain, and packaging standards, indirectly fuel demand for advanced packaging chemistries including acrylate esters.
On the regulatory and safety side, food safety and packaging chemical scrutiny have heightened. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is strengthening its review process for chemicals in the food supply, in order to ensure transparency and safety of food-contact substances (May 2025). Parallel moves in other countries to restrict certain chemicals in food packaging (e.g. PFAS, certain plasticizers) push packaging manufacturers to look for safer, high-performance alternatives—again opening room for acrylate ester–based materials to fill gaps.
Restraints
Tightening Regulatory & Environmental Compliance Pressures
One of the most significant constraints on acrylate ester producers comes from stricter environmental regulations and societal pressure for cleaner, safer chemical production. As governments and regulatory bodies intensify scrutiny over industrial emissions, waste, and chemical safety, companies in the acrylate esters space must face rising compliance costs, technology upgrades, and potential scale limitations.
The global chemical industry already bears a heavy emissions burden: the sector is responsible for roughly 2 billion metric tons of CO₂ per year, making up about 5% of global greenhouse gas emissions. In Europe alone, the chemical sector emitted 155,495 kilotonnes CO₂-equivalent in 2021, accounting for 5% of total net GHG emissions in the European Union. Because acrylate esters lie downstream of chemical processes, their production is directly impacted by emissions-control mandates, carbon pricing, and energy regulations imposed upstream.
In the United States, emissions from chemical manufacturing reported under the EPA’s Greenhouse Gas Reporting Program reached 184.8 million metric tons CO₂-equivalent in 2022 (for non-fluorinated plus fluorinated chemicals) across about 462 reporting facilities. This underscores that the chemical value chain has mounting reporting obligations and exposure to carbon regulation.
Beyond emissions, regulatory regimes governing chemical substances add another layer of constraint. In the U.S., the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) mandates that chemicals, whether new or existing, be assessed for risk and potentially restricted. Many nations incorporate similar frameworks (such as REACH in the EU) that compel rigorous safety data, usage limitations, and potential bans of substances deemed harmful. These regulations raise the barrier to entry, slow down product launches, and increase R&D or testing costs.
Opportunity
Rise of Eco-friendly Food Packaging & Circular Economy Demand
One of the most promising growth paths for acrylate esters lies in serving the booming demand for eco-friendly food packaging. As consumers, governments, and food companies increasingly push for sustainable materials, acrylate esters—if adapted to low-VOC, recyclable, or bio-compatible formulations—can play a key role in coatings, barrier layers, adhesives, and functional films that meet strict food safety and environmental criteria.
This differential growth shows that sustainable packaging is not just a niche, but a mainstream transition. Food companies are under pressure to reduce plastic waste, limit migration of chemicals, and comply with stricter regulations. In response, many are seeking packaging materials that combine performance with recyclability, lower toxicity, or biodegradability. Here, acrylate esters modified for low-emission, post-consumer recycling compatibility, or even bio-derived feedstocks can gain traction.
Governments and regulatory bodies are also backing this shift with policies, incentives, and standards. For example, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) runs programs and guidelines around sustainable packaging to encourage innovation and recycling infrastructure. In agriculture and food export sectors, the Sustainable Packaging Innovation Lab (U.S.) supports research into new packaging variants that reduce environmental impact, especially for perishable produce. These kinds of support mechanisms can de-risk R&D and encourage adoption of advanced acrylate-based materials.
Beyond regulation, consumer behavior changes strongly favor sustainable packaging. One survey found that 58% of consumers are more likely to purchase items that use reusable or recyclable packaging. That consumer willingness to pay more for sustainable packaging lends financial viability to investments in greener acrylate ester formulations.
Regional Insights
Asia-Pacific leads with 43.9% share in 2024, valued at USD 4.3 billion, driven by industrial expansion and infrastructure growth
In 2024, the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region emerged as the dominant market for acrylate esters, capturing a substantial 43.9% share, equating to an estimated value of USD 4.3 billion. This commanding position underscores APAC’s pivotal role in the global acrylate esters industry. The region’s growth trajectory is propelled by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and significant investments in infrastructure, particularly in countries like China, India, and Southeast Asia.
The demand for acrylate esters in APAC is primarily fueled by their extensive applications in industries such as construction, automotive, and consumer goods. The construction sector’s robust expansion, driven by urban development and infrastructure projects, necessitates high-performance materials like acrylate esters for coatings, adhesives, and sealants. Similarly, the automotive industry’s growth in the region amplifies the need for acrylate esters in various manufacturing processes.
Key Regions and Countries Insights
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- India
- Australia
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- GCC
- South Africa
- Rest of MEA
Key Players Analysis
BASF SE, a German multinational, is a dominant player in acrylate esters with a strong production base across Europe and Asia-Pacific. The company manufactures butyl acrylate, methyl acrylate, and 2-ethylhexyl acrylate for coatings, plastics, and adhesives. BASF integrates digital production systems and sustainability frameworks to enhance efficiency and reduce emissions. With the “Verbund” production model, BASF optimizes feedstock utilization, achieving lower energy intensity while supporting the transition to bio-based acrylates and circular chemical processes.
LG Chem Ltd., based in South Korea, is a major producer of acrylate esters and acrylic monomers catering to coatings, adhesives, and plastic modifiers. The company emphasizes product diversification and expansion into environmentally friendly materials. LG Chem’s investments in sustainable chemical production and high-purity acrylate lines support global demand growth. With advanced R&D in polymer synthesis and collaboration with renewable energy sectors, LG Chem strengthens its position as a leading Asian player in the global acrylate market.
Top Key Players Outlook
- The Dow Chemical Company
- Sibur Holding
- Arkema SA
- BASF SE
- LG Chem Ltd.
- Nippon Shokubai Co. Limited
- Momentive Specialty Chemicals Inc.
- Mitsubishi Chemical Holdings Corporation
Recent Industry Developments
In 2024, Arkema SA posted sales of about €9.5 billion with EBITDA of €1,532 million (a margin of ~ 16.1 %) after volumes rose by 2.4 % despite a negative price effect of –3.0.
In 2024, LG Chem Ltd. recorded consolidated revenue of KRW 48,916.1 billion with an operating profit of KRW 916.8 billion.
Report Scope
Report Features Description Market Value (2024) USD 9.8 Bn Forecast Revenue (2034) USD 19.5 Bn CAGR (2025-2034) 7.1% Base Year for Estimation 2024 Historic Period 2020-2023 Forecast Period 2025-2034 Report Coverage Revenue Forecast, Market Dynamics, Competitive Landscape, Recent Developments Segments Covered By Type (Methyl Acrylate, Ethyl Acrylate, Butyl Acrylate, 2-EH Acrylate, Others), By Application (Surface Coatings, Adhesives and Sealant, Plastic Additives, Textiles, Others) Regional Analysis North America – US, Canada; Europe – Germany, France, The UK, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe; Asia Pacific – China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, Singapore, Rest of APAC; Latin America – Brazil, Mexico, Rest of Latin America; Middle East & Africa – GCC, South Africa, Rest of MEA Competitive Landscape The Dow Chemical Company, Sibur Holding, Arkema SA, BASF SE, LG Chem Ltd., Nippon Shokubai Co. Limited, Momentive Specialty Chemicals Inc., Mitsubishi Chemical Holdings Corporation Customization Scope Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. Purchase Options We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF) 
-
-
- The Dow Chemical Company
- Sibur Holding
- Arkema SA
- BASF SE
- LG Chem Ltd.
- Nippon Shokubai Co. Limited
- Momentive Specialty Chemicals Inc.
- Mitsubishi Chemical Holdings Corporation










