Quick Navigation
Introduction
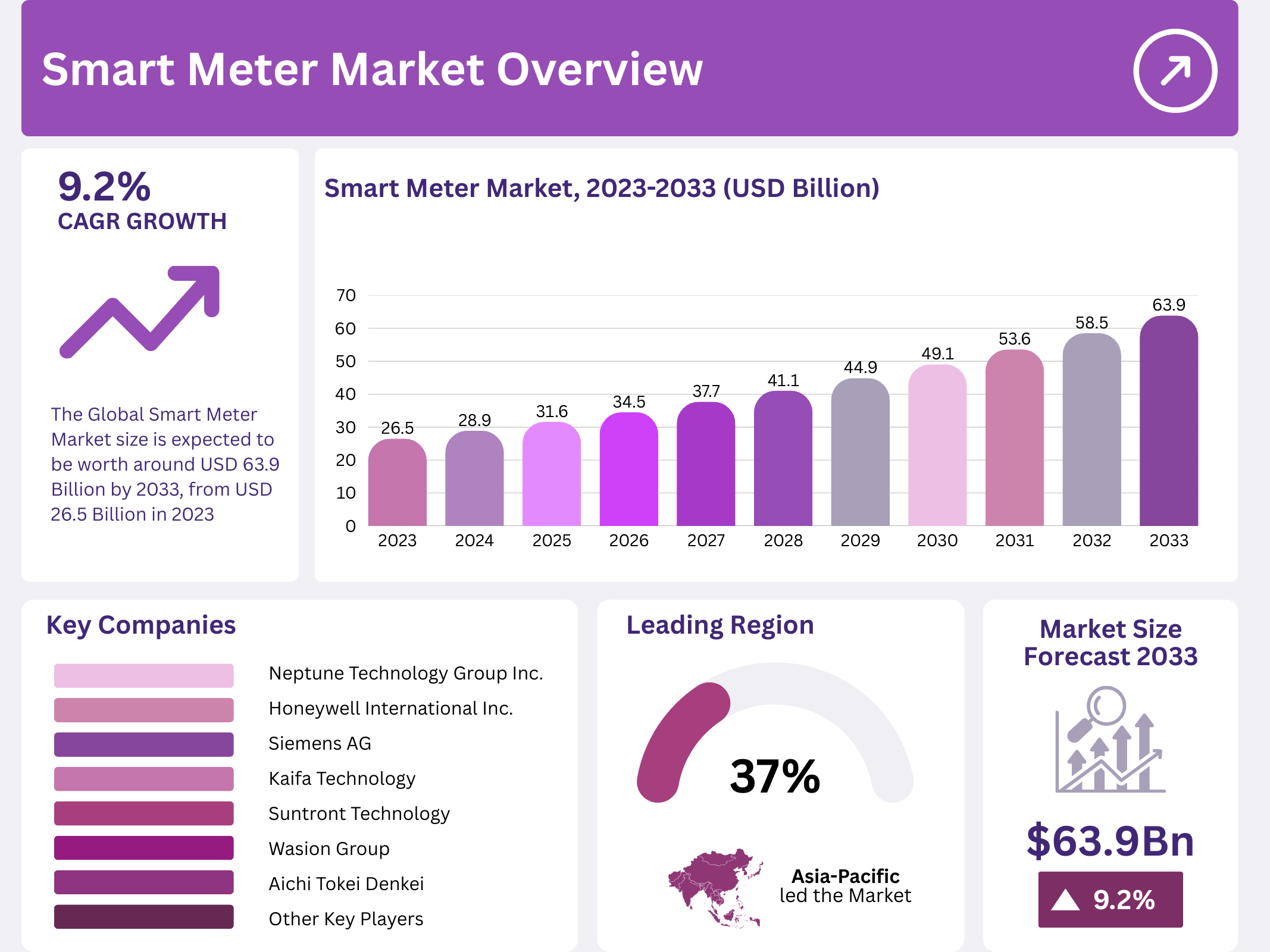
The Global Smart Meter Market continues to accelerate, driven by rapid digital transformation across energy and utility sectors. With the market expected to grow from USD 26.5 Billion in 2023 to USD 63.9 Billion by 2033, smart metering technology is now a critical enabler of efficient and sustainable resource management worldwide.
Smart meters allow two-way communication between consumers and utility providers, enabling real-time monitoring, transparent billing, and improved grid reliability. As governments, businesses, and households transition toward smarter infrastructure, adoption of intelligent metering systems is expanding across electricity, water, and gas distribution networks.
The fast pace of urbanization, integration of renewable energy resources, and ongoing global smart grid initiatives continue to propel market growth. Technology providers, utilities, and policymakers jointly contribute to the expanding smart metering ecosystem.
Key Takeaways
- The Smart Meter Market was valued at USD 26.5 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 63.9 billion by 2033, with a CAGR of 9.2%.
- In 2023, Smart Electric Meters dominated the product segment, driven by widespread adoption in utilities for real-time monitoring.
- In 2023, Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) led the technology segment, enabling better data analytics and efficiency for utilities.
- In 2023, Residential was the leading end-user, highlighting the growing demand for smart meters in households.
- In 2023, Asia Pacific dominated the market with 37.0%, supported by rising investments in smart grids and infrastructure.
Market Segmentation Overview
By product type, smart electricity meters remain dominant because they enable real-time electricity usage tracking and efficient grid management. Their role in supporting renewable integration and reducing peak loads continues to strengthen market leadership, while water and gas meters steadily expand to enhance consumption accuracy and safety.
By technology, Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) leads due to its capability for two-way communication, remote monitoring, and dynamic pricing applications. AMI empowers utilities with advanced analytics and outage management, while Automatic Meter Reading (AMR) remains viable for basic automation but offers limited system intelligence.
By end-user, the residential sector holds the largest share as households increasingly adopt smart meters to gain visibility into consumption patterns and reduce utility bills. Commercial and industrial users follow, leveraging smart meters to optimize operations and improve energy efficiency across large-scale facilities.
Drivers
Government mandates and incentives: Many countries are issuing strict regulatory frameworks and targets to accelerate deployment of smart metering systems to reduce energy loss and modernize utility networks. These policies significantly boost implementation across both developed and developing regions.
Technological advancements: The evolution of AMI, IoT connectivity, and real-time analytics enhances smart meter functionality, improving billing accuracy, outage response, and grid automation. Advanced features continue to elevate consumer experience and operational value for utilities.
Use Cases
Energy consumption optimization: Smart meters provide consumers with real-time insights into usage, allowing them to reduce consumption during peak hours and achieve lower utility bills. Utilities also gain tools to better balance energy distribution and forecast demand.
Power theft and leakage prevention: In high-risk markets, smart meters enable automated alerts and remote monitoring to detect unauthorized usage or system leakages. This capability significantly decreases losses for utility operators and improves service transparency.
Major Challenges
High installation cost: Initial deployment and system integration demand substantial investment, making adoption difficult for cost-sensitive markets. Utilities often face financial constraints in upgrading legacy networks to support smart meters at scale.
Data privacy and regulatory complexity: Smart meters generate and transmit sensitive consumer usage data, raising privacy and cybersecurity concerns. Varying regional compliance requirements further complicate widespread standardization.
Business Opportunities
Smart city and infrastructure expansion: Global smart city initiatives rely heavily on real-time metering data to improve energy distribution, water management, and sustainability outcomes, creating long-term revenue opportunities for technology vendors and utilities.
IoT-enabled smart metering solutions: Increasing integration of IoT devices fuels demand for connected meters that enable remote control, predictive maintenance, and AI-based energy management, opening new pathways for innovation and service-based business models.
Regional Analysis
Asia Pacific leadership: With 37.0% market share, the region dominates due to rapid urbanization, smart grid investments, and accelerated installation programs in China, Japan, and India. Initiatives focused on rising energy efficiency and modernization further strengthen market expansion.
Growing momentum in Europe and North America: These regions benefit from advanced infrastructure, strong regulatory policies, and high residential adoption rates. The U.S. and U.K. continue to advance full smart meter rollouts to improve grid reliability and support renewable integration.
Recent Developments
- Oakter launched OakMeter in May 2024, integrating AMI, IoT, and real-time analytics for next-generation energy monitoring.
- Kerala Water Authority announced prepaid water meters in March 2024 to improve water management and billing transparency.
- Adani Transmission formed BEST Smart Metering Ltd in December 2022 to accelerate smart meter deployment under India’s RDSS scheme.
- Avanci launched its 4G smart meter patent licensing program in October 2023, onboarding EDMI as its first licensee.
Conclusion
The Global Smart Meter Market is entering a transformative decade powered by the convergence of smart grids, IoT adoption, and sustainability priorities. As governments and utilities invest in digital infrastructure, smart meters are becoming indispensable across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. With strong technological progress and expanding smart city initiatives, the market is poised for sustained growth through 2033.










