Quick Navigation
Overview
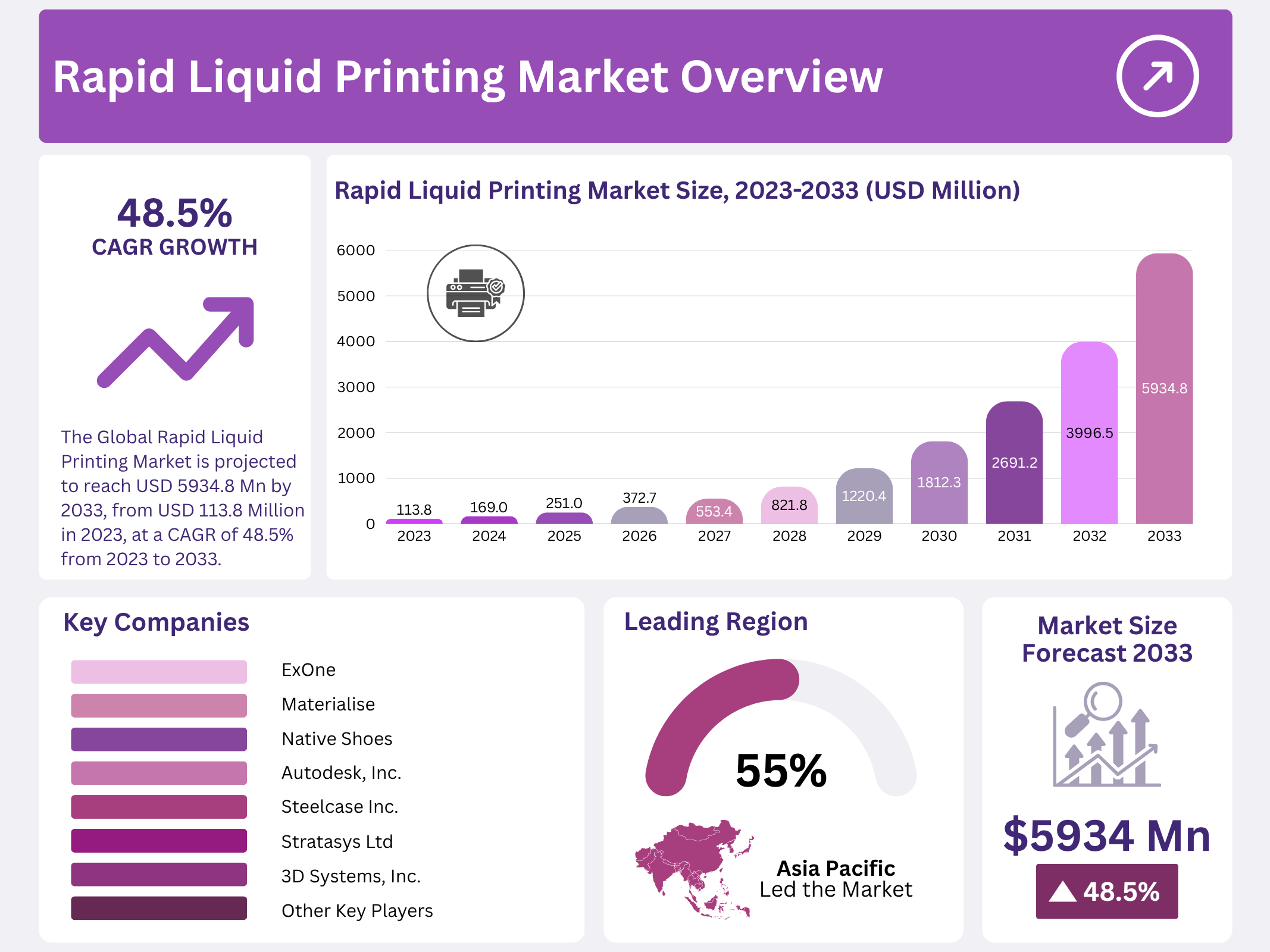
New York, NY – November 11, 2025 – The Global Rapid Liquid Printing (RLP) Market is projected to reach approximately USD 5,934.8 million by 2033, rising from USD 113.8 million in 2023, with a strong CAGR of 48.5% between 2023 and 2033.
Rapid Liquid Printing is a breakthrough 3D printing technology that stands apart from conventional layer-by-layer additive manufacturing methods. It works by extruding liquid material directly into a gel-filled container, where it instantly solidifies, allowing the creation of complex and flexible structures with exceptional speed. Depending on the object’s complexity and size, RLP can produce finished designs within minutes.
One of its most notable advantages is the ability to print freely in three dimensions without support structures, which are often necessary in traditional 3D printing to maintain stability. This eliminates design limitations, accelerates production times, and enables the realization of intricate forms that were once impractical or impossible to achieve with conventional methods.
Key Takeaways
- The Global Rapid Liquid Printing Market is projected to reach USD 5934.8 Million by 2033, with a robust CAGR of 48.5% from 2023 to 2033.
- Photopolymers claimed a significant market share of over 42.7%, known for versatility and quick curing under light for detailed structures.
- Stereo-lithography (SLA) led in 2023 with a market share exceeding 37.4%, chosen for its precision and smooth finishes in the dental, jewelry, and automotive sectors.
- Prototyping held a dominant position with a share of over 48.2% in 2023, meeting the rising demand for fast and efficient model development.
- The Automotive sector dominated with over 28.4% market share in 2023, rapidly adopting RLP for innovative manufacturing methods and reduced development times.
Report Scope
| Report Features | Description |
|---|---|
| Market Value (2023) | USD 113.8 Million |
| Forecast Revenue (2033) | USD 5934.8 Million |
| CAGR (2024-2033) | 48.5% |
| Segments Covered | By Material Type(Photopolymers, Thermoplastics, Epoxy Resins, Others), By Technology(Stereolithography (SLA), Digital Light Processing (DLP), Continuous Liquid Interface Production (CLIP)), By Application(Prototyping, Tooling, Functional Parts, others), By End-User Industry(Automotive, Aerospace & Defense, Healthcare, Consumer Goods, Construction and Architecture, Education and Research, Electronics, Others) |
| Competitive Landscape | 3D Systems, Inc., Autodesk, Inc., Bayerische Motoren Werke AG (BMW), Dassault Systèmes, Block.one., ExOne, Materialise, Native Shoes, Steelcase Inc., Stratasys Direct, Inc., Stratasys Ltd, Native Canada Footwear |
Key Market Segments
By Material Type
In 2023, Photopolymers dominated the Rapid Liquid Printing (RLP) market with a 42.7% share. Their versatility and fast curing under light make them ideal for creating complex, high-precision structures. Widely used in medical devices, consumer goods, and design prototypes, photopolymers remain central to RLP’s expanding applications.
Thermoplastics followed as another key material, driven by demand for durable, flexible, and recyclable components. Their strong performance in automotive and aerospace manufacturing underscores their importance in developing sustainable and resilient products.
Epoxy Resins also secured a notable position, valued for their mechanical strength and resistance to heat and chemicals. These materials are essential in industrial and electronic applications, where long-lasting and precision-engineered components are critical.
By Technology
Stereolithography (SLA) led the RLP market in 2023, accounting for 37.4% of total revenue. Its ability to deliver high-accuracy models with smooth finishes makes it highly sought after in industries such as automotive, dental, and jewelry for detailed prototyping.
Digital Light Processing (DLP) ranked next, appreciated for its speed and production efficiency. Using digital light projection to cure photopolymer resin, DLP enables rapid part fabrication, making it ideal for consumer product manufacturing and short-run production.
Continuous Liquid Interface Production (CLIP) emerged as a promising technology, leveraging oxygen-permeable optics to print continuously rather than layer-by-layer. Although relatively new, CLIP is rapidly gaining attention for its high-volume manufacturing potential, particularly in aerospace, medical, and end-use part production.
By Application
Prototyping dominated the RLP market in 2023, holding a 48.2% share. The segment benefits from the increasing need for quick design validation and product development across automotive, healthcare, and consumer electronics sectors. It plays a vital role in reducing time-to-market and accelerating innovation cycles.
Tooling emerged as another strong segment, as RLP enables the creation of customized, complex tools without traditional manufacturing limitations. This allows industries to optimize production efficiency and lower costs. Functional Parts also witnessed rising adoption, thanks to RLP’s ability to produce end-use components with strength comparable to traditionally manufactured ones. Sectors like aerospace and defense particularly benefit from these precision-engineered, durable parts.
By End-User Industry
In 2023, the Automotive industry led the RLP market with a 28.4% share, driven by the need for lightweight prototypes, customized components, and rapid design iterations. The Aerospace & Defense sector followed, adopting RLP for precision-engineered, high-strength parts that meet strict performance standards.
The Healthcare industry leveraged RLP for personalized prosthetics, implants, and surgical tools, showcasing the technology’s adaptability in patient-centric manufacturing. Consumer Goods companies used RLP to develop customized, design-forward products such as wearables and lifestyle accessories.
Meanwhile, Construction and Architecture utilized RLP for complex model creation and structural components, demonstrating its potential in modern design and urban innovation. Education and Research institutions are integrating RLP to train students and advance experimental projects, while Electronics manufacturers apply it for rapid prototyping of precision parts essential for next-generation devices.
Regional Analysis
In 2023, Asia Pacific (APAC) dominated the global Rapid Liquid Printing market, commanding over 55.4% of total revenue. This leadership is driven by aggressive government incentives for advanced manufacturing, robust R&D ecosystems in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea, and rapid adoption across automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods sectors.
North America emerged as the innovation powerhouse, fueled by substantial federal and state-level funding for next-generation manufacturing technologies. The region recorded historic highs in clean energy deployment, with corporate purchasers signing nearly 20 GW of renewable Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) alone. This surge in sustainable energy procurement has accelerated demand for Rapid Liquid Printing’s energy-efficient, low-waste production capabilities.
Stringent EU environmental regulations, coupled with the bloc’s binding renewable targets, have propelled the technology’s adoption. European companies signed renewable PPAs totaling over 16.2 GW—a new annual record. Analysts project this figure will exceed 20 GW in 2024, further amplifying demand for Rapid Liquid Printing as corporations race to meet science-based carbon reduction commitments.
Top Use Cases
- Custom Prosthetics in Healthcare: Rapid Liquid Printing makes personalized silicone prosthetics that fit perfectly for each patient. Doctors scan the body part, and the printer creates a soft, comfy liner right away. This helps people move better with less pain, and it’s quicker than old methods. No extra support needed means less waste and faster delivery for better care.
- Flexible Car Parts in Automotive: Car makers use this tech to print soft seals and cushions that handle vibrations and heat well. Parts like gaskets or grips get made fast in one piece, blending hard and soft areas smoothly. It cuts costs for small batches and lets teams test designs quickly to build lighter, tougher vehicles.
- Fashion Accessories like Bags: Designers print unique handbags from liquid silicone that look fluid and stretchy. The process shapes complex curves without molds, perfect for limited-edition items. It speeds up from idea to runway, uses eco-friendly materials, and allows wild shapes that stand out in shows or stores.
- Ergonomic Furniture Components: This printing builds comfy chair cushions or table bases with lattice designs for support. Big items form in minutes using foam-like materials, customized to body shape. It skips heavy tools, reduces shipping bulk, and creates stylish, lightweight pieces for homes or offices easily.
- Prototyping Tools and Molds: Factories print custom tools or molds fast for testing new products. The gel holds tricky shapes steady, so teams make precise fixtures without delays. It saves time over carving metal, allows for quick changes, and boosts innovation in making everything from gadgets to machine parts.
Recent Developments
1. 3D Systems, Inc.
3D Systems has advanced Rapid Liquid Printing through its Figure 4 platform, leveraging a similar jetting principle. While not a direct “in a gel” RLP, its high-speed, scalable digital molding technology represents a parallel pursuit of ultra-fast, large-scale additive manufacturing. Recent developments focus on materials like durable polypropylene and high-temperature resins for production applications, pushing the boundaries of speed and throughput in industrial 3D printing.
2. Autodesk, Inc.
Autodesk’s primary contribution to RLP is its foundational research and development of the software and algorithms that drive the technology. As a key software partner in the original MIT project, Autodesk continues to integrate advanced generative design and simulation tools within its platforms. These tools are crucial for designing the complex, large-scale structures that RLP enables, optimizing them for performance and material use before printing.
3. Bayerische Motoren Werke AG (BMW)
BMW is applying Rapid Liquid Printing for the automated manufacturing of custom, non-standard components within its vehicles. The company has showcased a functional, 3D-printed window guide rail, printed directly within a gel suspension. This development highlights RLP’s potential for producing durable, end-use parts with the necessary quality and speed for the automotive industry, moving beyond prototyping into direct part production.
4. Dassault Systèmes
Dassault Systèmes advances RLP through its comprehensive 3DEXPERIENCE platform, which provides the virtual twin and simulation environment required for the technology. The company’s software enables the design and digital validation of large, complex objects made possible by RLP. By simulating the entire printing process and the part’s real-world performance, Dassault Systèmes ensures the feasibility and optimization of RLP-manufactured components from concept to physical reality.
5. Block. one
While Block. One’s direct involvement in RLP is not publicly documented; its legacy entity, the now-dissolved Beyond Fabric, was explicitly created to commercialize the RLP technology originating from MIT. The company’s formation and initial mission were dedicated to scaling RLP for industrial applications, focusing on printing large-scale, high-performance objects from established industrial-grade materials like silicone and polyurethane at unprecedented speeds.
Conclusion
Rapid Liquid Printing as a game-changer in manufacturing. It blends speed, flexibility, and top materials to unlock custom designs once too hard or slow to make. Industries from health to cars gain from less waste and on-demand production. With rising needs for personalization and green methods, this tech promises strong growth, reshaping how we build soft, smart products for everyday use.










