Quick Navigation
Overview
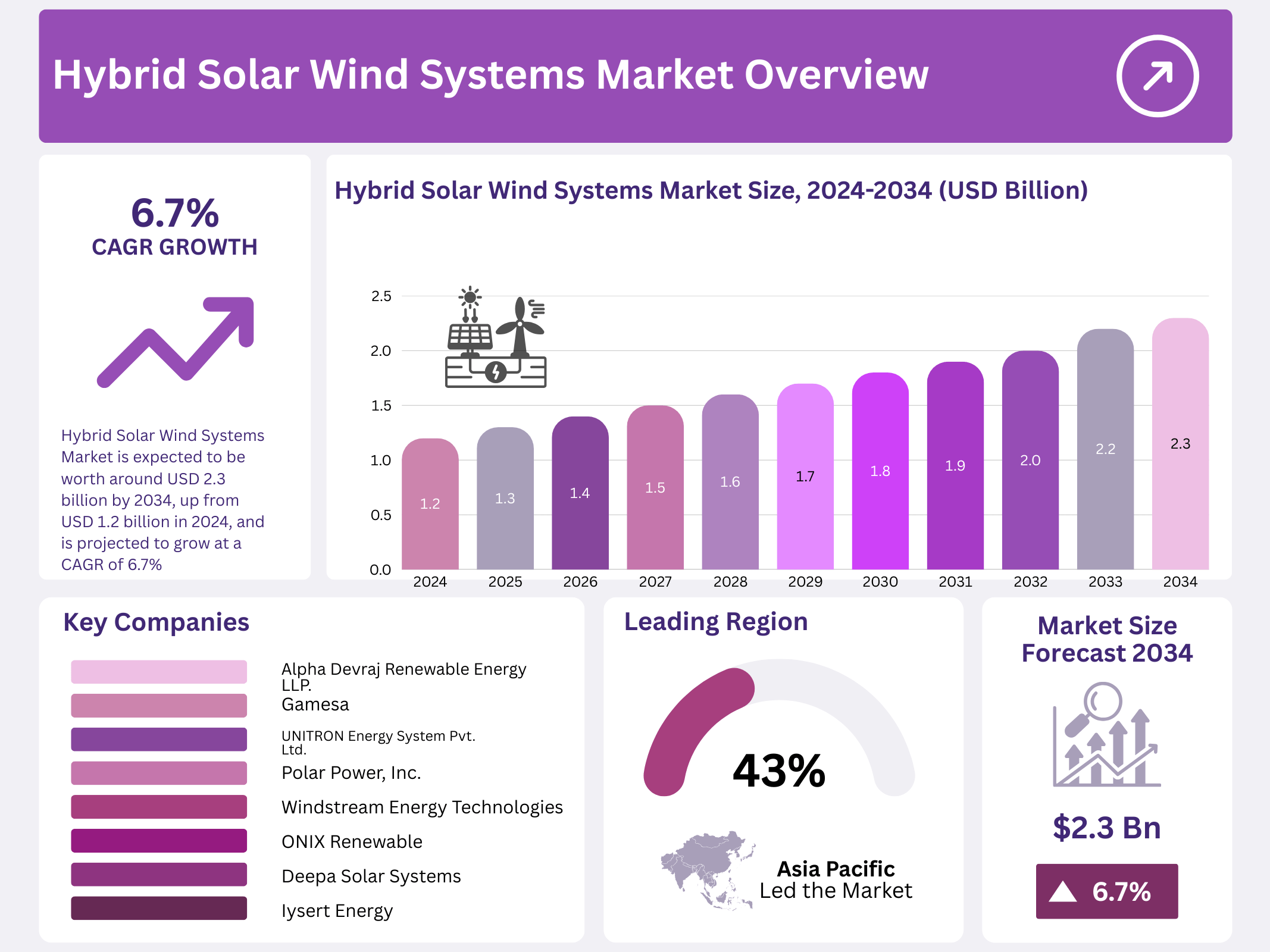
New York, NY – August 20, 2025 – The Global Hybrid Solar Wind Systems Market, valued at USD 1.2 billion in 2024, is projected to reach USD 2.3 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 6.7% from 2025 to 2034. The Asia Pacific region led the market in 2024, holding a 43.8% share worth USD 0.5 billion.
Hybrid Solar Wind Systems integrate solar photovoltaic (PV) panels and wind turbines to deliver reliable electricity. By leveraging the complementary nature of solar (daytime) and wind (often stronger at night or in cloudy conditions), these systems ensure consistent power output, reducing reliance on diesel generators or grid electricity, especially in remote or off-grid areas. The market is expanding steadily, fueled by the global push for sustainable, decentralized energy solutions. Rising electricity demand in rural areas, where grid expansion is costly or impractical, has boosted the appeal of hybrid systems.
Supportive government policies and clean energy goals in both developing and developed nations further drive growth. Significant investments are accelerating market activity. The demand for stable, uninterrupted power in off-grid locations, such as rural schools, telecom towers, and healthcare facilities, is a major growth factor. Hybrid systems mitigate the intermittency of solar and wind, ensuring energy reliability.
Declining costs of solar panels, wind turbines, and battery storage have also enhanced economic viability. For example, ACME Solar secured funding for a 300 MW solar-wind hybrid project and won a 300 MW PV project, reinforcing its market position. Stricter environmental regulations and climate change mitigation efforts are key catalysts. As countries aim to reduce carbon emissions and shift from fossil fuels, hybrid systems are increasingly vital for rural electrification, microgrids, and disaster-resilient infrastructure. Notable investments include Tata Power’s $4.25 billion from the Asian Development Bank for clean energy projects, including hybrids, and ACME Renewtech’s ₹19.88 billion financing for a 300 MW wind-solar hybrid project, highlighting robust policy and investor backing.
Key Takeaways
- The Global Hybrid Solar Wind Systems Market is expected to be worth around USD 2.3 billion by 2034, up from USD 1.2 billion in 2024, and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.7% from 2025 to 2034.
- Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Panels held a 38.4% share in the Hybrid Solar Wind Systems Market.
- On-Grid Systems dominated the Hybrid Solar Wind Systems Market with a 63.1% market share in 2024.
- The Commercial segment led the Hybrid Solar Wind Systems Market, capturing 44.2% of total demand.
- Strong renewable energy initiatives in the Asia Pacific supported a USD 0.5 billion market value.
Report Scope
| Market Value (2024) | USD 1.2 Billion |
| Forecast Revenue (2034) | USD 2.3 Billion |
| CAGR (2025-2034) | 6.7% |
| Segments Covered | By Component (Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Panels, Wind Turbines, Inverters, Batteries / Energy Storage, Others), By Connectivity (On-Grid System, Stand-Alone System), By End Use (Commercial, Residential, Industrial) |
| Competitive Landscape | Alpha Devraj Renewable Energy LLP., Gamesa, UNITRON Energy System Pvt. Ltd., Polar Power, Inc., Windstream Energy Technologies, ONIX Renewable, Deepa Solar Systems, Iysert Energy, Eagle Science & Technology (H K) Co., Ltd |
Key Market Segments
By Component Analysis
Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Panels led the Hybrid Solar Wind Systems Market in 2024, capturing a 38.4% share in the component segment. Their prominence stems from high efficiency, falling costs, and seamless integration with wind turbines and storage systems. PV panels excel in regions with abundant sunlight, providing consistent daytime power that complements wind energy’s variability.
Their modular design suits both small residential setups and large commercial off-grid applications, enhancing energy reliability. With durable, low-maintenance panels and advancements in PV cell efficiency, solar PV remains pivotal for hybrid microgrids and sustainable energy infrastructure, maintaining its leadership in the component mix.
By Connectivity Analysis
On-grid systems dominated the connectivity segment in 2024, holding a 63.1% market share. Preferred in urban and semi-urban areas with reliable grid infrastructure, these systems blend renewable energy with grid electricity, optimizing usage and enabling excess power to be fed back to the grid. This reduces costs and ensures a stable supply during peak demand or weather fluctuations. Supported by net metering and government incentives, on-grid systems appeal to commercial, industrial, and residential users.
By End Use Analysis
The commercial sector led the end-use segment in 2024, accounting for 44.2% of hybrid solar wind system installations. Businesses like offices, retail chains, hospitals, and data centers increasingly adopt these systems for reliable, cost-effective power. Hybrid systems meet the sector’s demand for uninterrupted electricity by combining solar and wind generation. Rising energy costs and carbon reduction pressures drive commercial investment, supported by available rooftop spaces and government incentives like tax benefits.
Regional Analysis
In 2024, Asia Pacific dominated the Hybrid Solar Wind Systems Market with a 43.8% share, valued at USD 0.5 billion. This leadership is driven by supportive policies, rural electrification initiatives, and demand for decentralized energy in countries like India and China. The region’s favorable solar and wind conditions boost hybrid system deployments in off-grid and semi-urban areas.
North America and Europe trail behind, focusing on sustainability but overshadowed by the Asia Pacific. The Middle East, Africa, and Latin America are emerging markets, with growing interest in hybrid solutions for remote areas, supported by pilot projects and international funding. Asia Pacific remains the global leader in adoption and market value.
Top Use Cases
- Rural Electrification: Hybrid solar wind systems provide reliable power to remote villages without grid access. Combining solar panels and wind turbines ensures steady electricity, supporting homes, schools, and clinics. These systems reduce reliance on costly diesel generators, offering a sustainable solution for off-grid communities with diverse weather patterns.
- Commercial Applications: Businesses like offices, retail chains, and data centers use hybrid systems for stable, cost-effective power. By integrating solar and wind energy, they meet high energy demands, cut electricity bills, and achieve sustainability goals, especially in urban areas with grid connectivity and supportive net metering policies.
- Agricultural Irrigation: Hybrid systems power irrigation in rural farms, ensuring a consistent water supply despite changing weather. Solar panels generate daytime power, while wind turbines work during windy nights, supporting drip irrigation for crops like bananas, enhancing productivity and reducing environmental impact compared to fuel-based pumps.
- Telecom Towers: Hybrid solar wind systems power telecom towers in remote or grid-unstable areas. They ensure uninterrupted service by combining solar and wind energy, reducing downtime and operational costs. Battery storage supports continuous power, making these systems ideal for maintaining connectivity in challenging environments.
- Disaster-Resilient Infrastructure: Hybrid systems provide reliable energy for disaster-prone areas, powering emergency shelters, hospitals, and communication hubs. Their ability to generate electricity from both solar and wind ensures functionality during outages, supporting critical operations and enhancing resilience in regions with unpredictable weather conditions.
Recent Developments
1. Alpha Devraj Renewable Energy LLP.
Alpha Devraj is actively expanding its portfolio in renewable EPC and consultancy, with a growing focus on integrated hybrid systems. Their recent developments involve designing customized solar-wind hybrid solutions for industrial and agricultural clients, aiming to maximize energy yield and reliability by leveraging both resources.
2. Gamesa (Now Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy)
As a global wind energy leader, Siemens Gamesa’s role in hybridization often involves integrating its powerful wind turbines with solar PV. Their recent focus is on large-scale, utility-grade hybrid projects and technological advancements for grid stability. They explore combining wind and solar with storage to create more dependable, dispatchable power plants.
3. UNITRON Energy System Pvt. Ltd.
UNITRON specializes in power conditioning products and has recently developed solutions tailored for hybrid renewable systems. Their key development is the creation of inverters and charge controllers capable of intelligently managing multiple input sources, including solar, wind, and grid/diesel generators. Their technology prioritizes solar and wind power, seamlessly switching to or blending with other sources to ensure an uninterrupted 24/7 power supply.
4. Polar Power, Inc.
Polar Power is a leader in DC power systems and has recently intensified its focus on hybrid solutions for the telecom and military markets. Their development centers on the “Polar Hybrid” series, which integrates solar panels and small wind turbines with their patented DC generators and lithium-ion battery storage. These systems are designed for extreme reliability in remote, off-grid locations.
5. Windstream Energy Technologies
Windstream is an innovator in distributed wind and is making strides with its flagship product, the SolarMill, a truly integrated hybrid system in a single unit. A key recent development is the advancement of the SolarMill SE, which combines vertical-axis wind turbines (VAWT) with solar panels and smart energy management on a single platform.
Conclusion
Hybrid Solar Wind Systems are transforming energy access by offering reliable, sustainable power across diverse applications. Their ability to combine solar and wind energy ensures consistent electricity, reduces costs, and supports environmental goals. As technology advances and costs decline, these systems are poised to drive growth in rural electrification, commercial sustainability, and resilient infrastructure, shaping a greener energy future.










