Quick Navigation
Overview
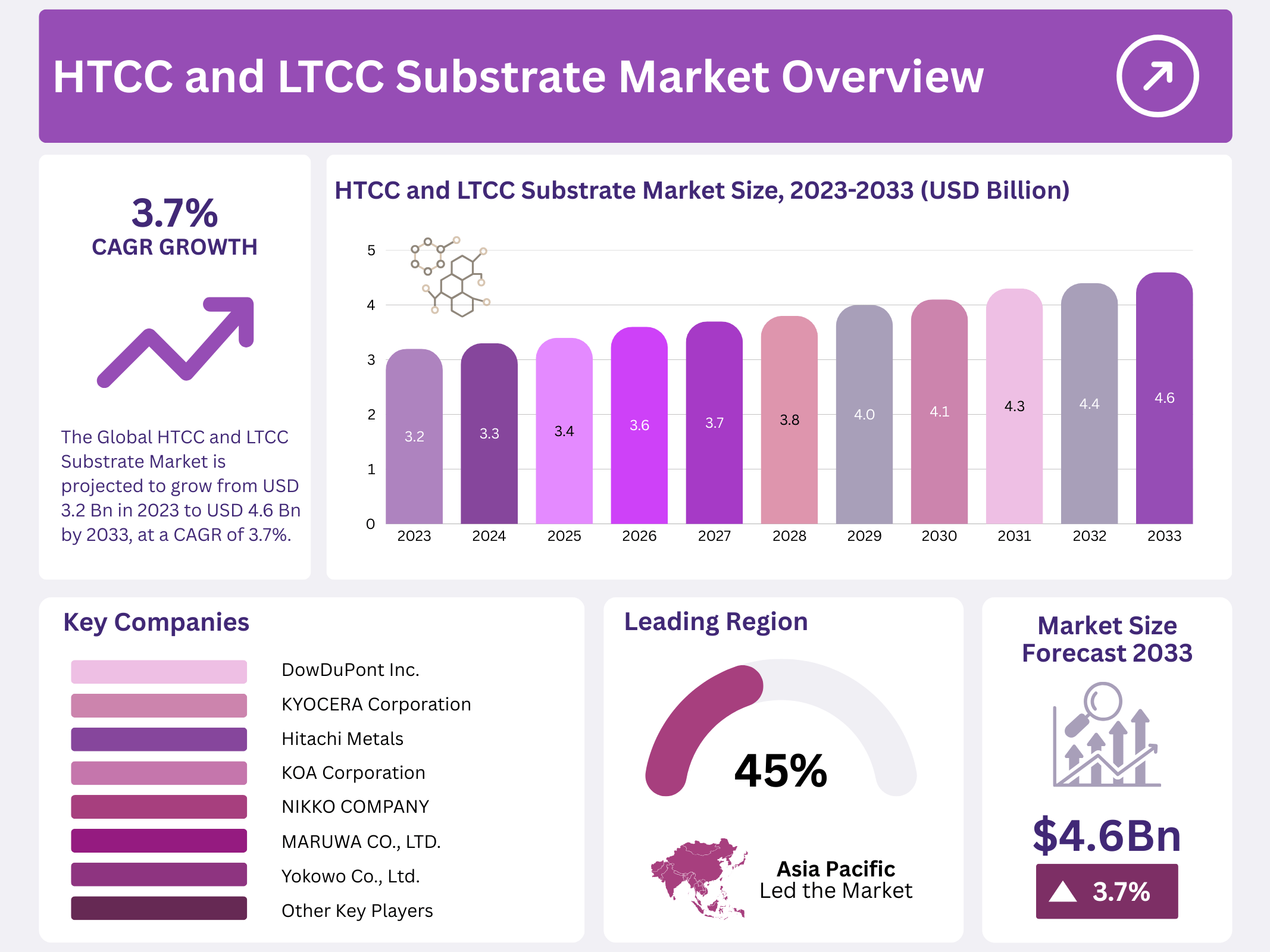
New York, NY – December 29, 2025 – The Global HTCC and LTCC Substrate Market is growing steadily as demand for advanced electronic packaging materials increases across multiple industries. The market size is expected to reach around USD 4.6 billion by 2033, up from USD 3.2 billion in 2023, expanding at a CAGR of 3.7% during the forecast period from 2023 to 2033. This growth is mainly driven by rising electronics complexity, miniaturization trends, and the need for reliable materials that perform well under thermal and electrical stress.
HTCC (High-Temperature Co-Fired Ceramic) substrates are manufactured through a co-firing process at very high temperatures, usually above 1,600°C. These substrates provide strong mechanical durability, excellent thermal conductivity, and high dimensional stability. Because of these properties, HTCC substrates are widely used in demanding environments such as aerospace systems, automotive electronics, power modules, and telecommunications equipment, where high heat resistance and long-term reliability are critical.
In contrast, LTCC (Low-Temperature Co-Fired Ceramic) substrates are co-fired at lower temperatures, typically below 1,000°C, allowing the use of low-cost conductive materials. LTCC technology supports multilayer circuit design and enables passive components to be embedded directly into the substrate during production. This makes LTCC ideal for compact and high-frequency applications such as sensors, antennas, RF modules, and consumer electronics, where space saving and performance integration are key priorities.
Key Takeaways
- The Global HTCC and LTCC Substrate Market is projected to grow from USD 3.2 billion in 2023 to approximately USD 4.6 billion by 2033, at a CAGR of 3.7% during the forecast period (2023–2033).
- LTCC substrates dominated the market in 2023, holding over 72.4% of the total market share.
- The automotive sector was the leading end-use industry in 2023, accounting for more than 47.1% of the market.
- The Asia-Pacific (APAC) region held the largest regional share in 2023, with over 45.6% of the global market.
Report Scope
| Report Features | Description |
|---|---|
| Market Value (2023) | USD 3.2 Billion |
| Forecast Revenue (2033) | USD 4.6 Billion |
| CAGR (2024-2033) | 3.7% |
| Segments Covered | By Product Type(HTCC, Alumina (Al2O3) HTCC Substrates, Aluminum Nitride (AlN) HTCC Substrates, LTCC, Glass-Ceramic LTCC Substrates, Other Material-Based LTCC Substrates), By End-Use Industry(Automotive, Consumer Electronics, Aerospace & Defense, Telecommunications, Healthcare, Others) |
| Competitive Landscape | KYOCERA Corporation, DowDuPont Inc., Murata Manufacturing, KOA Corporation, Hitachi Metals, NGK Spark Plug Co., Ltd., Yokowo, NIKKO COMPANY, MARUWA, Micro Systems Technologies, ECRI Microelectronics, Selmic Oy, American Technical Ceramics Corp., NEO Tech, Advanced Substrate Microtechnology Corporation |
Key Market Segments
By Product Type
In 2023, LTCC (Low-Temperature Co-Fired Ceramic) clearly dominated the market, accounting for over 72.4% of the total share. Its strong position reflects widespread adoption across the electronic substrate landscape, driven by multilayer capability, compact design, and cost efficiency.
Alumina (Al₂O₃) HTCC substrates remained a strong alternative, valued for their excellent mechanical strength and stable thermal performance. These substrates are widely preferred in applications that operate under high temperatures and harsh environments, where durability and long service life are critical.
Aluminum Nitride (AlN) HTCC substrates continued to gain momentum due to their superior thermal conductivity and high reliability. Industries such as aerospace and automotive increasingly adopted AlN-based HTCC substrates to support efficient heat dissipation in high-power electronic systems.
Glass-ceramic LTCC substrates showcased strong versatility, enabling the integration of multiple passive components during the co-firing process. This capability made them essential for compact electronic designs, particularly in sensors, antennas, and communication modules.
By End-Use Industry
In 2023, the Automotive Sector led the market, capturing more than 47.1% share. This dominance reflects the industry’s growing dependence on HTCC and LTCC substrates for applications that demand high thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and long-term reliability in vehicle electronics.
The consumer electronics segment emerged as a strong contributor, where HTCC and LTCC substrates supported the development of compact, lightweight, and high-performance components. These substrates enable sleek device designs while maintaining functional efficiency.
Aerospace and defense applications relied heavily on HTCC and LTCC substrates due to their proven performance under extreme temperatures, vibration, and pressure. Their reliability supports advanced electronic systems used in critical defense and aviation environments.
The telecommunications sector showed rising adoption of HTCC and LTCC substrates for high-frequency and signal-intensive applications. These materials play a vital role in enhancing system efficiency and ensuring stable communication performance.
Regional Analysis
The Asia-Pacific (APAC) region established itself as the dominant market for HTCC and LTCC substrates, capturing more than 45.6% of the global share. The regional market reached a value of USD 6.04 billion, reflecting strong and sustained growth supported by rising demand across multiple end-use industries.
This leadership position underscores the widespread adoption of HTCC and LTCC substrates throughout APAC. Key industries such as electronics, telecommunications, and automotive drove demand, as manufacturers increasingly relied on advanced ceramic substrates to support high-performance, compact, and thermally efficient electronic components.
Rapid economic growth across major APAC economies further strengthened market expansion. Large-scale infrastructure development and growing manufacturing capacity accelerated the consumption of HTCC and LTCC substrates, particularly in industrial electronics and communication equipment.
In addition, population growth and the expansion of the middle-class consumer base boosted demand for electronic devices, advanced communication systems, and modern vehicles. These products depend heavily on HTCC and LTCC substrates for reliability and performance, reinforcing APAC’s position as the leading regional market.
Top Use Cases
- Telecommunications and 5G Networks: HTCC and LTCC substrates play a key role in building antennas, filters, and modules for wireless systems. LTCC handles high-frequency signals with low loss, making it ideal for compact designs in mobile networks, while HTCC adds durability for demanding infrastructure, boosting connectivity speed and reliability in everyday communication tech.
- Automotive Electronics and Sensors: In vehicles, these substrates support radar systems, engine controls, and safety features like collision avoidance. LTCC offers thermal stability for advanced driver assistance, whereas HTCC excels in high-heat environments, ensuring consistent performance under vibrations and extreme conditions to enhance vehicle safety and efficiency.
- Aerospace and Defense Applications: HTCC substrates are favored for radar, navigation, and communication devices in harsh settings like space or military ops, providing heat resistance and reliability. LTCC complements high-density packaging for sensors, helping systems withstand radiation and temperature swings for mission-critical operations.
- Medical Devices and Implants: LTCC substrates enable miniaturized components in pacemakers, hearing aids, and diagnostic tools, integrating sensors for better biocompatibility and accuracy. HTCC adds robustness for long-term implants, supporting stable electronics that improve patient monitoring and treatment without compromising on size or safety.
- Consumer Electronics and Wearables: For smartphones, smartwatches, and IoT gadgets, LTCC substrates facilitate compact antennas and Bluetooth modules with efficient signal handling. HTCC ensures reliability in power-intensive parts, allowing seamless connectivity and functionality in portable devices that fit modern lifestyles.
Recent Developments
1. KYOCERA Corporation
Kyocera is advancing HTCC technology for 5G and automotive applications, focusing on materials for higher frequency and thermal dissipation. For LTCC, they are developing ultra-low-loss materials and fine-circuit patterning to enable miniaturized, high-performance modules for smartphones and IoT devices. Their R&D emphasizes reliability in harsh environments.
2. DuPont de Nemours, Inc. (formerly DowDuPont)
DuPont’s Electronics & Industrial segment innovates in LTCC materials, offering advanced dielectric compositions (9k7, 9k8 series) for superior high-frequency performance in 5G and automotive radar. Their green tape systems enable complex multilayer designs with high conductivity metallizations, supporting the trend towards integrated, miniaturized RF components.
3. Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd.
A leader in LTCC, Murata continuously develops new substrate materials and integration processes to create highly miniaturized, multi-functional modules (e.g., RF front-end, Bluetooth/Wi-Fi). Their “MetroCirc” flexible substrate technology combines LTCC with resin. For HTCC, they enhance packages for sensors and semiconductors requiring high reliability, hermeticity, and thermal resistance.
4. KOA Corporation
KOA focuses on LTCC-based multilayer devices, developing compact, high-frequency inductors, filters, and baluns for automotive infotainment and ADAS systems. Their recent developments include ultra-small, high-Q components using precision printing and co-firing technologies. They also work on HTCC substrates for power module packages, improving thermal cycling performance.
5. Hitachi Metals, Ltd. (now part of Proterial, Ltd.)
The company develops high-performance HTCC ceramic substrates and packages for power semiconductors and sensors, emphasizing superior thermal conductivity and mechanical strength. In LTCC, they offer materials for high-frequency applications, including antenna boards and RF modules, focusing on low dielectric loss for next-generation communication systems.
Conclusion
HTCC and LTCC substrates continue to be cornerstone technologies for high-reliability, high-frequency, and thermally challenging electronics. Their unique combination of compactness, signal performance, and durability positions them as vital enablers across rapidly growing sectors like 5G/6G connectivity, electric and autonomous vehicles, space exploration, advanced healthcare, and efficient power systems.










