Quick Navigation
Overview
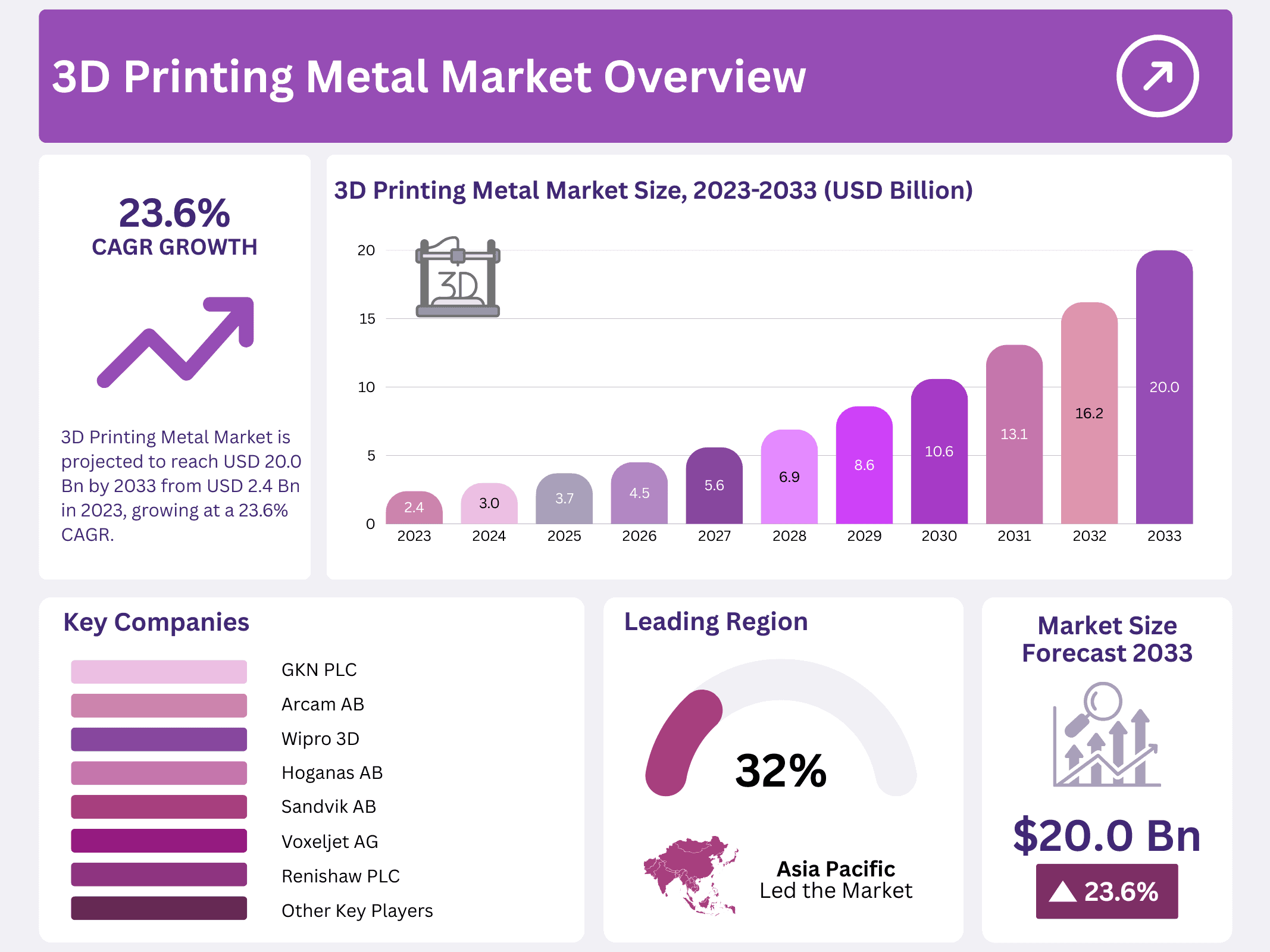
New York, NY – December 05, 2025 – The Global 3D Printing Metal Market is projected to expand rapidly over the coming decade. Market size is expected to reach USD 20.0 billion by 2033, rising from USD 2.4 billion in 2023. This strong expansion reflects a robust 23.6% CAGR during the forecast period from 2023 to 2033, driven by increasing adoption across industrial and healthcare manufacturing.
Market demand is gaining momentum due to higher investment inflows from 3D printer manufacturers and technology developers. Companies are actively scaling production capabilities and advancing metal additive manufacturing systems to meet growing end-use requirements. These investments are accelerating commercialization and widening the addressable market for metal 3D printing solutions.
Mantle Inc., a 3D component manufacturer that raised USD 25 million in 2022 to deploy commercial 3D printers. The company has already produced over 1 million parts for applications including medical devices, dishwasher components, and deodorant packaging. Mantle’s TrueShape 3D printing technology has significantly improved production efficiency, cutting lead times and reducing manufacturing costs by approximately 65%, reinforcing the economic benefits of metal additive manufacturing.
Key Takeaways
- Market Growth: Expected to reach USD 20.0 billion by 2033 from USD 2.4 billion in 2023, growing at a 23.6% CAGR.
- Form Dominance: Powder form leads with over 89.3% revenue share; optimal particle size ranges from 15–75 μm.
- Metal Type: Titanium holds the largest share at 42.4%, driven by aerospace demand and corrosion resistance.
- Applications: Aerospace & defense lead with 29.6% share; medical & dental grow fastest at 27.4%.
- Regional Outlook: Asia Pacific leads with 32.5% share; Europe shows fastest growth at 26.2% CAGR.
Report Scope
| Report Features | Description |
|---|---|
| Market Value (2023) | USD 2.4 Billion |
| Forecast Revenue (2033) | USD 20.0 Billion |
| CAGR (2024-2033) | 23.6% |
| Segments Covered | By Form (Filament and Powder); By Metal Type (Titanium, Stainless Steel, Nickel, Aluminum, and Others); By Application (Aerospace & Defense, Medical & Dental, Automotive, Electronics, and Others) |
| Competitive Landscape | Proto Labs, Inc., Voxeljet AG, Stratasys LTD., The ExOne Company, Renishaw PLC, EOS GmbH Electro Optical Systems, 3D Systems Corporation, General Electric Company, Materialise NV, Hoganas AB, Wipro 3D, SLM Solutions Group AG, Markforged, Inc., GKN PLC, Arcam AB, Carpenter Technology Corporation, Sandvik AB, Titomic Limited |
Key Market Segments
Form Analysis
The powder form represents the largest segment in the market, accounting for a revenue share of more than 89.3%. The performance of metal powders is influenced by several critical parameters that directly affect both the additive manufacturing process and the quality of the final component. These include the physical and chemical characteristics of raw materials, which must be precisely measured and well characterized to ensure consistent results.
The need for high-quality metal powders is expected to rise further. For advanced printing applications, metal particles are typically very fine, generally ranging between 15 and 75 microns, enabling detailed surface finishes and accurate geometries. Uniform particle distribution is also essential to achieve optimal printing results.
Filaments, by contrast, are usually composed of metal particles blended with polymers such as PLA or ABS, where the metal is coated within a polymer matrix. Manufacturers are actively working on developing more cost-efficient filament-based printing methods to reduce reliance on selective laser melting. These advancements are expected to support increasing filament adoption over the forecast period.
By Metal Type Analysis
The titanium segment accounted for the largest revenue share of 42.4% in 2022 and is projected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period. Titanium’s resistance to corrosion, lightweight nature, and ability to withstand harsh operating environments make it especially suitable for high-performance applications. Growth in this segment is also supported by the ability of conventional polymer-based 3D printers to produce semi-metallic components using metal-filled filaments.
The aerospace and defense sector, in particular, is well positioned to adopt titanium powder due to its capacity to absorb high initial costs and rapidly integrate emerging technologies. The shift toward complex geometries and lightweight structural designs in aerospace manufacturing is expected to further accelerate demand for titanium-based 3D printing materials.
Application Analysis
In 2023, the aerospace and defense segment held the largest market share at over 29.6%, driven by the technology’s ability to produce complex parts with reduced lead times. The sector continues to benefit from institutional support, as demonstrated by Senvol receiving funding from the U.S. Department of Defense in 2023 to advance 3D printing adoption.
Medical and dental applications are expected to register the fastest revenue growth, with a projected CAGR of 27.4% in terms of volume. Companies are increasingly using 3D printing to develop customized implants, prosthetics, and medical devices. For example, Monogram leverages 3D printing for orthopedic implants, while Open Bionics has introduced affordable robotic prosthetics using additive manufacturing.
Regional Analysis
The Asia Pacific region dominated the global 3D printing metal market in 2023, holding the largest market share of 32.5%. This leadership is supported by strong manufacturing activity, rising investments in advanced production technologies, and expanding adoption across aerospace, automotive, and industrial applications. The region continues to see increasing use of metal additive manufacturing as manufacturers focus on faster production cycles, lightweight components, and localized manufacturing capabilities.
Europe is expected to register the fastest regional growth, with a CAGR of over 26.2% from 2023 to 2032. Key European countries such as France, Germany, Italy, Spain, and the Netherlands are leading adoption, particularly across healthcare and aerospace end-use industries. Several governments in the region have also integrated additive manufacturing into national Industry 4.0 and advanced manufacturing strategies, which is further accelerating technology deployment.
In the U.K., companies such as Attenborough Dental and Renishaw use metal 3D printing for dental crowns and bridges, while Bowman International applies the technology to bearing boxes, and GKN manufactures aerospace and automotive components. Despite these developments, overall adoption across the U.K. remains relatively limited, highlighting substantial untapped potential for future growth.
Top Use Cases
- Aerospace Components: Metal 3D printing allows engineers to craft lightweight, intricate parts like turbine blades and engine brackets that traditional methods struggle with. This speeds up design testing and reduces aircraft weight, leading to better fuel efficiency and performance. Companies use it to create custom fittings that fit perfectly, cutting down on assembly time and boosting overall aircraft reliability in demanding flight conditions.
- Automotive Parts: In the car industry, metal 3D printing produces complex gears and exhaust systems tailored for high performance. It enables quick prototyping of new designs, helping teams iterate faster without expensive molds. This approach supports electric vehicle innovation by making lightweight components that enhance range and speed, while also allowing small-batch production for luxury or custom models.
- Medical Implants: For healthcare, metal 3D printing builds personalized implants like hip joints or dental prosthetics from biocompatible metals. It creates porous structures that promote bone growth and fit patients exactly, improving recovery times. Surgeons appreciate the precision for complex anatomies, making surgeries less invasive and outcomes more successful, especially for unique patient needs.
- Tooling and Jigs: Factories rely on metal 3D printing for custom tools, fixtures, and end-of-arm grippers that handle tough tasks. These printed items are stronger and more ergonomic than off-the-shelf options, reducing wear on production lines. It cuts setup costs and time, allowing manufacturers to adapt quickly to new assembly processes without long lead times.
- Legacy Part Replacement: Metal 3D printing revives hard-to-find spare parts for old machinery in industries like energy or defense. By scanning and reprinting exact replicas, it maintains equipment without stockpiling inventory. This keeps operations running smoothly, avoids downtime from shortages, and supports sustainable practices by extending the life of existing assets through on-demand production.
Recent Developments
1. Proto Labs, Inc.
Proto Labs continues to expand its metal 3D printing services, focusing on Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) for rapid prototyping and end-use parts. Recent developments include the addition of more metal alloys like Aluminum AlSi10Mg and Stainless Steel 17-4 PH to its digital portfolio. They emphasize speed and automated quoting, integrating 3D printing seamlessly with traditional manufacturing services for complex, low-volume components.
2. Voxeljet AG
Voxeljet is advancing binder jetting for metals, notably through its partnership with GE Additive to develop the H2 series printer for mass production. They focus on large-format printing and high-volume sand casting molds. A key recent development is progress in industrializing the process for serial production of metal parts, aiming to improve productivity and reduce costs for automotive and aerospace customers.
3. Stratasys LTD.
Stratasys offers the Direct Metal Printing (DMP) Factory 500 solution, originally from acquired company Desktop Metal. A recent key development is the strategic focus on sustainable metal binder jetting, highlighting the ability to reuse over 99% of unfused powder. They are targeting high-throughput production of metal parts with consistent mechanical properties for industries like automotive and heavy equipment.
4. The ExOne Company (Acquired by Desktop Metal)
Now operating as part of Desktop Metal, ExOne’s binder jetting technology continues to be developed. Recent advancements center on qualifying new metals, including copper and refractory alloys like tungsten, for the production of complex, high-performance components. The integration focuses on scaling the ExOne process for industrial series production, emphasizing repeatability and material innovation under the Desktop Metal brand umbrella.
5. Renishaw PLC
Renishaw focuses on precision laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) systems like the RenAM 500 series. Recent developments include enhanced process monitoring software (InfiniAM) for quality assurance and the promotion of “right-sizing” printers for specific applications to improve efficiency. They emphasize solutions for demanding sectors like medical and aerospace, with ongoing research into parameter optimization and multi-laser processing for productivity gains.
Conclusion
Metal 3D printing as a game-changer in manufacturing, shifting from simple prototypes to full-scale production of durable, customized parts. Its ability to handle complex shapes and materials drives adoption across aerospace, automotive, and healthcare, where lightweight designs and quick iterations save time and resources. Emerging trends like hybrid processes and sustainable sourcing point to broader accessibility.










